BIOL4415 - Adult Stem Cell Niche
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What things comprise a stem cell niche microenvironment?
Stem cells
Support cells
Soluble factors
ECM
Progenitor cells
Where do stem cells reside in hair follicles?
In the hair bulge
Where do stem cells reside in cornea?
Limbus, they are called Limbal stem cells?
Where do liver stem cells reside? What can they differentiate into?
Canal of Hering
They can differentiate into hepatocytes or cholangiocytes
How does population asymmetry work
Stem cell divides into multiple transient cells
Some revert back to stem cells, other differentiate
Factors responsible for maintain HSCs in their niche during asymmetric division
Wnt
FGF
BMP
SCG - c kit interactions
VCAM - Integrin
N-Cadherins
Jagged - Notch
What cells to stromal cells differentiate into?
Osteoblasts, which then become osteocytes
List 2/3 signaling molecules in HSC microenvironment
Erythropoietin (EPO)
G-CSF
M-CSF
3 Molecules involved in cell-cell contact in HSC microenvironment
Desmosome
Adherens Junctions
Gap junctions
3 Molecules involved found in ECM in HSC microenvironment
Fibronectin
Collagen
Laminin
3 forces involved HSC differentiation in HSC microenvironment
Compression
Stiffness
Elasticity
4 major factors determining HSC differentiation in their microenvironment
Cell-cell signaling
Soluble factors
ECM interactions
Forces
What cells are found in the HSC niche
Adipocytes
Stromal cells
Osteoblasts
Progenitors
What cytokines do perivascular stromal cells release
CXCL12
SCF
During what time of the day to HSCs differentiate and proliferate? What causes it?
At night they divide
During the day they migrate into the vascular niche
Caused by release of noradrenaline during the day, which decreases CXCL12 expression in CAR and stromal cells, freeing up cells to go into the blood
Where do long-term quiescent HSCs reside
Attached to osteoblasts
Where do short-term active HSCs reside
In the perivascular niche attached to endothelial, stromal cells or CAR cells
What cells are found in intestinal stem cell niche
Intestinal stem cells
Paneth cells
Where does cell removal take place in small intestines
Anoikis, via apoptosis
How long is turnover in stem small intestines
2-3 days
Role of Paneth cells
Secrete Wnt and Delta to activate Notch signaling, which stimulates proliferation of ISCs, and is antagonistic to BMP signaling from upper cells
What happens after CBCC divison?
One cell stays next to P-cell and remains stem cells, other goes on to differentiate
Wnt vs BMP signaling
Wnt promotes stemness, BMP promtoes differentiation
Transit Amplifying cell
Differentiated cell which migrates upwards
How to visualize ISCs from the crypt?
Use Cre-Lox system
Put Cre in front of stem-cell specific promoter
Put stop codon flanked by Lox sites in front of a ubiquitous promoter, followed by a color which can be detected
Where are epidermal stem cells found?
Attached to basal lamina?
How do epidermal stem cells mature?
Notch signaling from mature keratinocytes induces asymmetric division
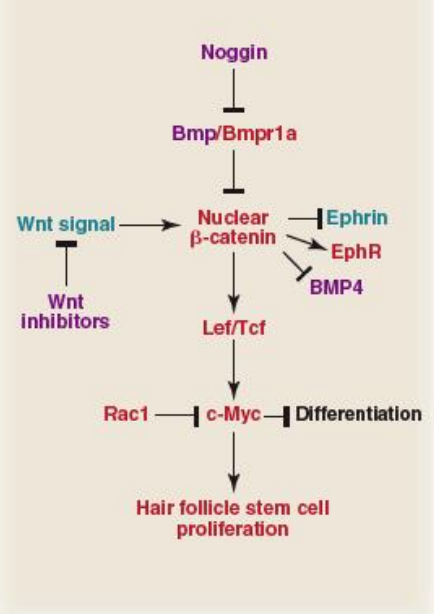
Cell signaling involved in follicle stem cell differentiation (image)
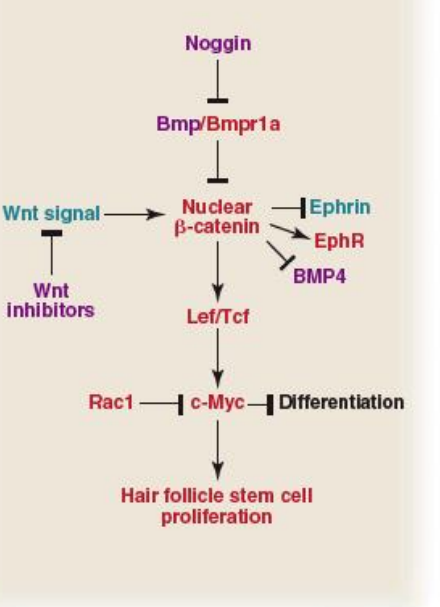
What stops bulge cells from migrating to dermal papilla
BMP4, from dermal fibroblasts and FGF16 and BMP6 from the inner bulge
What induced telogen to anagen transition
Underlying dermis and adipocytes release FGF6, FGF10, BMP inhibitions, and TGF-beta2 and Wnts
What maintains stemness of HFSCs
Shh signaling
How does Anagen end
HFSCs closer to the dermal papilla divide faster, pushing it away, thus decreasing the strength of it’s signaling and ending the anagen phase
Cord Blood vs Bone marrow when it comes to bone marrow transplant
Cord Blood is less mature, so lymphocytes will not be able to cause GVHD as often as mature lymphocytes from bone marrow
Cord Blood does not need an invasive surgery
Bone marrow need’s willing participants and may be in limited supply
Cord blood is cheaper
Describe the stem cell niche
Osteoblasts on the sidelines with HSCs
Osteoblasts ensure these HSCs remain quiescent
Release thrombopoietin which prevents blood vessel formation, decreasing oxygen supply, ensuring HSCs quiescence
HSCs divide slowly
Perivascular niche with HSCs associated with CAR and mesenchyme cells
CAR and mesenchymal cells release CXCL12, keeping the HSCs in the niche
Noradrenaline from neurons blocks CXCL12 transcription
At night, with less noradrenaline, more CXCL12 is produced, keeping the cells in the niche
During the day, with more noradrenaline, less CXCL12 is produced, allowing HSCs to escape into blood vessels
what is anoikis
Cell death due to loss of attachment or shedding
Name of the crypt base stem sells
Columnar cells
Describe intestinal stem cell niche
Wnt gradient from bottom up, BMP from top down
Crypt has
Paneth and Paneth progenitor cells
Crypt base columnar cells (Intestinal stem cells)
Signaling from Paneth cells causes asymmetric division
CBCC next to Paneth cells stays in the niche, other one becomes part of transit amplifying cells (TAC) which migrate upwards along the BMP gradient
At the top, the cells die via anoikis
Intestinal crypt cell cell-marker
Lgr5
Describe the skin stem cell niche
Basal layer is formed by epidermal stem cells
Attach to basal lamina via laminin-integrin interactions
Notch signaling causes differentiation into keratinocytes
Dead keratinocytes form stratum corneum
Primary regulator of hair follicle stem cell proliferation. Show the regulatory map
c-Myc and Shh
What stem cells does umbilical tissue have
Stem cells needed for 1. cartilage
Cartilage
Blood vessel tissue
Skin
Neurons
Sensory organs
Three important qualities of umbilical cord cells
Engraftment - they can unite with other tissues
Homing - they can travel to the site they are needed at
Plasticity
What diseases can be trated using umbilical cord stem cells
Fanconi’s anemia
Leukemia
Metabolic disorders
What can treat Huntington’s or Parkinson’s disease
Umbilical Cord matrix stem cells (UCMS cells), such as the neuronal progenitors
Limitations of cord blood stem cells
Limited amount can be extracted from umbilical cord, and the donor can only donate it once
Delayed platelet and neutrophil engraftments, due to low numbers of these cells in the cord
How to use umbilical cord stem cells for gene therapy
Transduce them with retroviruses
Transplant them