Cardiac Muscle
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Physiology Exam 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
How much blood circulates through the body per minute normally?
5 - 7 L/min
What is a normal cardiac output?
2.5 - 4 L/m²
Which side of the heart experiences lower pressures?
Right
What are the functions of the pericardium?
Anchor, protect, limit filling
What is the function of the pericardial space?
Reduce friction
What is found in the epicardium?
Coronary arteries
What is the myocardium, and what does it do?
Cardiac muscle tissue, contraction
What makes up the endocardium?
Conduction system (pacemaker cells) and valvular system (4 primary valves)
What aspect of syncytium structure increases susceptibility to depolarization?
Intercalated discs
What generates the initial action potential for contraction?
Sinus node
What area of the heart compiles action potentials to make sure the entire system contracts in rhythm?
Atrioventricular (AV) node
What is unique about cardia muscle structure that increases calcium access and why does it have that feature?
Few but wide T tubules - more uniform contraction
What is unique about myocardial action potentials?
Longer action potential and has a plateau
Fast sodium channels
Slow calcium channels = plateau
What are the electrical properties of cardiac muscle?
Automatic, All or none
What is the pressure needed to open RV valve?
8 mm Hg
What is the pressure needed to open the LV valve?
80 mm Hg
How is cardiac output calculated?
stroke volume X heart rate
How is stroke volume calculated?
volume ejected / contraction
(50 - 100 ml per contraction)
How does an excessive increase in HR affect CO?
Decreases (less filling, impaired SV)
How is stroke volume calculated?
End Diastolic Volume (EDV) - End Systolic Volume (ESV)
(volume prior to contraction - volume after)
What is Ejection Fraction defined as?
Percentage of end diastolic volume ejected per cardiac cycle?
How is Ejection Fraction calculated?
SV / EDV
What is the normal heart rate range?
50-100 BPM
What are the four phases of the cardiac cycle?
Chamber filling (end diastolic volume)
Isovolumetric contraction (pressure to open semilunar valves)
Ejection
Isovolumetric relaxation (end-systolic volume)
What makes the ventricular muscle stretch to provide a better contraction?
Atrial kick - pumps 15-30% more blood to ventricles
How is External Work calculated?
SV x mean arterial pressure (MAP)
As MAP increases, how does that affect EW?
Increases proportionately
What two structures differ in fetal circulation?
Foramen Ovale
Ductus Arteriosus
Both divert blood away from lungs - Less oxygenation if openings don’t close.
What is the purpose of the Atrioventricular (AV) valves?
Prevent backflow during ventricular systole
What is the function of the papillary muscles - Chordae tendineae?
Prevent the AV valve from bulging into atria during ventricular systole
Which valves are Semilunar?
Pulmonary and Aortic
What is unique about semilunar valves?
Fast closure due to high pressure and small diameter
No chordae tendineae
Describe the sound caused by valvular closure.
Clean, crisp, distinct

Which sounds are normal heart sounds?
S1 and S2
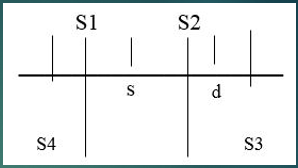
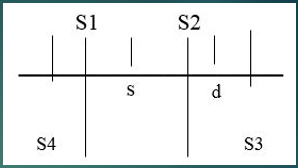
Which sounds are Gallops?
S3 and S4
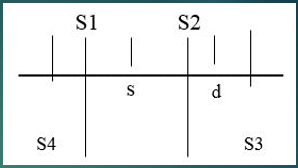
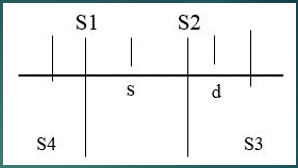
What happens to cause S1?
Atrial valve closure
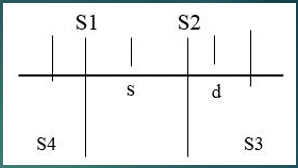
What happens to cause S2?
Semilunar valve closure
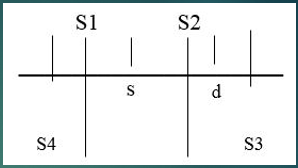
What happens to cause S3?
Ventricular gallop
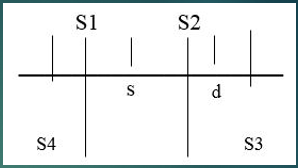
What happens to cause S4?
Atrial gallop
What is preload and what is its effect?
Volume of venous return - stretches tissues - increases SV
What is afterload, and what does it cause?
Resistance into aorta - blood pressure
What three things regulate HR?
Frank Starling Mechanism
ANS (Sinus-atrial node, Atrial ventricular node)
Catecholamines