General Science – Flashcard
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ASVAB
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Catalyst
A substance that reduces the activation energy of a chemical reaction, making it possible and increasing its speed
Enzyme
A protein that catalyzes a chemical reaction
What is DNA’s function?
DNA carries hereditary information that controls the protein synthesis in living organisms
Ions
Electrically charged atom or substances
Prokaryotic Cell
A cell that doesn’t have an enclosed nucleus
Eukaryotic Cell
A cell with a nucleus enclosed in a membrane
What are the three main parts of a eukaryotic cell?
Cell membrane, Cytoplasm, and Nucleus
The mathematical formula for gravity is _____.
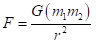
Metric System/SI
The system of measuremnt that’s based on a decimal system of multiples and fractions of ten
Omnivores
Animals that eat plants and meat
The brain is part of the _____.
Nervous System
Bones, joints, tendons, and cartilage are part of the _____.
Skeletal System
Skeletal Muscle
The muscles that control your voluntary movements
Plants can reproduce in _____.
Sexually and Asexually
In human genetics, a healthy person has _____ pairs of chromosomes.
23
What is the method by which scientists develop and test theories called?
Scientific Method
What is the smallest part of an element that still retains the characteristics of the element?
Atom
Neutrons
Particles with no charge
Electrons
Negatively charged particles
Protons
Positively charged particles
An element’s atomic number corresponds with _____.
Number of protons it has
What are the states of matter?
Solid, liquid, and gas
When a substance transforms from a gas to a liquid, it goes through the process called _____.
Condensation
Compunds
Elements joined by chemical bonds in a specific ratio
Chemical Reaction
The process that rearranges a substance’s molecular structure
The pH scale ranges from _____.
0 to 14
What is the base unit of length in the SI system?
Meter
What unit measures force?
Newton
What unit measures energy, work, and quantity of heat?
Joule
The amount of matter an object contains is called its _____.
Mass
What is Newton’s first law of motion?
An object at rest and in motion tends to stay at rest, and in motion with the same speed and in the same direction, unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
Sound wares are measured in what two units?
Amplitude and Wavelength
All wavelengths and frequencies of radiation are on the _____.
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Refraction of Light
The bending of light as it passes from one medium to another
Reflection of Light
Occurs when light bounces off an object
Thermal Equilibrium
A condition in which no heat is flowing between objects
What are the three ways heat energy transfers between objects?
Through conduction, convection, and radiation
What foes the first law of thermodynamics say?
Energy can be neither created nor destroyed, but it can be transferred and converted
Product
An element or molecule that results from a chemical reaction
Geology
The study of Earth’s physical appearance
What is Earth’s surface called?
Crust
What is the solid rock below Earth’s crust called?
Mantle
What do scientists believe is in Earth’s core?
Contains iron and nickel
Hypothesis
A testable explantion of why something happens
How do scientists test a hypothesis?
By experimenting and observing outcomes
What does the prefix milli- mean in the metric system?
One-thousandth/0.001
What does the prefix centi- mean in the metric system?
One-hundredth/0.01
What does the prefix deci- mean in the metric system?
one-tenth/0.1
One foot is approximately equal to how many meters?
About 0.3 meters
Ecosystem
A biological community of interacting organisms and their environment
What do plants need to grow?
Sunlight, good soil or environmental nutrients, the right temperatures, and water to grow
Biodiversity
The term scientists use to talk about the variety of life within ecosystems
What are the clasifcations in the Linnaean taxonomix classification system?
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, and Species
What are the kingdoms in the Linnaean taxonomic classification system?
Animals, Plants, Fungi, Protists, Bacteria, and Achaea
What is the nervous system responsible for?
Receiving, Processing, and Responding to Physical Stimuli
What is the respiratory system responsible for?
Inhaling air, using oxygen from the air to release energy, and exhaling carbon dioxide
What is the purpose of the renal system?
Filters toxins out of the body
What are the three types of human muscles?
Cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and skeletal muscle
What are the six major types of bone joints?
Hinge, ball and socket, pivot, fixed, saddle, condyloid, and gliding
What do ligaments and tendons do?
Ligaments join the bones, and tendons connect muscle tissue to bones and other structures in the body
What types of nutrients do animals need for fuel?
Carbohydrates, fats, fiber, minerals, protein, vitamins, and water for fuel
A plant’s root system includes _____.
Vascular tissue, primary roots, and secondary roots (branches)
What does a plant’s root system do?
A plant’s root system absorbs water and nutrients from the soil, holds the plant in place, and stores nutrients
What are the two stages of photosynthehsis?
Light-dependent reactions and Calvin cycle
Every cell has what four things in common?
A nucleus, cytoplasm, a membrane, and ribosomes
What is the function of a cell’s nucleus?
Controls cellular activity and holds the cell’s genetic material (DNA)
What do plant cells contain that animal cells do not?
Contain chloroplasts, which help plants create food with the help of sunlight
Osmosis
The movement of liquid throught the cell membrane (and the main way that water goes in and out of cells)
Photosynthesis
The conversion of electromagnetic energy from the sun to chemical energy that the cell can use
Kinetic Energy
The energy a body possesses by virtue of being in motion
What are the four general blood types?
A, B, AB, and O
What are the eight planets in order of their distance from the sun, starting with the closest?
Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune
What is the function of White Blood Cells?
Fight infection
Crystal Lattice
The very rigid molecular structure of repeating patterns found in solids
What is water’s boiling point at sea level, in degrees ºC and ºF?
100ºC & 212ºF
Sublimation
When it takes place, a substance change from solid to gas without ever passing through a liquid phase
What is the rate of gravity on Earth?
9.8 m/s
What is the formula for work in physics?
W represents Work, F represents Force, and D represents Displacement
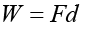
What are the layers of the Earth, beginning with the outermost layer?
Earth’s crust, followed by Mantle, Outer Core, and Inner Core
What are the layers of Earth’s mantle?
Mesosphere, Asthenosphere, and Lithosphere
What forms sedimentary rock?
Sediment, such as particles of sand, seashells, and bone fragments that harden over time
What causes metamorphic rock to form?
Intense heat and pressure below Earth’s surface
What is igneous rock made form?
Cooled Magma
Fault Line
Space between Earth’s tectonic plates
What are the five oceans classified by scientists?
Atlantic, Pacific, Indian, Arctic, and Southern Oceans
How thick is Earth’s atmosphere?
Approximately 300 miles thick
In whcih layer of Earth’s atmosphere do mot weather changes occur?
Most of Earth’s weather changes happen in the troposphere
What is the most prevalent gas in Earth’s atmosphere?
Nitrogen at about 78%
Climate
Refers to patterns in weather overtime (usually 30 years or more)
What three scales do scientists use to measure temperature?
Fahrenheit, Celsius (Centigrade), and Kelvin
What formula converts ºC to ºF
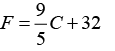
What are the major ways scientists determine the ages of fossils?
Through radiometric dating, relative dating, paleomagnetism, and biochronology
What’s at the center of the Milky Way galaxy?
A supermassice black hole
What type of star is Earth’s sun?
Yellow dwarf star
Terrestrial planets
The inner four planets in Earth’s solar system are Earthlike planets comprised mainly of iron and rock
Meteoroid
A rock from space that hits Earth’s atmosphere and glows as it heats up
What does DNA do?
Determines an organism’s traits and genetic makeup
Gram
The basic unit of mass or weight in the metric system
Medium’s refractive index
The ratio by which light is slowed while passing through medium
Ribosome
An organelle that processes genetic instructions so the cell can create proteins