Organelles
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
150 Terms
Cell Wall Location
Prokaryotic – Bacteria and Eukaryotic – Plant
Cell Wall Description
*outer layer
*rigid, strong, stiff
*made of cellulose
Cell Wall Function
*Defensive structure that allows H2O, O2, CO2 to pass into and out of cell but not harmful materials like dirt, bacteria, and toxins
* Structural support
* Helps create turgor pressure (pressure created in a plant cell by water pushing against the cell wall and cell membrane) for a plant to help it remain standing or wilt
Plasma (Cell) Membrane Location
Prokaryotic – Bacteria
Eukaryotic – Plant &
Animal
Plasma (Cell) Membrane Description
Outer boundary of the cell
Made of a bilayer of lipids with proteins embedded
Plasma (Cell) Membrane Function
Selectively permeable (allows certain molecules in/out)
Small molecules like H₂O and O₂ pass directly
Larger molecules (e.g., glucose) require protein channels
Maintains homeostasis
Cytosol (Cytoplasm) Location
All cells (Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic)
Cytosol (Cytoplasm) Description
Jelly-like fluid fills the cell interior
Cytosol (Cytoplasm) Function
Site of many chemical reactions
Dissolves solutes (proteins, carbs, etc.)
Provides internal support/pressure
Organelles float and move in it (cytoplasmic streaming)
Cytoskeleton (Cytoplasm) Location
Eukaryotic – Plant & Animal
Cytoskeleton (Cytoplasm) Description
Network of protein fibers in the cytoplasm
Cytoskeleton (Cytoplasm) Function
Microtubule - hollow tubes for structure, movement, and spindle fibers
Microfilament - thin fibers for support and movement
Intermediate filament - provides strength and stability
Provides shape, structure, and internal organization. Aids in the movement of organelles
Ribosome Location
All cells (Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic)
Ribosome Description
Small dots, free-floating or attached to rough ER
Made of RNA and proteins
Ribosome Function
Site of protein synthesis
Link amino acids into polypeptide chains (translation)
Nucleus Location
Eukaryotic – Plant & Animal
Nucleus Description
Large round structure containing DNA
Nucleus Function
“Control center” or headquarters. Directs the activities of the cell
Nucleolus – makes ribosomes
Chromosomes - DNA instructions for proteins
Nuclear envelope (Membrane) Location
Eukaryotic – Plant & Animal (surrounds the nucleus; continuous with rough ER)
Nuclear envelope (Membrane) Description
Double phospholipid bilayer (inner & outer membranes)
Studded with nuclear pores (protein complexes)
Encloses the nucleoplasm and contents (chromatin + nucleolus)
Nuclear envelope (Membrane) Function
Protects DNA and separates nuclear processes from cytoplasm
Selectively regulates transport through nuclear pores:
Out: mRNA, tRNA, ribosomal subunits
In: proteins (e.g., transcription factors), nucleotides, enzymes
Continuous with rough ER; outer membrane can have ribosomes
Disassembles/reassembles during cell division (mitosis)
Helps maintain nuclear shape via the nuclear lamina (protein scaffold)
Endoplasmic reticulum Location
Eukaryotic – Plant & Animal
Endoplasmic reticulum Description
Network of tubes and membranes connected to the nucleus
Endoplasmic reticulum smooth Function
no ribosomes, makes lipids, detoxifies toxins
Endoplasmic reticulum rough function
covered with ribosomes, transports proteins makes proteins
Golgi Apparatus Location
Eukaryotic – Plant & Animal
Golgi Apparatus Description
Stack of flattened membranes
Golgi Apparatus Function
Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins
Places proteins into vesicles for export
Vesicle - A Small membrane “envelope” that transports proteins and other molecules inside and outside the cell
Mitochondria Location
Eukaryotic – Plant & Animal
Mitochondria Description
Oval-shaped with a double membrane, inner folds (cristae)
Mitochondria Function
“Powerhouse of the cell” Performs cellular respiration → makes ATP (energy). Has its own DNA & ribosomes (supports endosymbiosis theory)
Matrix- internal fluid space
Inner membrane- site of ATP production
Vacuole Location
Eukaryotic – Plant & Animal
Vacuole Description
Membrane-bound sac
Vacuole Function
Central – (Plants) Stores food, water, waste, pigments
Contractile – (Protists) pumps excess water out
Stores food, water, waste, pigments
Lysosome Location
Eukaryotic – mostly Animal (some plants)
Lysosome Description
Small vesicle filled with enzymes
Lysosome Function
Breaks down food into smaller molecules
Destroys pathogens (bacteria/viruses) in white blood cells
Responsible for autolysis (cell self-destruction of old/damaged cells)
Chloroplast Location
Eukaryotic – Plant & some protists
Chloroplast Description
Green organelle containing chlorophyll
Chloroplast Function
Site of photosynthesis → makes glucose & oxygen
Has its own DNA & ribosomes (endosymbiosis evidence)
Grana- stacks of thylakoids
Thylakoid Membrane- absorbs light (chlorophyll is located here)
Stroma- fluid around grana, where sugar is made
Cilia Location
Eukaryotic – some Animal cells, protists
Cilia Description
Numerous short, hair-like projections
Cilia Function
Cell movement or moving substances across the cell surface
Example: lining of the respiratory tract moves mucus
Flagella Location
Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic – sperm, some protists, bacteria
Flagella Description
Long, whip-like tail (usually one or a few per cell)
Flagella Function
Enables cell motility (e.g., sperm swimming to the egg)
Microtubule
hollow tubes for structure, movement, and spindle fibers
Microfilament
thin fibers for support and movement
Intermediate filament
provides strength and stability
Nucleolus
makes ribosomes
Chromosomes
Chromosomes - DNA instructions for proteins
Vesicle
A Small membrane “envelope” that transports proteins and other molecules inside and outside the cell
Matrix
Internal fluid space
Inner membrane
Site of ATP production
Central Vacuole
(Plants) Stores food, water, waste, pigments
Contractile Vacuole
Contractile – (Protists) pumps excess water out
Grana
stacks of thylakoids
Thylakoid Membrane
absorbs light (chlorophyll is located here)
Stroma
fluid around grana, where sugar is made
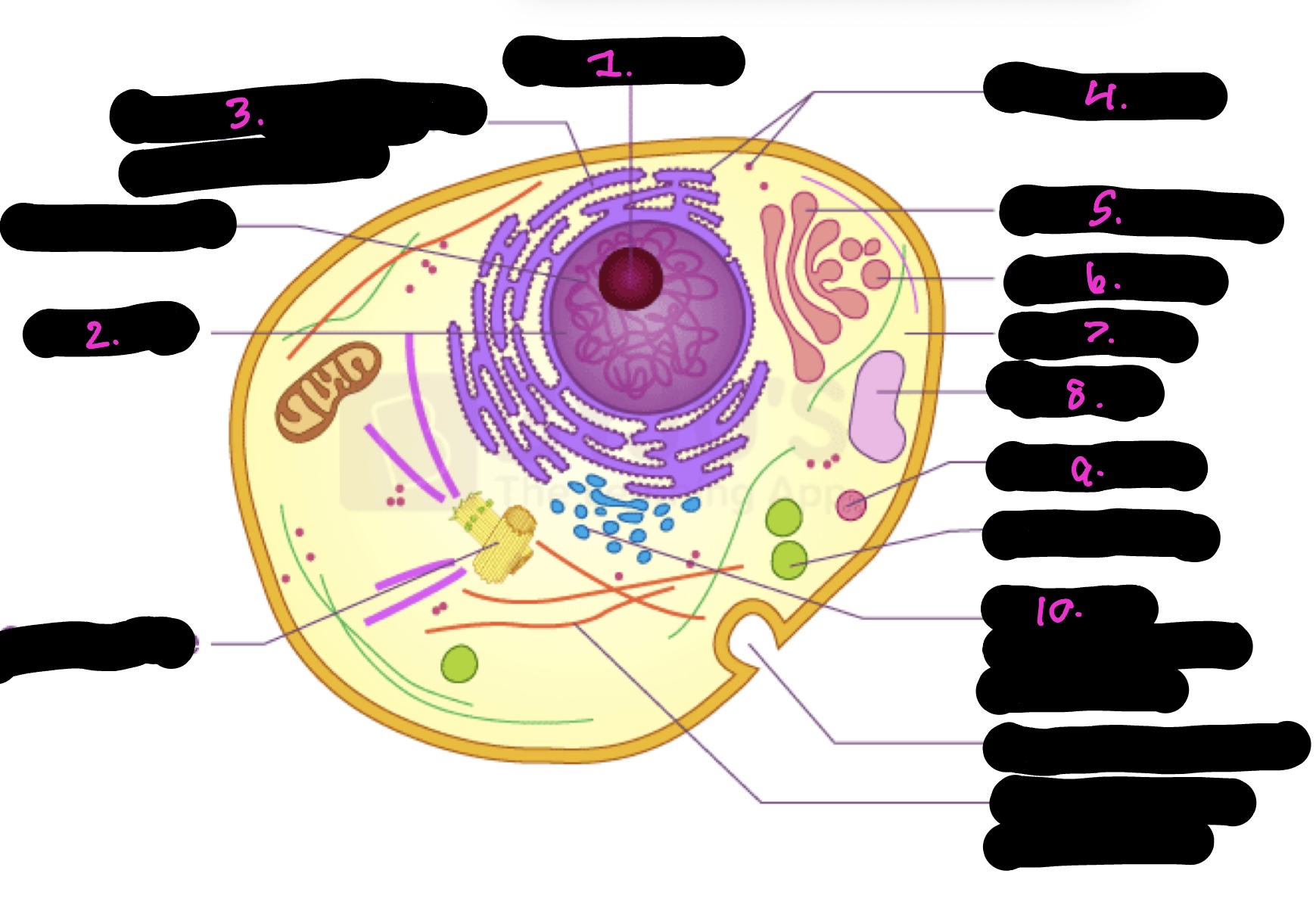
What cell is this
Animal
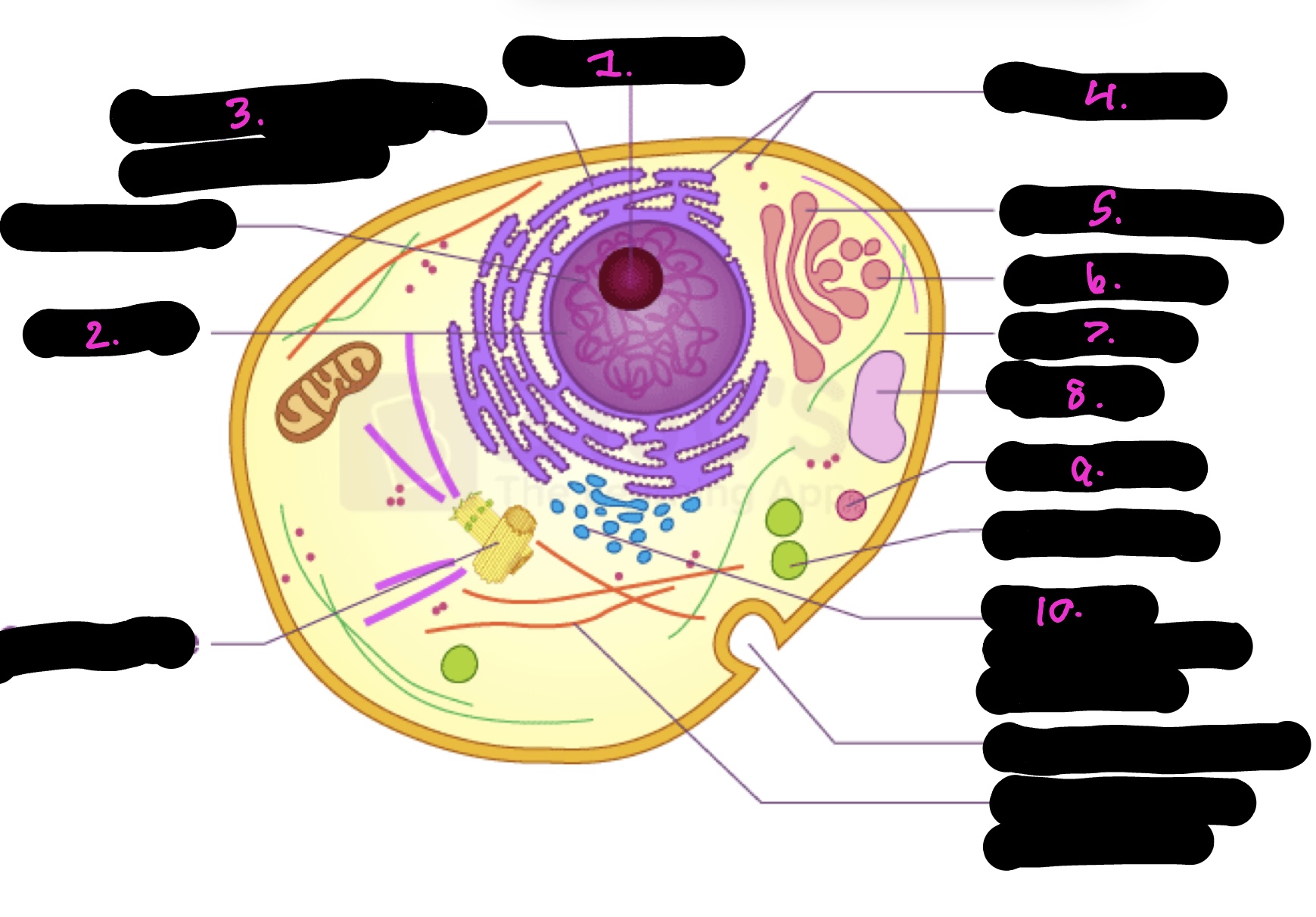
What is 1
Nucleolus
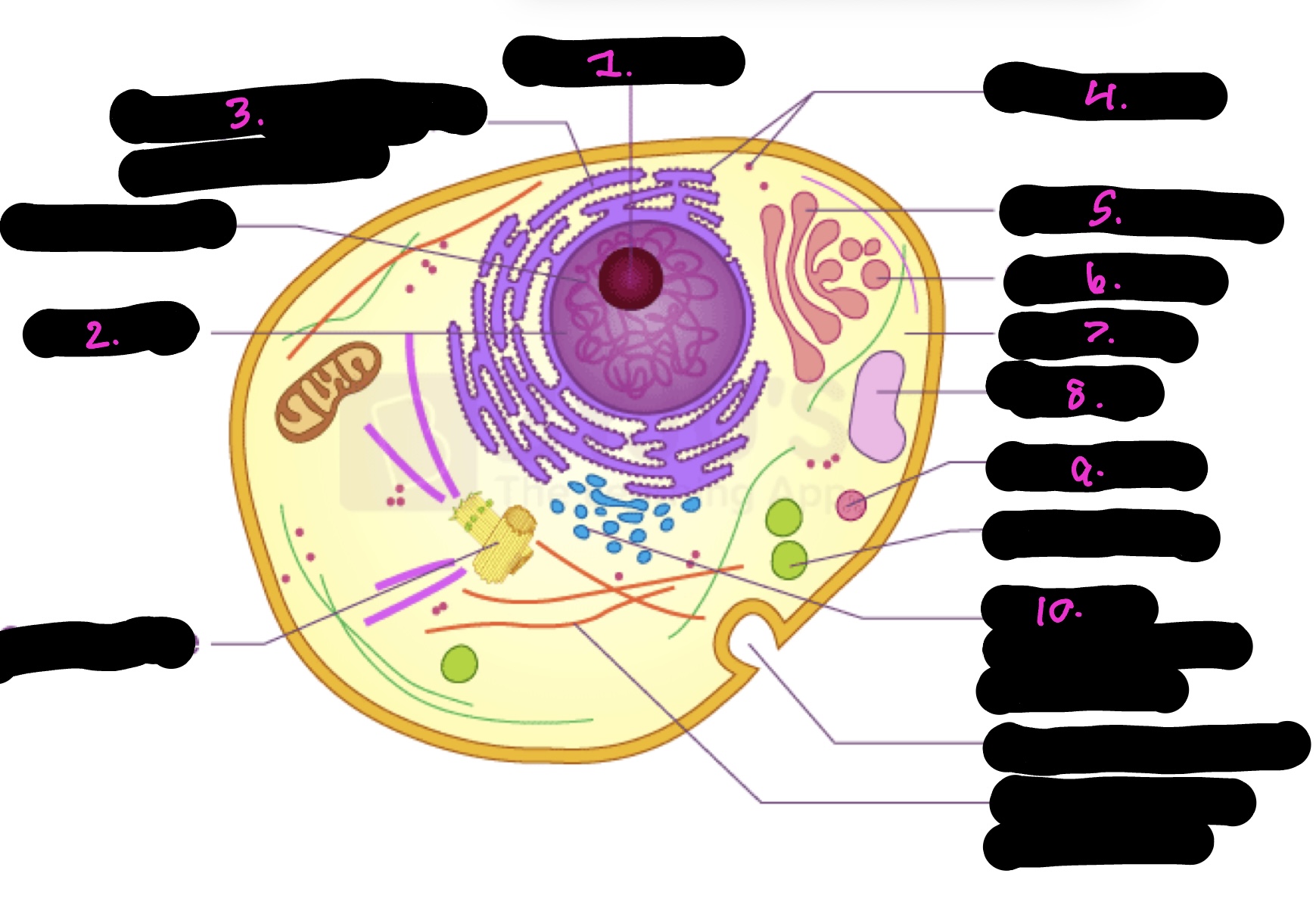
What is 2
Nucleus
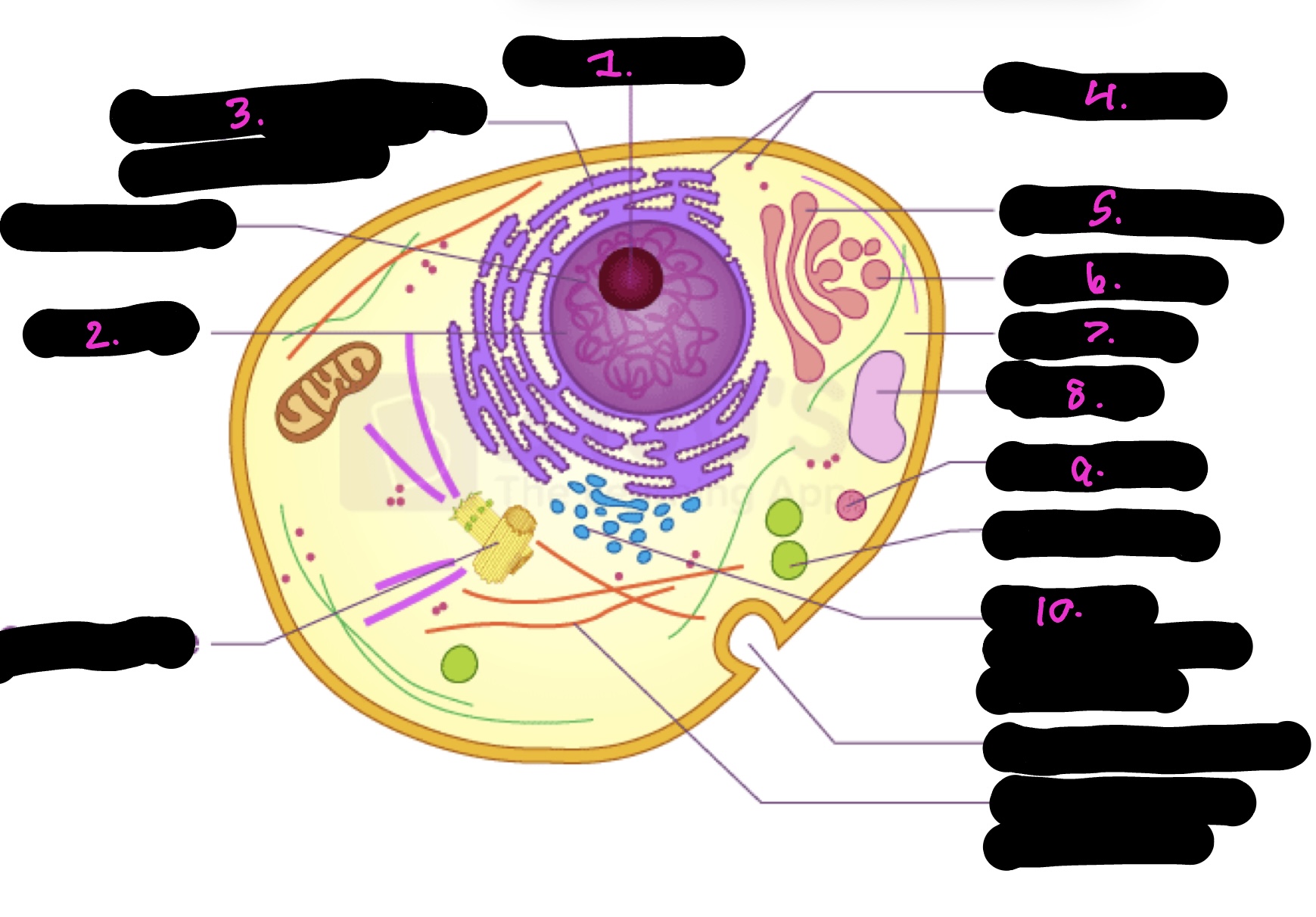
What is 3
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
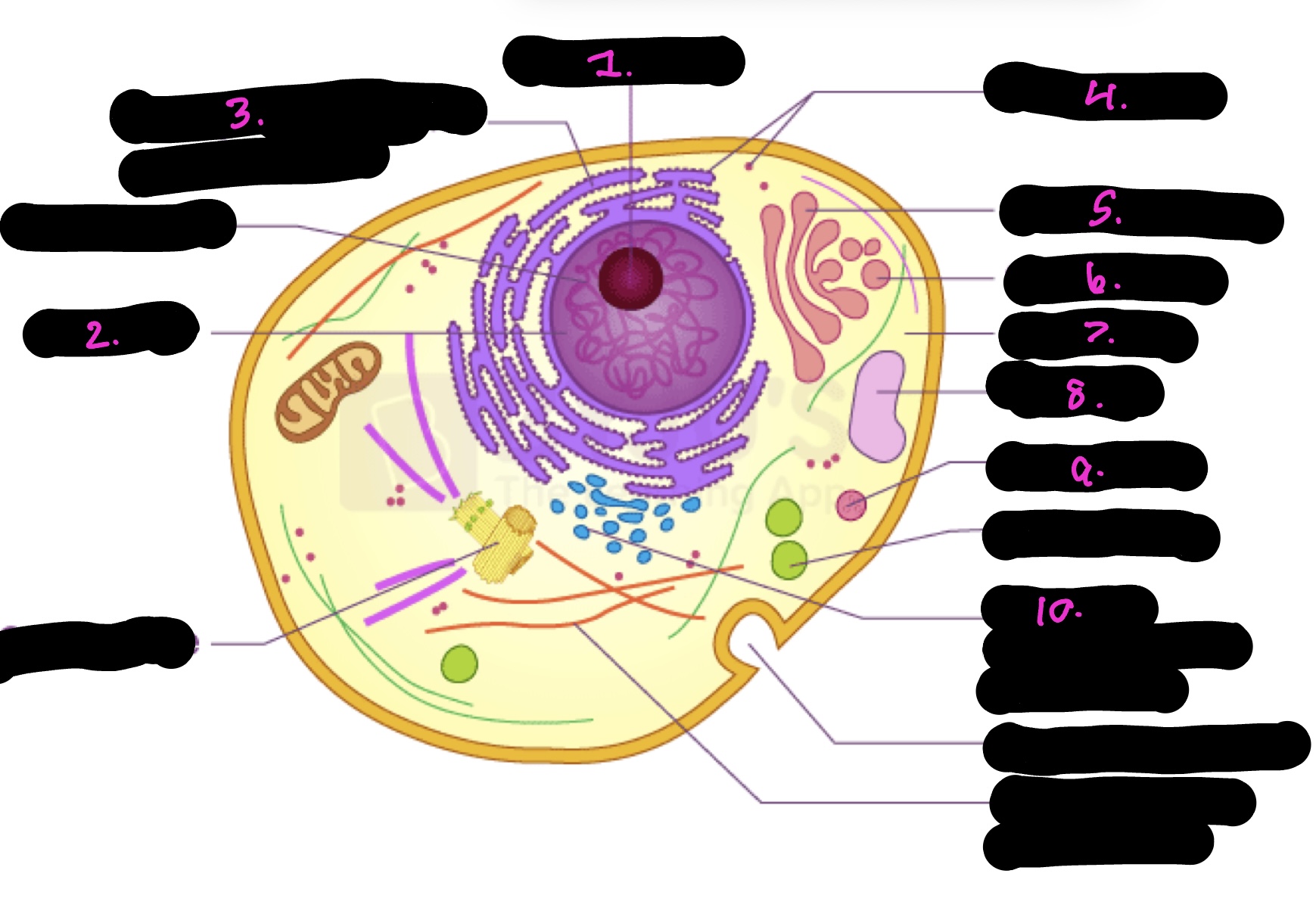
what is 4
Ribosomes
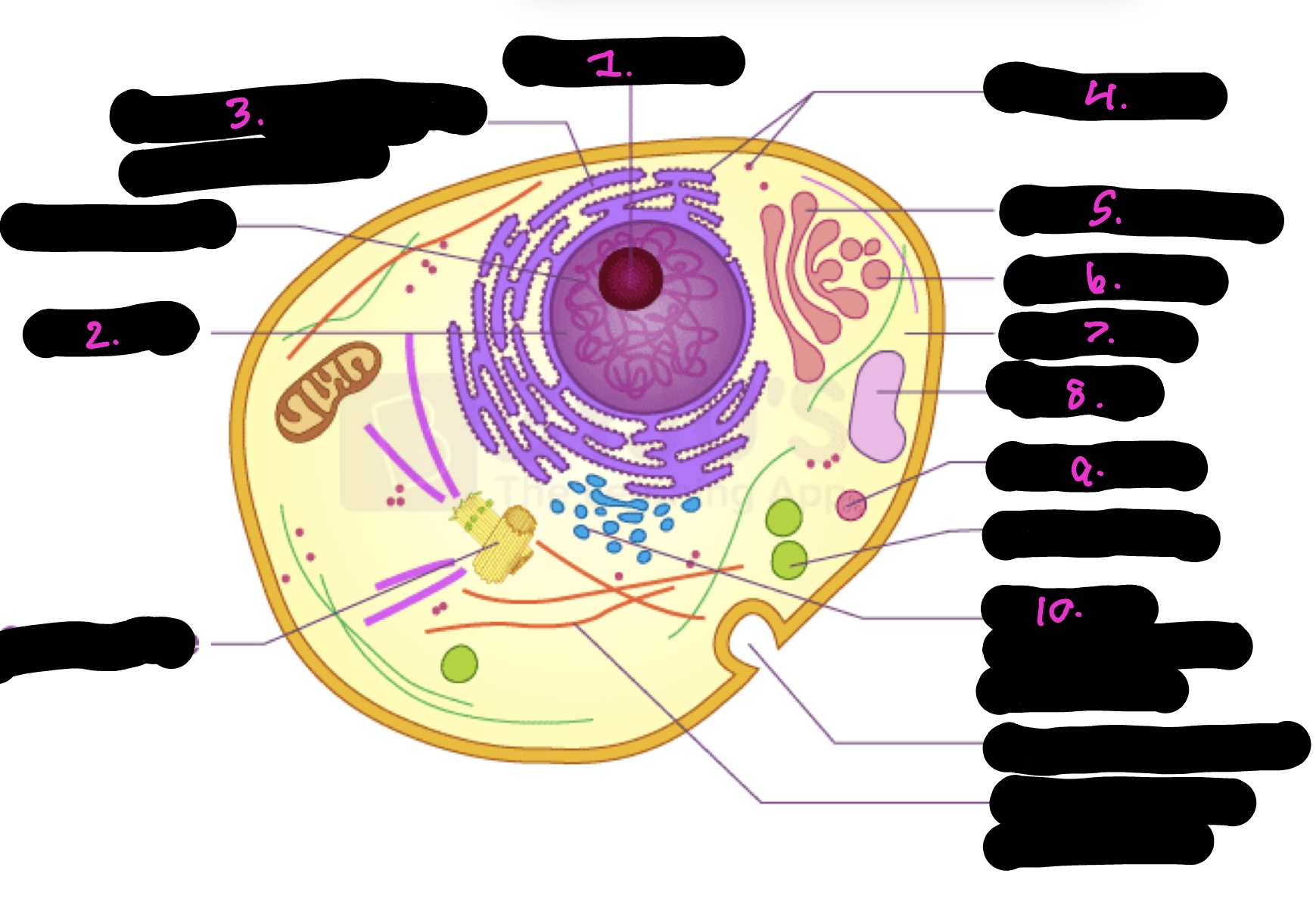
What is 5
Golgi apparatus
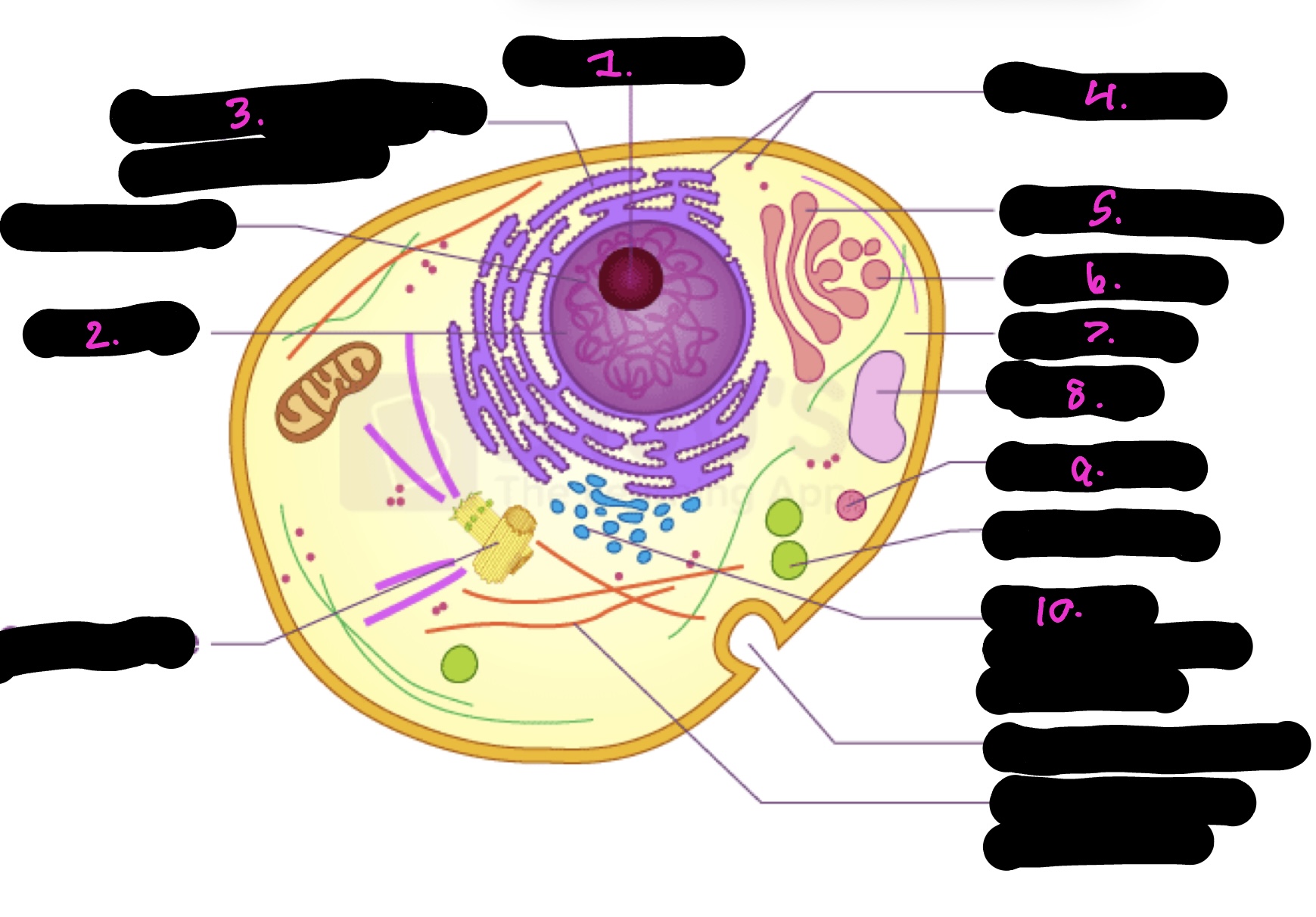
What is 6
Golgi vesicle
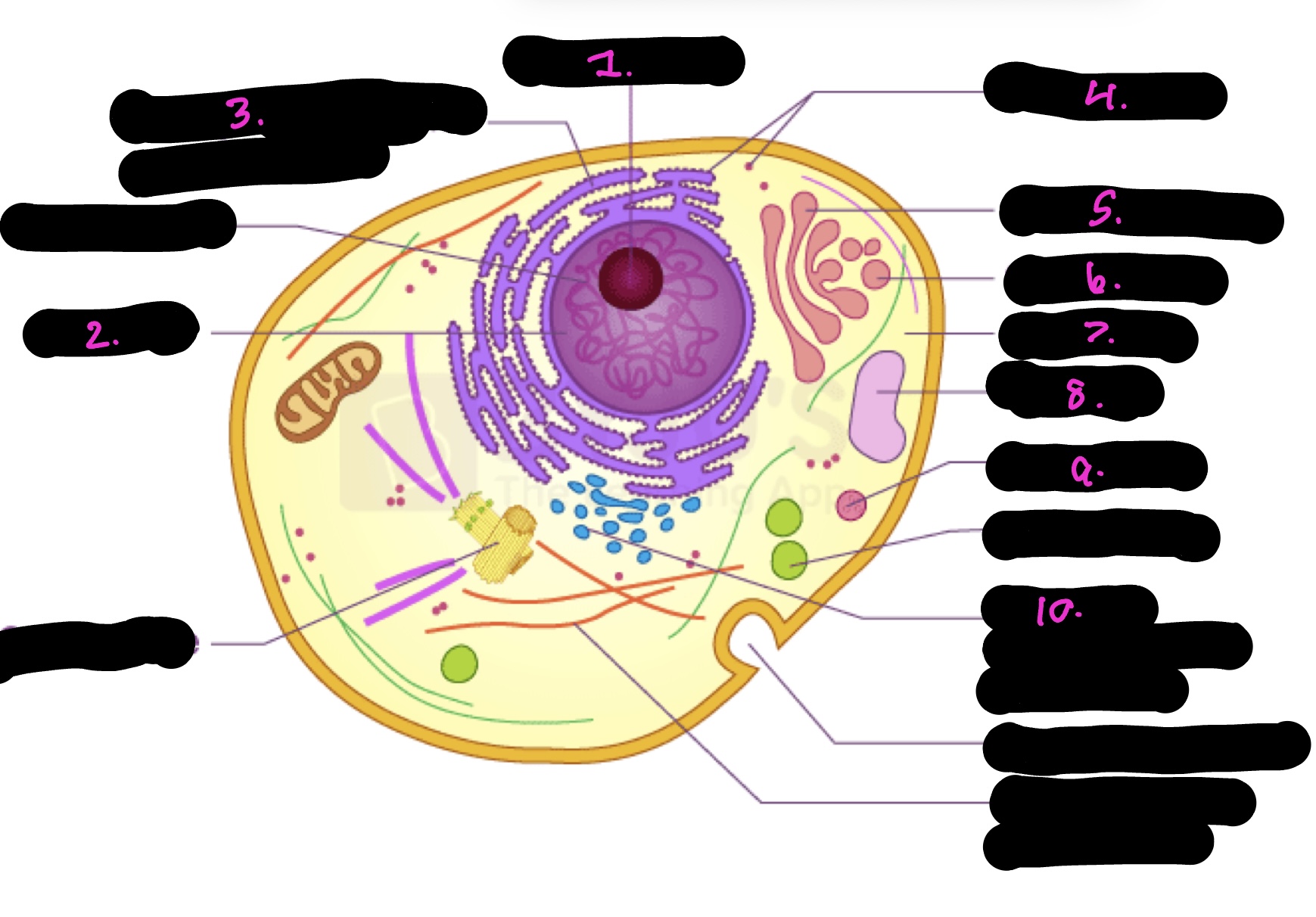
What is 7
cytoplasm
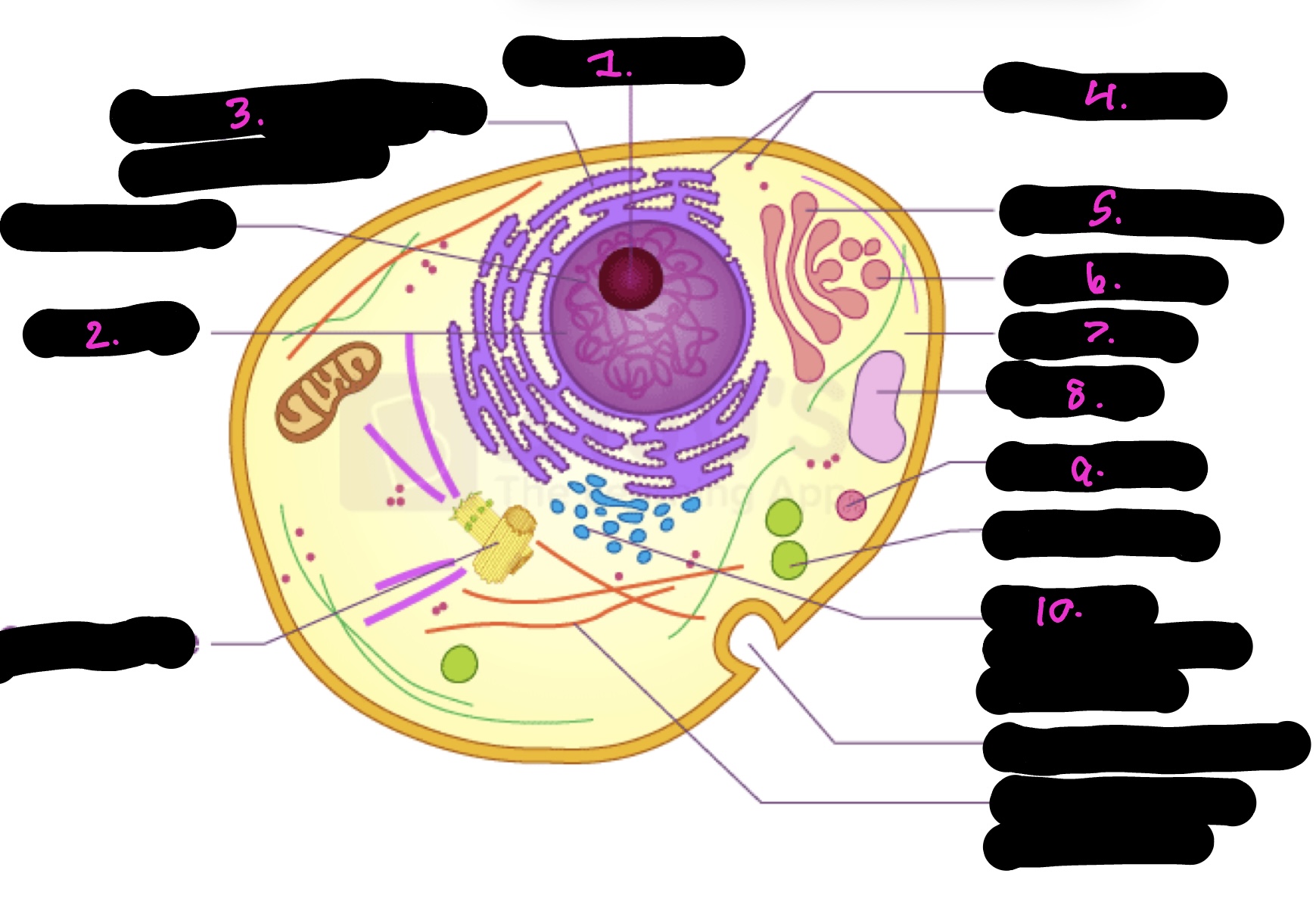
What is 8
Vacuole
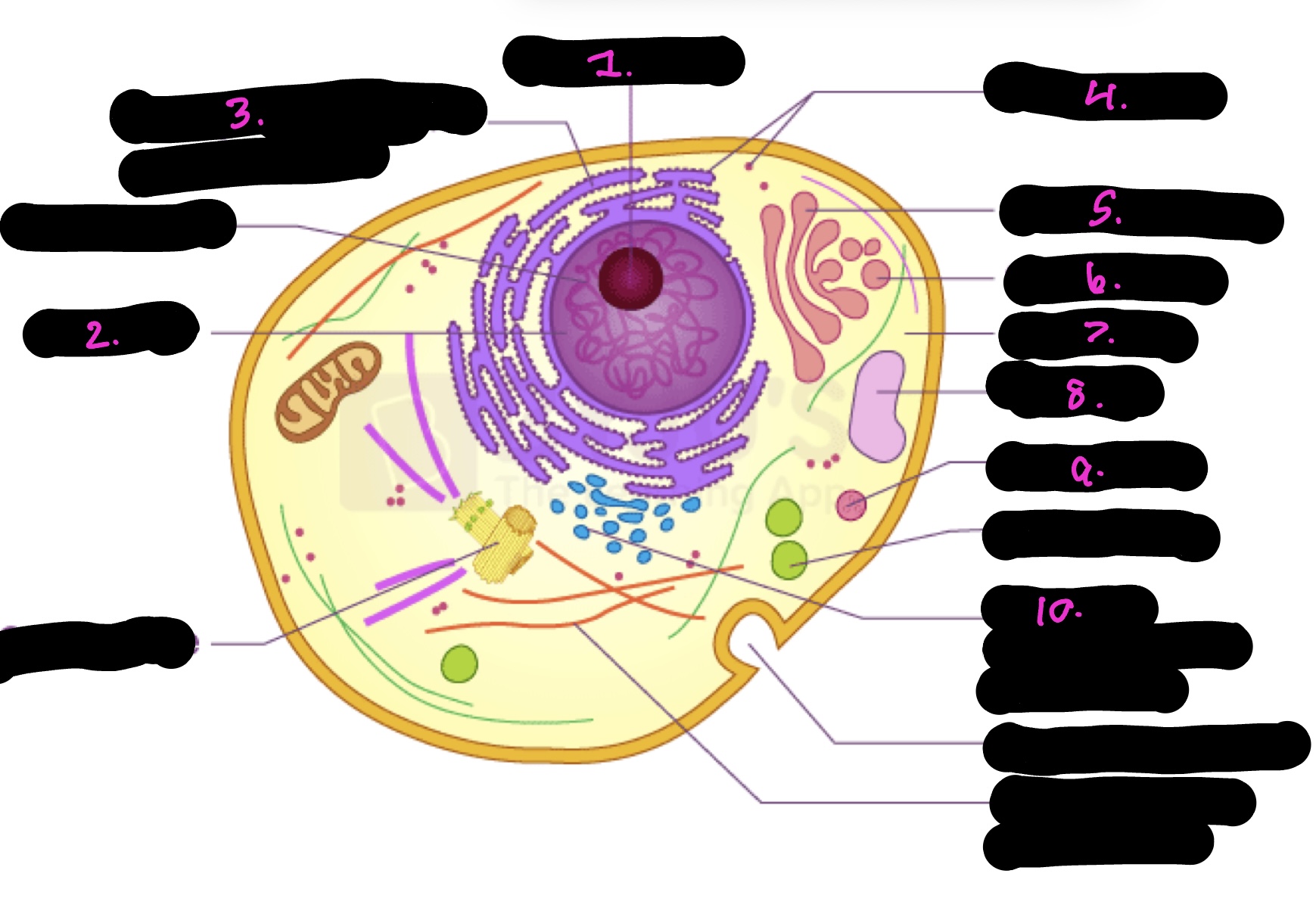
What is 9
Lysosome
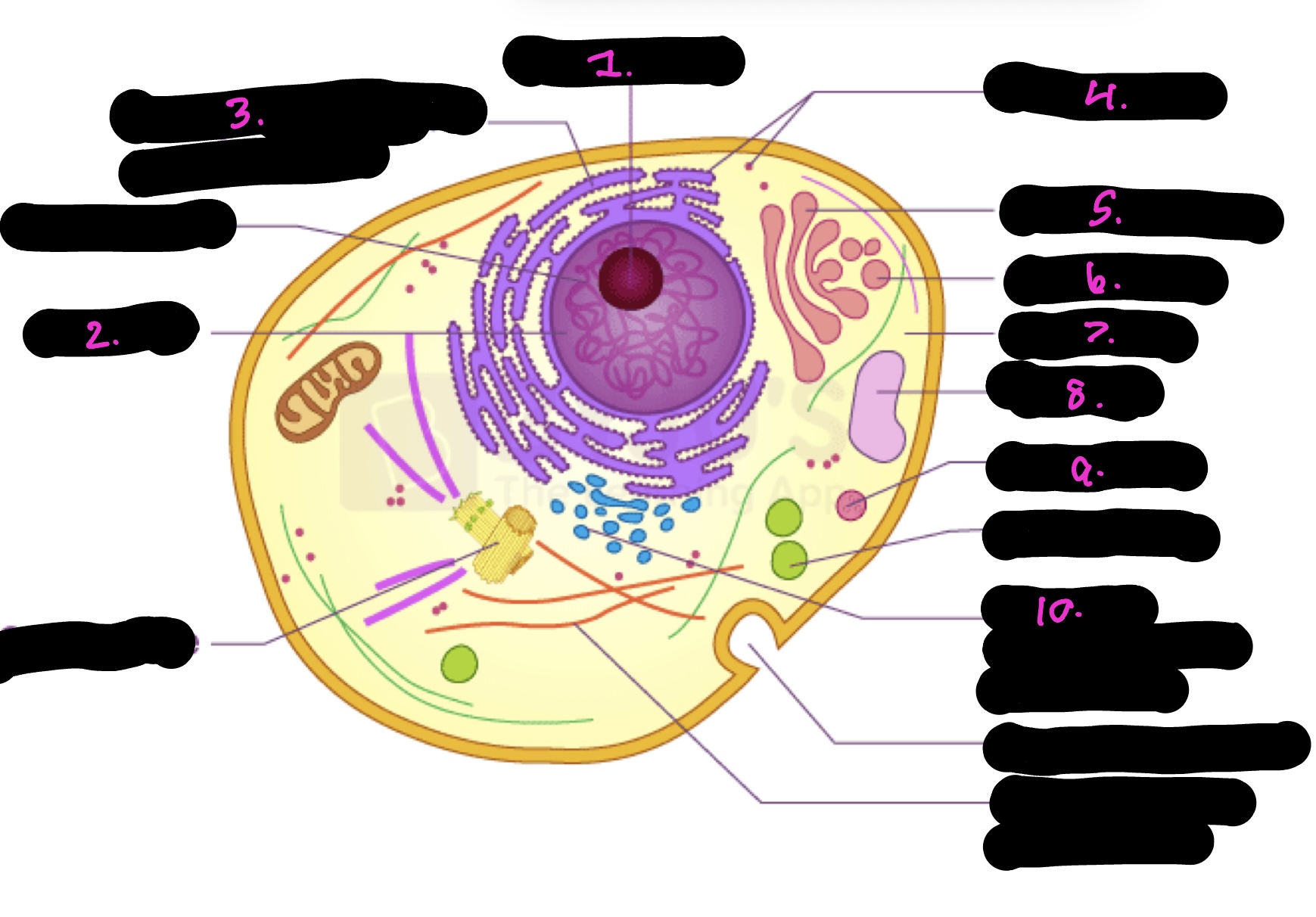
What is 10
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
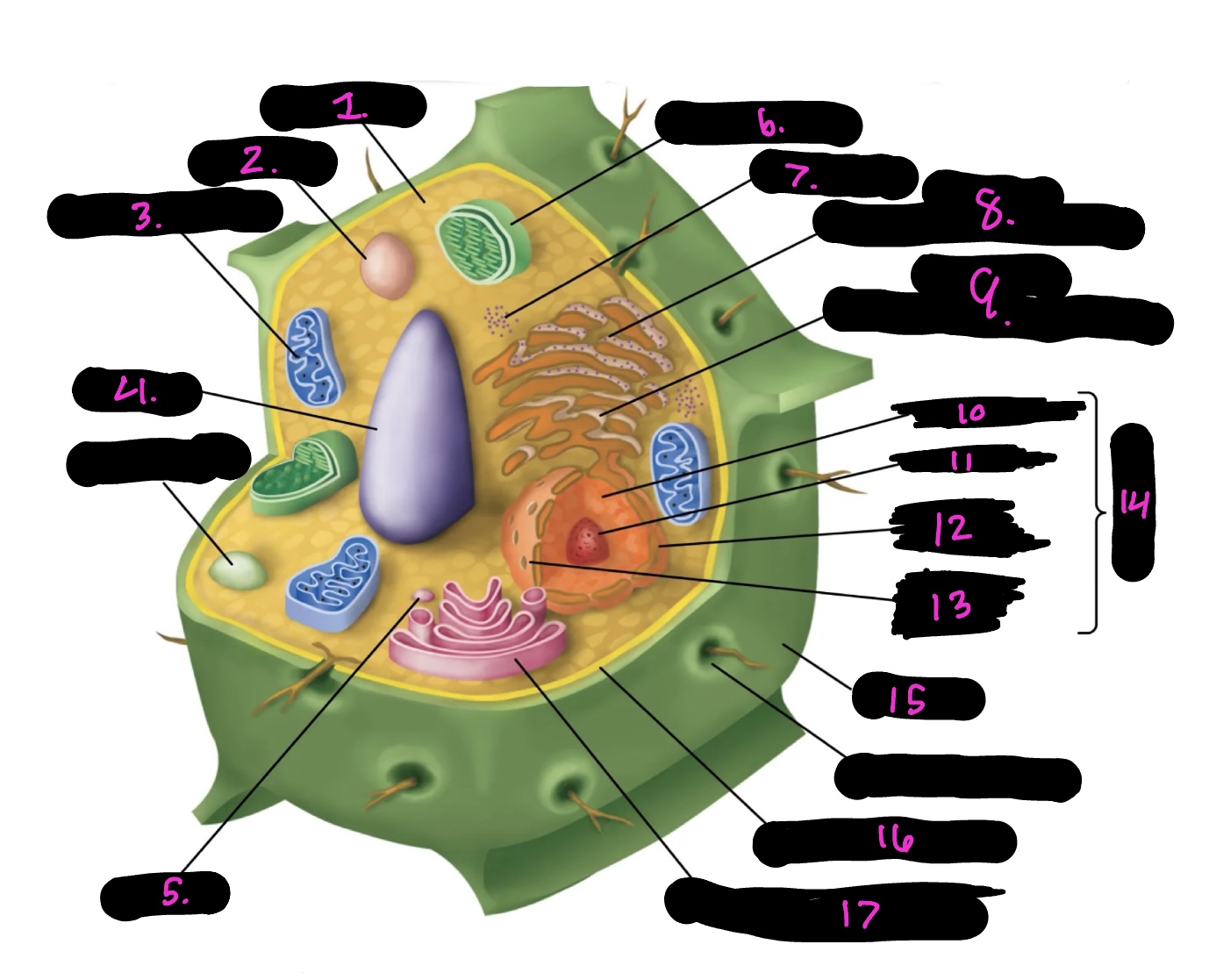
What cell is this
plant
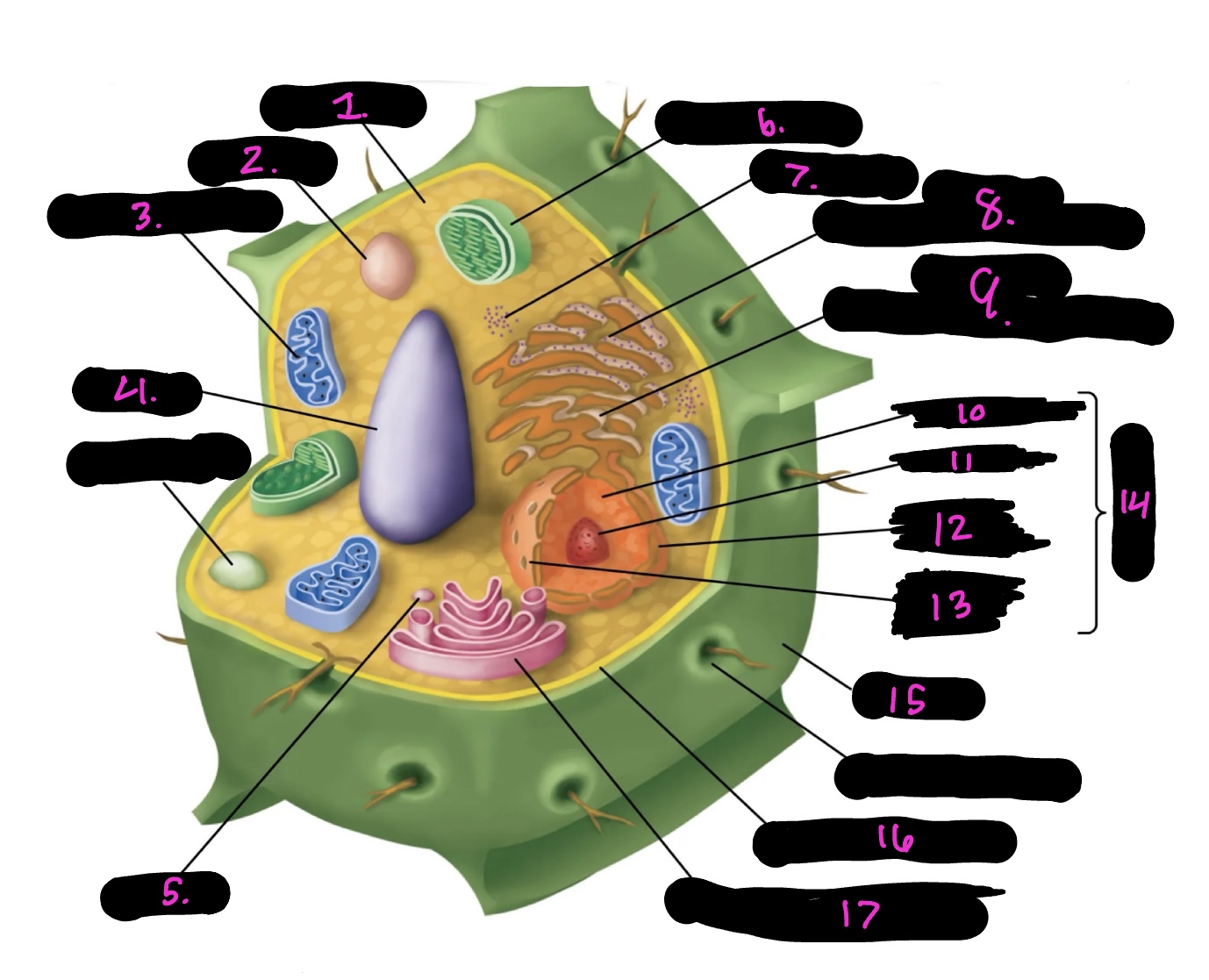
What is 1
cytoplasm
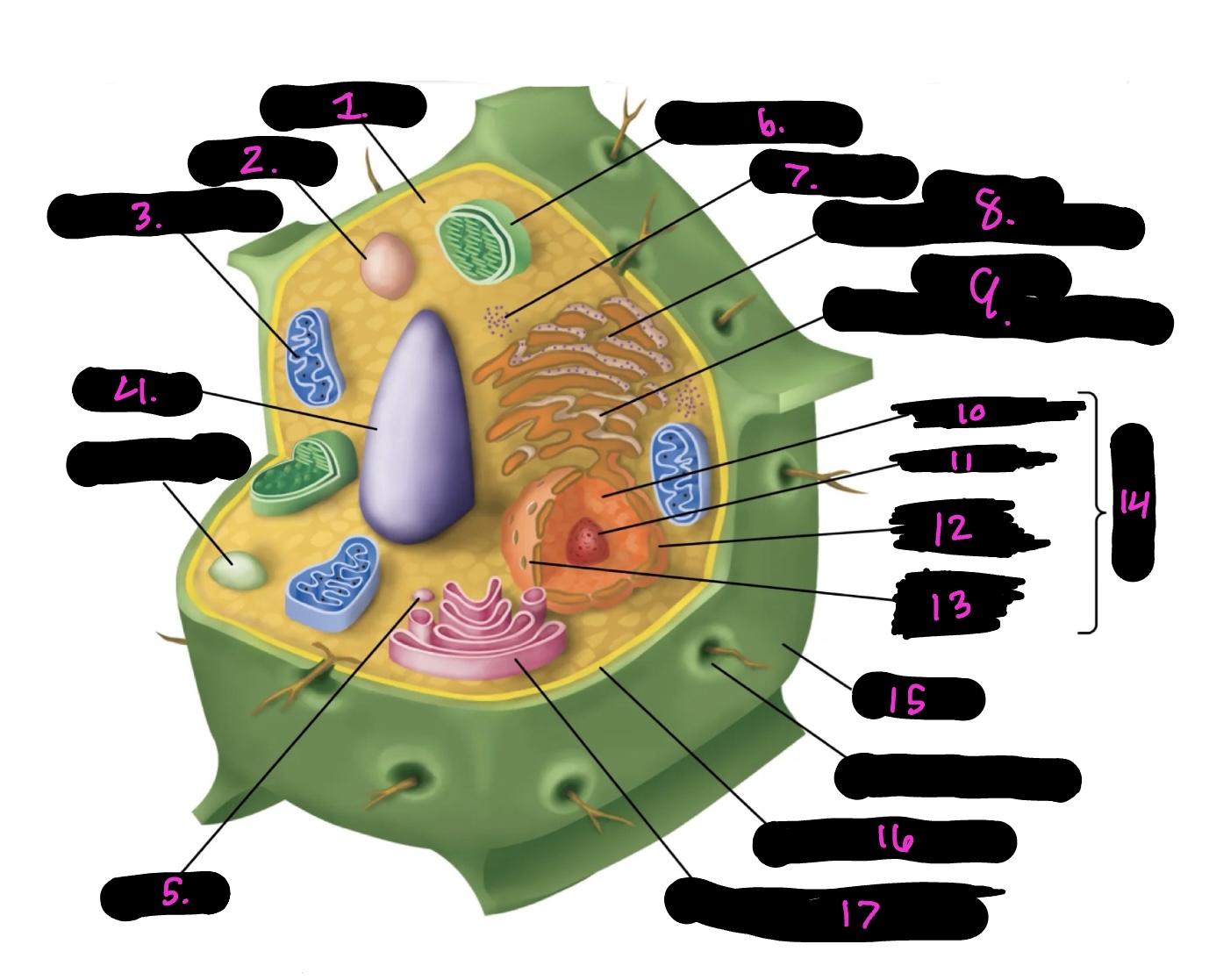
What is 2
lysosome
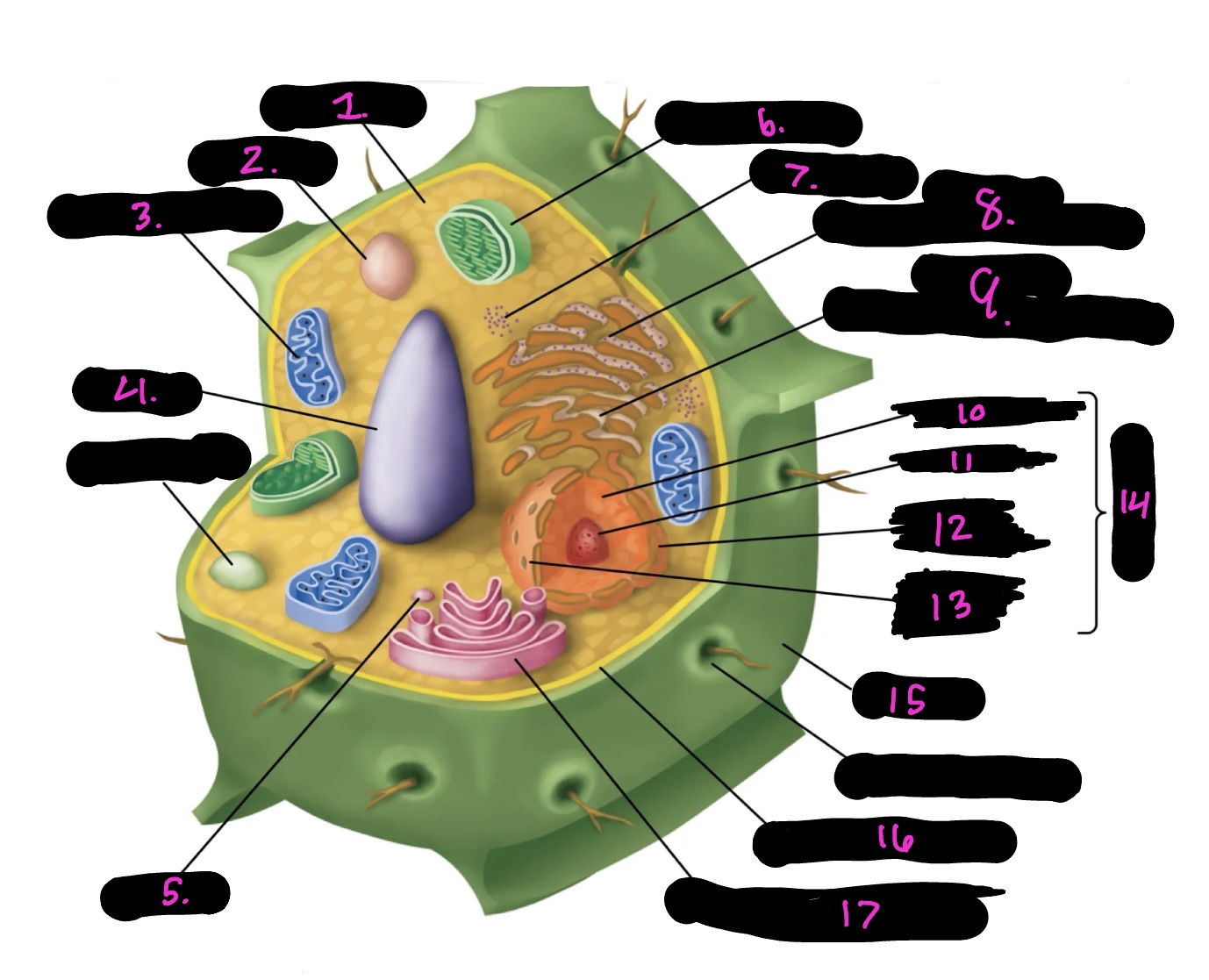
What is 3
mitochondria (same as animal)
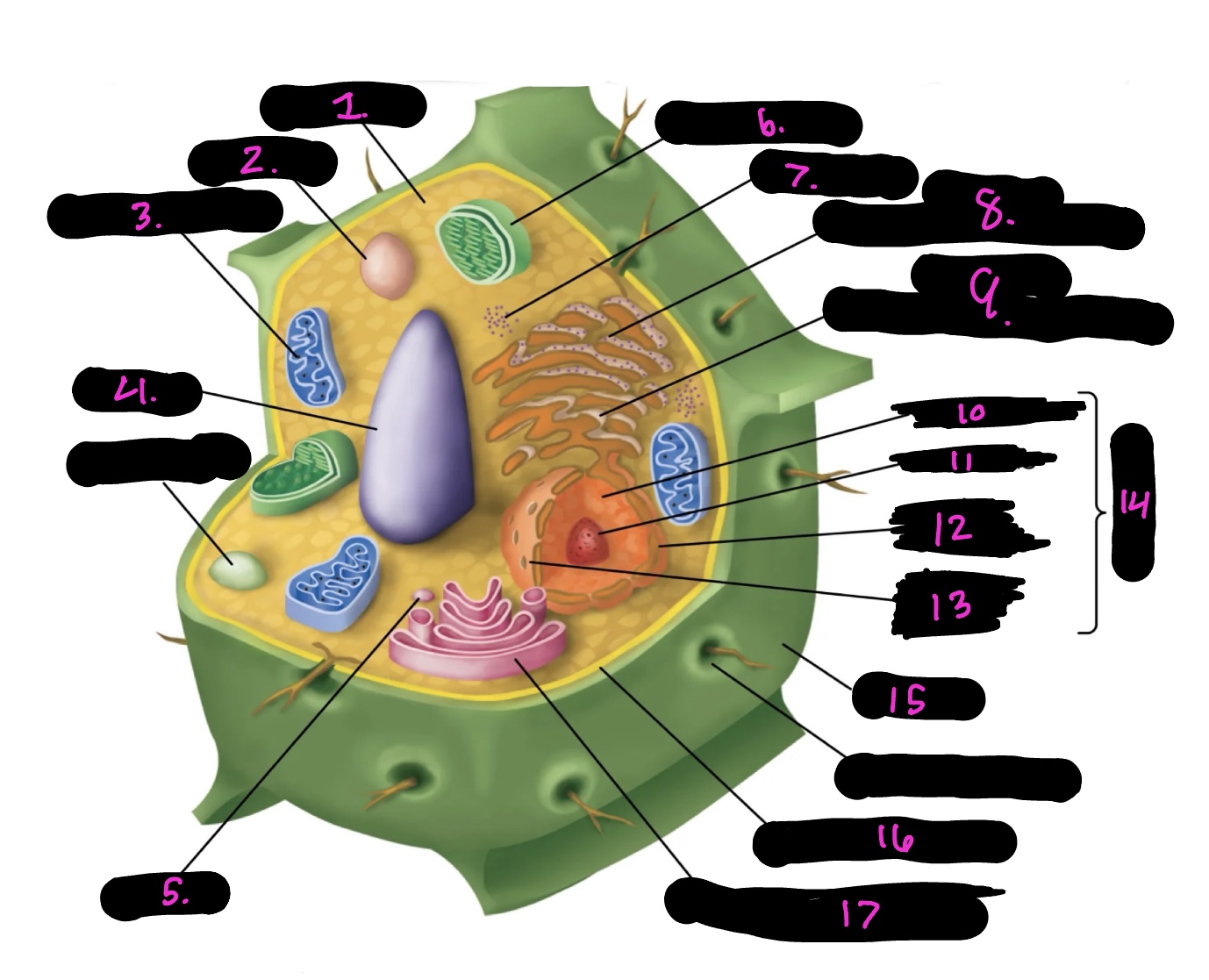
What is 4
Vacuole
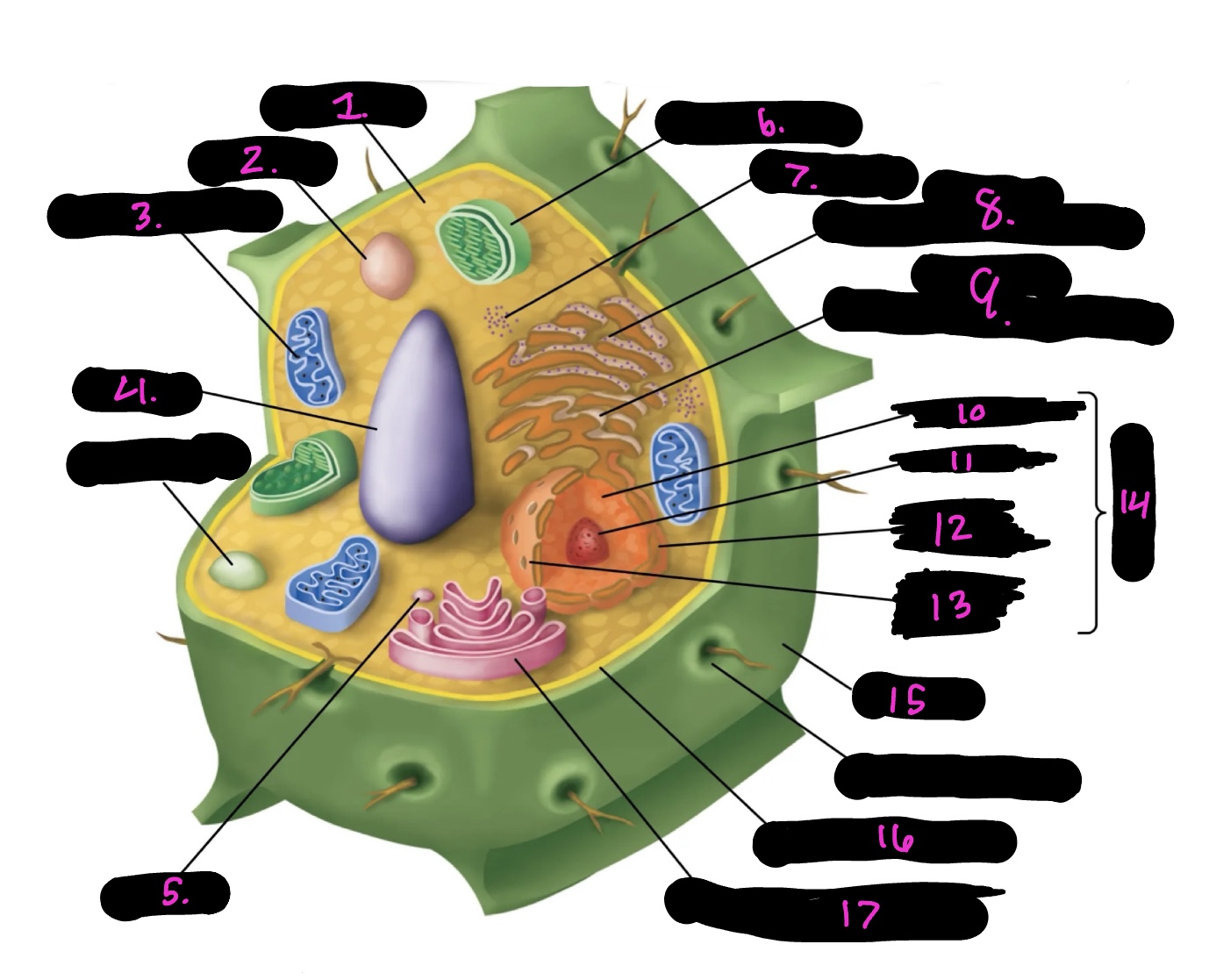
What is 5
vesicle
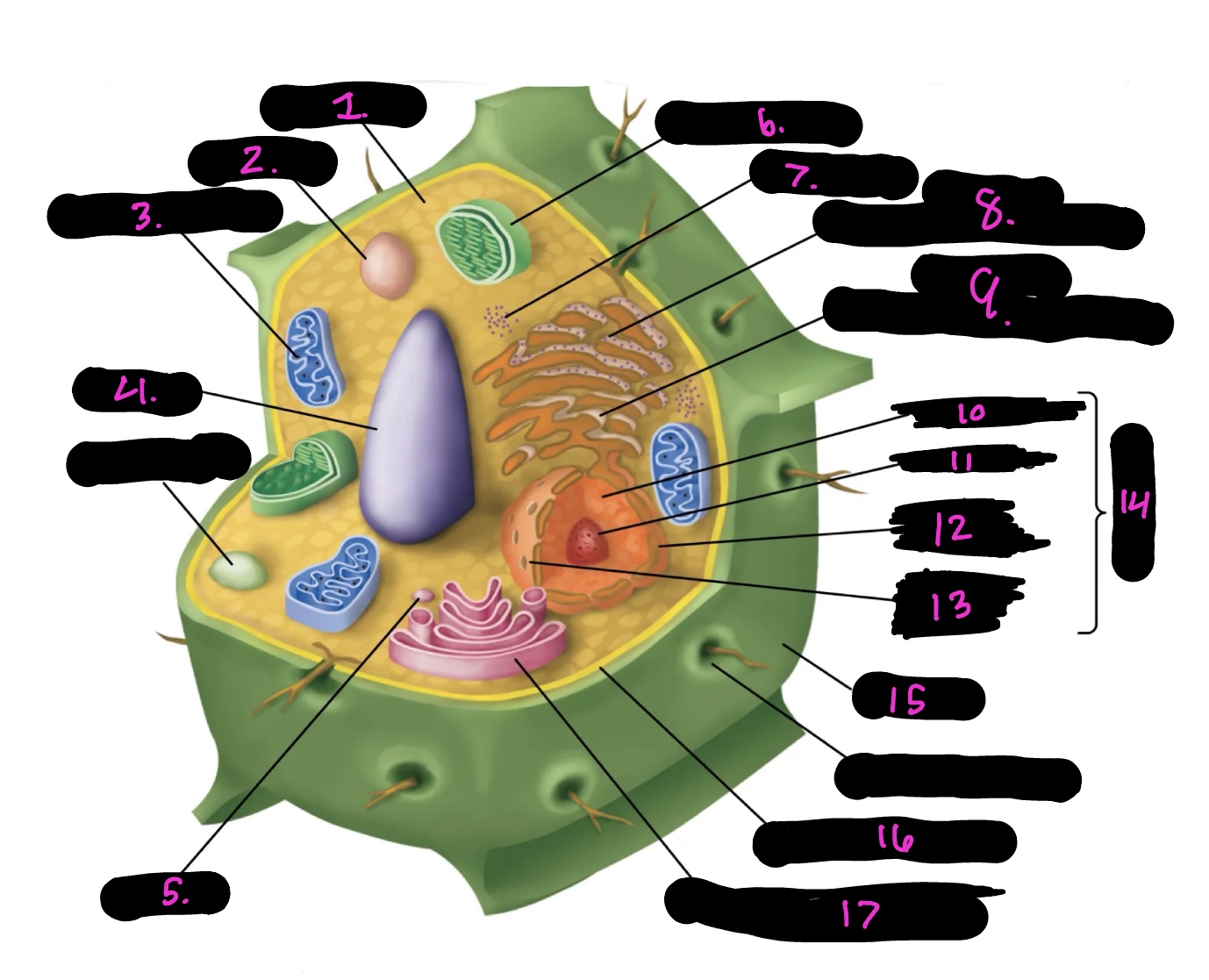
What is 6
Chloroplast
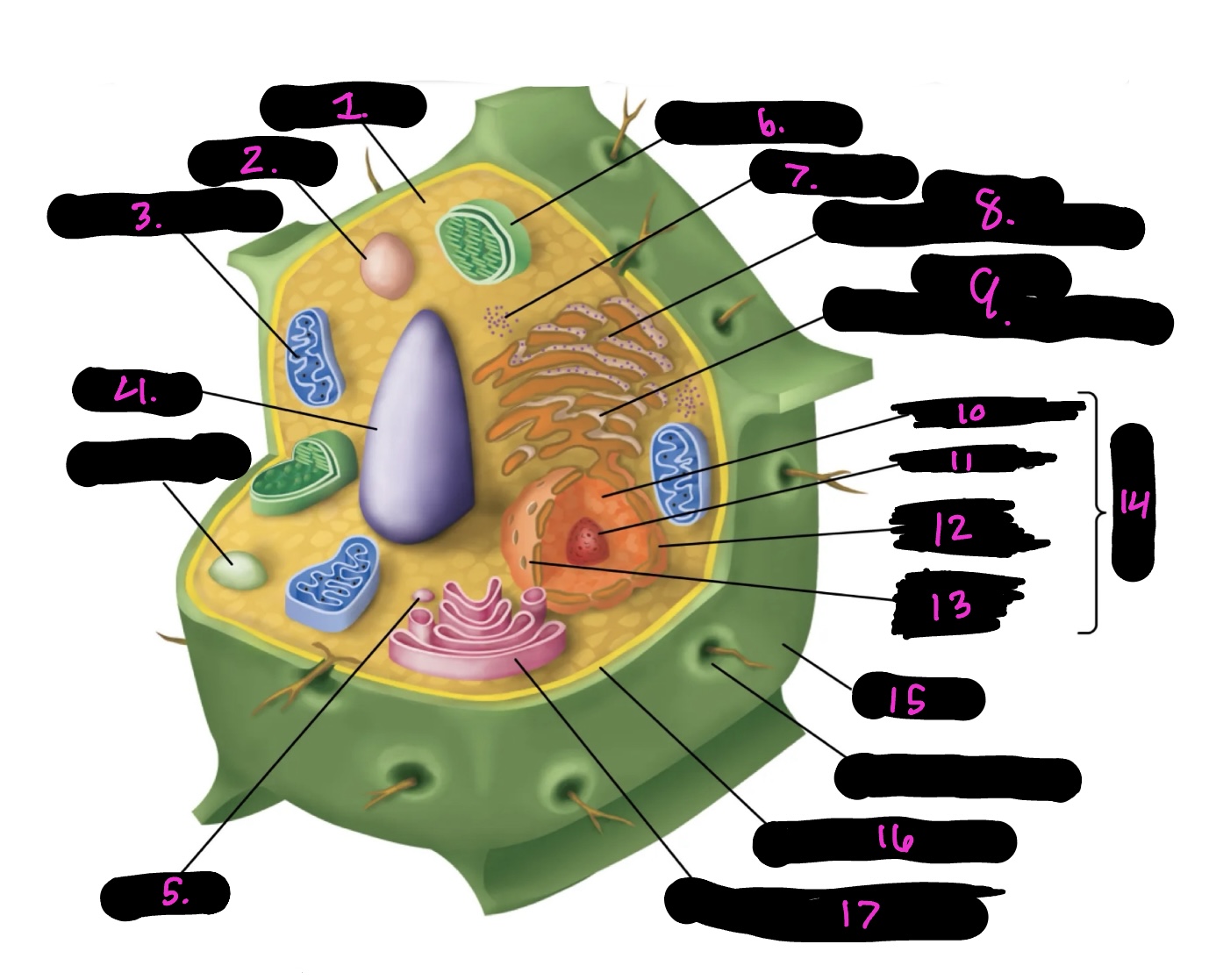
What is 7
Ribosomes
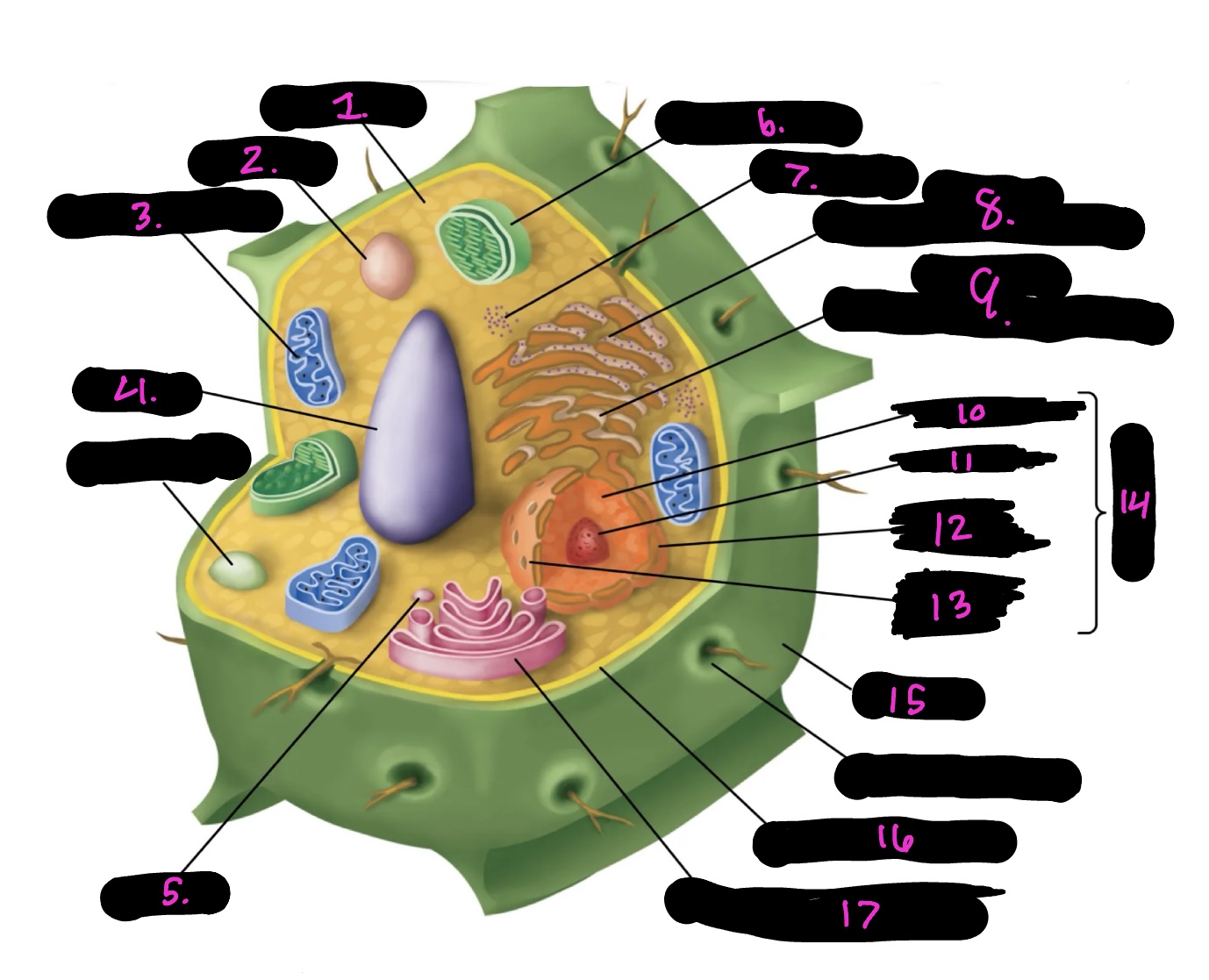
What is 8
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
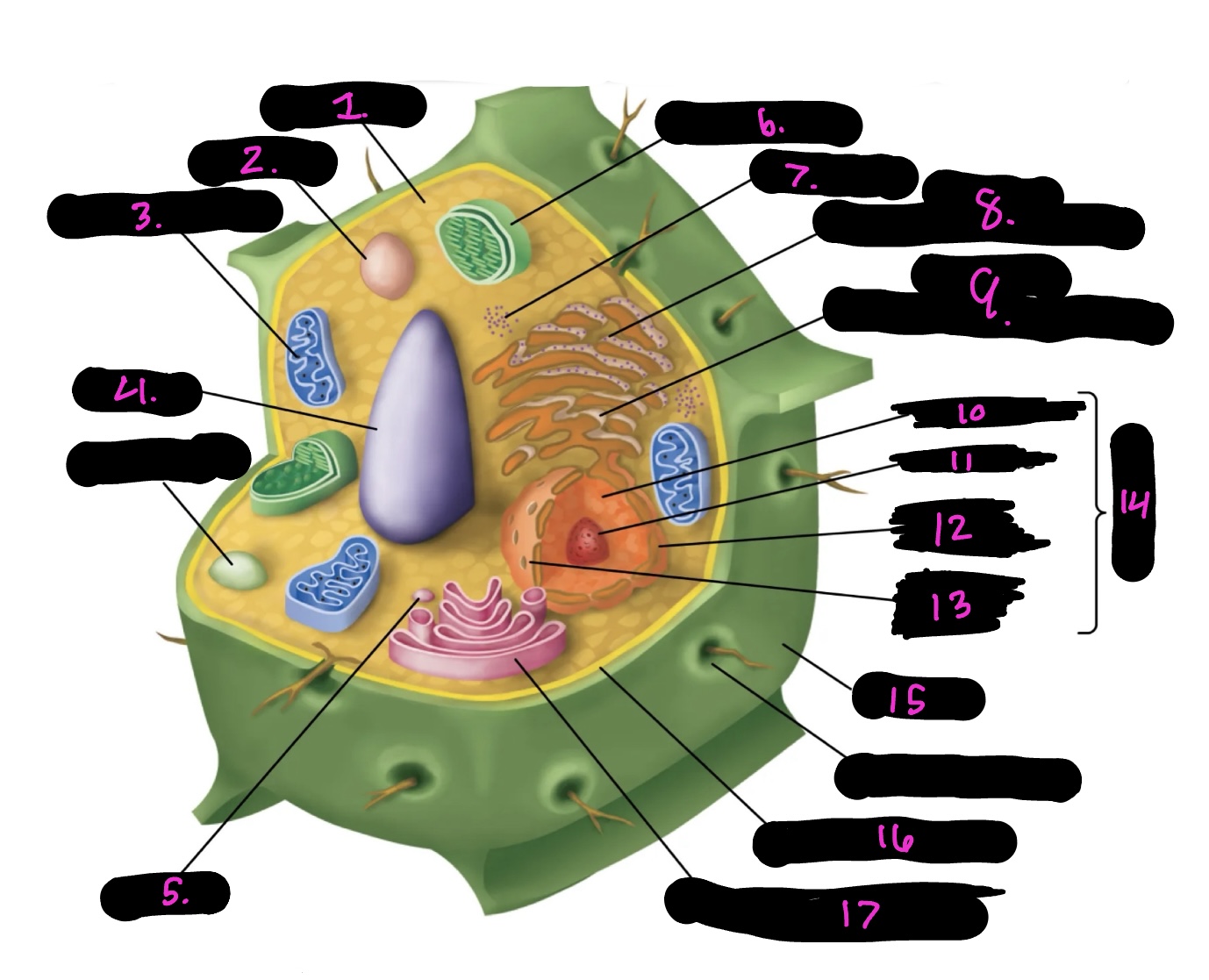
What is 9
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
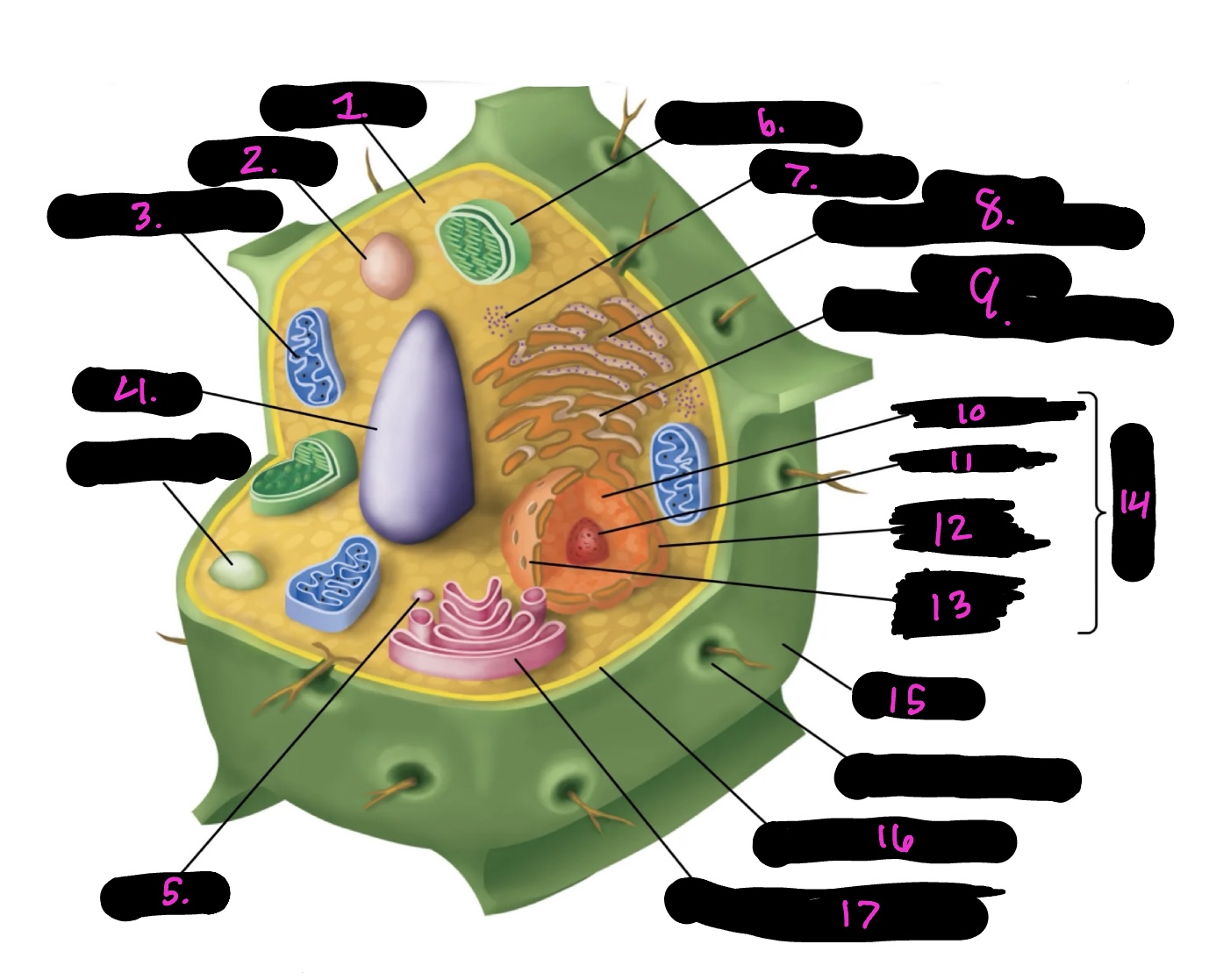
What is 10
Nucleoplasm
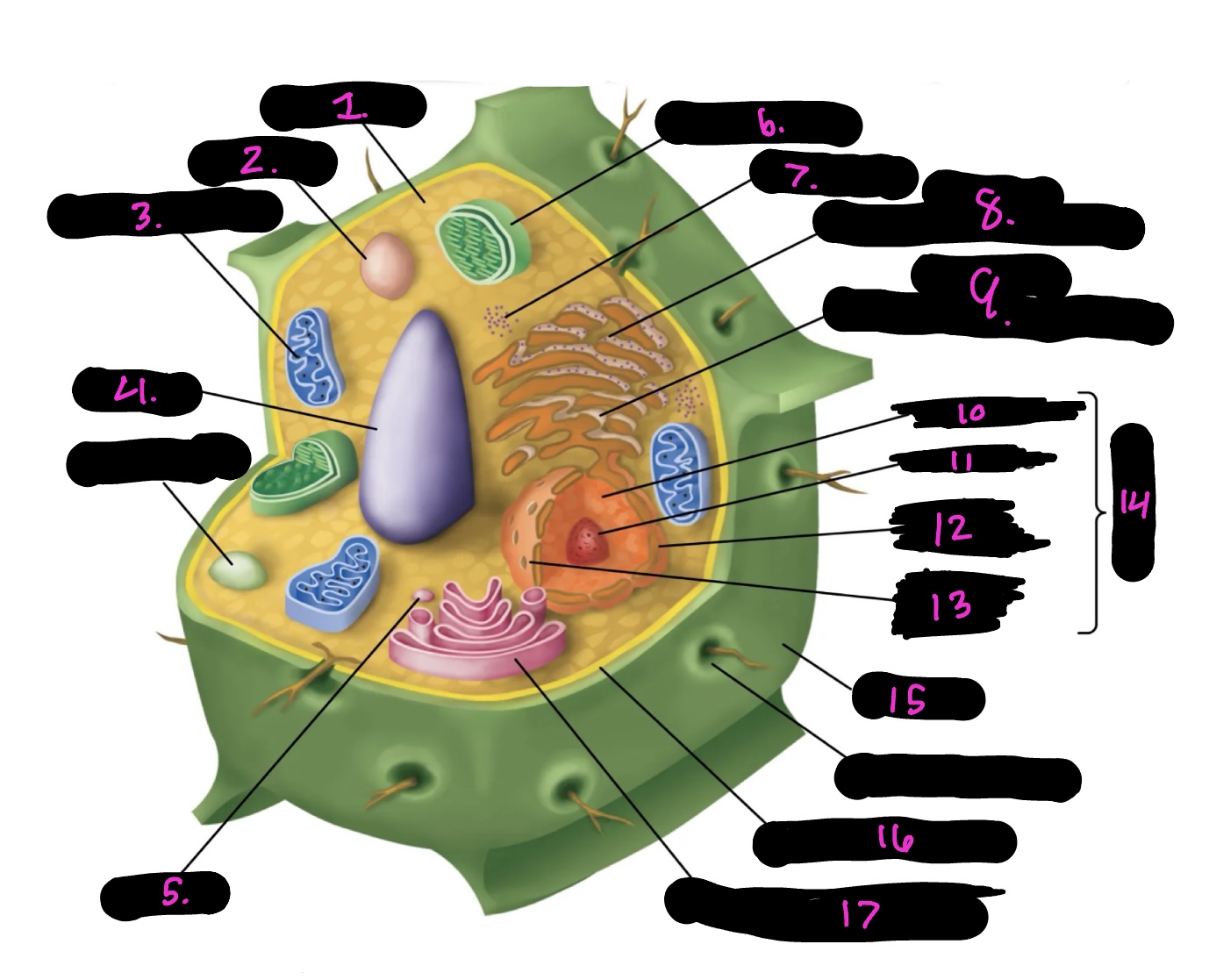
What is 11
Nucleolus
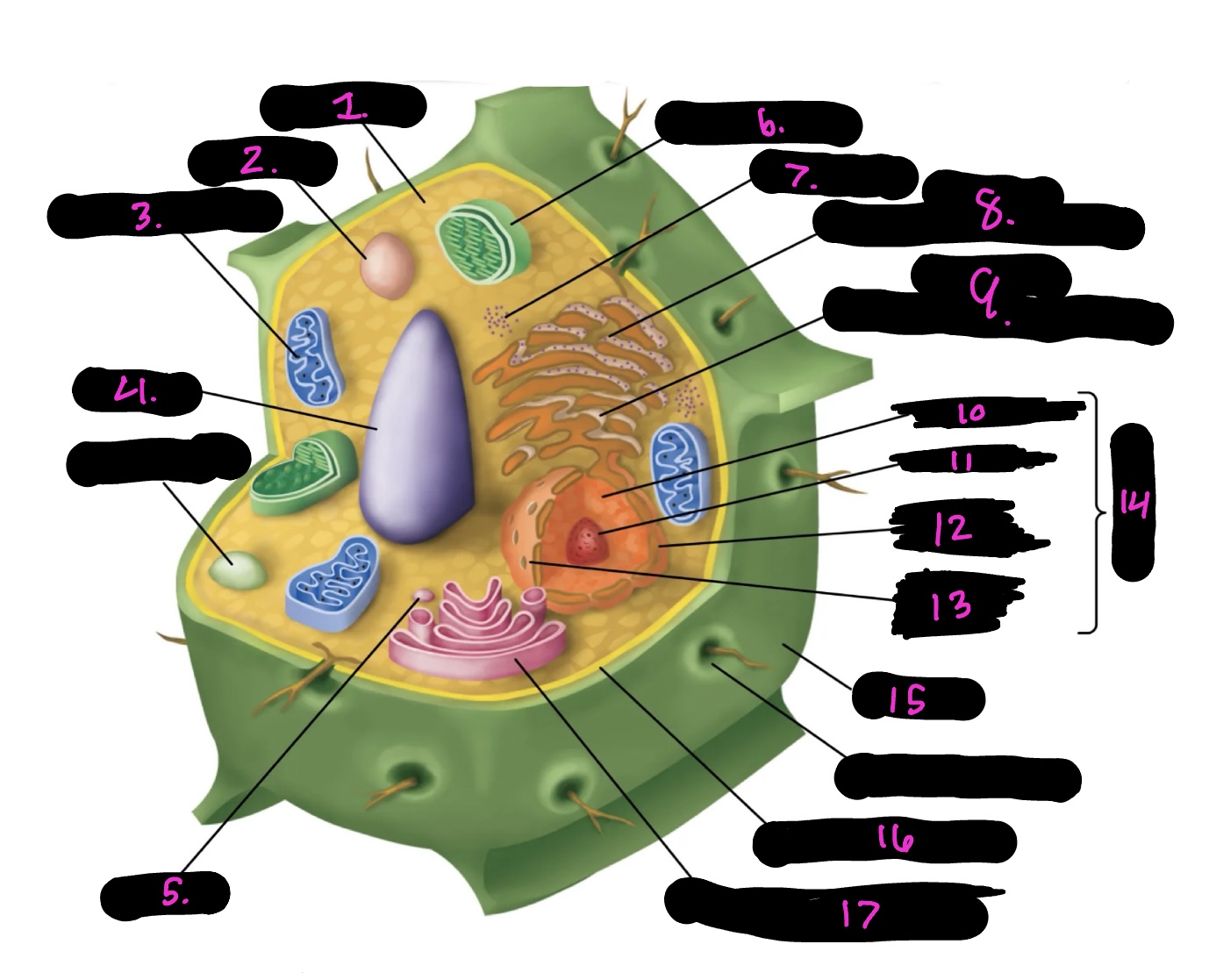
What is 12
Nuclear envelope
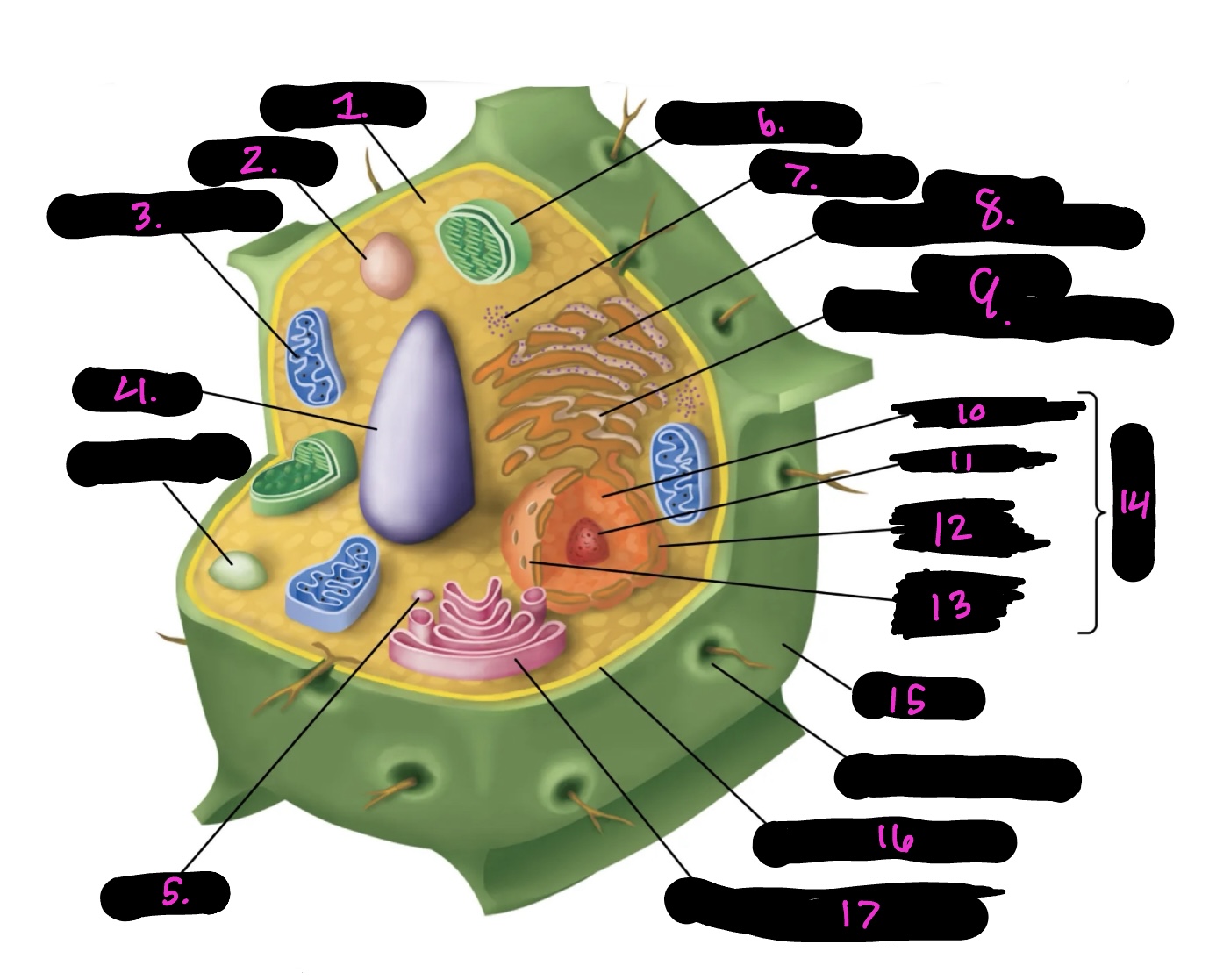
What is 13
Nuclear pore
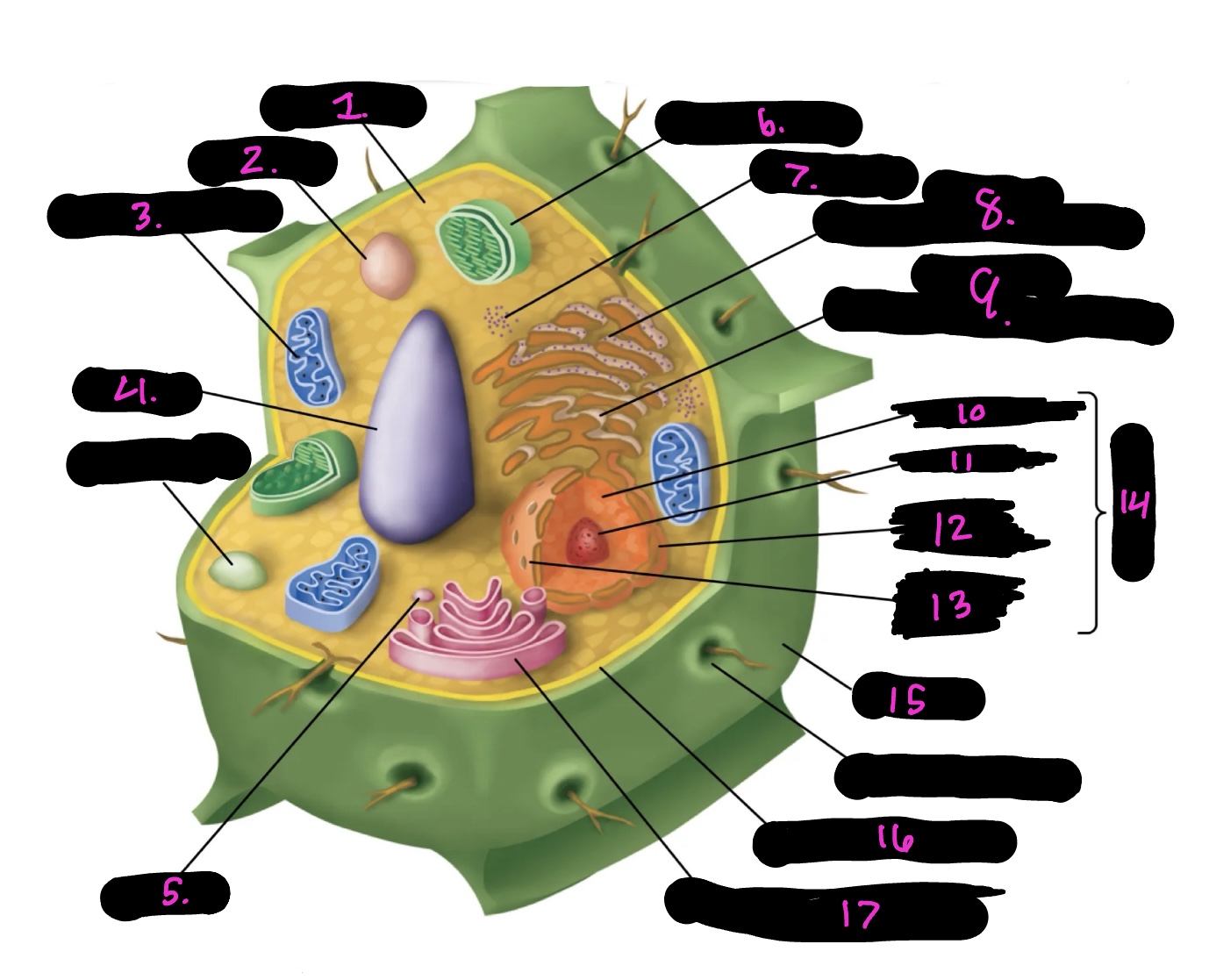
What is 14
Nucleus
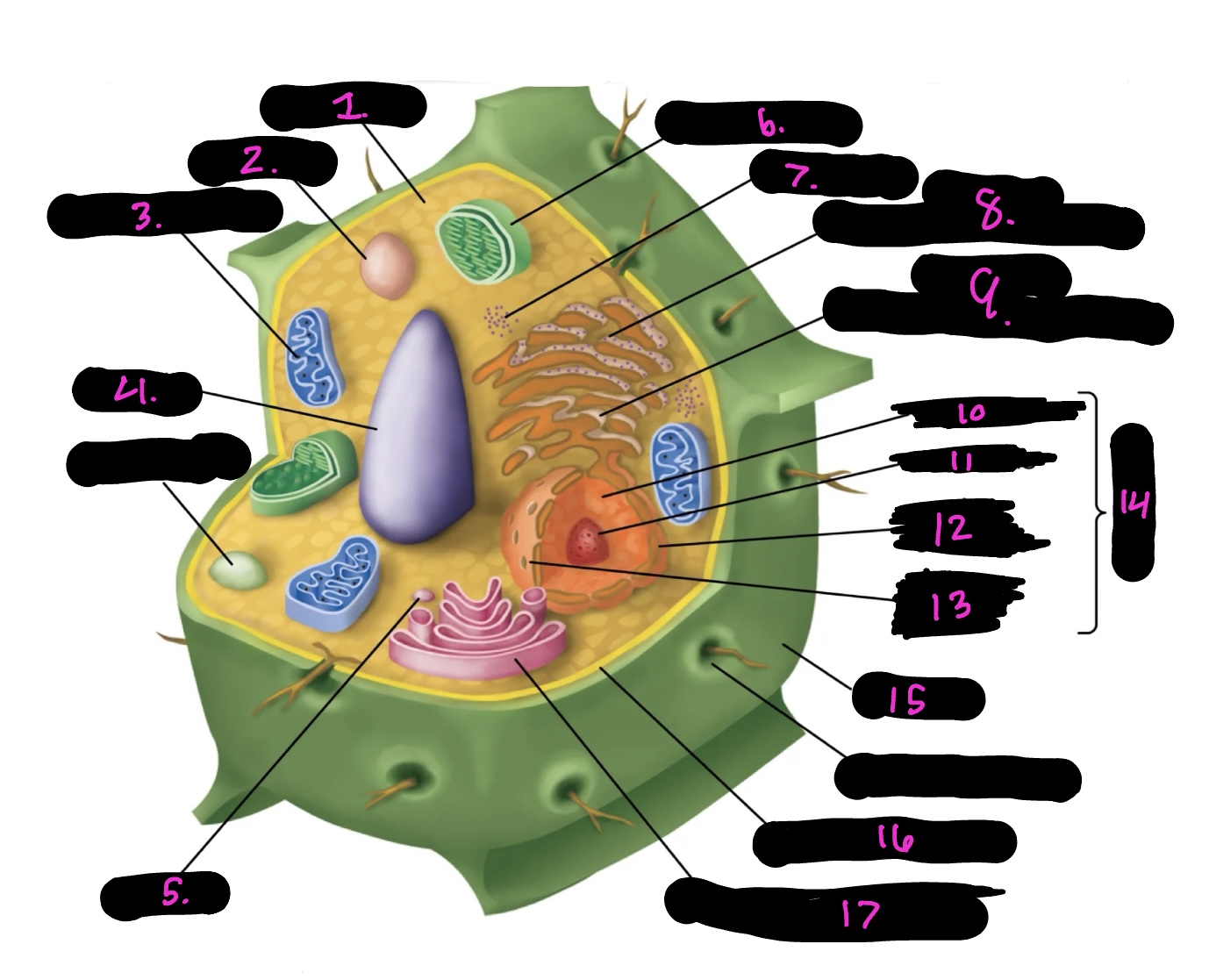
What is 15
Cell wall
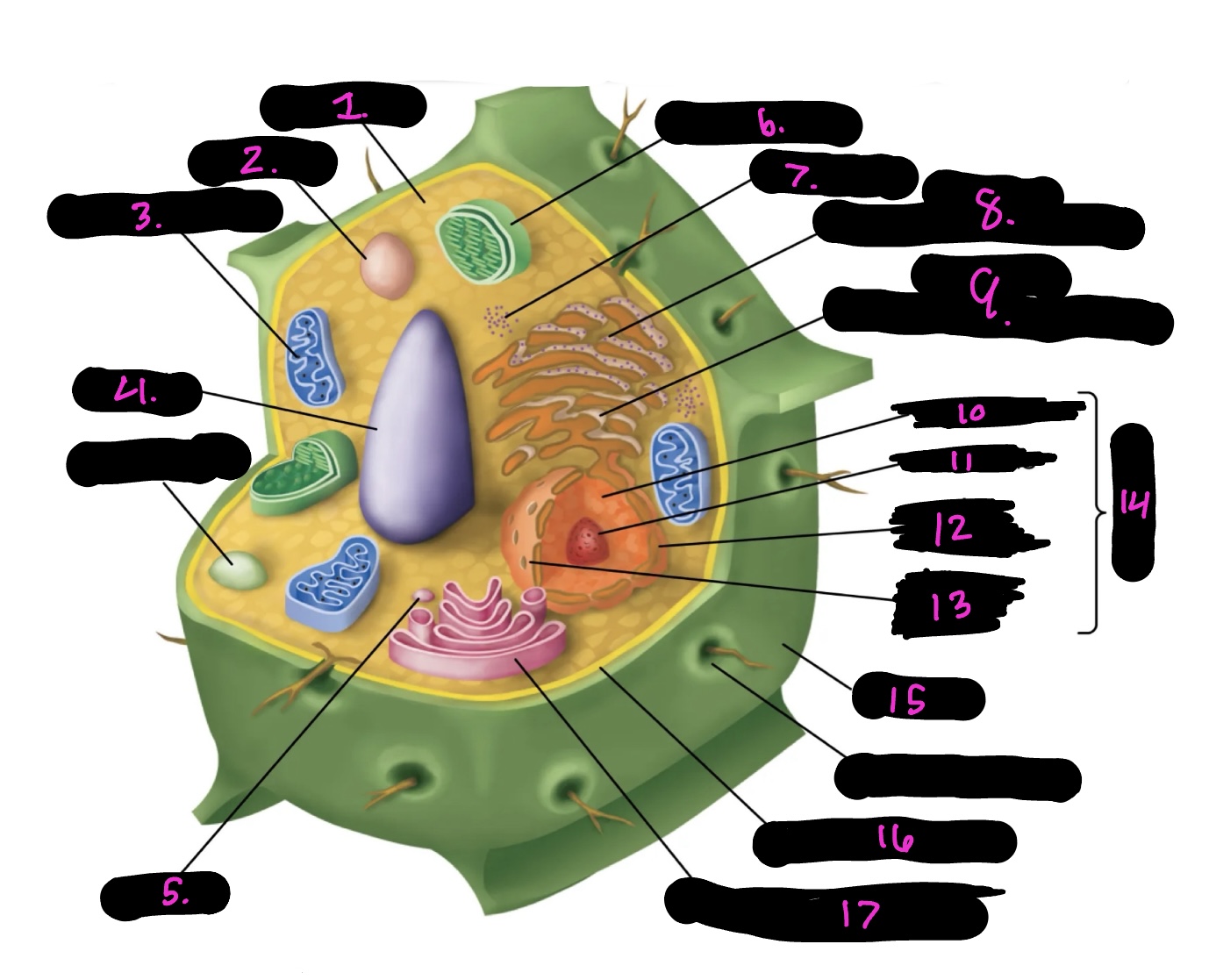
What is 16
Cell membrane
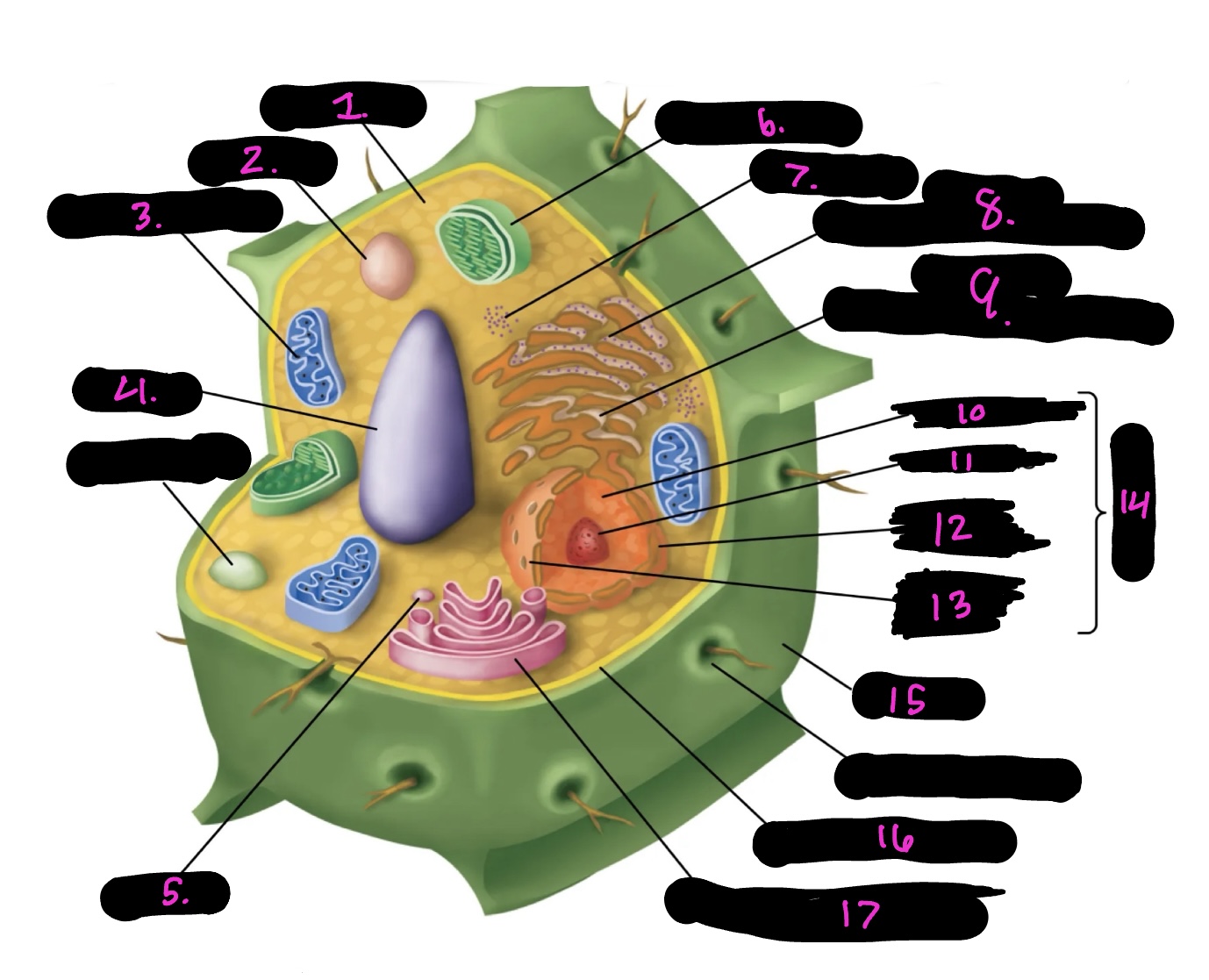
What is 17
Golgi apparatus
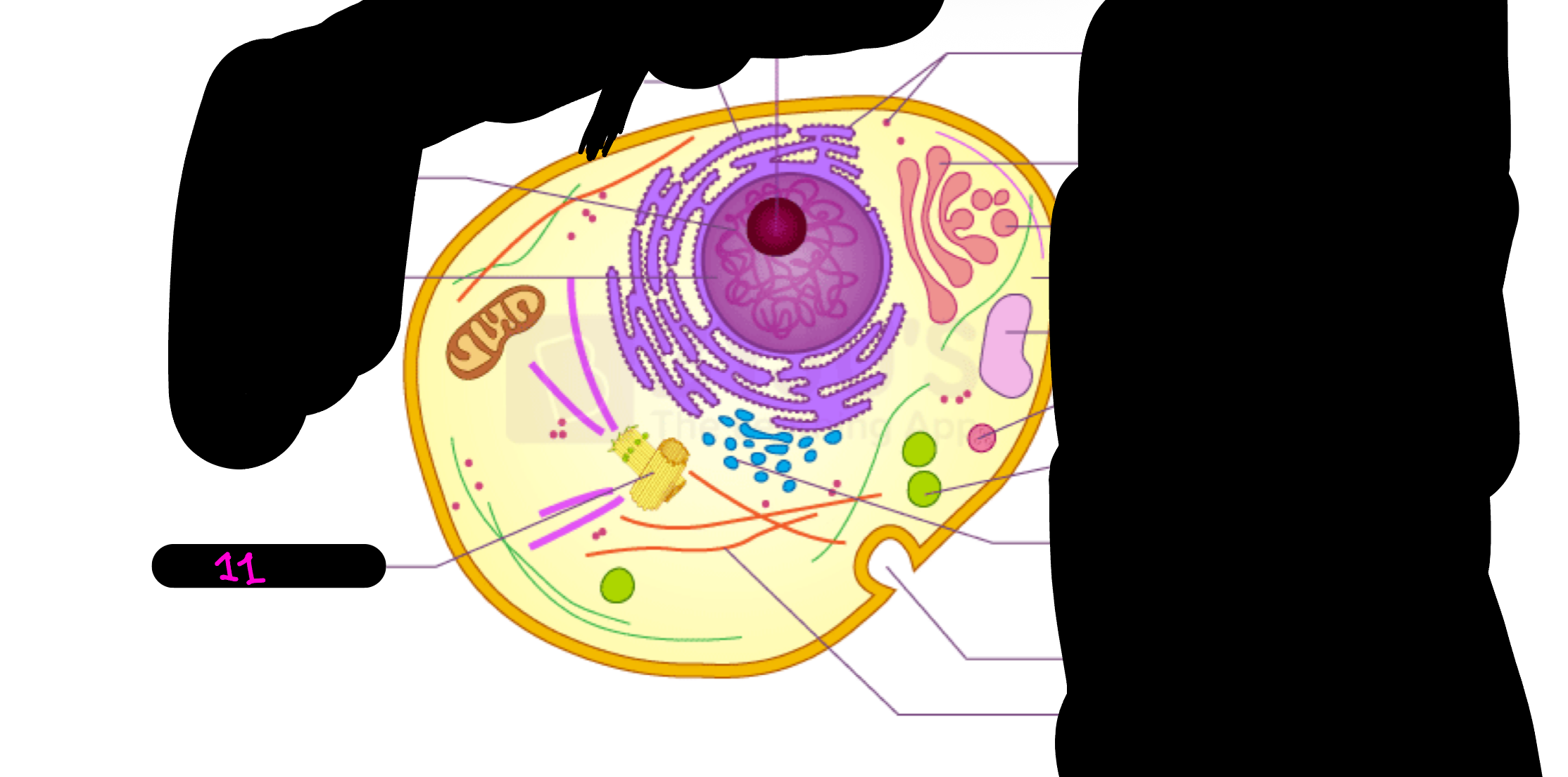
What is 11
Centrosome
What do centrioles do and what are they made of?
Pull chromosomes during cell division and made of microtubules.
English scientists who first saw “little boxes” in CORK that he named cells
Hooke
Dutch microscope maker who was the first to observe LIVING cells
Van Leeuwenhoek
Botanist who concluded that ALL PLANTS are made of cells
Schleiden
Zoologist who concluded that ALL ANIMALS are made of cells
Schwann
Doctor who reasoned that cells COME ONLY FROM EXISTING CELLS
Virchow
How are Chromatin and Chromosome different
Chromatin - DNA wrapped around a histone protein and uncoiled and floating in the nucleus, can not be seen w/o a strong microscope.
Chromosome - Chromatin condensed and coiled - then duplicated and tied together at the centromere. Condensed and can be seen with the naked eye
How are Cilia and Flagella different
Cilia - Short pieces of microtubules. Usually many of them moving in a side to side wave-like motion.
Flagella - Long pieces of microtubules. Usually one to a few move in a whiplike action or wiggle.
Small structure in a cell that performs a specific function is the
Organelle
Dark spot(s) in the nucleus where ribosomes are made would be the
Nucleolus
Sac of digestive enzymes =
Lysosome