Neu mod 4, lecture 29 motor cortex
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
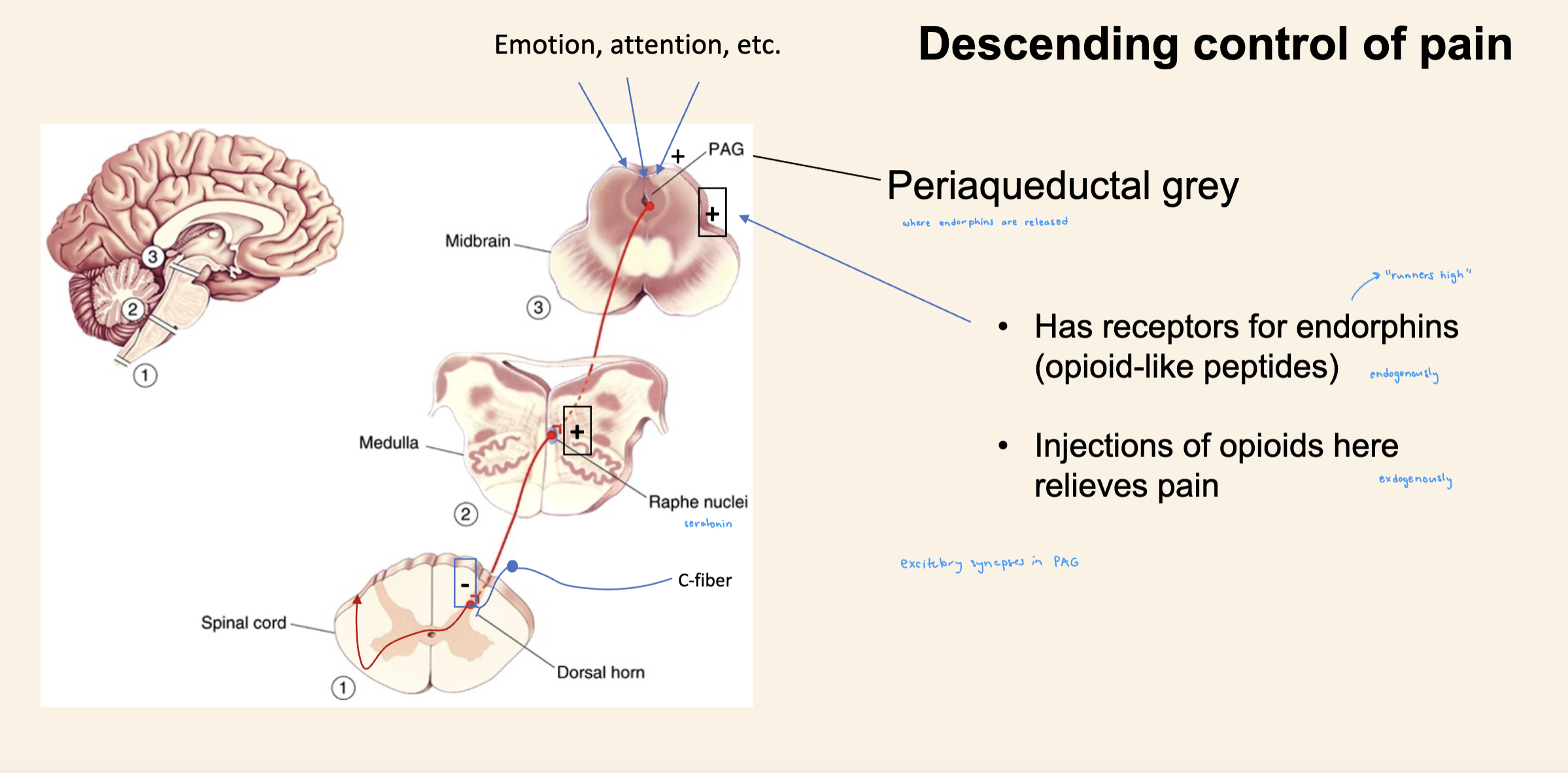
descending control of pain
certina brin centers which control emotion and atteniton will synape to periadaquetal gray
activate endorphins
which stimulate synapses between PAG neurons and medulla raphae nuclei
raphae: serotonin
Serotongeineric neurons form INHIBITORY synapses within the dorsal horn of the projection neurons
Will inhibit info from spihinothalamic neuron which will be carrying pain information
Layer 5 or area 4 in context of motor neurns
origination for control of movement
upper motor neurons (betz cells)
pyramidal shaped
lower motor neurons
direct connection to muscle fibers
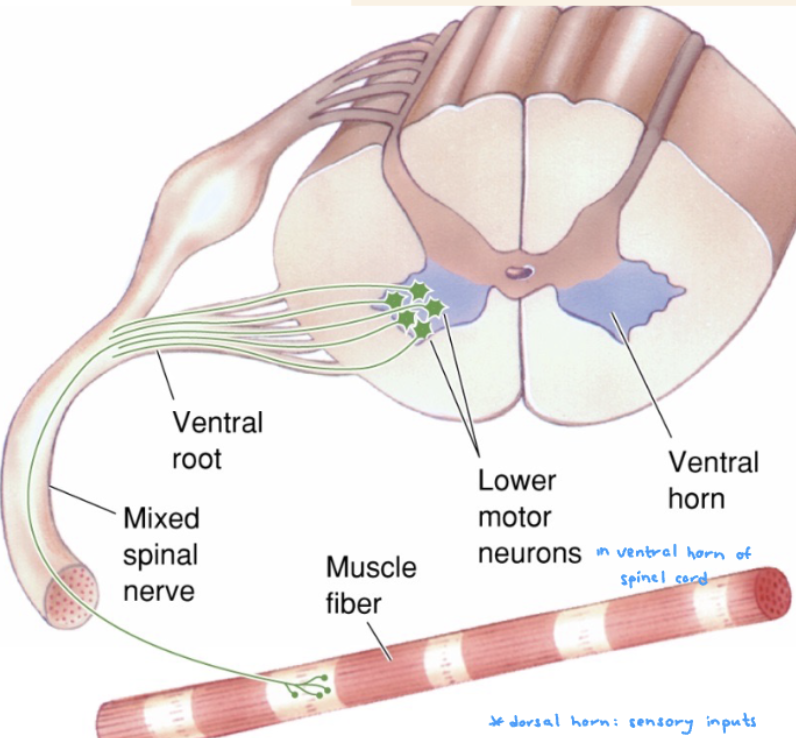
neurotransmotter used by motor neurons
acetylcholine
Corticospinal tract
travel thorugh midbrain and meedulla
crosses over at pyramidald dessucation of the medulla
first synapse onto lower motor neuron
in ventral horn
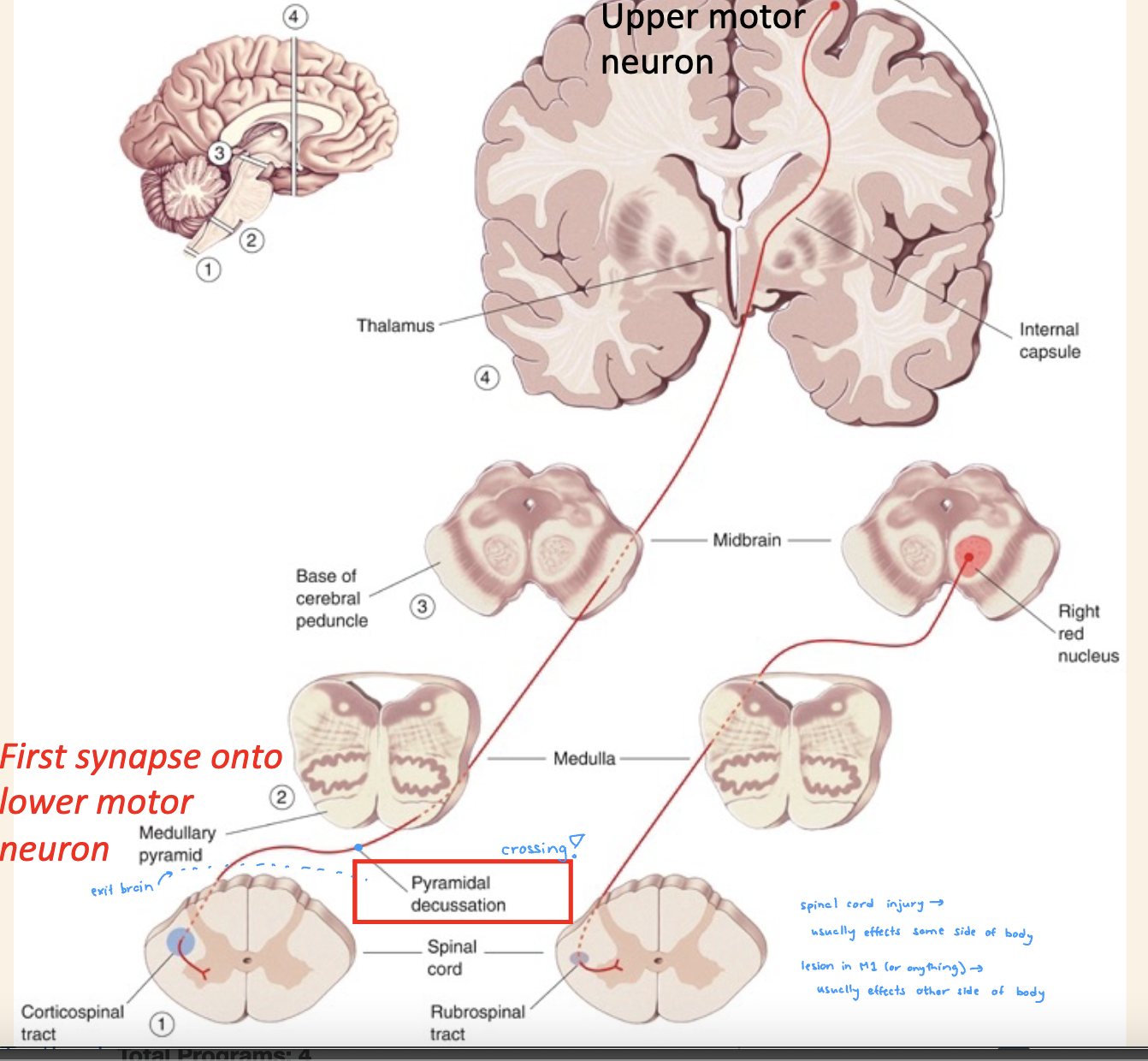
everything above medulla represents control over
contralateral side of body
descending pathway
everythign below medulla represents
same side of body
descending pathway
spinal cord injruy on one side of hte body will affect motor ability on what side
SAME side
after crosses over
upper motro neuron lesion signs
initial flaccid paralysis followed by SPASTIC paralysis
loss of voluntary movement
hypertonia/clonus
babinski sign (toes curl otward when damaged)
lower motor neuron lesion signs
flaccid paralysis
decreased reflexes, twitching
hypotonia
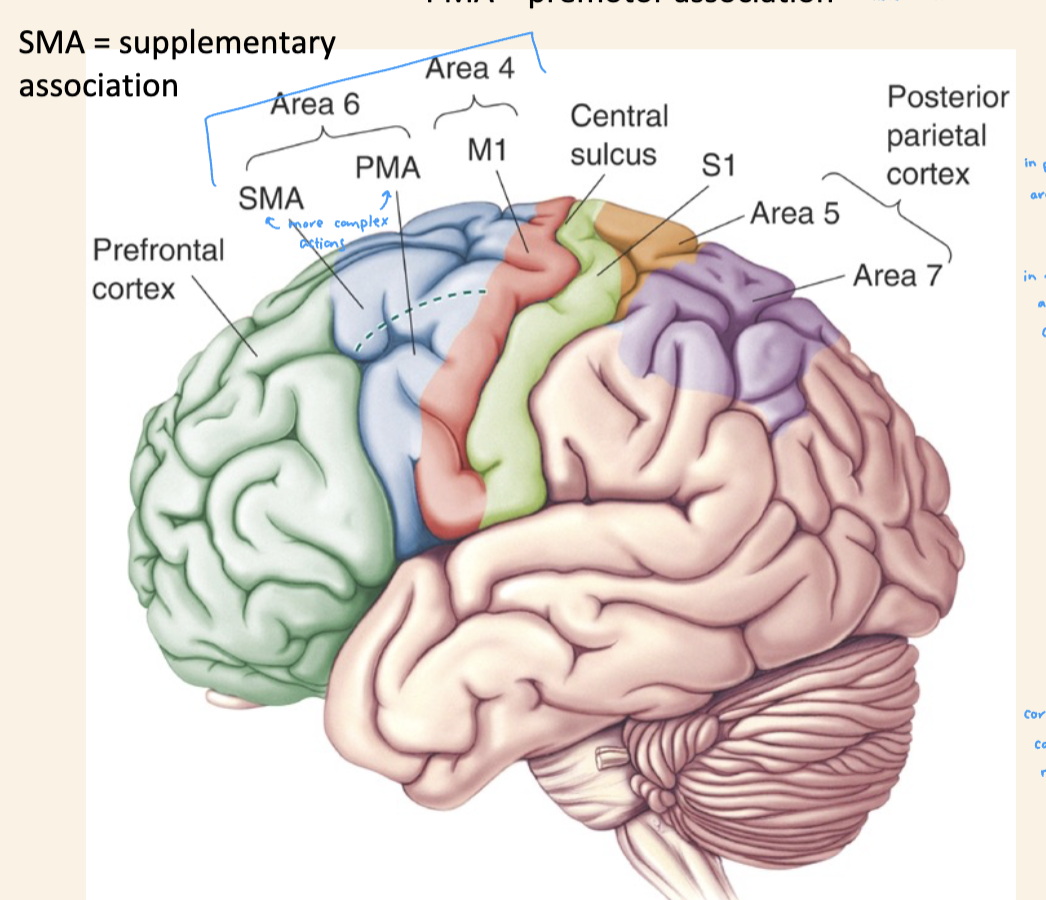
Premotor and supplementary motor cortex
More complex actions
Planning and gripping in more complex way
Neurons there that think and plan the action
Area 6 and association areas important in planning
Area 4 will only light up
Area 4 will only light up with area 6 during theACTUAL movement
Corpus callosum
White matter which connect right and left brain
Communication between PMA SMA On one side and other side
Often a site of lesion
Apraxia
inability to perform actions on command
Damaged association motor cortex
Lesion in connections between right and left cortex
(experiment) Do M1 neurons initiate muscle movement?
Correlation experiment (this )
If neurons controlling those muscles, then they should fire before the signal would arrive in muscle (contracts)
To test → recorded from M1 neuron
Action potentials, record EMG activity which looks very messy
Rectifier
Makes allahabad ata of APs in positive direction
Spike triggered averaging
Want to know how son before or after a particular event some response occurs
Event we are interested in is EMG activity and when it occurs in relation to the upper motor neuron activity
Hypothesis
Spikes hapepn before muscle
Take action potential and average 9000 of them and average EMG response before and after
To get feeling of bulk activity in relation to activity of spikes
Result
On average, signal in muscle is happening after about 100 to 200 milliseconds after primary motor neuron
First evidence that muscle is follower of the upper motor neuron
Decoding response properties of M1 neurons