soan test 2
1/198
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
199 Terms
What is the Tri-Council Policy Statement?
A document that provides principles to guide the design, ethical conduct, and ethics review process of research involving humans in Canada.
What are the four key principles of research ethics?
Respect for Persons, Concern for Welfare, Confidentiality and Justice.
What does 'Respect for Persons' entail in research ethics?
It is a moral obligation to respect autonomy and protect those with diminished autonomy.
How is 'Concern for Welfare' defined in research ethics?
It refers to the quality of a person's experience of life in all aspects, including physical, psychological, economic, and social welfare.
What does 'Justice' mean in the context of research ethics?
It involves understanding and respecting power relations among individuals and groups.
What is the ethical duty associated with confidentiality in research?
Researchers assume an ethical duty to protect the confidentiality of participants, which is central to respect for participants and the integrity of the research.
When can confidentiality be breached in research?
Confidentiality can be breached only if there are justifiable benefits that outweigh the risks.
What is informed consent in research?
Consent must be given voluntarily, be an ongoing process, and be informed about the nature of the research.
What is the significance of the Zimbardo experiment in research ethics?
It demonstrated how normal individuals can engage in cruel behavior when given power over others, raising ethical concerns about participant treatment.
What was the outcome of the U.S. Public Health Service study involving sharecroppers?
The study, which enrolled impoverished African American sharecroppers without their informed consent, continued until a whistleblower exposed it.
Who is Russel Ogden and what is his contribution to research ethics?
Russel Ogden is known for his legal precedent regarding confidentiality in research, specifically the Wigmore criteria.
What ethical issues arise from covert ethnography?
Covert ethnography raises questions about participant consent and the ethical implications of integrating into a group without disclosure.
What is 'data dredging' in research?
Data dredging, also known as hypothesizing after the results are known, refers to the practice of analyzing data to find patterns without prior hypotheses.
What are the implications of data fabrication in research?
Data fabrication undermines the integrity of research and can lead to false conclusions, as seen in cases like Marc Hauser's study.
What is the role of ethics in public anthropology and sociology?
Ethics in public anthropology and sociology emphasizes the responsibility of researchers to 'do good' rather than just 'do no harm.'
What are some challenges in conducting ethical research?
Challenges include balancing the benefits and harms of research, ensuring informed consent, and maintaining confidentiality.
What is the importance of debriefing in research involving deception?
Debriefing is crucial to inform participants about the true nature of the study and to address any potential harm caused by deception.
What ethical considerations are involved in research with Indigenous populations?
Research with Indigenous populations requires respect for their rights, cultural practices, and the need for community involvement in the research process.
What is the significance of the 'benefit-harm balance' in research ethics?
The benefit-harm balance assesses whether the potential benefits of research justify any risks or harms to participants.
What is the role of ethics review boards in research?
Ethics review boards evaluate research proposals to ensure they meet ethical standards and protect participants' rights and welfare.
How does the concept of 'power relations' affect research ethics?
Power relations can influence the dynamics between researchers and participants, necessitating careful consideration to ensure justice and respect.
What is the ethical principle of 'do no harm'?
The principle of 'do no harm' emphasizes that researchers should avoid causing physical, psychological, or social harm to participants.
What is the importance of transparency in research ethics?
Transparency fosters trust between researchers and participants, ensuring that ethical standards are upheld throughout the research process.
What are the implications of participant anonymity in research?
Participant anonymity protects individuals' identities and can enhance the integrity of the research by encouraging honest responses.
What are AI tools used for in literature searching?
AI tools assist in searching literature, enhancing natural language queries, and providing citation recommendations.
Name two examples of general-purpose large language models (LLMs).
ChatGPT and Claude.
What is a significant advantage of using AI tools for searching literature?
They can introduce users to unfamiliar topics and enhance search results with synonyms for conceptually similar findings.
What is a major disadvantage of AI tools in literature searching?
There is a high risk of errors and fabricated sources; output requires fact-checking.
What does the term 'opaque algorithms' refer to in the context of AI tools?
It refers to the difficulty in understanding why certain results appear in the search output.
What should users be cautious about when using AI-generated content?
Users should verify the reliability and transparency of the information, as coverage gaps may exist.
What are some features of scholarly articles that AI tools can help identify?
AI tools can help identify authors, associated institutions, and references to other scholarly literature.
What is the purpose of using Boolean operators in literature searches?
Boolean operators (AND, OR) help combine search terms to refine or broaden search results.
How can using keywords in a search strategy affect results?
Using keywords can broaden search results, while controlled vocabulary can narrow them.
What is the role of limits in literature searches?
Limits such as publication date and peer review status help narrow down search results.
What is the significance of using synonyms in literature searches?
Synonyms can help retrieve results that are conceptually similar, improving the comprehensiveness of search results.
What is the function of a thesaurus in research databases?
A thesaurus helps find the exact term or main subject for more precise searching.
What is an example of a search strategy for exploring gender differences in cyberbullying?
Using keywords like 'gender differences' and 'cyberbullying' combined with Boolean operators.
What is the importance of understanding the main concepts in a research topic?
It helps in formulating effective search queries and identifying relevant literature.
What does the term 'controlled vocabulary' refer to?
Controlled vocabulary refers to a standardized set of terms used to index and retrieve information in databases.
What is the impact of using 'Anywhere except full text' in a search?
It broadens the search to include important fields like title and abstract, rather than just the full text.
How can combining search terms with 'AND' affect search results?
'AND' returns results that include both terms, narrowing the search.
What is the purpose of using 'OR' in search queries?
'OR' returns results that include either term, broadening the search.
What does the term 'natural language search' imply?
It allows users to input queries in everyday language, making searches more intuitive.
What is a potential outcome of using AI tools for literature searching?
They may enhance the efficiency of finding relevant sources but require careful evaluation of the results.
What is a key feature of advanced search screens in research databases?
They allow users to specify search parameters and combine terms effectively.
What is the significance of peer-reviewed articles in literature searches?
Peer-reviewed articles are considered more credible and reliable sources of information.
What is the null hypothesis?
The null hypothesis (H0) states that there is no effect or no difference, often represented as H0: µ = 0.
What is the alternative hypothesis?
The alternative hypothesis (Ha) specifies that there is an effect or a difference, represented as Ha: µ (the mean)
We cannot test the alternative hypothesis directly
Instead, we look for evidence against the null hypothesis
If we find significant evidence against the null hypothesis, we can reject it in favour of the alternative hypothesis
What is a two-sided significance test?
A two-sided significance test is used when there is no specific theory about the direction of the effect.
What z-score indicates statistical significance at the 95% confidence level?
A z-score greater than 2 or less than -2 indicates statistical significance at the 95% confidence level (p-value < .05).
What z-score indicates statistical significance at the 99% confidence level?
A z-score greater than 2.6 or less than -2.6 indicates statistical significance at the 99% confidence level (p-value < .01).
What does it mean if a result is not statistically significant?
If a result is not statistically significant, it means we fail to reject the null hypothesis.
How do you calculate a z-score in hypothesis testing?
A z-score is calculated by plugging sample values into the z-score formula, which compares the sample mean to the population mean.
What is the significance of a p-value?
A p-value indicates the probability of observing the data, or something more extreme, if the null hypothesis is true.
What is the role of z-scores in hypothesis testing?
Z-scores are used to determine how far away a sample mean is from the population mean under the null hypothesis.
What is the first step in hypothesis testing?
The first step is to state the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.
What is the purpose of hypothesis testing?
Hypothesis testing is used to test claims about a population and determine if there is enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis.
What does it mean to reject the null hypothesis?
Rejecting the null hypothesis suggests that there is significant evidence to support the alternative hypothesis.
What is an example of a null hypothesis in a study of IQ?
In a study of IQ, the null hypothesis might state that the average IQ of students at Guelph is equal to 113 (H0: µ = 113).
What is an example of an alternative hypothesis in a study of IQ?
The alternative hypothesis might state that the average IQ of students at Guelph is different from 113 (Ha: µ ≠ 113).
What is the significance of a z-score of 2.60?
A z-score of 2.60 indicates that the result is statistically significant at the 95% confidence level, allowing rejection of the null hypothesis.
What does a confidence level of 95% mean?
A confidence level of 95% means that if the same study were repeated multiple times, 95% of the time the results would fall within the confidence interval.
What is the difference between a one-tailed and a two-tailed test?
A one-tailed test looks for an effect in one direction, while a two-tailed test looks for an effect in both directions.
What is the significance of the sample size in hypothesis testing?
Larger sample sizes generally provide more reliable estimates and increase the power of the hypothesis test.
What does it mean if a z-score is less than -2?
If a z-score is less than -2, it indicates that the result is statistically significant at the 95% confidence level, allowing rejection of the null hypothesis.
What is the relationship between z-scores and p-values?
Z-scores are used to calculate p-values, which indicate the probability of observing the data under the null hypothesis.
What is the purpose of conducting a hypothesis test?
The purpose is to determine if there is enough evidence to support a specific claim about a population parameter.
What does it mean to fail to reject the null hypothesis?
Failing to reject the null hypothesis means that there is not enough evidence to support the alternative hypothesis.
What is a common mistake in hypothesis testing?
A common mistake is to confuse failing to reject the null hypothesis with proving that the null hypothesis is true.
What is the significance of the standard deviation in hypothesis testing?
The standard deviation is used to determine the variability of the sample and affects the calculation of the z-score.
What is a Z score?
A Z score represents the number of standard deviations a data point is from the mean.
if we obtain a z-score greater than 2 or less than -2 then we can reject the null hypothesis (95% confidence)
If we obtain a z-score greater than 2.6 or less than -2.6 then we can reject the null hypothesis (99% confidence)
What does a Z score of +2 indicate?
It indicates that the data point is 2 standard deviations above the mean.
What does a Z score of -2 indicate?
It indicates that the data point is 2 standard deviations below the mean.
What is the significance level for a Z score greater than 2?
It is statistically significant at the 95% confidence level (p < .05).
What is the significance level for a Z score greater than 2.6?
It is statistically significant at the 99% confidence level (p < .01).
What is the purpose of calculating p-values?
To determine the statistical significance of a Z score.
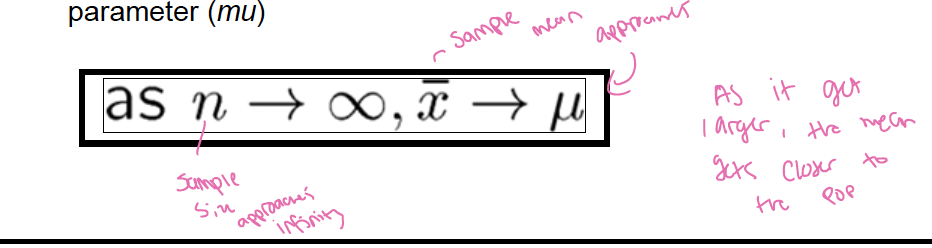
What is the Law of Large Numbers?
If we repeat a random phenomenon many times the average value will get closer and closer to the population parameter
The larger the sample, the more likely a statistic represents the true population parameter and the more confident you are in your estimates
In a very large sample, the statistic will almost certainly be very close to the true population parameter (mu)
What is the Central Limit Theorem?
Regardless of the population distribution, with repeated sampling the shape of the sampling distribution is approx normal or bell shaped with the population parameter at its centre
The approximation improves as the sample size increases
If you take a bunch of random samples from any group of people or things, and you look at the average of each sample, those averages will start to form a nice, even bell curve (normal distribution) — even if the original data was messy or uneven — as long as your sample size is big enough.
A bunch of averages from random samples will always look normal — even if the original data doesn’t
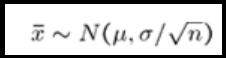
What are the three types of distributions in statistics?
Sample distribution, population distribution, and sampling distribution.
What is a sampling distribution?
It is the theoretical distribution of a statistic from all possible samples of the same size from a population.
What is the relationship between sample size and the standard deviation of a sampling distribution?
The standard deviation gets smaller as the sample size increases.
What is the significance of a p-value less than .05?
It indicates that the results are statistically significant.
What does it mean if a Z score is not statistically significant?
It means the Z score does not exceed the threshold values of 2 or -2.
What is the importance of random sampling in statistical inference?
It ensures that conclusions drawn from the sample are valid and can be generalized to the population.
What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative research methods?
Qualitative methods focus on understanding concepts and experiences, while quantitative methods focus on numerical data and statistical analysis.
What does a positive correlation in a scatter plot indicate?
It indicates that as one variable increases, the other variable also increases.
Positive correlation
What does a negative correlation in a scatter plot indicate?
It indicates that as one variable increases, the other variable decreases.
Negative relationship
What is the significance of a correlation coefficient?
It quantifies the strength and direction of a relationship between two quantitative variables.
the closer the dots the higher the correlation
What is the primary goal of statistical inference?
To draw conclusions about a population based on sample data.
What is a common cut-off for statistical significance in research?
A common cut-off is p < .05.
What happens to the sampling distribution as the sample size increases?
It becomes more normally distributed regardless of the population distribution.
What is the relationship between Z scores and statistical significance?
Z scores help determine whether a result is statistically significant based on their distance from the mean.
What is the importance of the central limit theorem in statistics?
It allows researchers to make inferences about population parameters using sample statistics.
What is the threshold for a Z score to be considered statistically significant at the 99% confidence level?
A Z score greater than 2.6 or less than -2.6.
What role do scatterplots play in exploring relationships between two quantitative variables?
Scatterplots play an important role when exploring the relationship between two quantitative variables
They allow us to identify problem cases, the form of the relationship (whether it is linear or not) and have a preliminary estimate of the strength of the relationship
Only when the relationship is linear does it make sense to use the correlation coefficient
The correlation coefficient is a good summary measure of the direction and strength of a linear relationship
It ranges from –1 (perfect negative linear relationship) to +1 (perfect positive linear relationship); 0 means no linear relationship
It does not tell us the slope of the line
What does the correlation coefficient summarize?
It summarizes the direction and strength of a linear relationship between two variables.
What is the range of the correlation coefficient?
It ranges from -1 (perfect negative linear relationship) to +1 (perfect positive linear relationship), with 0 indicating no linear relationship.
What should be considered when dealing with outliers in data?
Outliers are rare and unusual observations that may indicate a coding error or significant deviations from the general pattern.
What is necessary for establishing causation between two correlated variables?
Correlation is necessary for causation, and we infer causal relationships based on the temporal relationship between the variables.
What are independent and dependent variables?
Independent variables are the cause, while dependent variables are the effect.
I = Y
D = X