Pre-OPC: Final Exam
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards for the WRPS Pre-OPC Final Exam
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
What are the three sources of laws?
Statute and Regulation
Common
Case Law
What are the three levels of government that create laws, and what do we call these types of laws? Give an example of a type of law for each level.
Statute Laws by the Federal, Provincial and Municipal governments.
Federal: Criminal Code
Provincial: HTA
Muni: Parking Laws
What is a criminal offence?
Breach of a federal statutes
What is a Statute?
Written law enacted by various levels of government
What are the two authorities that allow us to use force?
Criminal Code and Provincial Offences Act
When do we use PRICE vs. PRICES?
PRICE = When we arrest someone
PRICES = When we release someone
What are the four elements of the “S” in PRICES?
Safety of the…
Witness
Subject
Public
Victim
What is the written format in our notebooks?
English Long Hand
What are the steps for correcting an error in our notebooks?
Cross out the error
Initial where we crossed out the error
According to the Charter, define the following terms:
Right (may not be on test)
Arbitrary (may not be on test)
Detained
A right is a power, privilege or immunity secured to a person by law.
Arbitrary is without fair, solid and substantial cause.
Detained is to arrest, to check, to restrain from proceeding, to delay, to hold or to stop someone.
What are the three types of criminal offences in order of most to least severe?
Indictable, Dual Procedure & Summary Convictions
What is the difference in the statute of limitation between Indictable and Summary Convictions?
No limit on indictable. 12-month limit on summary.
With Dual Procedures, how are they treated for arrest purposes versus prosecution purposes?
Indictable for arrest purposes, but the crown will determine how they will proceed (i.e. summarily or by indictment).
For Summary Convictions, what is the critical element required to arrest someone?
(May not be on test)
Must FIND COMMITTING the offense in order to arrest
Define “arrest.” And do you have to make an arrest?
Take or get physical control of a person with the intent to detain him or her.
It is discretionary, hinged upon the words “MAY” vs. “SHALL”
Define Finds Committing?
SEEING a person ACTUALLY COMMIT an offence
or…
SEEING a person COMMIT an offence and pursuing them IMMEDIATELY and CONTINUOUSLY until arrested.
Define Reasonable Grounds?
A set of facts or circumstances which would satisfy an ordinary, cautious and prudent person that there is a reason to believe and which goes beyond mere suspicion
In the Criminal Code, what are the two basic authorities citizens have regarding arresting people?
S494
Arrest without warrant by any person
or…
Arrest without warrant by owner, etc. of property
What are the circumstances in which a citizen can arrest without a warrant?
a person committing an indictable offence
or…
a person who, on reasonable grounds, he believes has:
committed a criminal offence, and…
is escaping from and freshly pursued by person who have lawful authority to arrest that person
What are the circumstances in which a citizen, who is the owner or a person in lawful possession of property, can arrest without a warrant?
a person committing a criminal offence on or in relation to that property, and…
they make the arrest at that time;
or…
they make the arrest within a reasonable time after the offence is committed
and…
they believe on reasonable grounds that it is not feasible in the circumstances for a peace officer to make the arrest
Under what circumstances can a Peace Officer arrest without a warrant?
A person who he finds or has committed an indictable offence, or who, on reasonable grounds, he believes has committed or is about to commit an indictable offence.
or…
a person whom he finds committing a criminal offence
or…
a person in respect of whom he has reasonable grounds to believe that a warrant of arrest or committal, in any form set out in Part XXVIII in relation thereto, is in force within the territorial jurisdiction in which the person is found.
What are the limitations of an arrest without a warrant by a Peace Officer?
SHALL NOT arrest a person…
Indictable offence in S553
Offence that may be prosecuted by indictment or for which he is punishable on summary conviction, or…
A summary conviction offence.
Additional Notes (Do Not Need to Know): S553 are indictable offences that are prosecuted in provincial court with no option for mode of trial. These are less serious offences including:
Theft, fraud, false pretenses, mischief under S430(4) & possession of stolen property under $5K
Common Assault
What does PRICE stand for?
P = believes on reasonable grounds that it is in the public interest.
R = prevent the continuation or repetition of the offence or the commission of another offence.
I = cannot establish or confirm the person’s identity
C = has no reasonable grounds to believe that, if he does not arrest the person, the person will fail to attend court to be dealt with according to the law
E = is necessary to secure or preserve evidence relating to the offence.
What are the Decisions to Arrest?
Recognize: Is it a criminal offence? Yes or no
Classify:
Summary = Finds Committing
Dual / Indictable = Reasonable Grounds
Authority
Summary - Yes = Do they violate at least one of PRICE
Summary - No = Summons or Appearance with Notice
What are the steps to making an arrest?
Identify Yourself
Tell them they are under arrest
Tell them the reason for the arrest
Take or Get Physical Control
Read them their rights to counsel
Make sure they understand
What are the conditions in which we release someone?
PRICES (aka. the same as PRICE) except…
S = Safety of the victim, witness, subject or public… and also the accused
They do not satisfy all the conditions of PRICES, then they are in custody until they can be seen by a judge within 24 hours.
In what direction should you never open your batton?
Never sideways
Once compliance is gained, what must an officer do?
Escalation of force must stop.
Define Defensive Tactics
a system of control that incorporates communication and physical options
The Purpose of Defensive Tactics
Always maintain CONTROL and a position of advantage
What are the four steps of a search?
Look
Ask
Clear
Touch
What are the 4 Rules of a Search?
Legal
Thorough
Methodological
Safe
How to Clear a Malfunction in your Firearm
Tap, Rack and Asses
What are four rules of Firearm Safety?
Know your target
Never put your finger on the trigger until you want to shoot
Never point unless serious bodily harm or death
Assume it is loaded
Know your muzzle direction at all times
Four Perceptions Police Officers have when deciding what type of force to use?
Abilities
Size
Injury
Experience
Three things we search for:
Weapons
Evidence
Means of Escape
What are the three universal cover modes:
Pistol on _____, finger _____ trigger.
On, On
On, Off
Off, Off
Name 5 Type of Summary Convictions:
Pick whatever ones you want, but they cannot be from the same category (e.g. you can only have Disturbance once, you cannot have five different types of Disturbances).
Here are five I felt were easy to remember:
Causing Disturbance
Trespass at Night
Nudity
Carrying Weapon While Attending Public Meeting
Engaging in Prize Fighting
Please don’t judge me, but I remember this by saying:
a person was causing a disturbance by trespassing at night, while naked and carrying a Weapon to a Public Meeting that was engaging in prize fighting
Define the following term, according to the POA: Police Officer
means a chief of police or other police officer but does not include a special constable or by-law enforcement officer; (“agent de police”)
Define the following term, according to the POA: Offence
means an offence under an Act of the Legislature or under a regulation or by-law made under the authority of an Act of the Legislature; (“infraction”)
Define the following term, according to the POA: Young Person
means a person who is or, in the absence of evidence to the contrary, appears to be,
(a) twelve years of age or more, but
(b) under sixteen years of age, and includes a person sixteen years of age or more charged with having committed an offence while he or she was twelve years of age or more but under sixteen years of age. (“adolescent”) R.S.O. 1990, c. P.33, s. 93.
Define the following term, according to the POA: Premises
“premises” means lands and structures, or either of them, and includes,
(a) water,
(b) ships and vessels,
(c) trailers and portable structures designed or used for residence, business or shelter,
(d) trains, railway cars, vehicles and aircraft, except while in operation. (“lieux”) R.S.O. 1990, c. T.21, s. 1 (1).
Define the following term, according to the POA: Occupier
1.(1) “occupier” includes,
(a) a person who is in physical possession of premises, or
(b) a person who has responsibility for and control over the condition of premises or the activities there carried on, or control over persons allowed to enter the premises, even if there is more than one occupier of the same premises;
(“occupant”)
According to the POA, if not stated elsewhere, how long after an offence has been committed can you lay a charge?
6 months
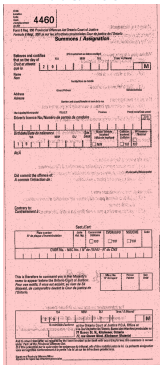
What is this ticket called?
Part I Summons

What is this ticket called?
What III Summons

What is this ticket called? And what is the colour and name of the other ticket associated with this ticket?
Part I -Provincial Offence Notice (the white paper is called a Certificate of Offence)
The Green ticket that comes with it is a Part I Offence Notice, which is given to the offender.
Answer the following questions comparing these three tickets:
Part I Offence Notice
Part I Summons
Part III Summons
When do we use each of them?
What are the statute of limitations for each?
What colour are the tickets?
Part I Offence Notice
Has a Set Fine that is less than $1000
30 days after the offence
White = Certificate of Offence & Green = Offence Notice
Part I Summons
No Set Fine, you want them appear in court, or they are classified as a Young Person (12 to 15 years old)
30 days after the offence
Pink
Part III Summons
No set fine & the defendant is found at or near the place where the offence occurred.
6 month
Yellow
What are the two parts of the HTA?
The Act and the Regulations
What section of the POA do we get the authority to arrest?
Section 145
What section of the LLCA outlines our arrest provisions?
S.62
What section of the LLCA outlines our authority to arrest for public intoxication?
S.31(2)
Under the TPA, what are the four ways to give notice?
Written
Orally
Signage
Marking System
What are the three types of arrests under the TPA Section 2?
Section 2(1)(a)(i) - Enter premises when entry prohibited
Section 2(1)(a)(ii) - Engage in prohibited activity on premises
Section 2 (1)(b) - Fail to leave premises when directed
Under the TPA, what are the critical elements of Section 10 regarding arresting someone without warrant when off the premises?
A police officer…
on reasonable and probable grounds
in contravention of section 2, AND
Fresh departure from premises, AND
Refuses to provide Name or Address, OR
Believe it is false
May arrest the person without warrant
EXACT WORDING
10. Where a police officer believes on reasonable and probable grounds that a person has been in contravention of section 2 and has made fresh departure from the premises, and the person refuses to give his or her name and address, or there are reasonable and probable grounds to believe that the name or address given is false, the police officer may arrest the person without warrant. R.S.O. 1990, c. T.21, s. 10.
What are the four elements to prove an offence in the POA?
THIS IS INCOMPLETE… WILL UPDATE AFTER OUR NEXT REVIEW
Date & Time
Place of the Offence
Identity of the Individual
POA S.145 - Any person may____________ a person who he or she has ________________________ to believe has committed an ________________ and is ___________ from and _______________________ by a police officer who has _________________ to arrest that person, and, where the person who makes the arrest is not a police officer, shall ____________________ the person arrested to a police officer. R.S.O. 1990, c. P.33, s. 145.
Any person may arrest without warrant a person who he or she has reasonable and probable grounds to believe has committed an offence and is escaping from and freshly pursued by a police officer who has lawful authority to arrest that person, and, where the person who makes the arrest is not a police officer, shall forthwith deliver the person arrested to a police officer. R.S.O. 1990, c. P.33, s. 145.
Name two statues that allow you to use force?
Criminal Code-25(1)
POA-146(1)
You do not need to know the sections, just CC and POA.
Define Roadway vs. Highway
Roadway: Actual travelled portion - not including the shoulder
Highway: (AKA Fence to Fence) includes a common and public highway, street, avenue, parkway, driveway, square, place, bridge, viaduct or trestle, any part of which is intended for or used by the general public for passage of vehicles and includes the area between the lateral property lines thereof;
Define Vehicle and what the following stand for:
M___________
T___________
T___________
F___________
R___________
B___________
Any vehicle drawn, propelled or driven by any kind of power including muscular power except a motorized snow vehicle or a street car and includes:
M: Motor Vehicle
T: Trailer
T: Traction Engine
F: Farm Tractor
R: Road-Building Machine
B: Bicycle
Name all the classifications of Driver’s Licence
A: Tractor Trailer
B: School Bus
C: City or Coach Bus
D: Dump Truck
E: Special Ed School
F: First Air & Passenger Bus
G: Standard Licence
A person with a B License Classification can operate vehicles in what other classifications?
Bonus Marks… What about these classifications?
A
C
D
E
F
I don’t think we need to know these but I threw them in anyway
B = C, D, E, F and G
Bonus
A = D &G
C = D, F & G
D = G
E = F & G
F = G
Define Trailer
Any vehicle drawn on a highway by a motor vehicle… Excludes MMIST
M - Motor vehicle being towed
M - Mobile Home
I - Implement of Husbandry
S - Side car on a motorcycle
T - Thing (any device or apparatus that is not designed to transport person or property and is temporarily drawn on highway (i.e. cement mixer)
Match the Following For Terms with the Below Definitions
A. Common Area
B. Public Place
C. Private Place
a place to which the general public is invited or permitted access
any part of a residence that is used in common by persons occupying more than one dwelling in the residence.
An indoor place to which the public is not ordinarily invited or permitted is a private place except at the times when the public is invited or permitted access to it.
A = 2
B = 1
C = 3
Under POA Section 149, what are the responsibilities after an arrest?
Summarized as: A police officer shall, as soon as is practicable, release the person after serving a process (appeal or summons, unless they have reasonable and probable grounds that PRIER is an issue:
P: Public interest
R: Repetition
I: Identity
E: Evidence
R: Residence
Exact wording of S149
Where a police officer, acting under a warrant or other power of arrest, arrests a person, the police officer shall, as soon as is practicable, release the person from custody after serving him or her with a summons or offence notice unless the officer has reasonable and probable grounds to believe that…
Under the POA, what are the different types of charges we can issue?
If you can, also list the following for each:
When we use them
How long we have to issue the ticket
Part I - Provincial Offence Notice
Set Fine Offence or Fine is less than $1K
30 days
Part I - Summons
No Set Fine, want them to attend court or a Young Person (12-15 years old at the time of the offence)
30 days
Part III - Summons
No set fine and defendant found at or near the place where the offence occurred
6-month limit
Define Motor Vehicle
A: Automobile
M: Motorcycle
M: Motor-Assisted Bicycle
O: Other vehicle not muscle power
NOT
Snow: Snow Machine
P: Power-assisted bicycle
F: Farm Tractor
I: Implement of Husbandry, self-propelled
R: Road-Building Machine
S: Street Car
T: Traction Engine
Where do we find Set Fines?
Short Form Wording Book
In the HTA, how many passengers can someone with a G Licence have in their vehicle?
If they have more than this number, what license(s) do they require if it is not for school purposes and what are the passenger limits?
What about if they are for school purposes?
Not sure if we need to know more than the first question.
9 or less (i.e. a vehicle with 10 or more passengers is a bus, requiring an F licence or greater)
F for 10 to 23 and C for 24 or more passengers.
E for 10 to 23, B for 24 or more passengers.
What is the L Classification used for and what is the limit of this classification?
It is for limited-speed M Classification Licences (i.e. motorcycles), and the limit is 80 kph.
What section of the HTA gives you Arrest Authorities?
HTA 217(2)
CC Section 494. (1) Any one may ____________________
(a) a person whom he _________________ an ____________________; or
(b) a person who, on ___________________, he believes
(i) has committed a _________________, AND
(ii) is ___________ from and _________________\by persons who have _______________________ to arrest that person.
Section 494. (1) Any one may arrest without warrant
(a) a person whom he finds committing an indictable offence; or
(b) a person who, on reasonable grounds, he believes
(i) has committed a criminal offence, AND
(ii) is escaping from and freshly pursued by persons who have lawful authority to arrest that person.
CC Section 494.(2) - The________ or a person in _________ ___________ of property, or a person _____________ by the owner or by a person in __________ _____________ of property, may arrest a person ___________ ____ ___________ if they _______ ______ ____________ a ___________ _____________on or in relation to that property _____,
(a) they make the arrest at that time; OR
(b) they make the arrest within a ___________ ______after the offence is committed AND they believe on __________ ___________________that it is _____ _____________ in the circumstances for a peace officer to make the arrest.
CC Section 494.(2) - The owner or a person in lawful possession of property, or a person authorized by the owner or by a person in lawful possession of property, may arrest a person without a warrant if they find them committing a criminal offence on or in relation to that property AND
(a) they make the arrest at that time; OR
(b) they make the arrest within a reasonable time after the offence is committed AND they believe on reasonable grounds that it is not feasible in the circumstances for a peace officer to make the arrest.
CC Section 495.(1) A peace officer may arrest without warrant,
(a) a person who has committed an ________________ or who, on ____________________, he believes has committed or is about to commit an ____________________;
(b) a person whom he finds committing a ______________; or
(c) a person in respect of whom he has _____________________ to believe that a ____________________ or committal, in any form set out in Part XXVIII in relation thereto, is in force within the territorial jurisdiction in which the person is found.
CC Section 495.(1) A peace officer may arrest without warrant,
(a) a person who has committed an indictable offence or who, on reasonable grounds, he believes has committed or is about to commit an indictable offence;
(b) a person whom he finds committing a criminal offence; or
(c) a person in respect of whom he has reasonable grounds to believe that a warrant of arrest or committal, in any form set out in Part XXVIII in relation thereto, is in force within the territorial jurisdiction in which the person is found.