Path cardioresp: canine infectious resp
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Indications for antimicrobial treatment of URT infection
if persists for 10 days
if concurrent fever, lethargy and anorexia
infective agents involved in kennel cough
vanine parainfluenza virus (very common)
canine adenovirus 2
canine herpesvirus 1
Bordetella bronchiseptica
Mycoplasma cynos
Full name for kennel cough
infectious canine tracheobronchitis
Canine infectious respiratory disease complex
Clinical signs and onset/offset of kennel cough
symptoms appear 3-7 days after exposure
Coughing (dry or productive)
Retching (especially during exercise or on lead)
Nasal ± ocular discharge
Sneezing
Usually recovers in 1-3 weeks
Pathogenesis of kennel cough
Virus or Bordetella infect respiratory epithelium.
Pathogen toxins cause cell damage
Damage to ciliated cells inhibits ciliary clearance
Risk of secondary infections in some cases
Symptoms of canine parainfluenza virus
Mild respiratory disease
More severe if combined with Bordetella
Symptoms of canine adenovirus 1 and 2
1 = hepatitis , also reported in resp disease
2 = respiratory disease
not commonly associated with kennel cough
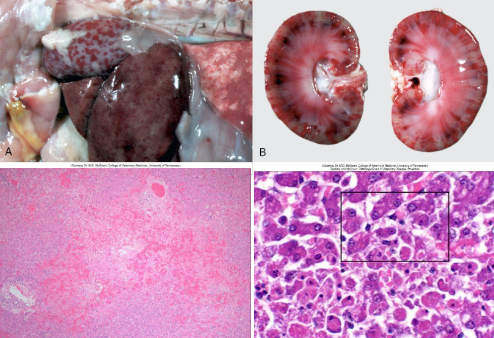
Causative agent
Canine herpesvirus 1
Symptoms of canine herpesvirus 1
fatal systemic disease in puppies <2 weeks “fading puppy syndrome”
<35.5 Celsius
Mild tracheobronchitis in adults (kennel cough)
Multifocal necrotising hepatitis with eosinophilic intranuclear inclusion bodies
necrotising nephritis
Treatment options for Bordetella bronchiseptica
doxycycline
amoxicillin with clavulanic acid
Symptoms of canine respiratory coronavirus
Mild respiratory disease
Newley discovered virus in 2010 involved in kennel cough
canine pneumovirus. Often co-infects with another virus. 93% dogs have antibodies from past exposure.
What strain is canine influenza
H3N2
Symptoms of canine influenza virus (greyhound kennels)
mild respiratory disease (fever, cough)
Haemorrhagic pneumonia
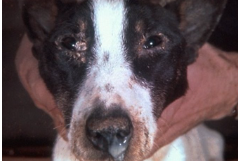
What disease does this dog have
Canine distemper
Symptoms of canine distemper
Nasal and ocular discharge
Cough
Diarrhoea
Vomiting
Depression
Anorexia
Pathogenesis of canine distemper
Virus enters via respiratory tract
Spreads to tonsils and local lymph nodes
Infection of monocytes/macrophages = viraemia and systemic dissemination
some dogs develop good immune response after 2-3 weeks and develop milder form of disease
Dogs with insufficient immune response get viral infection of respiratory, gastrointestinal and genitourinary epithelium, and central nervous system
Virus causes immunosuppression, secondary bacterial infections
4 causes of pneumonia in dogs (LRT infection)
Viral infection
Aspiration of liquid
Inhalation of foreign bodies
Bacterial infection (rare to be primary)
4 causes of pyothorax in dogs (LRT infection)
penetrating wound to chest wall
Rupture of oesophagus or traches due to foreign body
Migration of foreign bodies
Pneumonia (rare), more likely to be consequential
Example lower respiratory pathogens in dogs
Bordetella bronchiseptica
Pasteurella multocida
Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidermicus, streptococcus canis
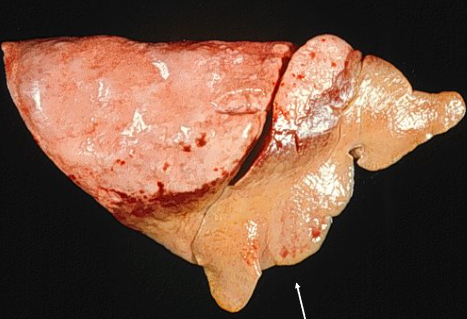
Describe the lesion.
cranio-ventral consolidation : suppurative bronchopneumonia.
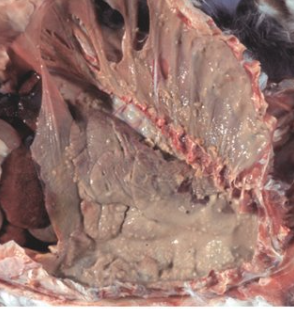
Describe the pathology and state causative agent
Severe suppurative pneumonia and pleuritis - pyothorax
Associated with cat bite wounds
Pasteurella multocida
Causative agent
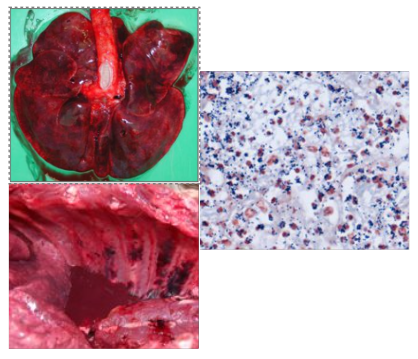
Streptococcus equii subsp. zooepidermicus
Clinical signs of Streptococcus subsp. zooepidermicus antemortum and postmortum
antemortum: pyrexia, haemorrhagic nasal discharge, sudden death
Postmortem: severe necro-haemorrhagic and fibrino-suppurative bronchopneumonia
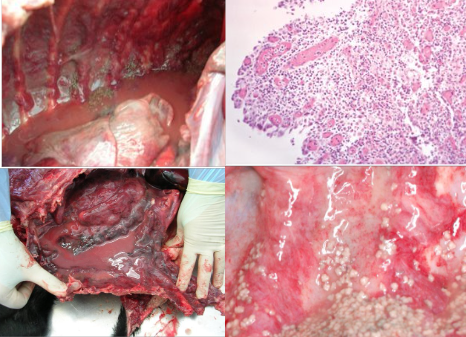
Description, possible causative agents and their features
Pyogranulomatous thoracic infection. Copious red-brown exudate in pleural cavity, contains sulphur granules.
Actinobacteria(gram positive, forms branching filaments: Actinomycetes viscosus - commenal oral- and Nocardia spp (asteroides) - found in soil. Both have same clinical appearance
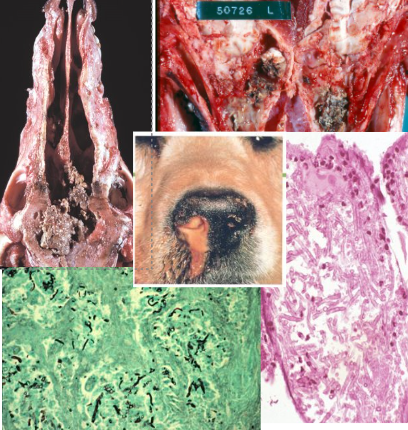
Causative agent and describe the lesions
Aspergillus fumigatus
Progressive destruction of nasal turbinates by chronic pyogranulomatious (and eosinophilic) inflammation.
Possible yellow mycotic exudate in caudal nasal cavity
Best medium for Aspergillus growth
Sabouraud Dextrose agar (low ph of 5.5 and antibiotics to stop bacterial growth) Grows in 2-3 days.
Describe the two types of aspergillosis infections in dogs
Nasal: invasive sinusitis with persistent sanguino-purulent(blood/pus) nasal discharge (usually unilateral)
Systemic: affects immunosuppressed animals. Signs depend on the locations affected. Difficult treatment, poor prognosis.
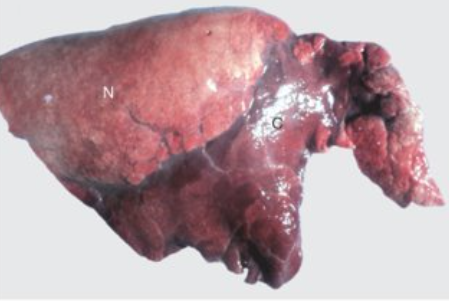
What is this pneumonia/lung lesion
Bronchopneumonia caused by aspiration pneumonia. Necrosis present if there are toxin-producing bacteria
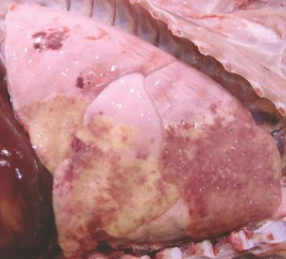
Whats this
Lobar pneumonia. Common appearance in cats and dogs
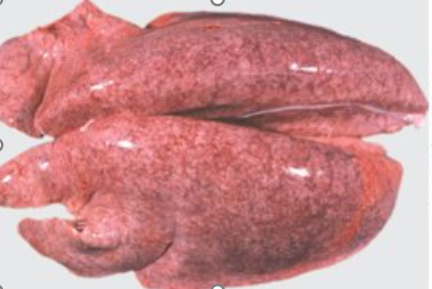
Whats this? causes
Interstitial pneumonia
Haematogenous damage = diffuse distribution
5 acute and 3 chronic causes of interstitial pneumonia
Acute = Infectious (distemper), inhaled chemicals, ingested toxins, systemic conditions (uraemia), hypersensitivity reactions (lungworm)
Chronic = infections (jaagsiekte in sheep), inhaled dust, hypersensitivity reactions (Farmers lung/Saccharopolyspora rectivigula)
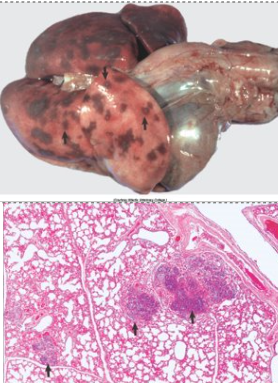
What is this and its causes (what it occurs secondary to-3)
Embolic pneumonia.
pulmonary abscesses resulting from septic emboli in the pulmonary vessels.
Secondary to endocarditis, hepatic abscessation and phlebitis
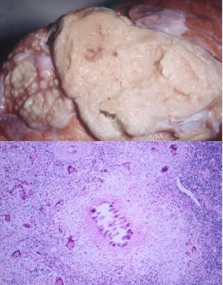
Whats this and causative agent (and how to detect)
Granulomatous pneumonia
Mycobacteria - Ziehl-Neelsen stains red due to acid fast
Fungi/aspergillosis