A5 - Glycan metabolism by the Microbiota I
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
What are glycans?
It’s an umbrella term for polysaccharides, oligosaccharides and glycoconjugates
Why are simple sugars from our diet, not available to the gut microbiota?
Because the human body is very efficient at absorbing them meaning the gut microbiota isn’t able to access them as easily
Xylans and beta-glucans are examples of what?
Plant cell wall polysaccharides
Most CAZymes are _________ which cleave _______ bond using _____.
Most are glycoside hydrolases which cleave glycosidic bonds using water
Approximately, how many CAZymes does the human genome encode?
Around 17 enzymes.
This is significantly less than the hundreds of CAZymes which some bacteria encode
What are the three main roles of glycan metabolism in host heath?
Production of Short Chain Fatty Acids
Production of the mucus barrier
Metabolism drives and maintains microbiota diversity
Short Chain Fatty Acids are a waste product of what?
A waste product of anaerobic fermentation of glycans by gut bacteria
Only around __% of SCFAs are excreted as faeces. This suggests __% is used by humans and other gut bacteria.
Only around 5% is excreted as faeces. This suggests 95% is used by humans and other gut bacteria
What are the three main types of SCFA produced by the gut microbiota?
Acetate
Propionate
Butyrate
Which gut bacteria produce Acetate?
Most gut bacteria produce Acetate.
What is the role of Acetate in host health?
Prevents colonisation by some pathogens by lowering the pH
Increases Butyrate production
Which gut bacteria produce Propionate?
Mostly produced by Bacterodota.
What is the role of Propionate in host health?
Maintains glucose homeostasis
Reduces appetite
Which bacteria produce Butyrate?
Mostly produced by Firmicutes
What is the role of Butyrate in host health?
Main energy source of colonocytes
Anti-cancer role
Suppresses cell proliferation and induces apoptotic cell death
All three SCFA types stimulate pro-inflammatory pathways.
True or False?
False.
All three stimulate anti-inflammatory pathways.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease is characterised by what?
Chronic inflammation
Has both a genetic and dietary component
Inflammatory Bowel Disease is associated with what kind of diet?
High fat, low fibre diet.
Why could lower SCFAs potentially contribute to IBD?
Lower concentrations of SCFA in the lower colon compared to the proximal colon.
A lot of IBDs affect the lower colon meaning the lower SCFA could explain why there is less inflammation dampening.
Gut mucus is composed of what complex glycoproteins?
Mucins which are produced constantly to replenish the mucus layer
How can the mucus layer be degraded if you don’t have enough dietary fibre?
Less dietary fibre means less nutrients for the gut microbiota
Mucins can instead be used as a nutrient source by some members of the microbiota
This causes the mucus layer to be degraded and become much thinner and vulnerable.
Which are the main bacterial phyla which break down glycans in the gut?
Gram negative: Bacteroidetes
Gram positive: Firmicutes and Actinobacteria
Bacteroides. spp are very specialised to breakdown specific glycans in the gut.
True or False.
False.
Bacteroides. spp are generalists which can breakdown a wide range of glycans
Firmicutes and Actinobacteria are the much more specialised bacteria
Which two Bacteroides species use most of the glycans found in nature between them?
B. Thuringiensis and B. Ovatus
Bacteroidetes machinery for glycan degradation is encoded in what loci?
Polysaccharide utilization loci (PULs)
Polysaccharide utilization loci (PULs) encode what?
Sus-like systems
What does Sus mean in the context of glycan metabolism?
Starch utilisation system (Sus)
Each Sus-like system degrades a specific glycan
What are PULs defined by?
Homologues of SusC/D as well as the presence of glycoside hydrolase (GH) genes
Normally these are linked to sensor-regulators
What is the function of SusD?
SusD binds target glycan with low affinity and is required for oligosaccharides larger than 5 sugars
Role of SusD is to deliver large oligosaccharides to SusC transporter
What is the role of SusC?
To transport glycans through the bacterial cell membrane.
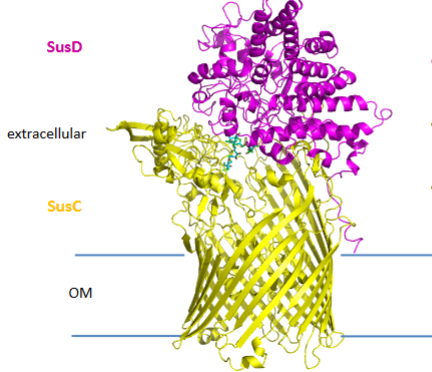
What is the structure of SusC/D?
SusD sits on top of SusC
Like a barrel and a lid
SusD opens to ‘capture’ ligand and closes once captured
What is the role of Surface Glycan Binding Protein (SGBP)?
Most PULs will also have a SGBP
Part of the SusC/D complex and binds glycan target with high affinity
Role is to capture glycans and help provide a competitive advantage in the densely populated gut
What is the utilisome of the gut microbiota?
All the components involved in glycan metabolism.
SusC/D, Glycoside hydrolases, SGBP, etc
What is the process of glycan metabolism by Bacteroidetes?
SGBP binds a glycan and glycan is cleaved by Glycoside hydrolase enzyme.
These smaller glycans are then taken up by the transporter complex, SusC/D to take them into the cell