ap psych 5--states of consciousness
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
exposure effect + priming
exposure effect—we prefer stimuli we have seen before over novel stimuli subconsciously. we have different levels of consciousness that add nuance to our lives
priming: people respond more quickly to questions they have seen before even if they don’t remember seeing them
blind sight: people who are blind can accurately describe how things are moving
conscious level
what you are currently aware of in your environment
nonconscious level
body processes we are not usually aware of like breathing
preconscious level
info abt urself ur not thinking about but could come into ur consciousness
subconscious
info we are not consciously aware of but could bring back like from priming and stuff
unconscious
some events and feelings are repressed into our unconscious mind, disputed idea
how do drugs work?
psychoactive drugs change the chemistry of the brain/body into altered state of consciousness
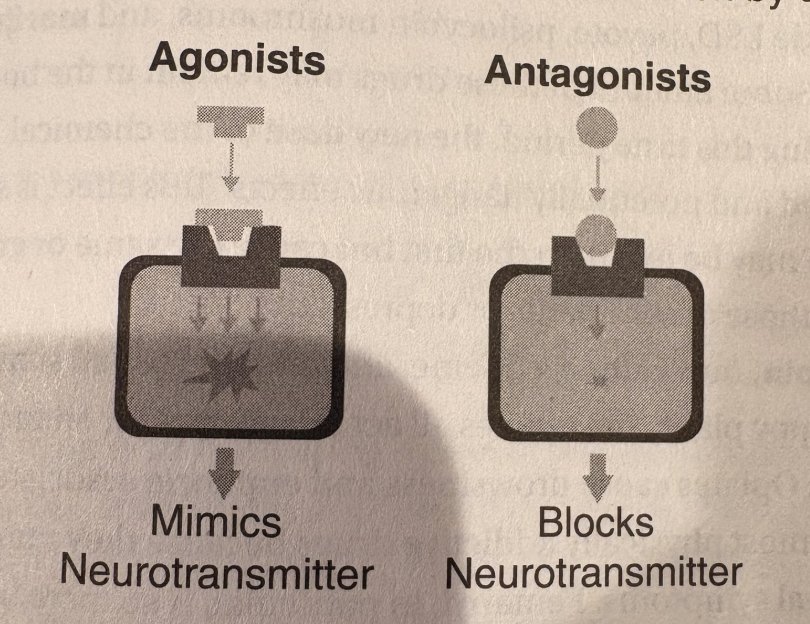
brain is protected from harmful chemicals in the bloodstream with thick walls surrounding the brain’s blood vessels (blood-brain barrier). molecules in these drugs are small enough to pass through and they either mimic neurotransmitters (agonists) or block neurotransmitters (antagonists) see pg 37
some drugs prevent neurotransmitters from being REABSORBED into a neuron, aka reuptakes
neurotransmitter levels are gradually effected which causes tolerance meaning that you want more of that drug, and also
different types of drugs
caffeine, cocaine, nicotine, etc. are stimulants because they speed up processes and make you feel invincible
depressants slow down body systems, alcohol is one of them
hallucinogens cause changes in perceptions of reality like marijuana
opiates like heroin and fentanyl are always agonists for endorphins and make you feel better, most addictive because they rapidly change brain
circadian rhythm
circadian rhythm is just our pattern of our body, your sleep schedule is part of it (see pg 39)
what is sleep onset
we enter sleep onset which is the bridge between awake and asleep, where we might experience hallucinations
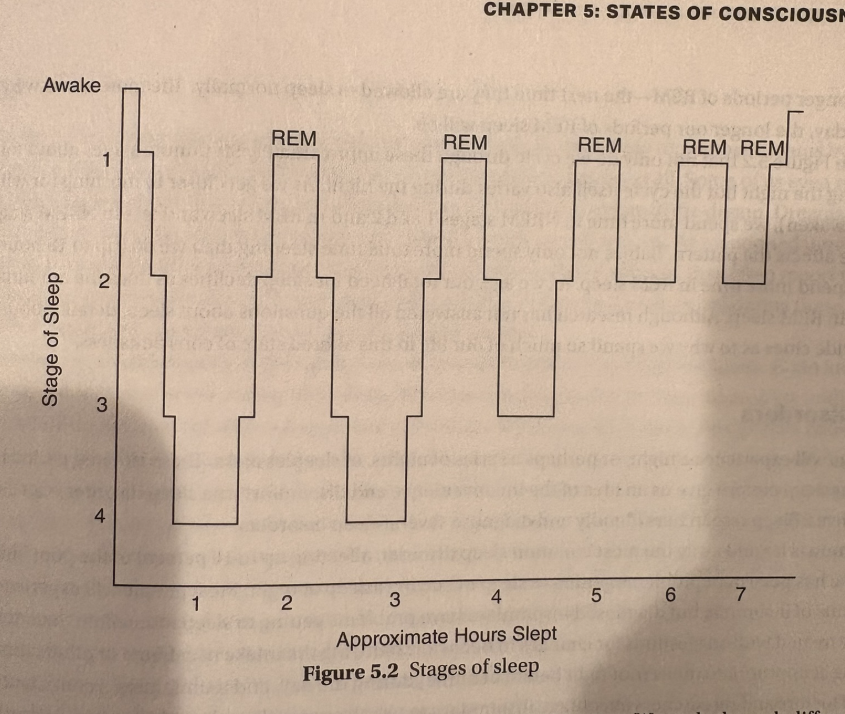
phases of non-REM
in NREM1 and 2, your brain produces theta waves which are pretty high-frequency
towards the end of stage 2, you show sleep spindles (bursts of brain waves)
in 3 and 4, you are in delta sleep, or deep sleep, because of low and slow waves
after some time in delta sleep you go back in the direction of stage 1 and began to produce REM (rapid eye movement), which is also your “paradoxical sleep phase” because your brain waves appear to be very intense
if sleep is affected, what might happen
not enough delta sleep=physically tired and sick, not enough REM sleep=REM rebound, more REM the next time they sleep normally. we also spend more time in REM due to stress
insomnia
insomnia means having problems going/staying asleep
narcolepsy
means falling asleep at random times (that cheerleader girl on yt) but can be treated sometimes with medication
sleep apnea
sleep apnea means your breath stops at some point during the night, and thus you wake up. you can use a breathing machine to help you stay asleep
somnambulism
somnambulism is sleepwalking/night terrors
dreams
activation synthesis theory argues that dreams are just a physiological reflex without much deeper meaning, just a way the brain interprets things
other people think that brains process the events of the day (information processing theory)
consolidation theory—one of the functions of dreams could be to help us get stuff in our short-term memory into our long-term mem