Phylogeny card 1
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Natural Selection
depends on the differential success, in terms of surviving and reproducing, of variants in a pop.
How does natural selection happen?
Genetic Variation (existing at multiple scale)
Species
a group of individuals that can exchange genetic material through interbreeding or share alleles through reproduction
Genes
functional unit of heredity, affects one or more traits
Alleles
different form of gene, correspond to different DNA
Speciation
species are not set but are challenge to define something over a period time —> formation of new species
Gene pool
all the alleles present in all individuals in a species
Population
an interbreeding group of organisms of the same species living in the same geographic area
genetic diversity
the gene pool is all alleles in a species / more different alleles = greater genetic diversity
Evolution
change in allele frequencies across generation
Where does genetic variation comes from?
Mutation 2. Recombination
Mutation
its random
changes the DNA sequence of gene
can be somatic (cant pass) or germ-like (can pass trait)
can be harmful / neutral / advantageous
Recombination
occurs in meiosis
crossing over homologous chromosome result in new combination of alleles
these alleles can be new and inherited from parent
Hardy-weinberg equilibrium
NO difference in survival and reproductive success of individuals in the population
The population size is not changed by the movement of individuals
No mutation in the gene being studied in the population
The population is large enough to prevent sampling errors
Individuals in the population mate at random
= allele frequencies are in equilibrium
Diploid (somatic)
some cell has pairs of each chromosome
haploid (germ-like cells)
singlets of each chromosome
Students kick-netting in a creek are asked to return the largest crayfish from the samples they collect. If this practice continues for a long period of time and the distribution of crayfish moves away from the smallest size of animals this would be…
Directional selection
The concept of parsimony states:
Constructing phylogenetic trees with the fewest evolutionary steps possible
phylogeny
a hypothesis of ancestor descendent relationship
Nodes
represent common ancestor
sister taxa
2 species that are the most related to each other compared to any other taxa in phylogenetic
For a gene, 2 individuals in a population can have different genotypes, but the same phenotype.
True
Animals with spherical symmetry can be described as:
having any possible plane that passes through the centre of the body, creating mirrored halves
which of the follwoin gis best defined as a uniquely derived trait
autopomorphy
homology
similar traits inherited from common ancestor
Analogy
similar traits that evolved independently, not from common ancestor
Synapomorphies
A shared derived trait is a new trait that 2 or more species have due to getting it from common ancestor
Apomorphy
a character/trait that is new or different from the ancestor - derived trait
Plesiomorphy
a trait that is ancestral - inherited from earlier ancestor
autapomorphy
a uniquely derived character state
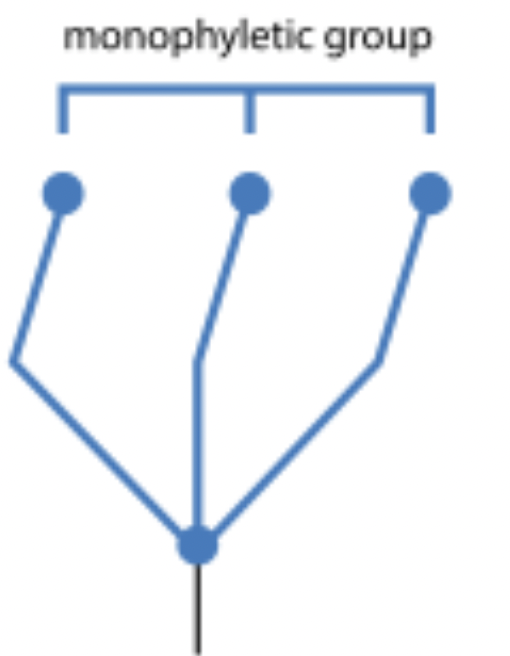
monophyletic group
includes a common ancestor and all of its descendants
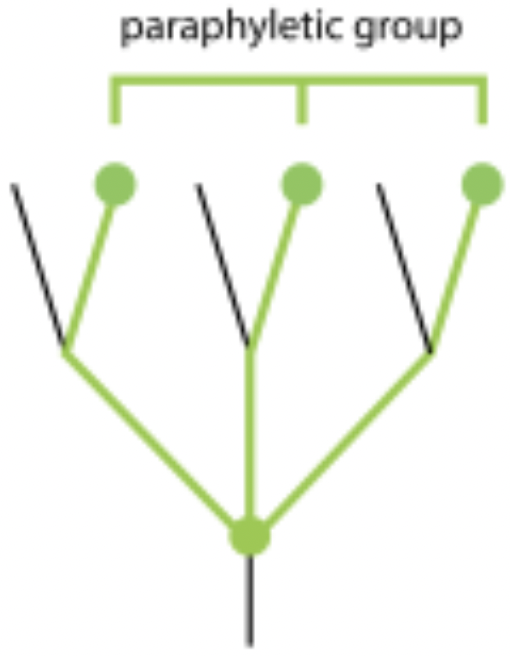
paraphyletic group
include common ancestor and some but not all of its descendants
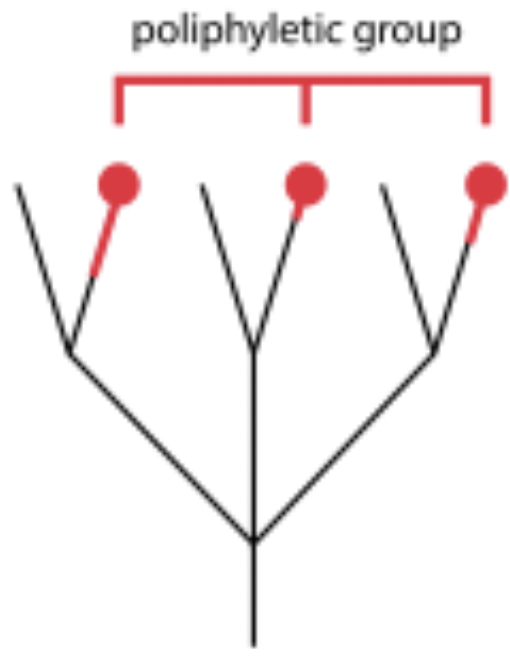
polyphyletic group
group is formed based on similar traits that evolved independently (not from common ancestor)
Parsimony
simplest explanation (requiring fewest evolutionary changes)
In order for natural selection to occur:
must be variation in population
Variation in population must be heritable
Competition for resources among individuals in the population must occur
individuals in the population that are better able to obtain resources must be more likely to survive and reproduce
Fitness
individuals with traits best suited to their environment leave more offspring, so those traits become more common
how much an individual’s genes are passed on to the next generation
type of selection
can inc. the frequency of a favourable allele (positive selection)
Decr. the frequency of harmful allele (negative selection)
balancing selection
natural selection that keeps an alleles at an intermediate frequency, maintaining multiple alleles in the population
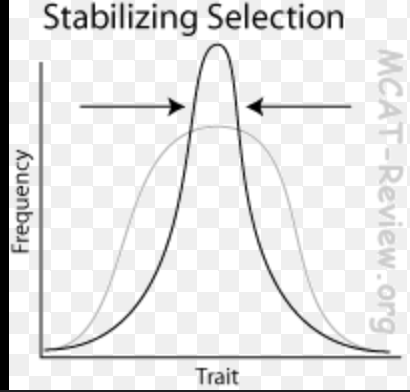
Stabilizing selection
favours average (reduce extreme / population middle)
negative selection against extreme values for a specific character, resulting in an increase in an individual with an intermediate character value
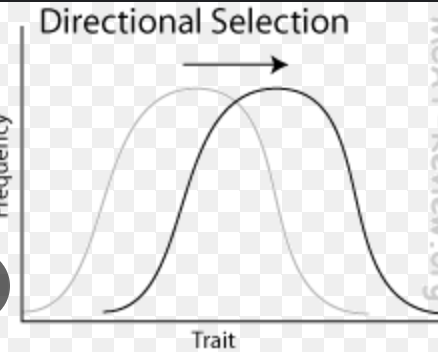
Directional selection
positive selection for a character value that is above or below the mean value for that trait
favours one extreme
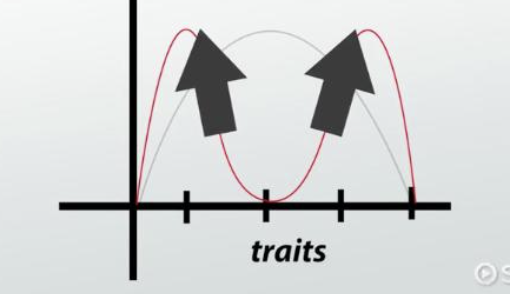
Disruptive selection
selects fro extreme character trait values, or againest intermediates values
artificial selection (directional selection)
successful genotypes are selected by the breeder, not through competition
gneotype
genetic info - every human have a gene for eyes
phenotype
physical traits - different eye
sexual selection
highlights how favourable traits can’t help with survival but inc mating success
intasexual selection
member of same sex complete with each other for a change to mate with other sex
intersexual selection
one sex (often males) advertises to attract the other sex (often females), like bright colour or displays
—> these traits can inc. mating success but may reduce survival
non adaptive mechanism of evolution
Genetic drift
migration / gene flow
mutation
nonrandom mating
Genetic drift
random changes in allele frequencies from one generation to the next
stronger in small population
what are the 2 type of genetic drift?
bottleneck
founder effect
founder effect
A few individuals start a new population
—> only carry a small sample of the original alleles
bottleneck
big population suddenly gets very small
—> lost of alleles lost
migration / gene flow
When individuals move between populations, they bring their alleles with them
—> makes the population more similar and reduces genetic differences over time
mutation
They are rare and usually do not change allele frequencies much by themselves
ex: in 100 individuals , 1 new mutation = very low frequency
Noonrandom mating
Some individuals choose mates based on traits, so certain phenotypes becomes more common
species and divergence
The population have lots of genetic variation. if pop. get separated or become genetically different enough, they can form new species
happens when pop. are genetically isolated, so mutations build up separately
Allopatric
When groups are geographically separated
types of allopatric
dispersal
vicariance
dispersal
individuals moved to a new area (like island to island)
vicariance
A physical barrier splits a pop. (like rising water)
if you made a taxonomic group that included both birds and bats on the basis of wing similarities, this group would be best described as:
polyphyletic
HW equilibrium assumes
mutations are rare and alleles are stable
homology refers to
similar traits due to common ancestry
fitness, in evolutionary context, means an organism
produces more offspring than other members of the pop
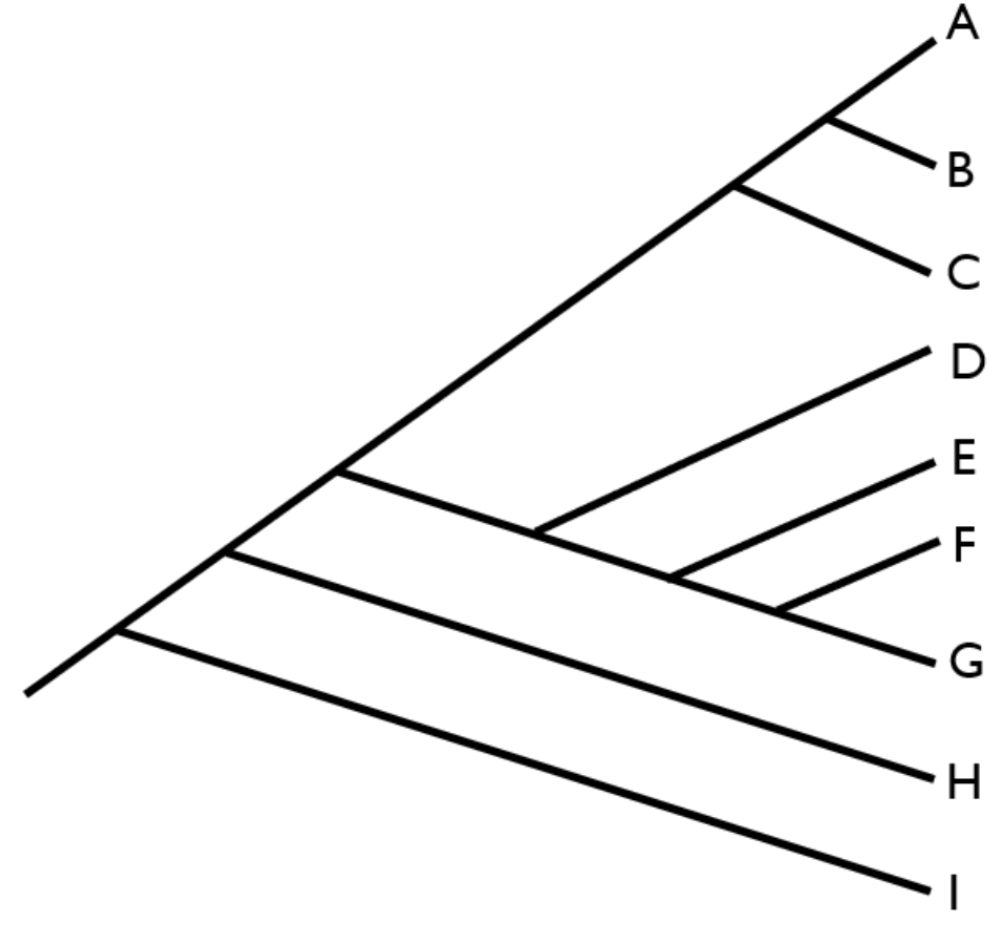
If you grouped the following taxa together (D,E,F,G,H) that group would be described as
paraphyletic
Members of the same (blank) can pass traits through interbredding ; these traits can be seen or measured as the individuals’s (blank)
species; phenotype
Students kick-netting in a creek are asked to return the largest and smallest crayfish from samples they collect. IF this practice continues for a long period of time and the distribution of crayfish moves closer to the average size of animals, this would be …
stabilizing selection
All animals
more than one of the above but not all of the above
which of the following is best defined as a shared derived trait
synapomorphy
A new alleles in a species may come from…
recombination
All animals
produce collagen in their extracellular matrix
Vultures are known for their bald (featherless) heads, which is quite unique among birds. Both New World Vultures and Old World Vultures share this features. However, this traits is not inherited from their common acestor, it developed independently through convergent evolution. If you were to group New Wold Vultures and Old World Vultures into taxonomic group called culture, this group would be described as:
polyphyletic
Jellyfish, which may be divided into mirrored portions if diveded like slice of pizza can be described as…
having at least 2 possible planes that pass through the centre of the body, creating mirrored halves