MKT 305 Midterm 2 (Module 5 Marketing Research)
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Module 5 Marketing Research
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Marketing Research
Process of Gathering Info Pertaining To Customers,Competitors, Channels, and Public Policy for Specific Decision Making
Marketing Information Systems
Provide Organized and Continuous Data Collection and Analysis to Gain Ongoing Marketing Intelligence
Scope Of Marketing Research
Customer Research
Channel Research
Public Policy Research
Competitor Research
Marketing Research Process
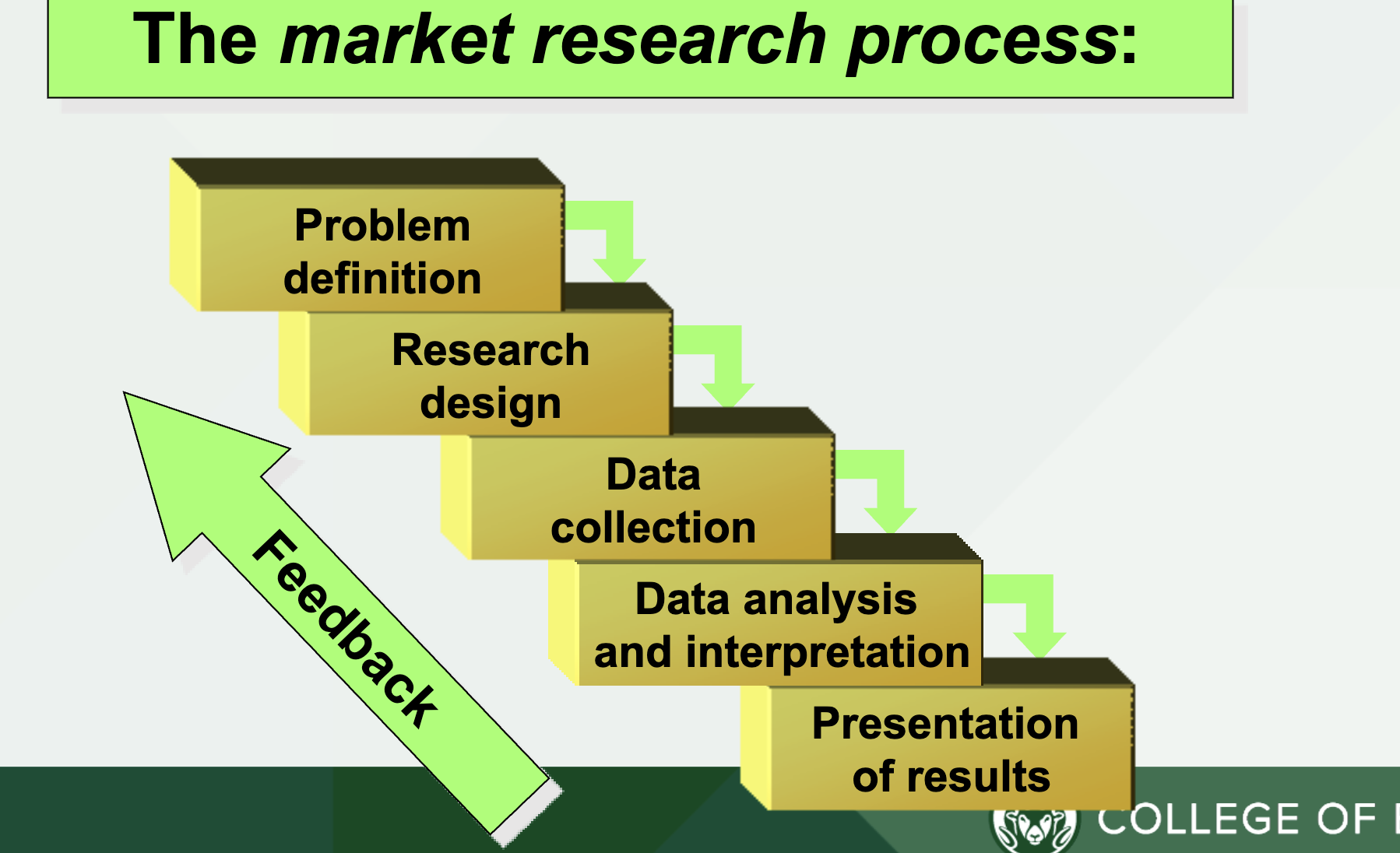
Problem Definition
Develop a Research Question
Most Difficult Step (Often Confuse Symptoms with Problems)
Exploratory (Types of Research)
Quick Additional Information
Descriptive (Types of Research)
More Formal (Customer Surveys)
Cross-Sectional: Response at a specific point in time
Longitudinal: Responses over a long period of time
Causal (Types of Research)
Experimental Research
Primary (Types of Data Collection)
New Data You Go Out And Collect
Secondary (Types of Data Collection)
Data that already exists
Internal: Already Exists Within the Company
External: Already Exists Outside the Company
Reliability (Data Collection)
A Measure of the Stability or Consistency of Responses
Validity (Data Collection)
Relevance of Measure
Primary {Qualitative} (Data Collection)
Hands-On Consumer Research: Become the people with the problem (e.g. Use a wheelchair for a week)
Observational Research
Motivation: What’s your motivation?
Focus Group: Invite 6-12 people to ask questions (Generalization)
Primary {Quantitative} (Data Collection)
Descriptive Research/Survey-Based
Personal Interviews
Telephone Surveys (Fast)
Mail Surveys (Cheap)
Online Survey (Fast and Cheap)
Non-Probability Sampling
Convenience Sample: Focus Groups
Quota Sample: Sampling with Quota in Mind
Judgement Sampling: Depends on Judgement of Interviewer
Probability Sampling
Simple Random Sample: Anyone can be sampled
Stratified Sample: Dividing by groups or characteristics (Age, Gender, etc.)
Cluster Sample: Sample based on location (Zip Codes)