Hardy-Weinberg and Agents of Evolution (3)
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
Genotype frequency
the % of individuals in a population with a specific genotype. It shows the distribution of allele combinations in a population (e.g. AA, Aa, aa)
Allele frequency
% of all copies of a certain gene in a population that carry a specific allele. Shows the distribution of genetic variation in a population (e.g. A or a)
What is evolution measured as?
as changes in allele frequencies in populations from generation to generation
How are gene alleles shown in chromosomes?
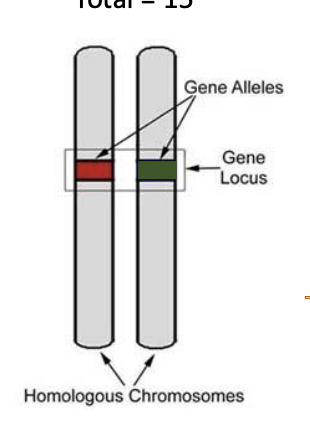
What is used to represent the frequency of alleles identified?
for gene loci with two alleles
‘p’ for frequency of one allele
‘q’ for frequency of other allele
How do you find genotype frequency?
# of individuals with that genotype/ total # of individuals
Genotype: CrCw, CrCw, Cw, Cr
How to find the allele frequency?
# of occurrences of that allele/ 2n (2 times the # of individuals)
Each individual has two alleles
What does finding the allele frequency assume?
the commonness or rarity of each allele in the gene pool assuming individuals are diploid, and both gametes contribute to the production of offspring
What does the sum of allele frequencies always have to add to?
p+q=1
What is one way to find genotype and allele frequency?
Count # of individuals with variant forms of trait
can only work purely on observable traits when one phenotype is encoded by one genotype
Why does counting based on observable traits not work for allele/gentype freq?
many traits encoded by large # of genes —> difficult to make inferences of underlying genotype through phenotype
phenotype is byproduct of genotype and environment
What is the modern way of measuring genotype and allele frequency?
Gel electrophoresis
How does the gel electrophoresis process work?
segments of DNA seperated according to size as they migrate through gel when electrical charge applied
rate of proteins move from ends of gel= determined by charge and size
individual that is heterozygote for a mutation changes amino acid ina. protein —> effects migration of protein in gel —> produces two distinct bands
What does DNA sequencing allow for?
unambiguous way to detect all genetic variation
variation studied through differences in DNA sequence (A instead of G at specified nucletiodie position in particular gene)
polymorphisms
What are polymorphisms?
variable nucleotide positions
How do you calculate allele frequency with DNA sequencing?
collect population sample and count # of occurrences of given mutation
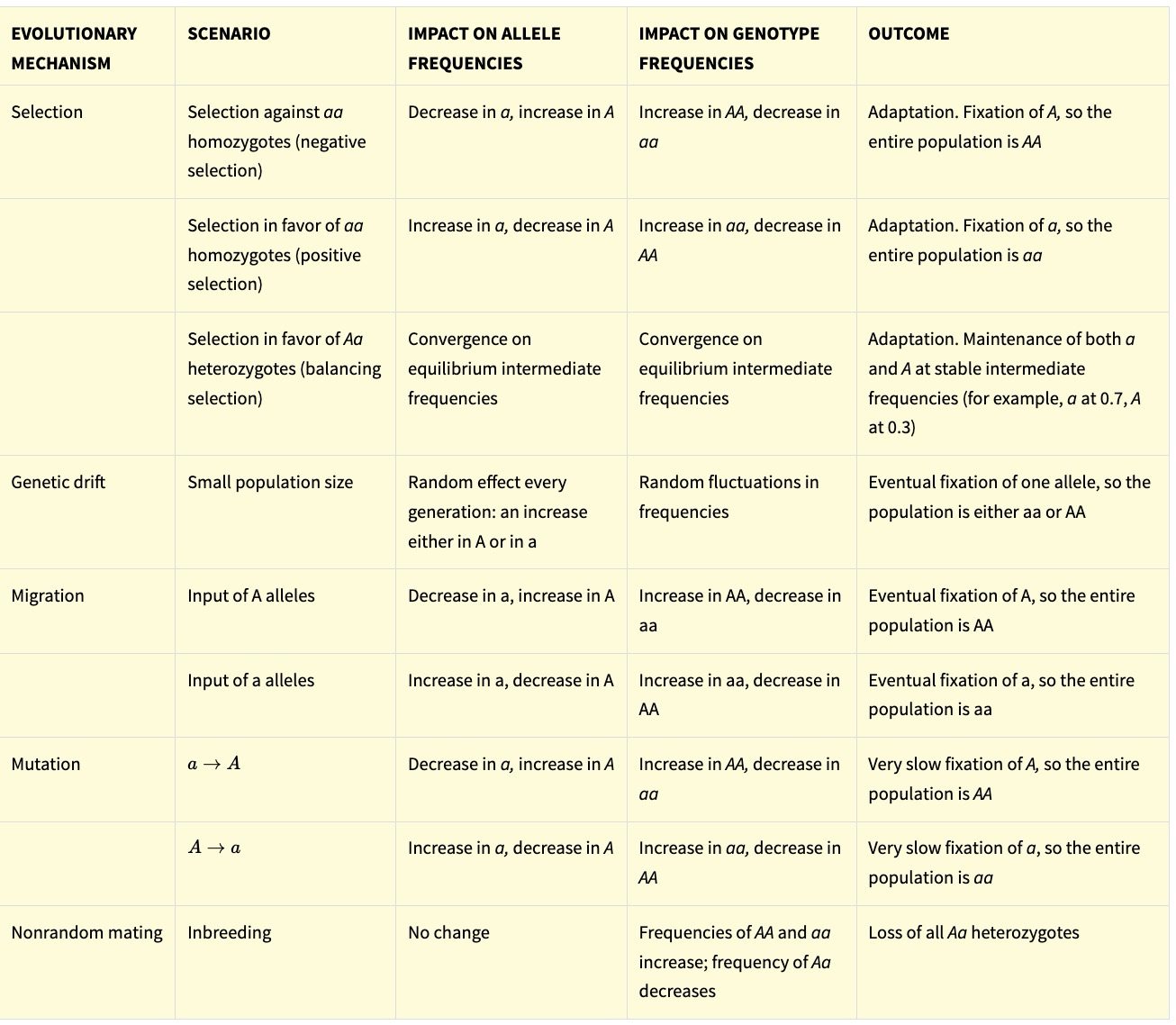
What equation is used to predict genotype frequencies in the next generation?
p2+2pq+q2
What do the variables in p2+2pq+q2 represent?
p2= aa or AA
q2= AA or aa
2pq= Aa (heterozygote)
What only situation does Hardy-Weinberg principle describe?
When allele and genotype frequencies do not change
What does the Hardy-Weinberg Principle show about evolution?
When no allele or genotype frequencies change —> absence of evolution
Data between Hardy-Weinberg to real world data= how much evolution has occurred
What model is used for the Hardy-Weinberg Principle?
The null model
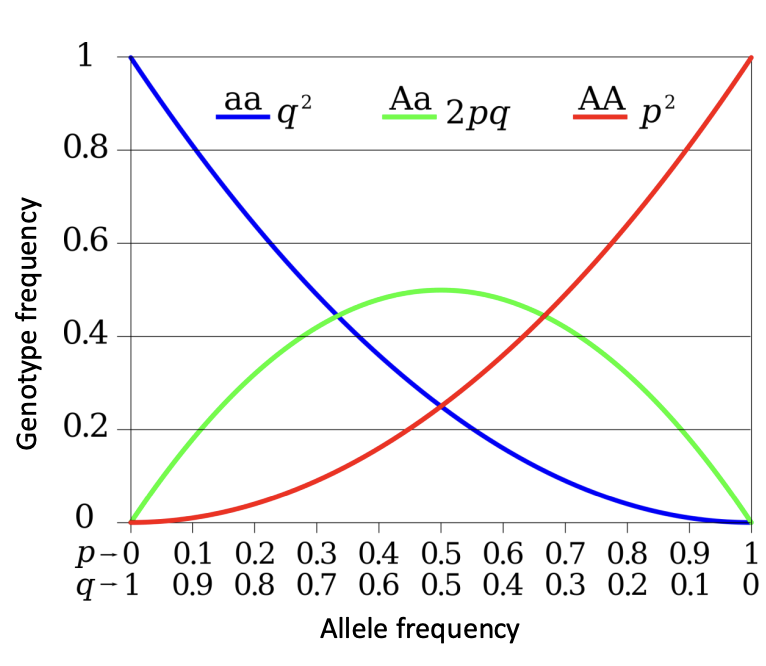
What does the null model show?
the relationship between allele and gene frequency in HDP
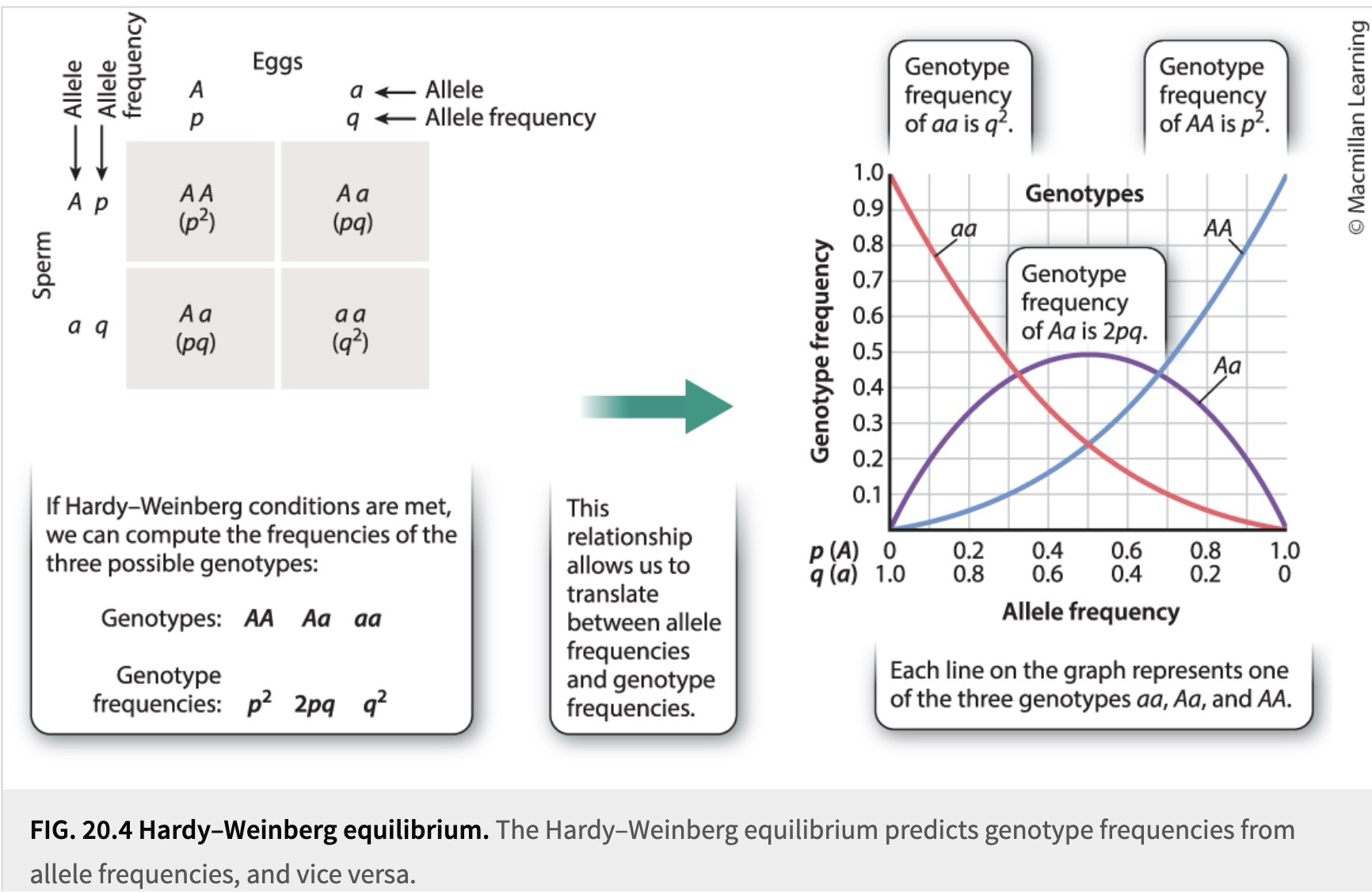
What is a Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium?
A population where frequencies of alleles and genotypes in a population will remain constant from generation to generation
population only Mendelian segregation and recombination of alleles are at work, and no other evolutionary agents (e.g., natural selection).
What conditions have to be met for the HDP?
No mutations are occurring
No gene flow (the population is closed to migration from other populations)
The population is infinite in size (very large)
sufficiently large to preventing sampling error
No natural selection (all genotypes survive and reproduce equally)
Individuals mate randomly with respect to genotypes
What happens when large population conditions are not met?
Large population: chance plays bigger role in small population
Ex: genetic drift more impactful in small population
What happens with HDE doesn’t meet natural selection condition?
Natural selection: harmful allele declines and helpful allele increases
What happens with HDE doesn’t meet immigration condition?
allele frequency will decline/increase in proportio to # of immigrants
What happens with HDE doesn’t meet mutation condition?
Mutations so rare —> small effect on allele frequencies on timescale studied by population genecisits
What happens with HDE doesn’t meet random mating condition?
affects genotype frequencies from generation to generation, but not allele frequency
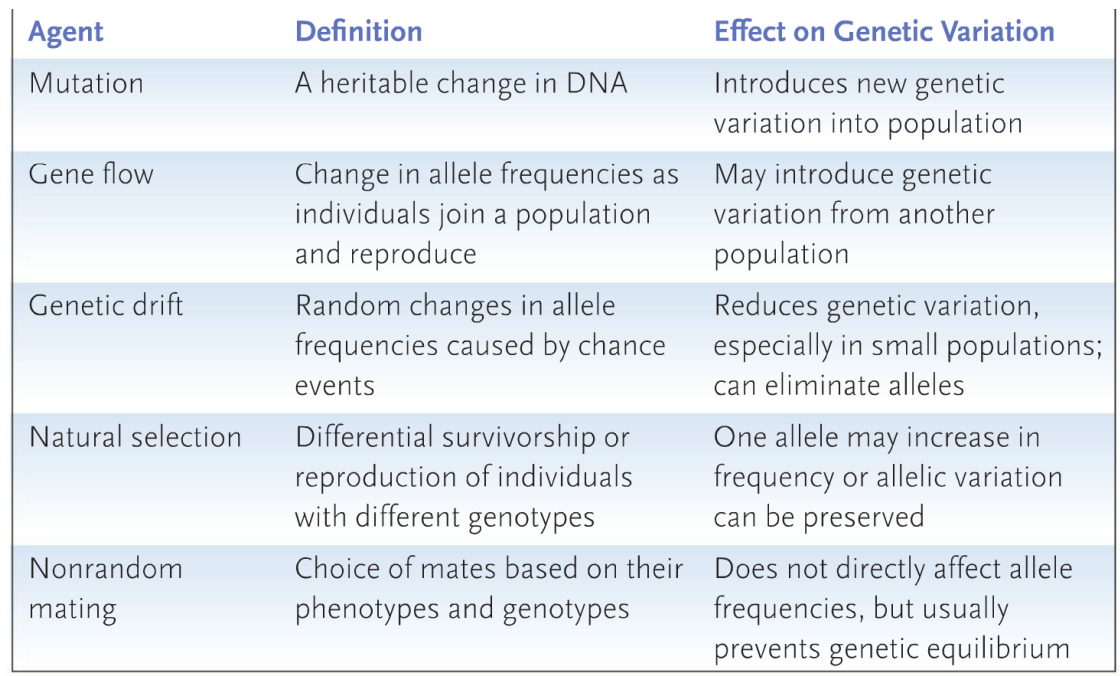
What are the agents of microevolutionary change?
mutation
gene flow
genetic drift
natural selection
nonrandom mating
What are mutations?
Spontaneous heritable variation in DNA
Rare event, significant over long time scales
What is mutation a major source of?
Major source of heritable variation
What is the relationship between neutral mutations and NS?
not governed by NS
mutation has no effect on fitness
Ex: mutation m has no effect on fittness —> presents in single individual heterozygote—> fails to reproduce —> m dies out —> random because nothing selects against m
What happens to lethal mutations in populations?
lethal mutations = death
may persist if recessive
What causes gene flow?
Migration
What is gene flow?
movement of alleles from one population to another
What can enhance gene flow?
life history
Behavior
Dispersal agents (ex pollinators) can enhance and facilitate gene flow
What can disrupt gene flow?
life history
behavior
Physical barrier that prevents populations from breeding
Chemical barriers (ex: pest control)
What is the impact of gene flow
homogenization
What is homogenization
makes both population more similar and decreases genetic variation between the population
Genetic Drift
Change in allele frequency due to random effects of small population size
Which populations are most impacted by genetic drift?
small populations
Ex: rare allele A is 1/1—→ destruction reduces population to one pair of individuals —> A in new population is ¼ (each indivi. has two alleles) —> loss of genetic variation
What is genetic drift equivalent of?
genetic drift=sampling error
small sample: extreme departures from expected outcome are common
What is the relationship between adaptation and genetic drift?
does not cause useful traits (adaptation) because allele frequencies changing does not affect indivudal ability to survive or reproduce
adaption: favors individuals with beneficial traits that increase their survival and reproduction in environment
genetic drfit: genetic drift doesn't consider an allele's fitness, meaning it can lose beneficial alleles or fix harmful ones
Impact of genetic drift
reduces genetic variability
population bottleneck
founder effect
What is a population bottleneck?
Part of genetic drift
Reduction in alleles due to population reduction
Leads to a drastic, but often temporary, reduction in population size
What is the founder event?
few individuals starting a new population
part of genetic drift
Impact of the founder effect
less genetic variety in smaller new population can lead to extinction
Deleterious allele can become dominant because of lack of genetic variation
relative to parent population —> allele frequencies randomly changed and genetic information lost
What is the impact of a bottleneck?
leads to smaller genetic variation —> individuals may not be able to survive new environment
can lead to fixation of alleles that are not best fit for environment
What is fixation?
process by which one allele replaces all other in a population
population shows only one allele at a particular gene → pop. is fixed to that allele
What happen to rebound populations after bottleneck?
Has smaller genetic variation
What often causes a population bottleneck?
Often caused by catastrophic factors: disease, starvation, drought
What is natural selection?
A process in which individuals that have certain inherited traits tend to survive and reproduce at higher rates than others because of those traits
How does NS impact allele frequency?
causes allele frequency to change generation to generation according to allele’s impact on survival and reproduction of individuals
Adaptation defintion
process where population progressively becomes better fitted to environment through natural selection
What claims (observations) does NS rely on?
variation among individuals of species
some of this variation is heritable
individuals compete for resources
genetic variation among individuals result in some individuals that are more likley to survive and reproduce —> pass genetic material to net generation —> has higher proportion of advantageous cells
What did Malthus say about population?
Natural populations have potential to increase in size geometrically (larger at an ever increasing rate) but competition for resources stop that
How is natural selection measured?
relative fitness
What is relative fitness?
measure of ability of an individual to survive and reproduce in an environment
relative to individuals in same species
depends on environment
What is competitive advantage?
how well an organsim is adapted to its environment
What does natural selection drive a variation in for reproduction?
Reproductive succsess
What is reproductive fitness?
baed on reproductive effort (number of offspring produced)
What is Mendelian Genetics?
units are unitary/discrete (ex: purple vs. white —> no light purple)
Genetic characters have alternate forms, each inherited from each parent (alleles)
One allele dominant over another —> the phenotype shows dominant allele
Gametes are created created by random segregation. Heterozygote individual produce gametes with equal frequency of two alleles
Genes are unlinked. Different traits have indenpendent assortment
Video:
Why did people question Mendelian genetics?
the pee’s were Discrete
most variation occurs on a spectrum and are not discrete
Discrete meaning?
Clear alternative states (yellow and green)
What is Modern Synthesis and combination of?
Darwins theory of evolution and Mendelian genetics —> completed by Ronald Fisher
What did Ronald Fishes discover?
several genes could contribute to one trait
What did Ronald Fisher add to Mendelian genetics?
extends Mendel’s theory to include multiple genes per trait that could explain patterns of continued variation
What is positive selection?
NS that increases frequency of advantageous alleles
What is negative selection?
NS reduces frequency of deleterious allele
How does negative selection impact deleterious alleles?
most mutations to genes are deleterious
if deleterious mutation is recessive —> NS inefficient to remove it
homozygotes will be rare
What are the types of natural selection?
Directional selection
stabilizing selection
Disruptive selection
Directional selection
Favors individuals near one end of phenotypic spectrum
Ex: pushing for larger tail feathers
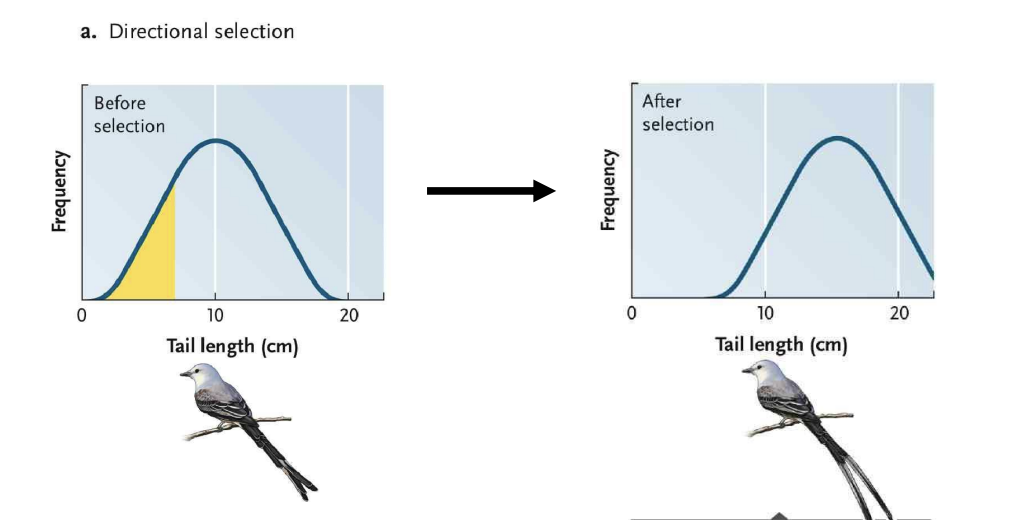
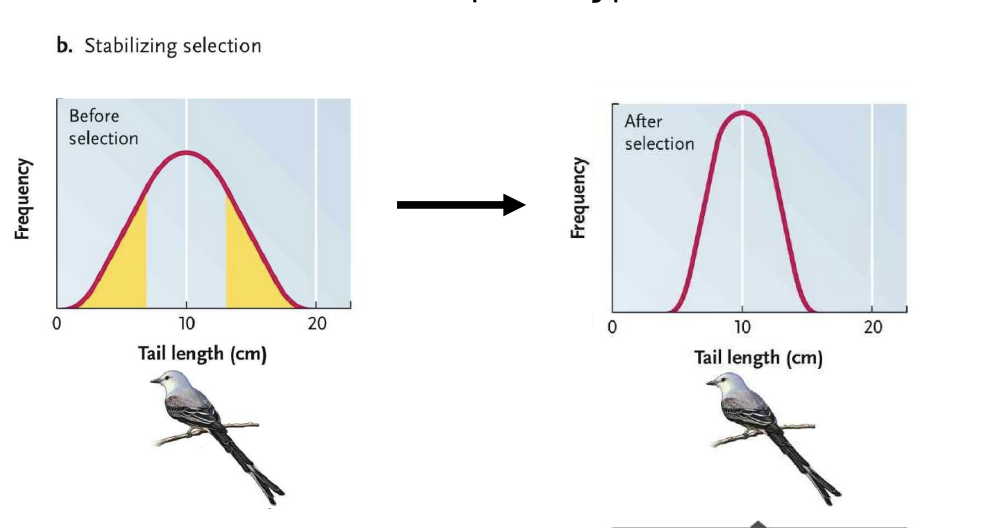
Stabilizing selection
Favours individuals with intermediate phenotypes
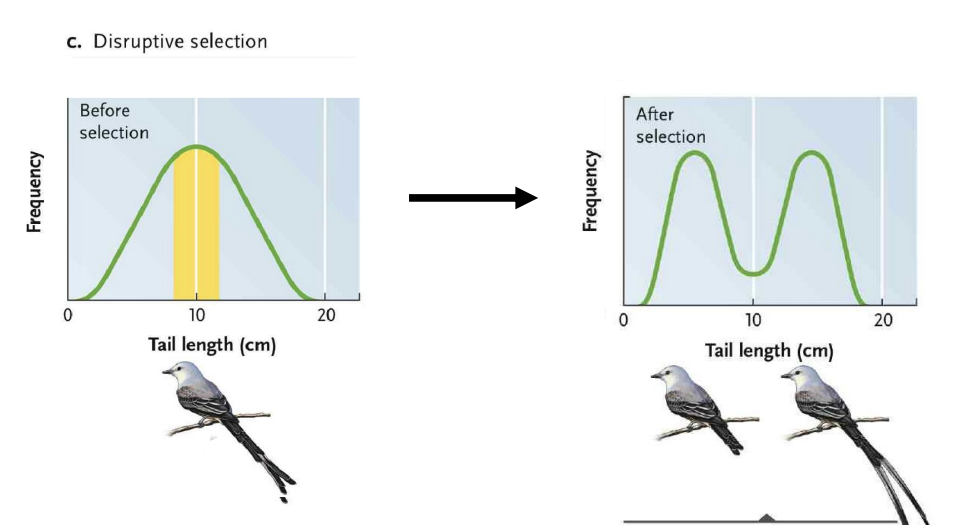
Disruptive selection
Favours individuals with extreme phenotypes over intermediate forms
Selection towards one type → major change → pushes for both extremes
What is artificial selection?
humans select for traits
What is intrasexual selection?
one sex (usually names) compete for acsess of other sex (usually femals)
focuses on competition between individuals of one sex
What is intersexual selection?
males (typically) compete for attention with bright colors or advertisment displays
females choose mate
What is random mating?
Individuals select mate w/out care for genotype
nonrandom mating?
individual preferentially choosing mates according to genotype
How does nonrandom mating impact alleles?
just redistributes alleles already in the gene pool and, unlike migration or mutation, does not add new alleles to the population.
genotype frequencies change in nonrandom mating, whereas allele frequencies do not.
Summary of agents of evolution