05: Trigonometry and Trigonometric Ratios
Trigonometry: the study of how sides and angles of a triangle are related to each other
The Right Angle Triangle
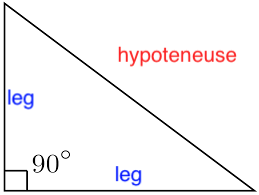
- A right angle triangle has a 90º angle
- The side opposing the 90º angle is called the hypotenuse
- the other two sides are called the legs
Labelling Triangles
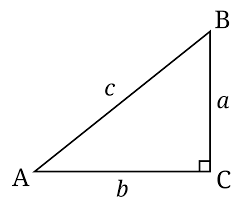
- The side opposite an angle and vertex becomes the lowercase letter of that angle and vertex
Pythagorean theorem
a² + b² = c²
leg² + leg² = hypotenuse²
- used only for side lengths, cannot be used for angles
Trigonometric Ratios
| Primary Trigonometric Ratios | Secondary Trigonometric Ratios |
|---|---|
| ==sinθ = O/H== | ==cscθ = H/O== |
| @@cosθ = A/H@@ | @@secθ = H/A@@ |
| tanθ = O/A | cotθ = A/O |
- Secondary trig ratios are primary trig ratios, flipped
cscθ = 1/sinθ
secθ = 1/cosθ
cotθ = 1/tanθ
→ you can solve by using the reciprocal when facing a secondary trig ratio
Angles of Elevation and Depression
Most often seen in word problems
Angle of Elevation
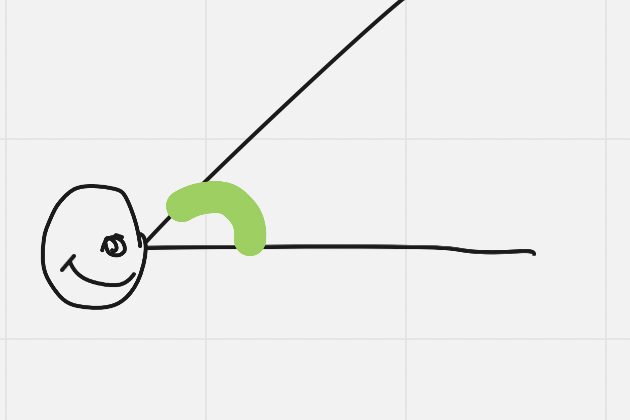
The angle between the line of sight and the horizontal from the eye
Angle of Depression
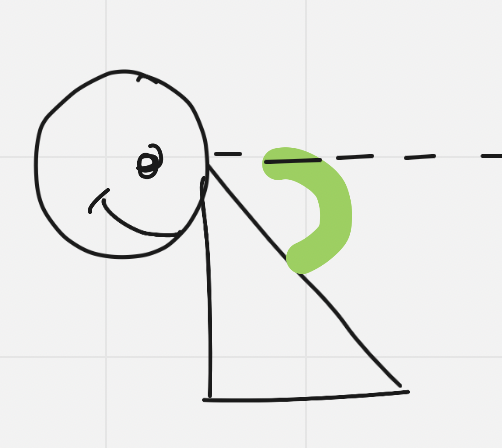
The angle when looking down, between the line of sight and the horizontal from the eye
- Because of Z pattern angles, the angle of elevation and depression are actually the same (and are dependent on a question’s phrasing)
Exact Values
You may not use decimals here, as that is not the true exact value
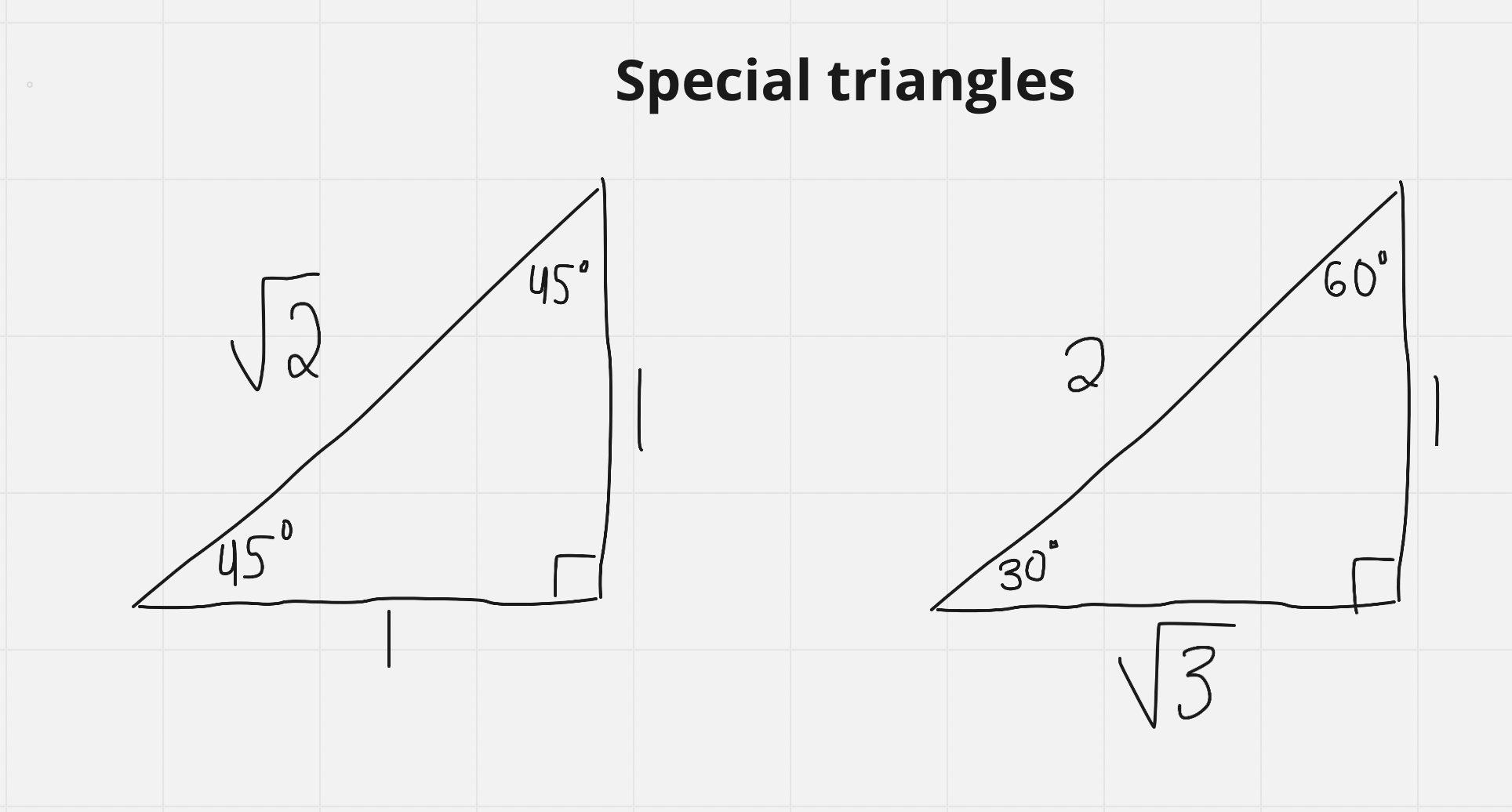
Special Triangles
Used to find the exact values for 45º, 45º isosceles triangles and for 60º, 30º triangles (remember: sum of a triangle’s angles must be 180º)
Remember that you must rationalize your final answer
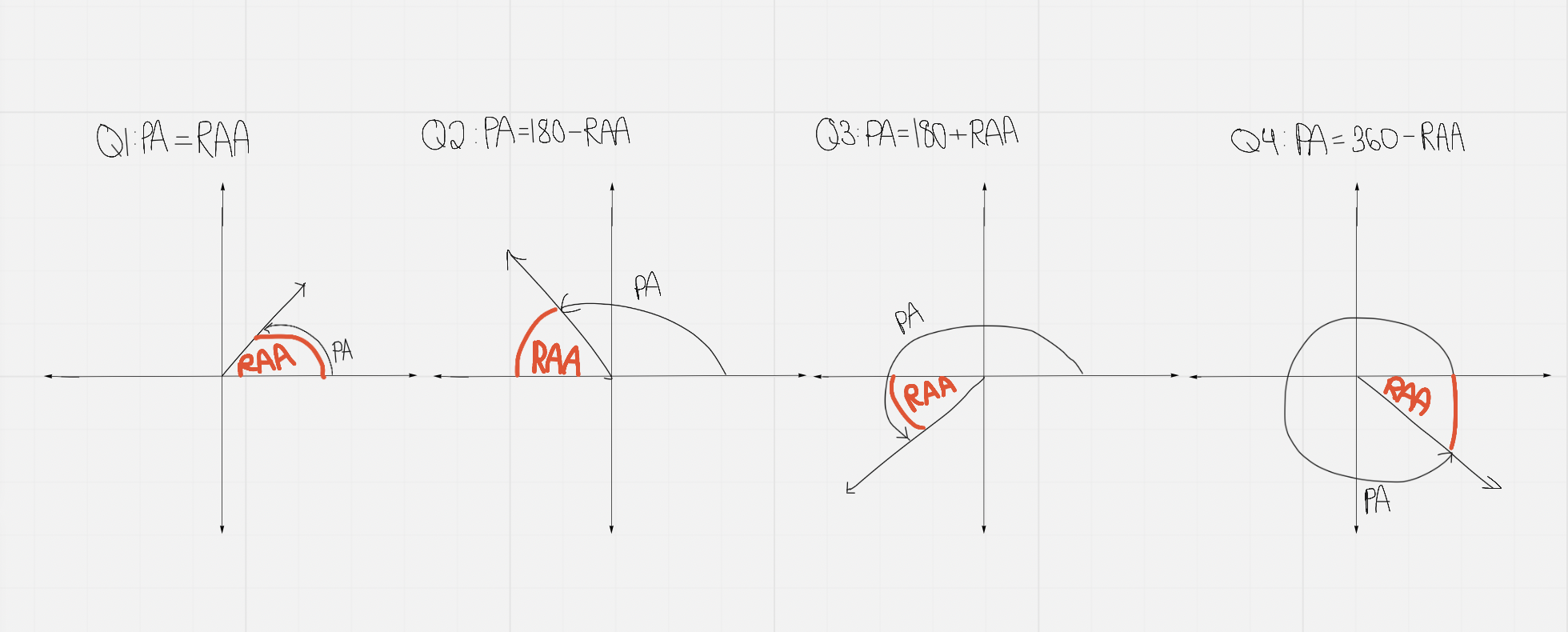
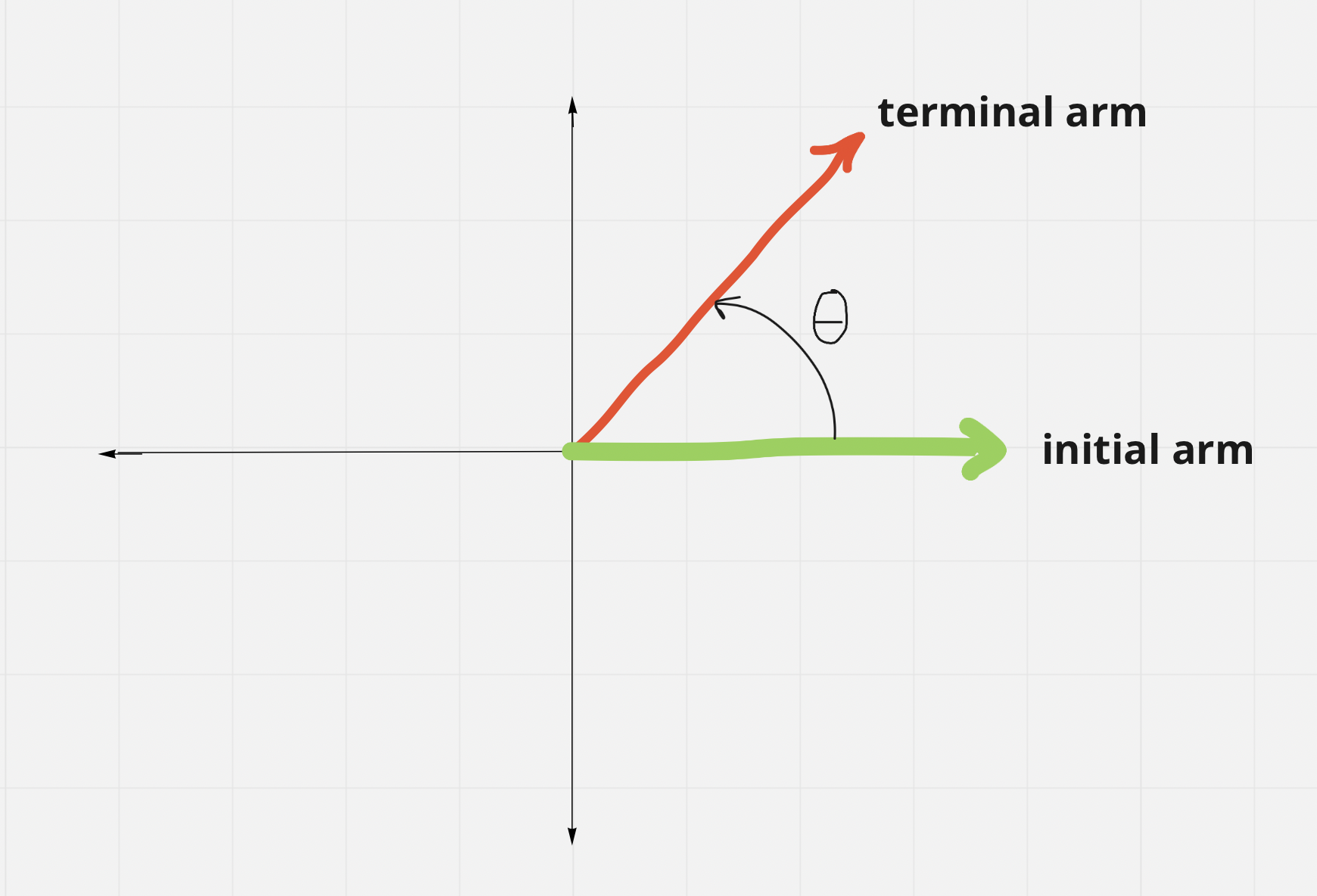
Trig Ratios, Angles Greater Than 90º
- Angles in standard position are always measured from the initial arm to the terminal arm, @@counterclockwise@@ (arrow always drawn)
- Angles measured closckwise are negative
The angle, θ, is known as the principal angle (PA)→ its value can fall between 0º and 360º depending on which quadrant the terminal arm is in
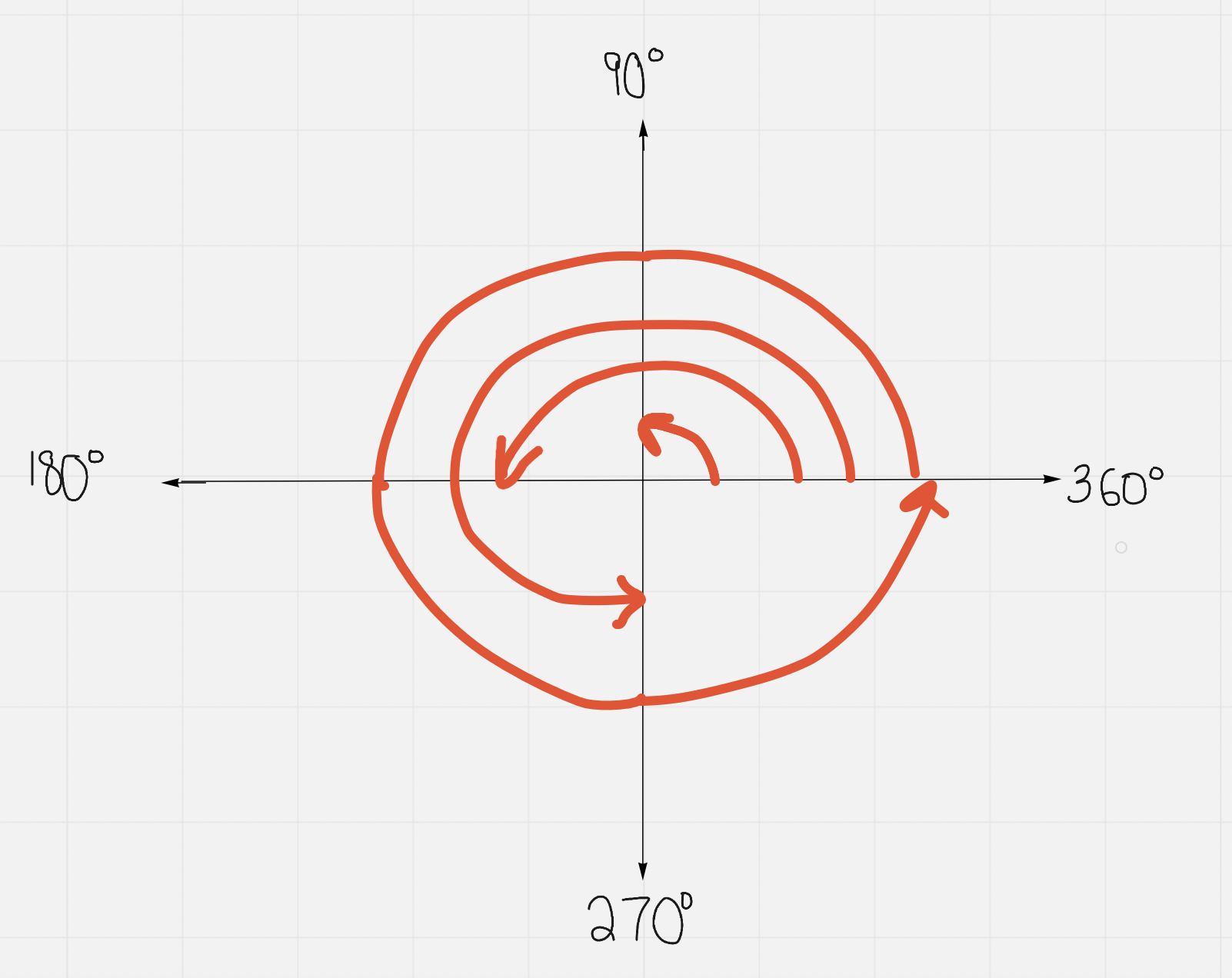
The related acute angle (RAA) %%sits between the terminal arm and the x axis%% in any quadrant