MCAT Biology - The Respiratory System
1/52
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
thoracic cavity
chamber of the body of vertebrates that is protected by the thoracic wall; contains lungs
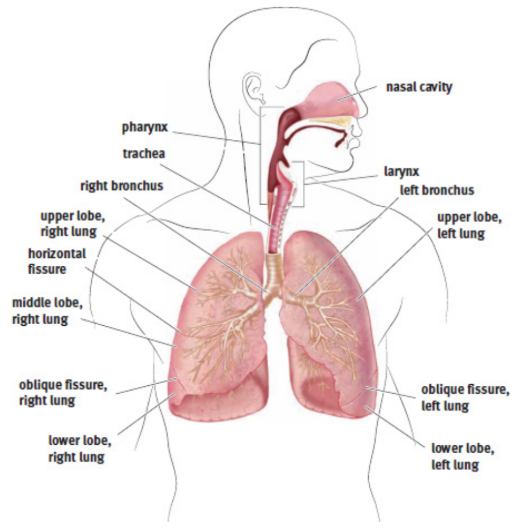
Lungs
the primary organs of the respiratory system; location of gas exchange
nares
nostrils; external orifice of the nose
vibrissae
nasal hairs
pharynx
resides behind the nasal cavity and at the back of the mouth; common pathway for both air destined for the lungs and food destined for the esophagus
larynx
lies below the pharynx and is only a pathway for air
glottis
the opening of the larynx, covered by the epiglottis
epiglottis
covers the glottis
vocal cords
two; maneuvered using skeletal muscle and cartilage
trachea
air passes her after larynx; epithelial cells to catch material that has made it past the mucous membranes in the nose and mouth
bronchi
two; pathway into lungs after trachea; epithelial cells to catch material that has made it past the mucous membranes in the nose and mouth
bronchioles
the bronchi continue to divide into smaller structures
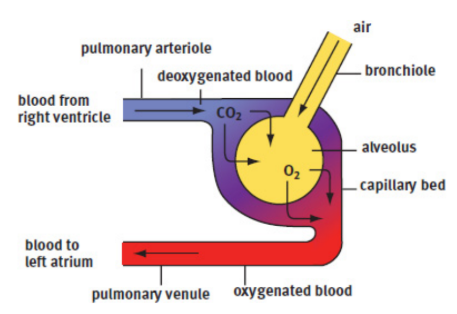
alveoli
tiny balloon-like structures in which gas exchange occurs at the end of bronchioles; network of capillaries surrounds to carry oxygen and carbon dioxide; an exceptionally large surface area for gas exchange, approximately 100 m2 in total
surfactant
a detergent that lowers surface tension and prevents the alveolus from collapsing on itself, coats alveoli
pleurae
membranes that surround the lungs
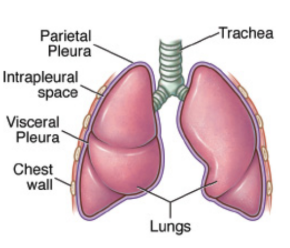
visceral pleura
surface adjacent to the lung
parietal pleura
outer part
diaphragm
a thin, muscular structure that divides the thoracic (chest) cavity from the abdominal cavity; under somatic control, even though breathing itself is under autonomic control
intrapleural space
space within the sac; contains a thin layer of fluid to lubricate the two pleural surfaces
Inhalation
active process; diaphragm flattens and the chest wall expands outward; volume increases and pressure decreases
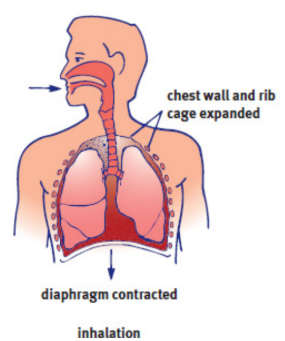
external intercostal muscles
one of the layers of muscles between the ribs; expand the thoracic cavity
intrathoracic volume
the volume of the chest cavity
negative-pressure breathing
the driving force is the lower (relatively negative) pressure in the intrapleural space compared with the lungs
Exhalation
passive process; Simple relaxation of the external intercostal muscles will reverse the processes of inhalation; decrease in volume and increase in pressure; speed up using internal intercostal muscles and abdominals
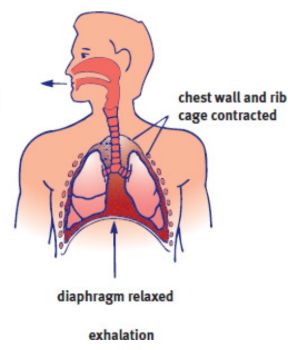
internal intercostal muscles
oppose the external intercostals and pull the rib cage down to speed up exhalation
Emphysema
disease characterized by the destruction of the alveolar walls → reduced elastic recoil of the lungs → exhalation becomes extremely difficult
mostly caused by cigarette smoking
spirometer
assess lung capacities and volumes (except residual volume)
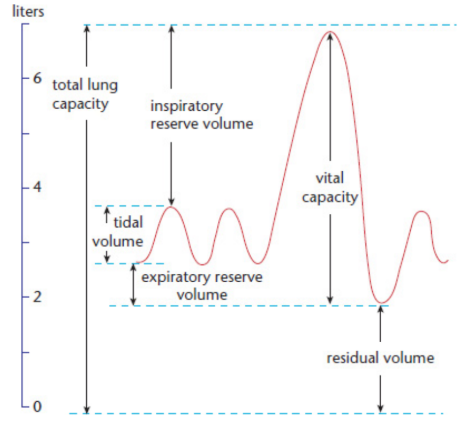
residual volume (RV)
the amount of air remaining in the lung after complete exhalation
Total lung capacity (TLC)
maximum volume of air in the lungs when one inhales completely; usually around 6 to 7 liters
Vital capacity (VC)
difference between the minimum and maximum volume of air in the lungs (TLC – RV)
Tidal volume (TV)
volume of air inhaled or exhaled in a normal breath
Expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
volume of additional air that can be forcibly exhaled after a normal exhalation
Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
volume of additional air that can be forcibly inhaled after a normal inhalation
ventilation center
collection of neurons in the medulla oblongata; fire rhythmically to cause regular contraction of respiratory muscles
chemoreceptors
specialized sensory receptor which transduces a chemical substance to generate a biological signal
ex. CO2 concentration in blood - ventilation center
hypercarbia/hypercapnia
partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the blood rises; increases respiratory rate
respiratory rate
the rate at which breathing occurs; set and controlled by the respiratory center of the brain; usually measured in breaths per minute
hypoxemia/hypoxia
low oxygen concentration in the blood
hypoventilation
lead to increased carbon dioxide levels and an override by the medulla oblongata which would jump-start breathing
hyperventilation
blow off too much carbon dioxide and ultimately inhibit ventilation
blowing into paper bag
pulmonary arteries
originate from the right ventricle of the heart, how deoxygenated blood gets to the lungs
pulmonary veins
how oxygenated blood leaves the lungs; returns to the left atrium of the heart
thermoregulation
regulation of body temperature
vasodilation
As capillaries expand, more blood can pass through these vessels, and a larger amount of thermal energy can be dissipated
vasoconstriction
As capillaries contract, less blood can pass through them, conserving thermal energy
panting
transfer heat to the environment through evaporation of water in mucous secretions
ex. dogs
lysozyme
nasal cavity, tears and saliva; attack the peptidoglycan walls of gram-positive bacteria
mucociliary escalator
internal airways are lined with mucus, which traps particulate matter and larger invaders. Underlying cilia then propel the mucus up the respiratory tract to the oral cavity, where it can be expelled or swallowed
Macrophages
engulf and digest pathogens and signal to the rest of the immune system that there is an invader
mast cells
preformed antibodies on their surfaces; releases inflammatory chemicals into the surrounding area
the bicarbonate buffer system
body attempts to maintain a pH between 7.35 and 7.45
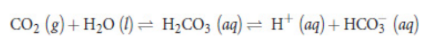
acidemia
blood pH is lower, and hydrogen ion concentration is higher; increase the respiratory rate
alkalemia
blood pH is higher, and hydrogen ion concentration is lower; decrease the respiratory rate