L1-2 cancer genetics flashcards
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This set of flashcards covers essential vocabulary related to cancer biology and treatment, focusing on key concepts and definitions for exam preparation.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Heterogeneous Tumor
A tumor composed of a diverse mixture of cell types, leading to variations in genetic and phenotypic characteristics.
Oncogenes
Genes that promote cell growth and division, which can lead to cancer when mutated or overexpressed.
mutations lead to dominant gain of function - promotes cell growth/division.
not usually inherited
dominant when inherited
Tumor Suppressor Genes
Genes that inhibit cell division and survival; mutations in these genes can result in uncontrolled cellular proliferation.
can be inherited - recessive
Selective Pressure
For cancer treatment, it refers to the application of therapies that eliminate certain cancer cells while allowing others to survive and potentially develop resistance.
Anaplasia
A condition of undifferentiated cells often seen in tumors, signifying a loss of normal cell features.
Angiogenesis
The formation of new blood vessels, which tumors stimulate to secure a blood supply for growth.
Intratumoral Heterogeneity
Variability within a single tumor mass, involving different cell subtypes and their unique genetic profiles.
Tumour Microenvironment
The surrounding cellular environment that influences tumor behavior and growth, including interactions with immune and stromal cells.
Genomic Instability
An increased tendency of the genome to acquire mutations, often contributing to cancer progression.
Four Main Stages of Cancer Progression
Initiation (abnormal cell proliferation)
Angiogenesis (developing a blood supply)
Invasion and Intravasation (entering the circulatory system)
Metastasis (spreading to distant sites and forming secondary tumors).
what are the intrinsic factors promoting cancer?
dysfunction in:
tumour suppressor + oncogenes
cell-cycle proteins
signalling pathways
chromosomal instability (2-hit)
what are extrinsic factors promoting cancer (Tumour microenvironment)
soluble (growth) factors
altered environment
infiltration of immune cells
ECM
angiogenesis
what is the evidence supporting cancer as a genetic disease
most carcinogens are mutagens
cancer is not a contagious disease
cancer incidence increases with age - accumulated DNA damage
chromosomal instability common in cancer
defects in DNA repair increases chances of developing cancer
what are the types of cancer genetic mutations
germine vs sporadic
mutations of tumour suppressor or oncogenes
mutations of caretaker, gatekeeper, or landscaper genes
what are germline mutations?
mutations inherited from parent-offspring - present in all cells
what are somatic mutations
mutations acquired from cumulative damage to genes (sporadic) - in non-germline cells
proto-oncogene
normal functioning oncogene - promotes controlled growth/proliferation
what tumour suppressor gene causes retinoblastoma
RB1
what tumour suppressor gene causes familial adenomatous polyposis
APC gene
what tumour suppressor gene causes Li-fraumeni Syndrome
TP53 gene
what type of mutation causes the fusion of BCR-ABL gene in chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML)
translocation (of the Philadelphia (Ph) chromosome
(exception) family cancers linked to oncogenes
RET - causes multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 (MEN2)
MET causes isolated hereditary papillary real cell cancer (HPRCC)
how are oncogenes activatied?
point mutations (Ras family genes) (usually missense)
amplification (Myc oncogene)
translocation (fusion protein BCR-ABL)
what type of genetic mutation is responsible for activating the oncogene H-ras in bladder carcinoma
missense point mutation (gly→val)
how are tumour suppressor genes mutations distributed on the gene?
usually spread across gene
evenly missense and premature termination codons (nonsense) point mutations
how are oncogene mutations distributed on the gene?
focused in particular regions/domains (Kinase)
biased towards missense point mutation
what are gatekeeper genes
genes that act directly on the cell-cycle to inhibit cell proliferation (tumour suppressor genes, some oncogenes)
what are caretaker genes>?
genes that act indirectly on the cell-cycle or proliferation that maintain genome integrity (health) (DNA repair genes)
disruption leads to genomic instability
what are landscaper genes?
genes that regulate the microenvironment and promotes the growth of cancerous cells (extracellular matrix genes)
what is genomic instability?
what is the role of DNA repair genes?
acts indirectly as ‘caretakers’ of genome integrity
what happens if DNA repair genes are inactivated by mutation?
DNA damage going unrepaired
accumulation of mutations in other cellular genes
increases likelihood of damaging mutations other critical genes
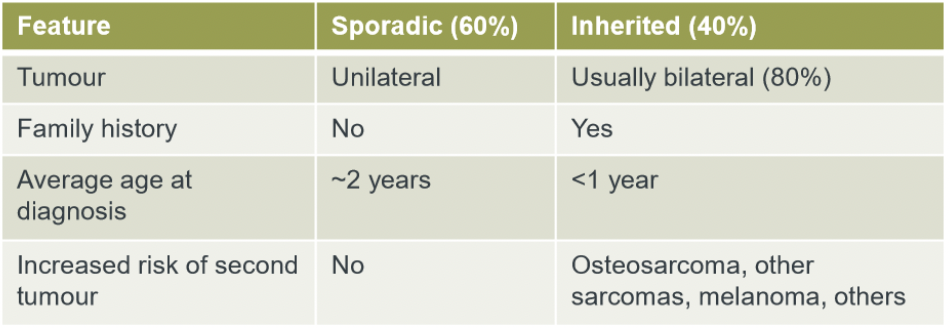
why does inherited retinoblastoma occur earlier?
inherited RB only requires 1 occurrence of somatic mutation as there is already a pre-existing germline mutation present, whereas sporadic RB would require a SECOND somatic mutation.
difference between sporadic and inherited blastoma
inherited retinoblastoma
autosomal dominant transmission
RB1 gene localised on chromosome13
Rb protein negatively regulates cell cycle
1 germline mutation, 1 somatic mutation
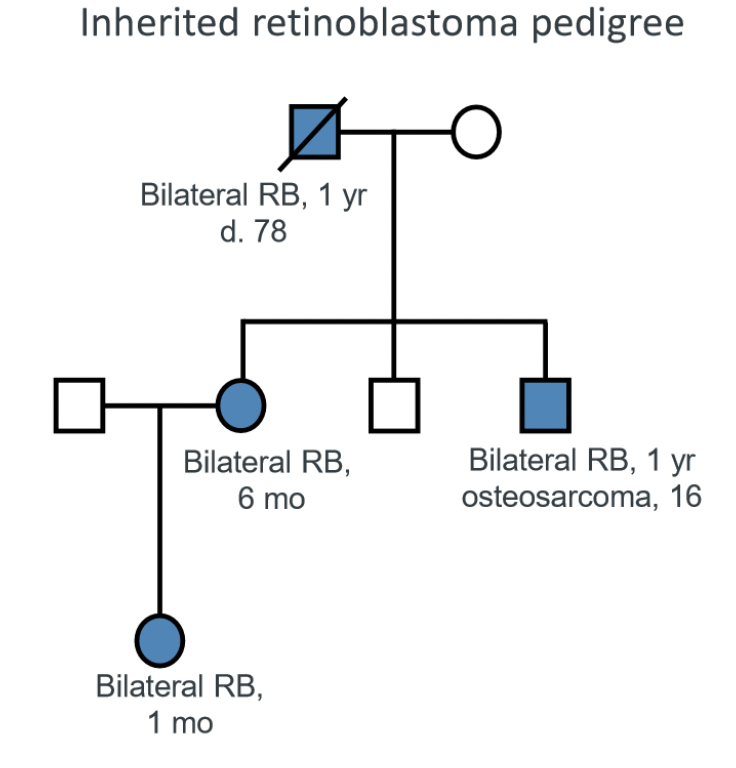
two-hit hypothesis
suggests that two genetic mutations are required for tumorigenesis.
1st hit is a germline mutation (point mutation)
2nd hit is a somatic mutation (LOH through mitotic recombination)
how does two-hit hypothesis explain sporadic retinoblastoma?
sporadic RB requires two independent mutations
rb1 allele is recessively acting
following a single mutation, cell is left heterozygous (Rb+/-) and would exhibit wild-type phenotype
therefore the other allele must be deleted for tumour development
sporadic retinoblastoma
Occurs when both RB1 alleles are mutated in somatic cells, leading to tumor development without inherited predisposition.
2 somatic mutations
why is sporadic retinoblastoma very likely?
retinal cells grow very rapidly in early life. the likelihood of a second somatic mutation is high when one gene is already out of action.
dominant inheritance of retinoblastoma
if you have 1 inherited copy of allele = 90% penetrance of RB
rb1 is a recessive allele
the rb1 allele must be mutated in both copies for retinoblastoma to develop; only one functioning allele is necessary for normal cell function.
allelic deletion (loss of heterozygosity)
mitotic recombination leading to loss of wild-type allele
haploinsufficiency (in tumour suppressors)
a condition where one functional copy of a gene is insufficient to maintain normal function, leading to tumorigenesis. (gene does not act recessively)
TP53 gene
encodes for p53 tumour suppressor protein
when DNA damage: p53 induces cell-cycle arrest for DNA repair to happen or induces apoptosis
multistep tumourigenesis
in sporadic cancers:
(aging, lifestyle, environment)
dominant negative effect exhibited by p53 inactivation
p53 subunits form tetramer
mutated p53 allele cancels out the normal function of p53
only 1 mutated subunit is required for an inactive p53 protein
define multi-step model (tumourigenesis) of sporadic cancer
acquisition of multiple mutations that lead to cancer
example of multistep tumourigenesis
sporadic colorectal cancer:
colon epithelial cells have high turnover (stem cells) - 15-20% cells die & replaced each day - HIGH RISK OF MUTATION
mutations only required in ~5 critical genes for cancerous adenomas to develop
requires screening every 5 years
BRCA1 and BRCA2
Genes associated with increased risk of breast and ovarian cancer when mutated; important for DNA repair.
anaplasia
A condition of undifferentiated cells often seen in tumors, signifying a loss of normal cell features.