Unit 4 VCE Biology: AOS 2
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
Absolute age
an estimate of the age (in years) of a fossil or rock
Absolute dating
a dating technique used to determine the absolute age of a fossil by measuring the relative amounts of radioisotopes to their products. Also known as radiometric dating
Adaptive potential
the ability for a population to adjust to new environmental selection pressures
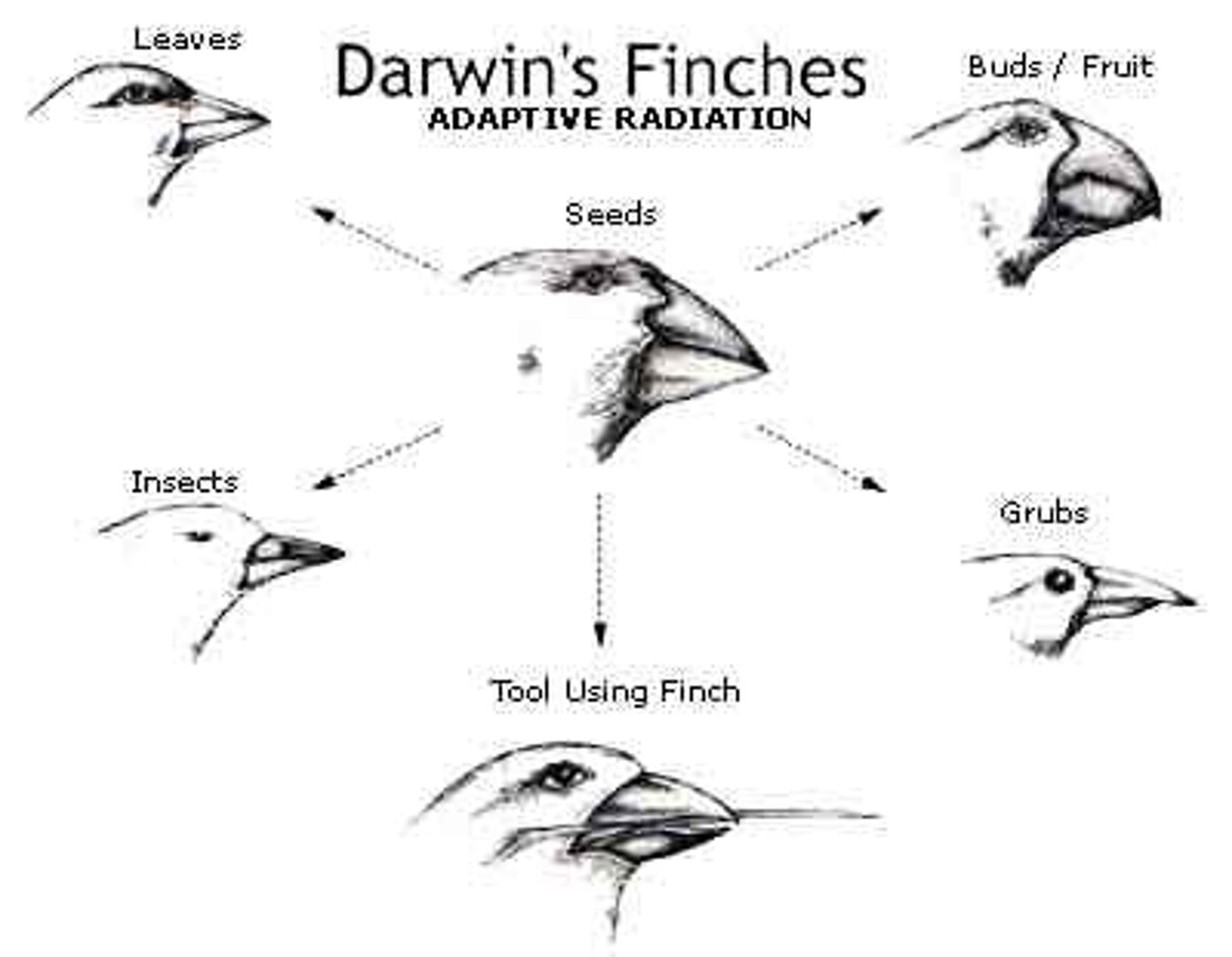
Adaptive radiation
the rapid divergent evolution of a species, thereby producing a wide array of species/forms
Advantageous phenotype
a biochemical, physical, or behavioural trait that increases an organism's fitness in its local environment
Allele
an alternate form of a gene
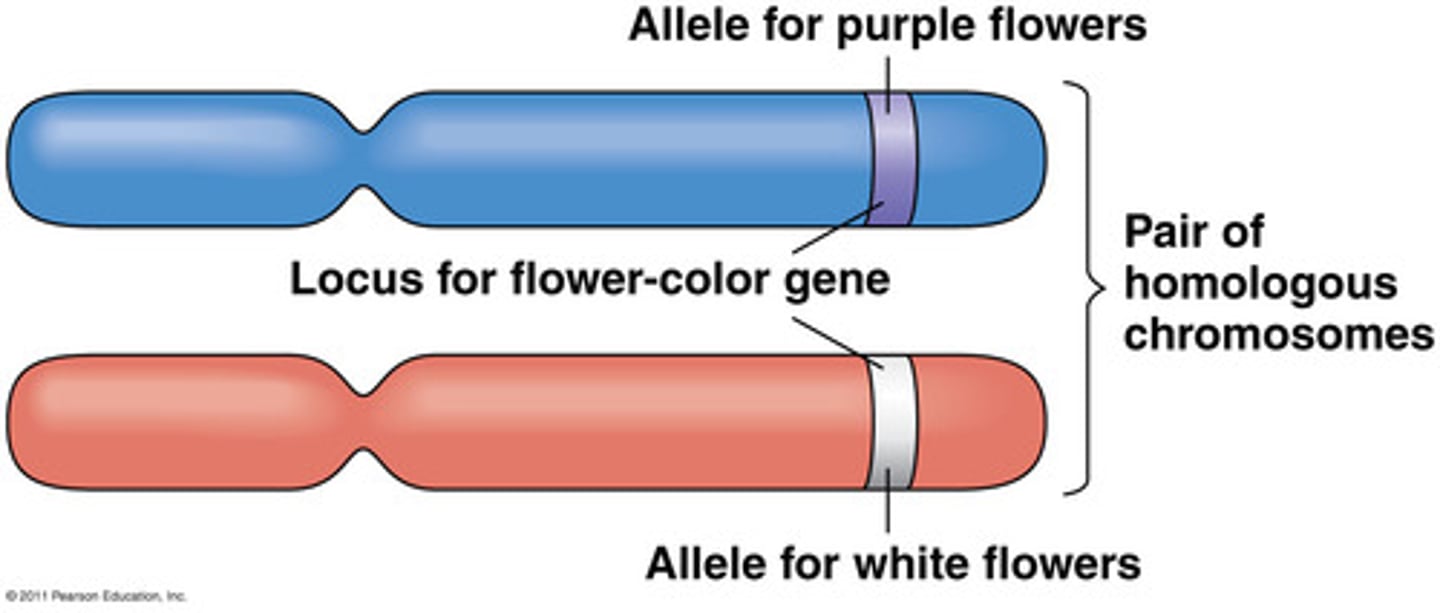
Allele frequency
the proportion of certain alleles in a gene pool

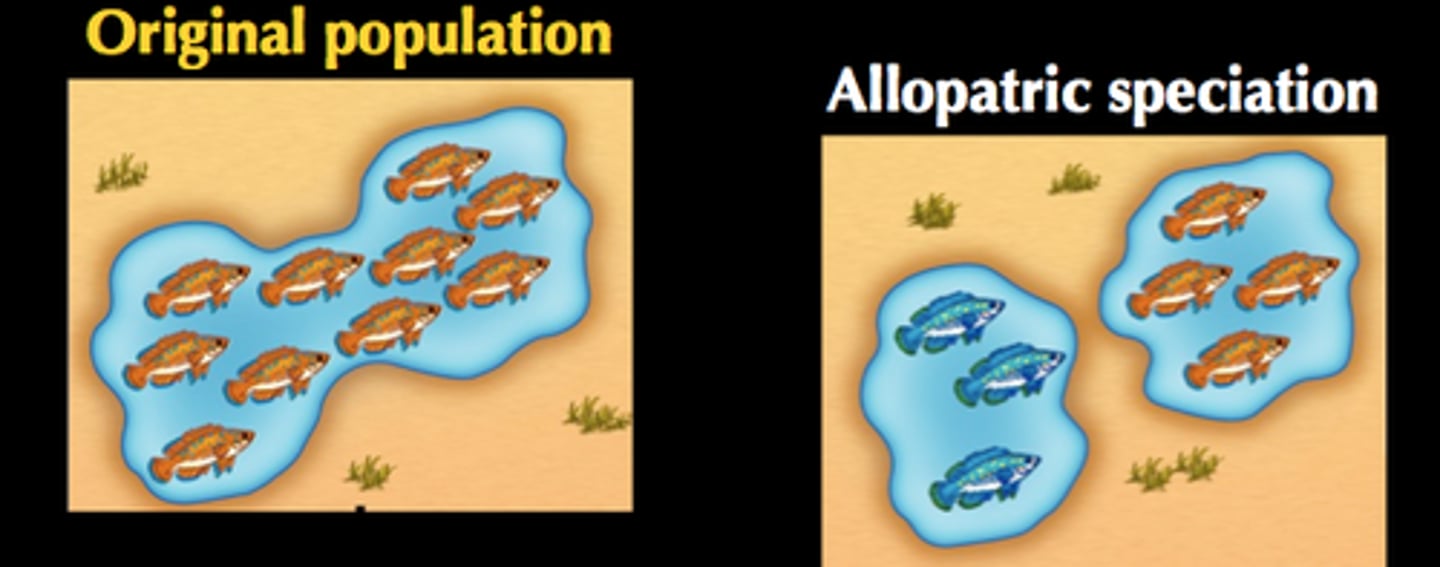
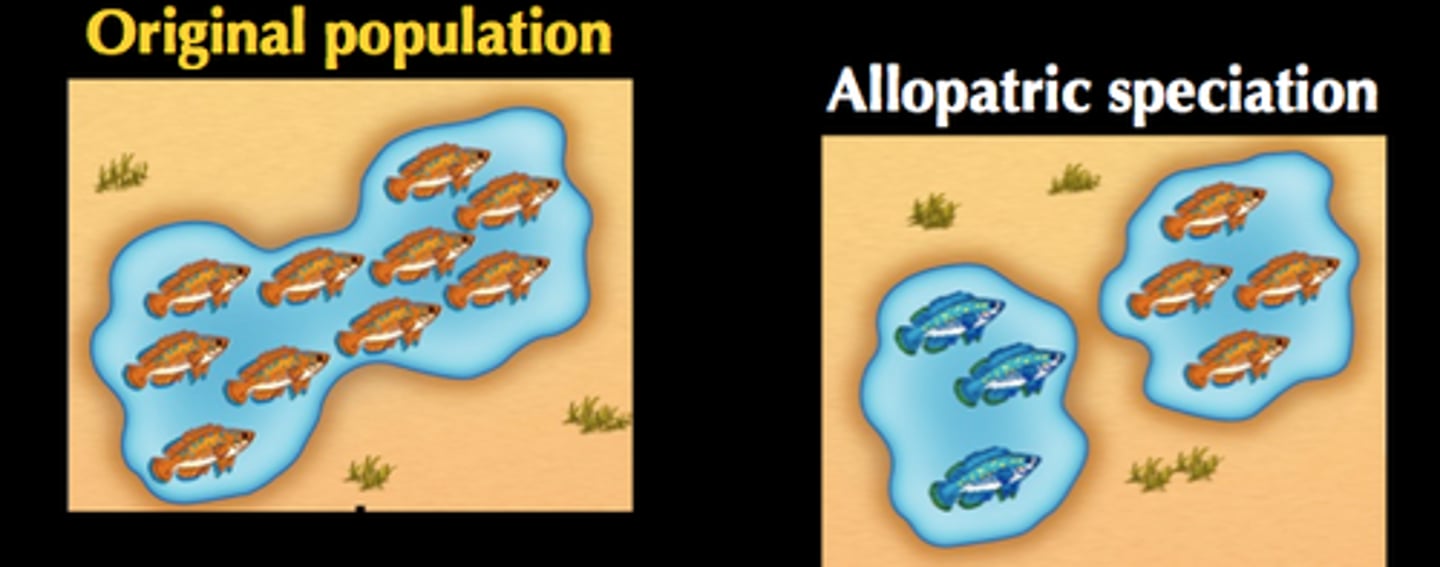
Allopatric speciation
the geographic separation of a population from a parent population resulting in the formation of a new species
Analogous structures
features present in two or more species that fulfil the same function but do not originate from a common ancestor
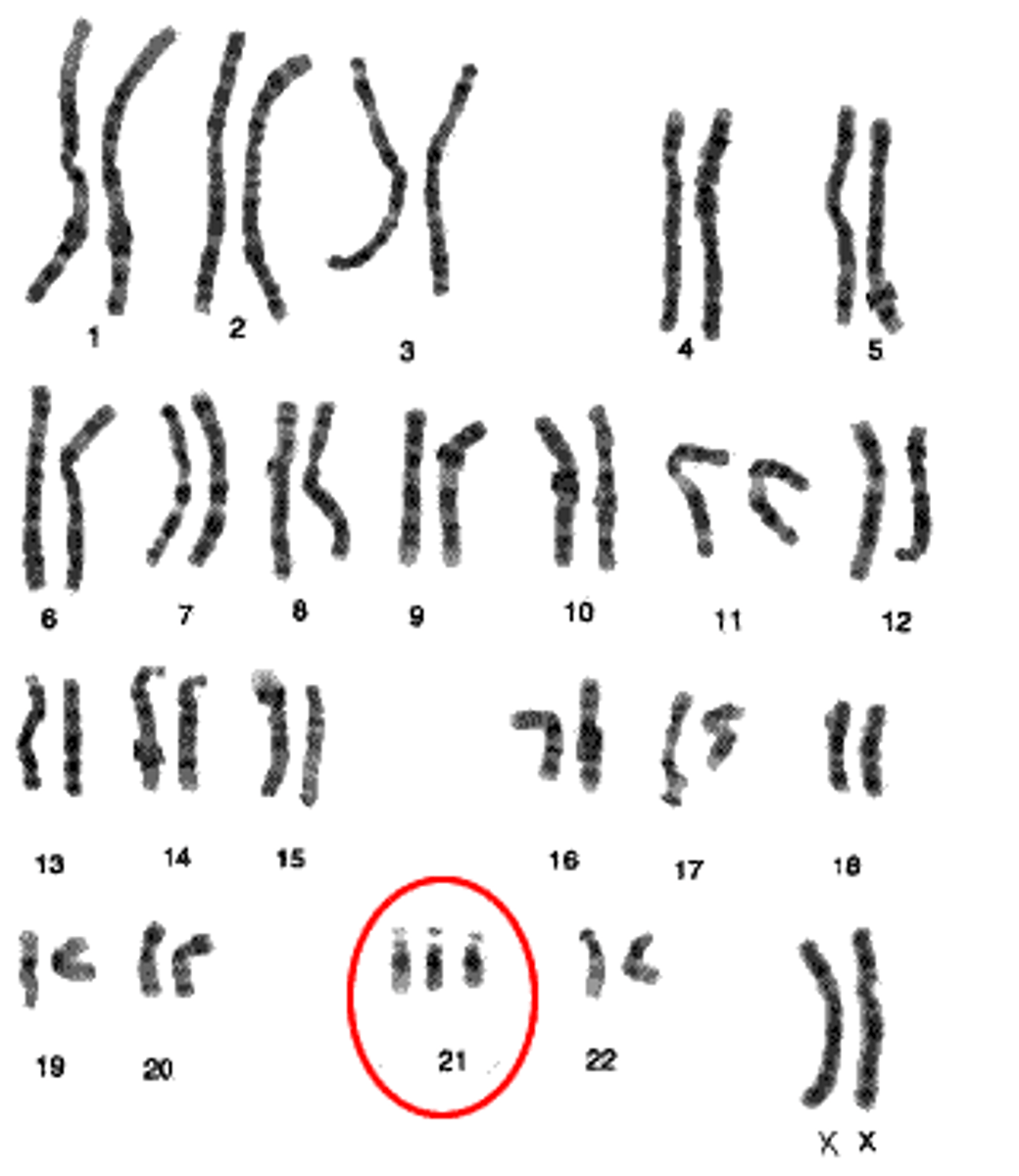
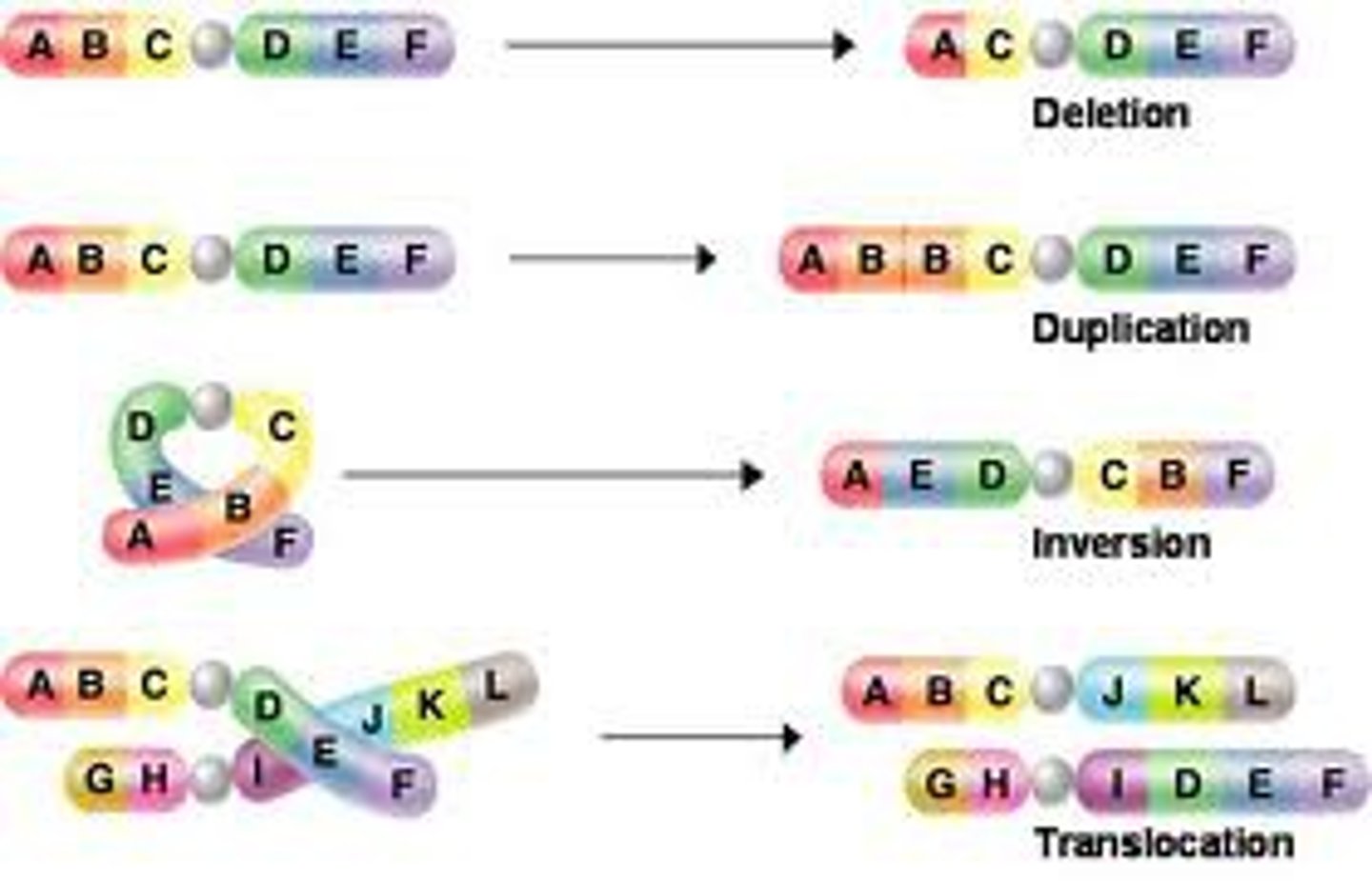
Aneuploidy
when a cell or organism varies in the usual amount of chromosomes in its genome by the addition or loss of a chromosome
Antibiotic
medications used to kill bacteria or slow their growth
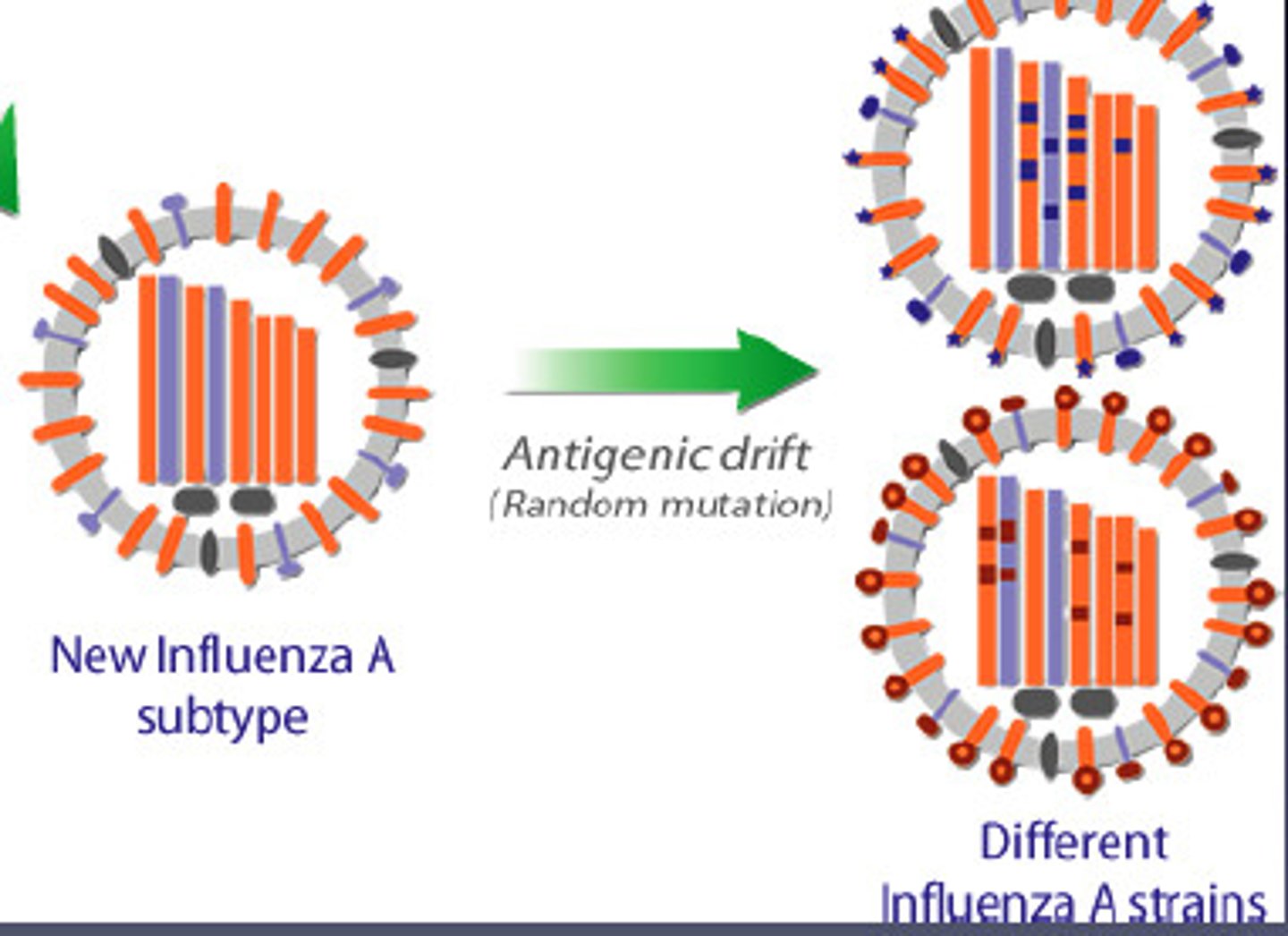
Antigenic drift
small and gradual mutations in the genes encoding for viral surface antigens
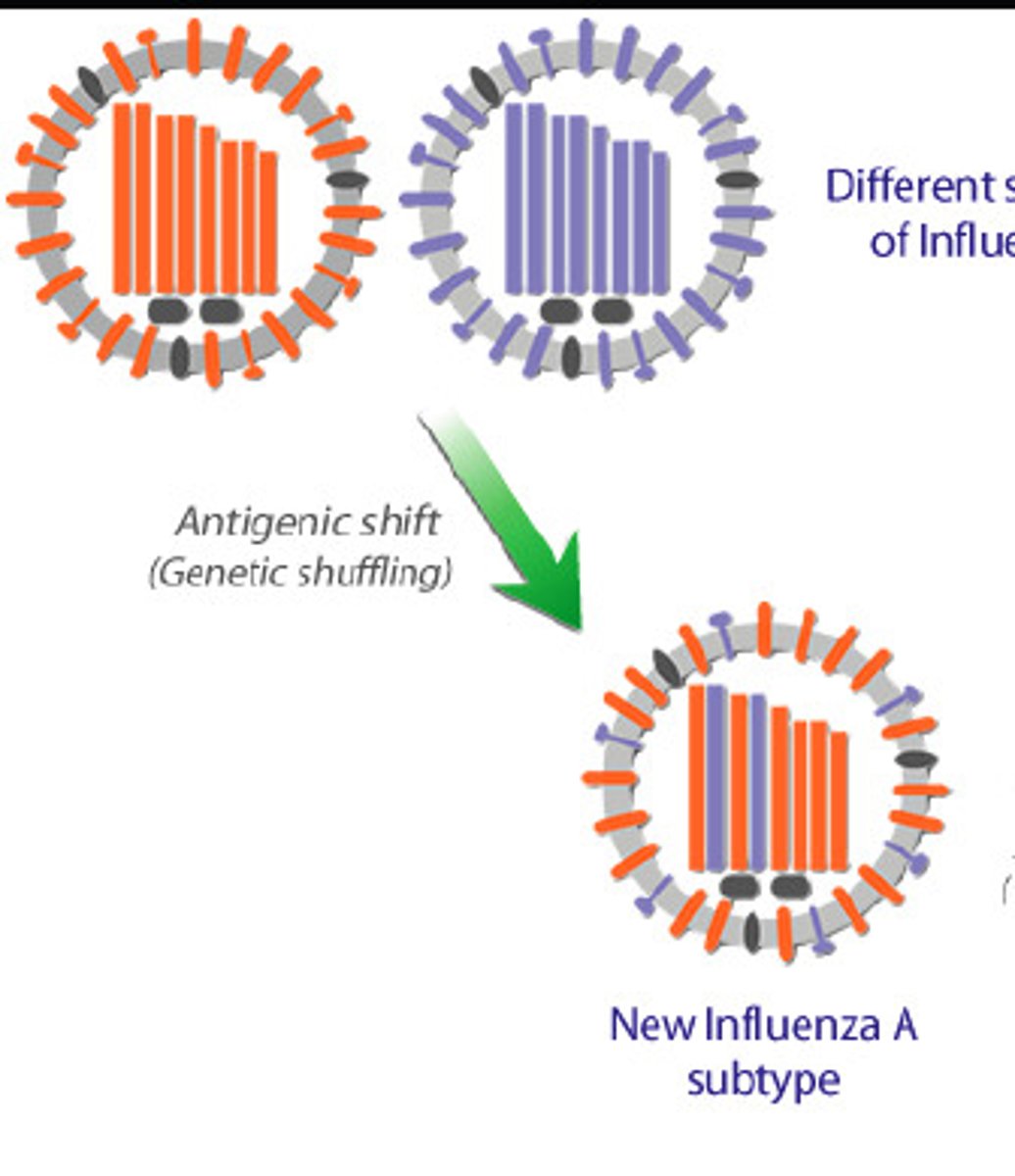
Antigenic shift
sudden and significant mutations in the genes encoding for viral surface antigens
Antimicrobial agent
an agent that kills or slows the growth of microorganisms. Examples include antiseptics, disinfectants, antifungals, antivirals, and antibacterial agents
Antimicrobial resistance
the ability of a microorganism to survive exposure to an antimicrobial agent
Antiviral
medications used to treat viral infections
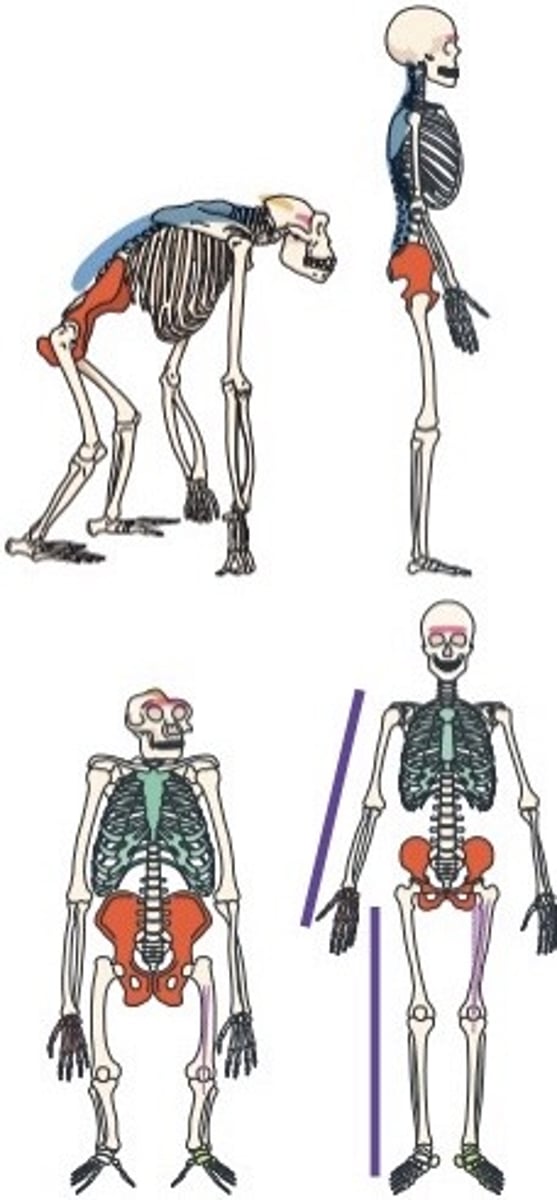
Arm to leg ratio
the ratio of arm length to leg length. Tree dwelling hominids have longer arms and shorter legs, or a larger arm to leg ratio
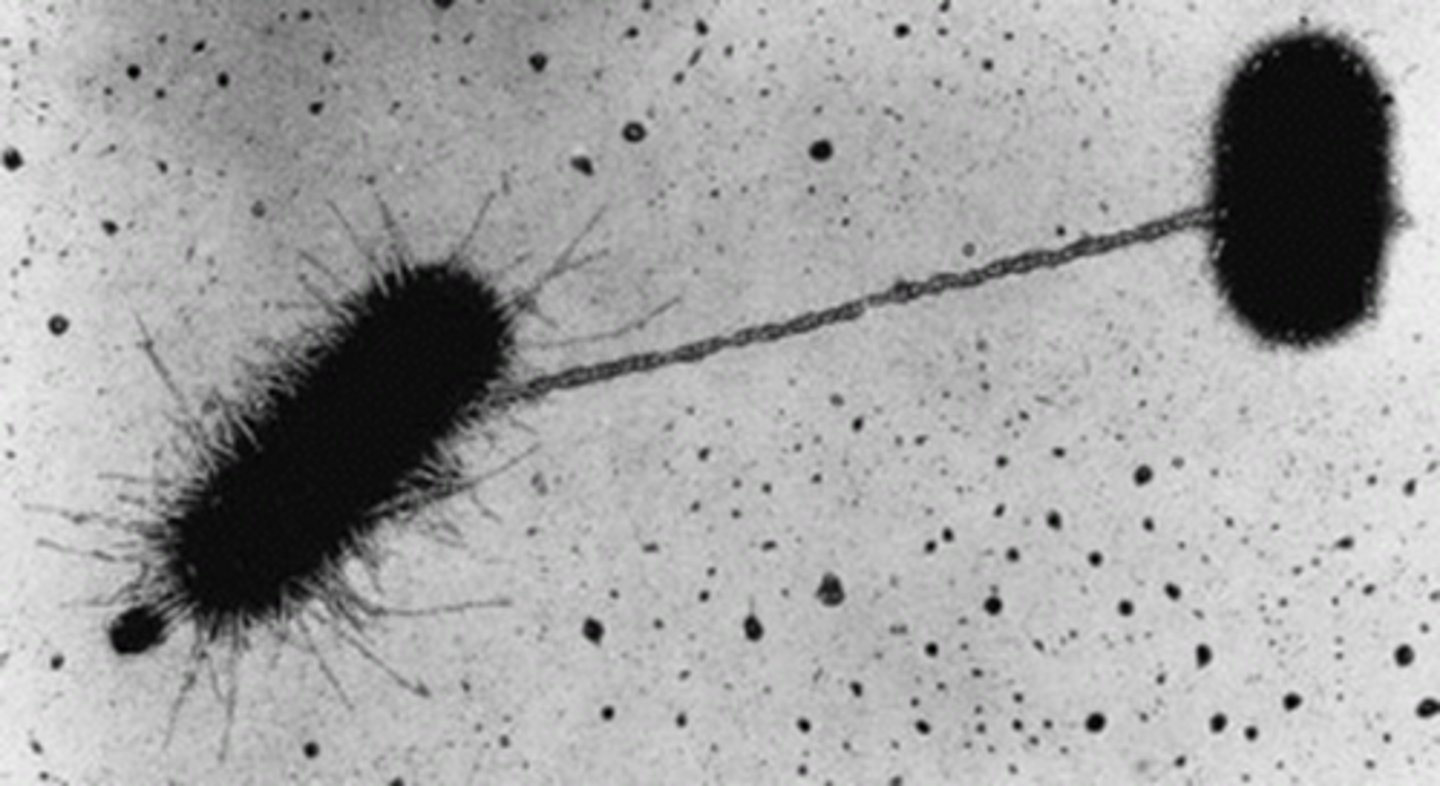
Bacterial conjugation
the process in which bacteria exchange genetic material via direct cell-cell contact
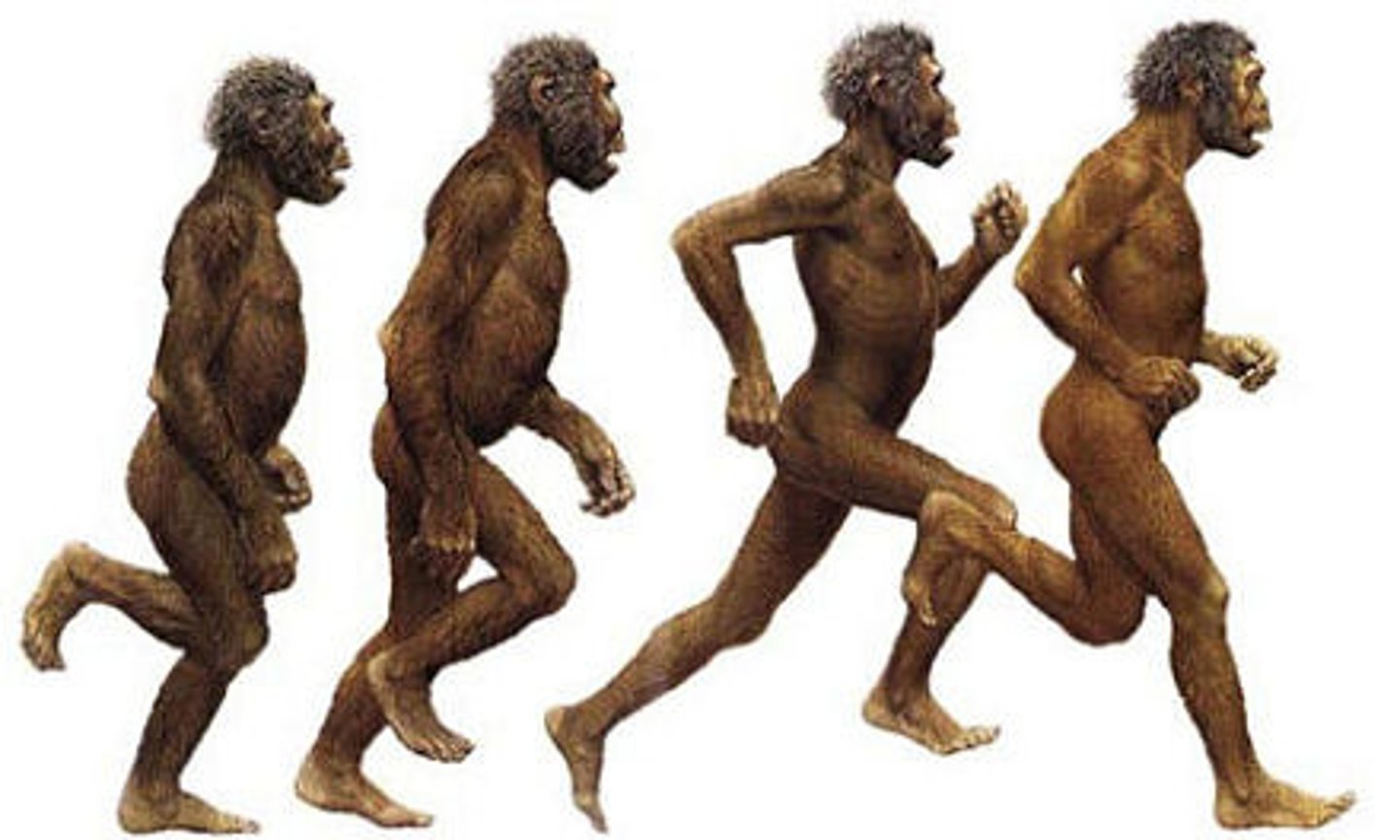
Biped
an individual that moves on two legs (upright walking)

Bipedalism
using two legs for walking upright
Block mutation
a mutation that affects a large chunk of DNA, or an entire gene
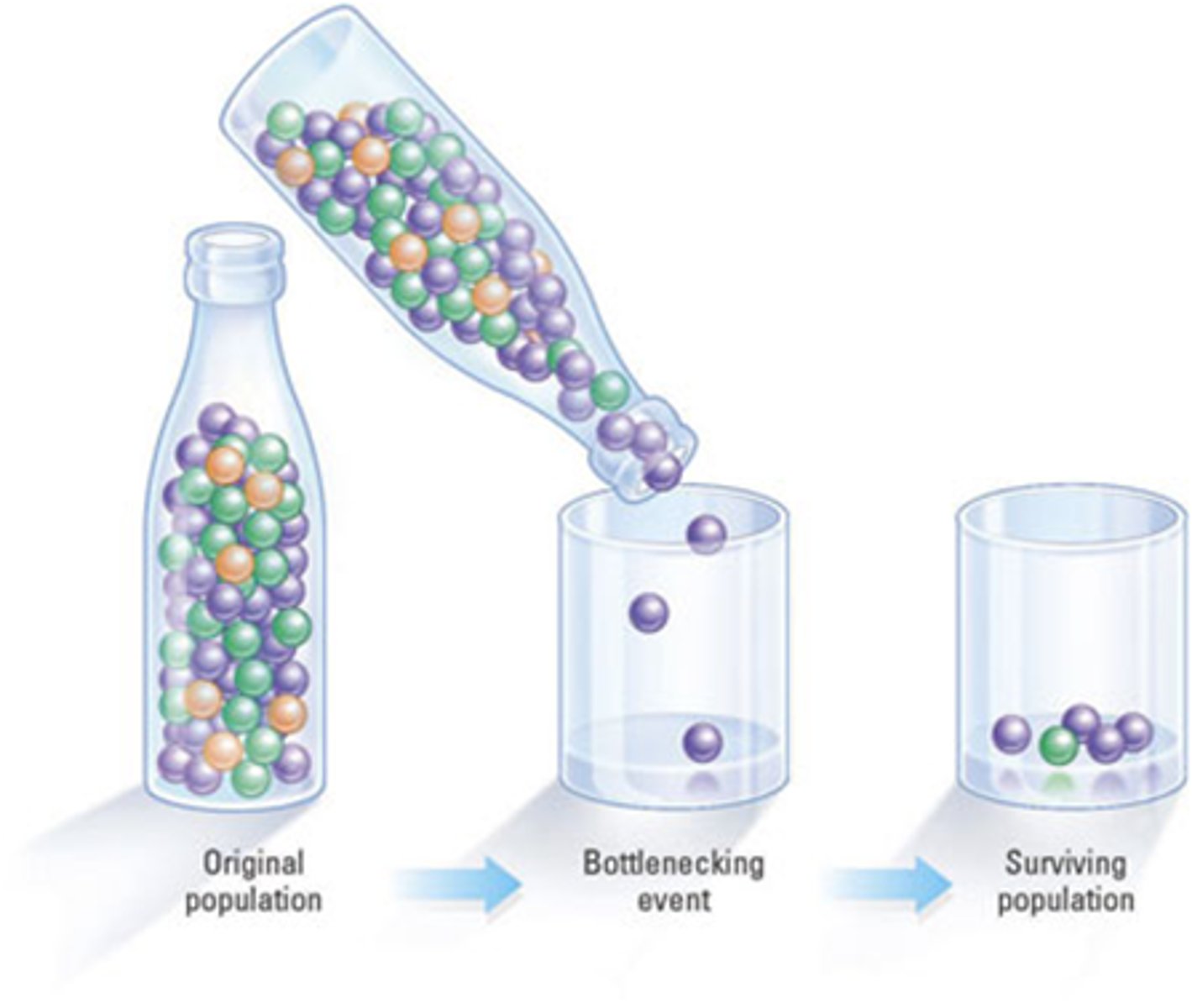
Bottleneck effect
the reduction in genetic diversity that occurs when a large proportion of a population is removed due to a chance event
Branch
a line on a phylogenetic tree that represents an evolutionary path
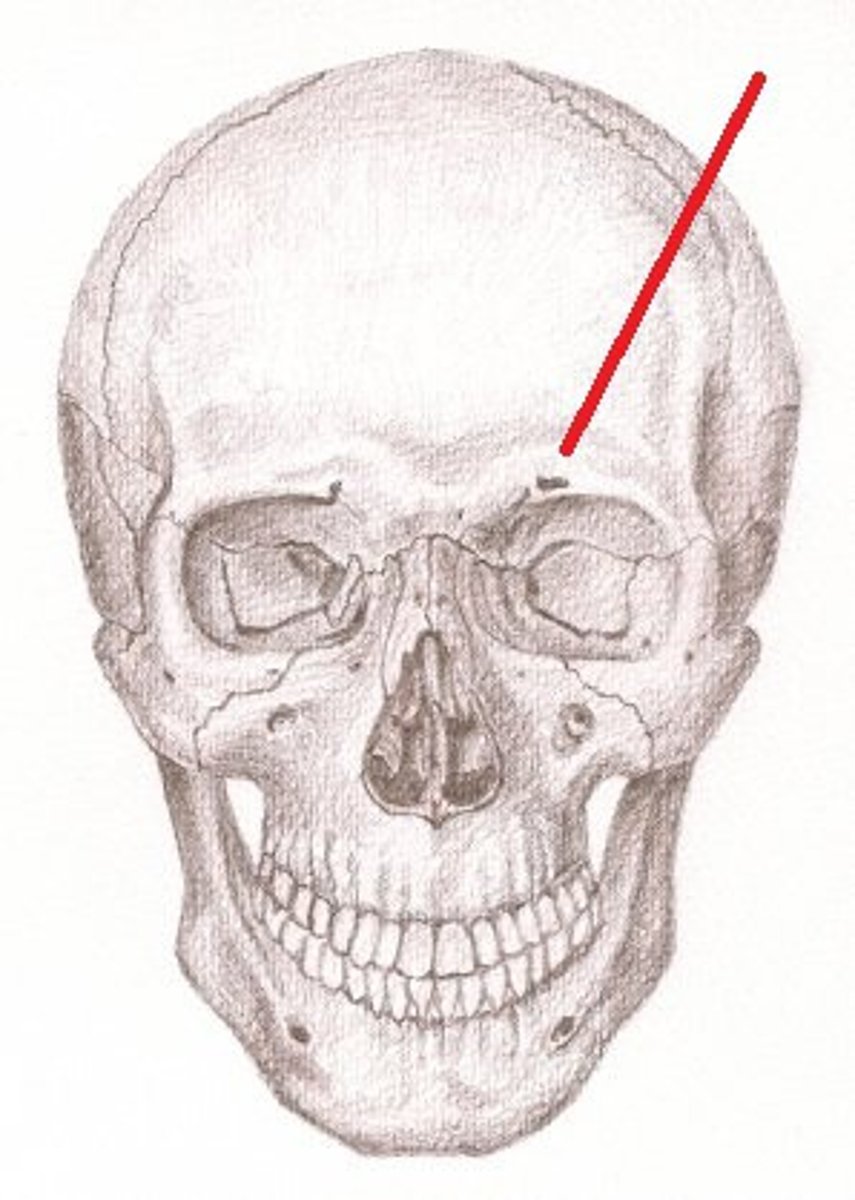
Brow ridge
a bony ridge above the eye sockets. It is found in all primates, but is greatly reduced in Homo sapiens
Cambrian explosion
a period (~ 535 mya) of rapid diversification of multicellular life, characterised by the evolution of hardened body parts such as shells or bones
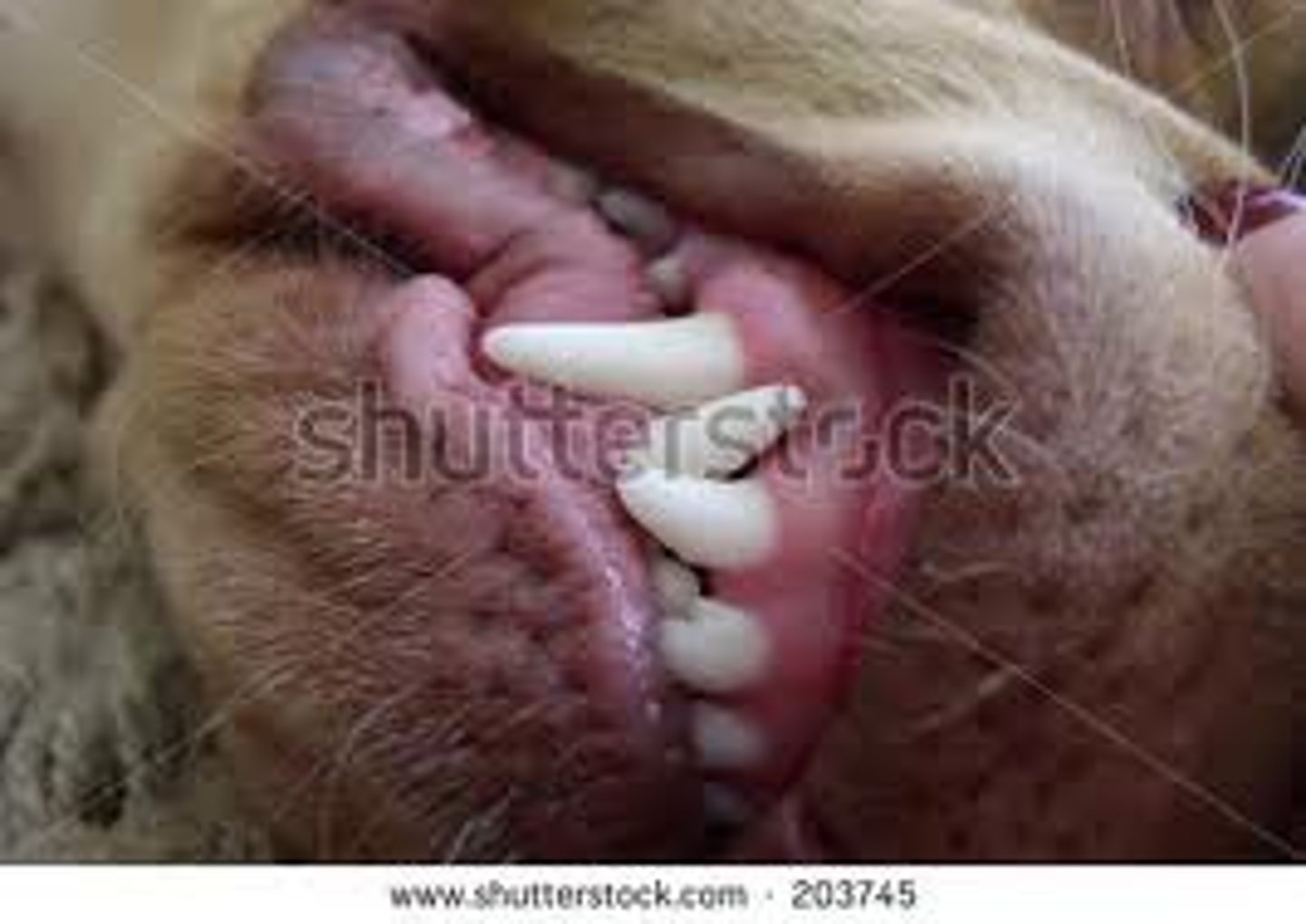
Canine teeth
a type of tooth in mammals that is relatively long and pointed
Cast fossil
fossil formed when a mould fossil is filled with sediment
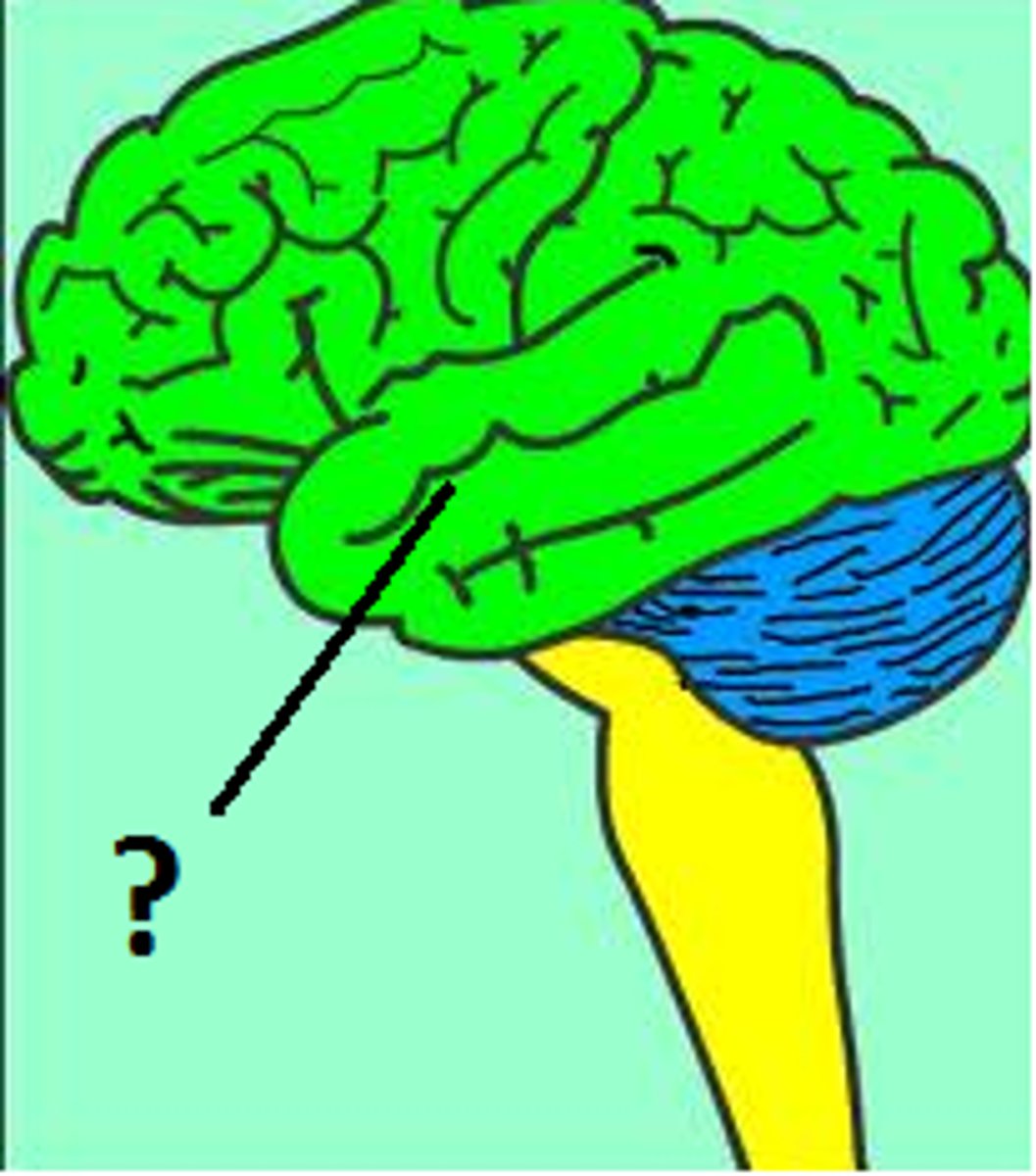
Cerebrum
the largest part of the brain, which comprises two-thirds of the brain's entire weight and is responsible for a large range of vital functions including sensory processing, motor control, and visual and spatial learning
Competition
interactions between organisms in which both are negatively impacted when vying for the same limited resource. Can exist within or between species
Connection to Country
a reciprocal relationship between First Nations people and their ancestral lands and seas
Conserved genes
genes that have remained largely unchanged throughout evolution, and are found across the genome's of many different species
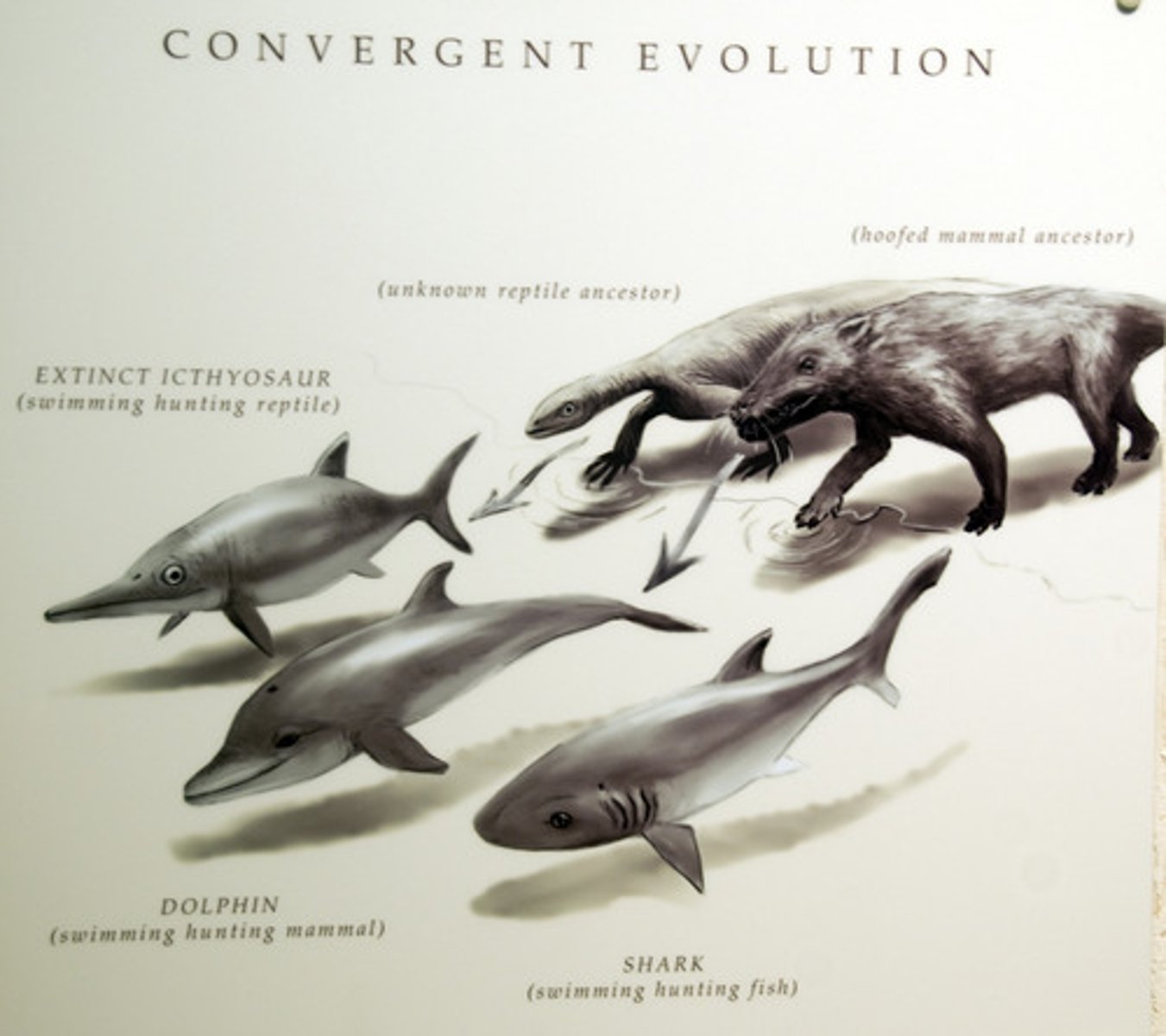
Convergent evolution
the process in which distantly related species evolve similar traits over time due to the action of similar selection pressures
Country
an area that is traditionally owned and looked after by an Aboriginal language group or community, or by certain people within that group. The term may indicate more than simply a geographical area - it is also a concept that can encompass the spiritual meaning and feelings of deep connection and attachment associated with that area
Cranium
the part of the skull that covers the brain
Dating period
the range of time since fossilisation in which a particular radioisotope series can be used. Beyond this period, most of the radioisotope will have broken down into its products, meaning that it is too difficult to estimate the fossil's age
Deleterious allele
alleles that have an overall negative effect on individual fitness when expressed
Deleterious mutation
a change in DNA that negatively affects an individual
Desirable trait
a heritable phenotype that humans select for during selective breeding
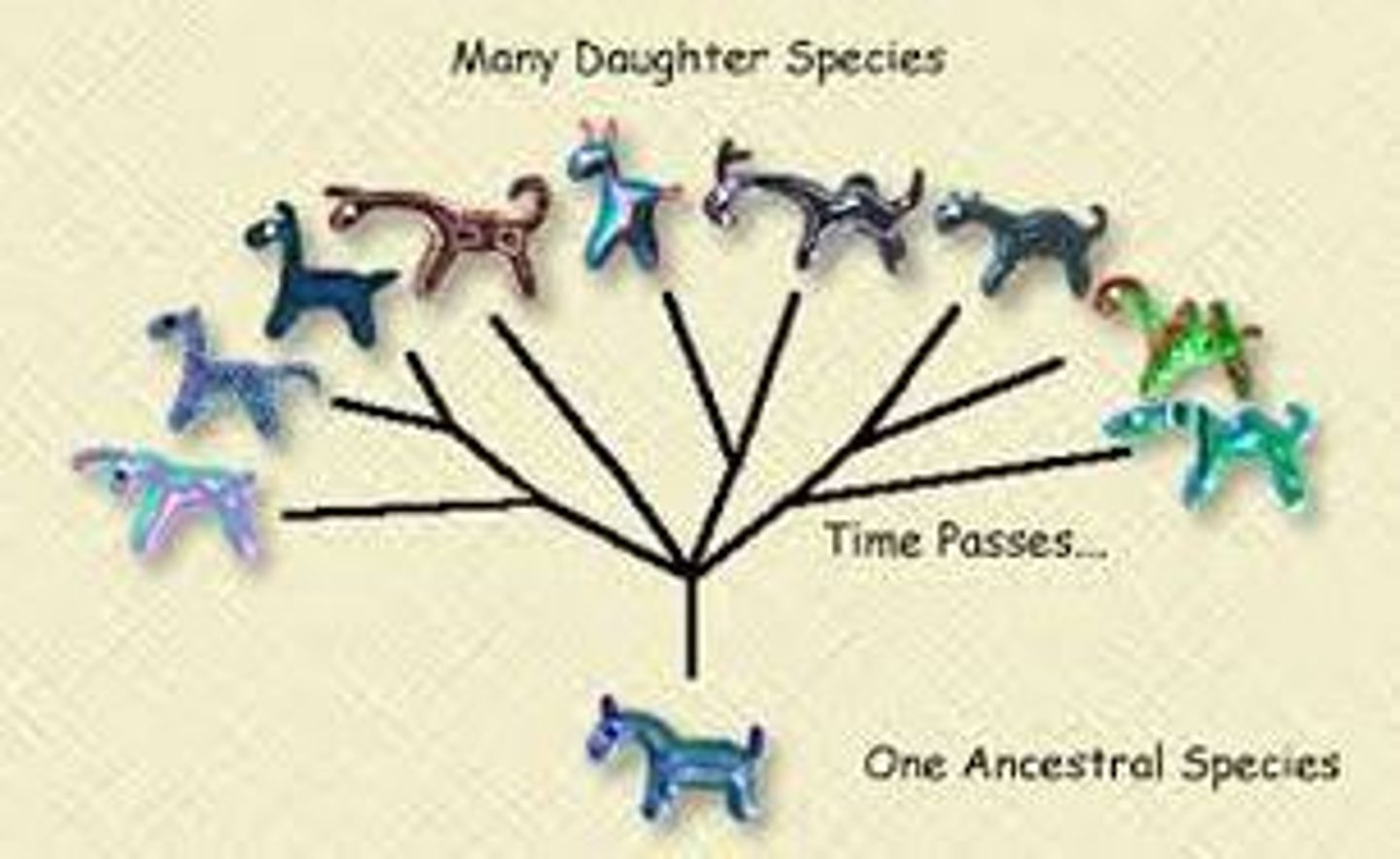
Divergent evolution
the process in which a common ancestor evolves into two or more descendant species
Dreaming
an Aboriginal philosophy that describes the time when Ancestral Spirits (Dreaming Beings) moved over the land and created life and important geographical sites. It explains the origins of the universe, as well as the relationships between humans, animals, and the land on which they live. The Dreaming is passed down through generations and governs familial, relational, communal and spiritual obligations for Aboriginal Australians. It is also known as The Dreamtime
Ecological niche
the specific environmental conditions and resources or selection pressures within a particular environment
Embryo
an early stage of development in an organism. In humans, used to refer to the organism during the first eight weeks of development
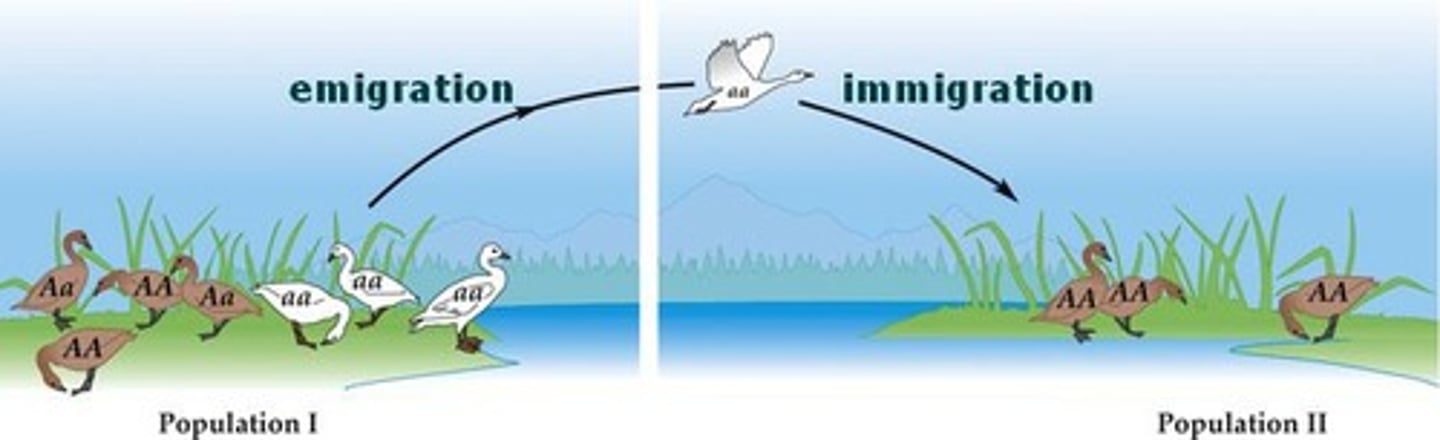
Emigration
the movement out of a population
Environmental selection pressure
a factor in the environment (e.g. limited resources, deforestation, changing temperature, predation) that impacts an organism's ability to survive and reproduce
Evolution
the change in the genetic makeup of a population over successive generations
Evolutionary relationship
the relatedness of organisms based on shared ancestry
Femur angle
the angle between the top and bottom of the femur when standing. It is greater in hominins when compared to other primates
Fertile
the ability to produce offspring
Fitness
a measure of how well an organism survives and reproduces in its environment
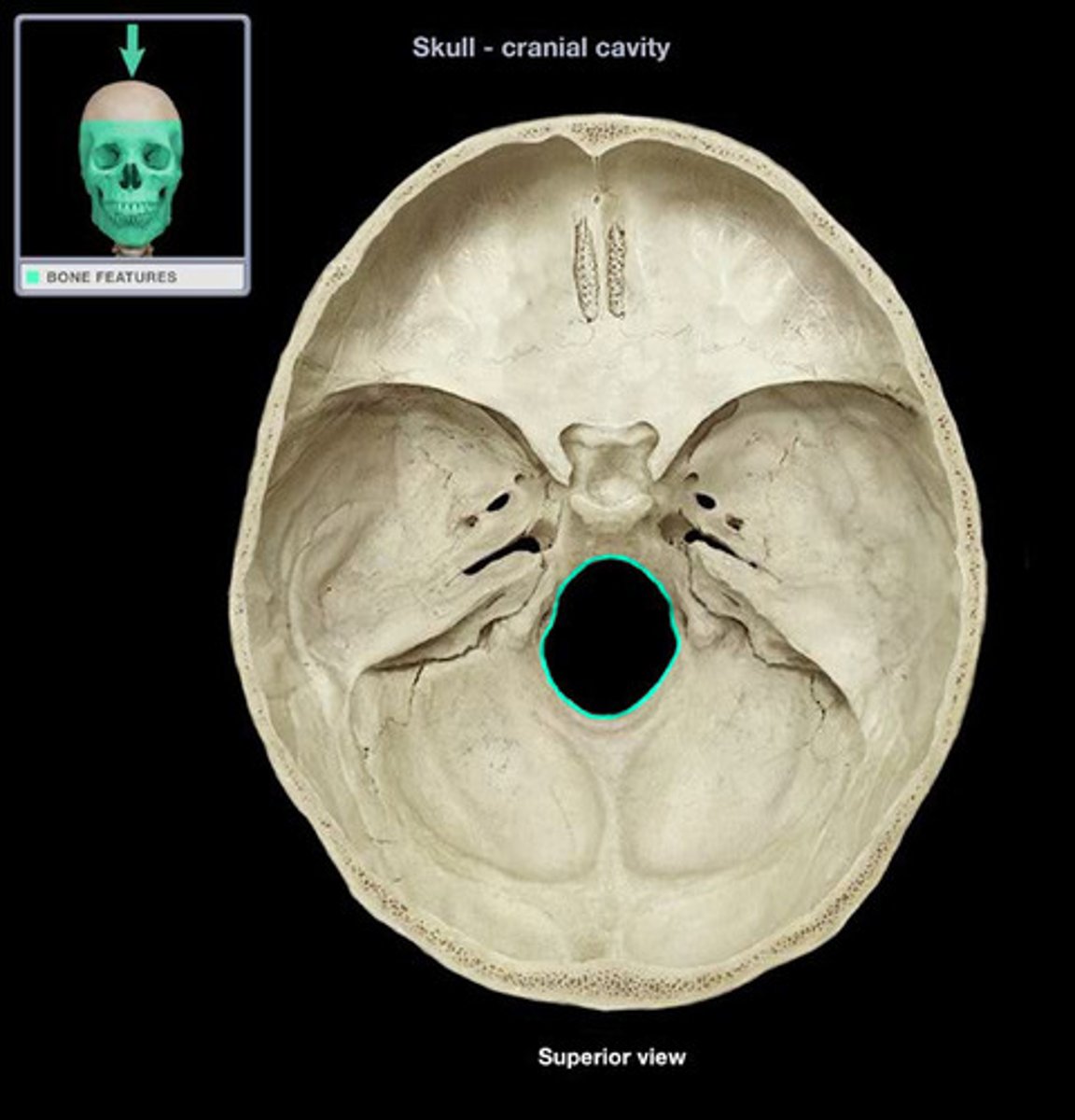
Foramen magnum
the hole in the base of the skull through which the spinal cord passes. A more centralised foramen magnum indicates bipedal locomotion
Fossil
the preserved body, impressions, or traces of a dead organism
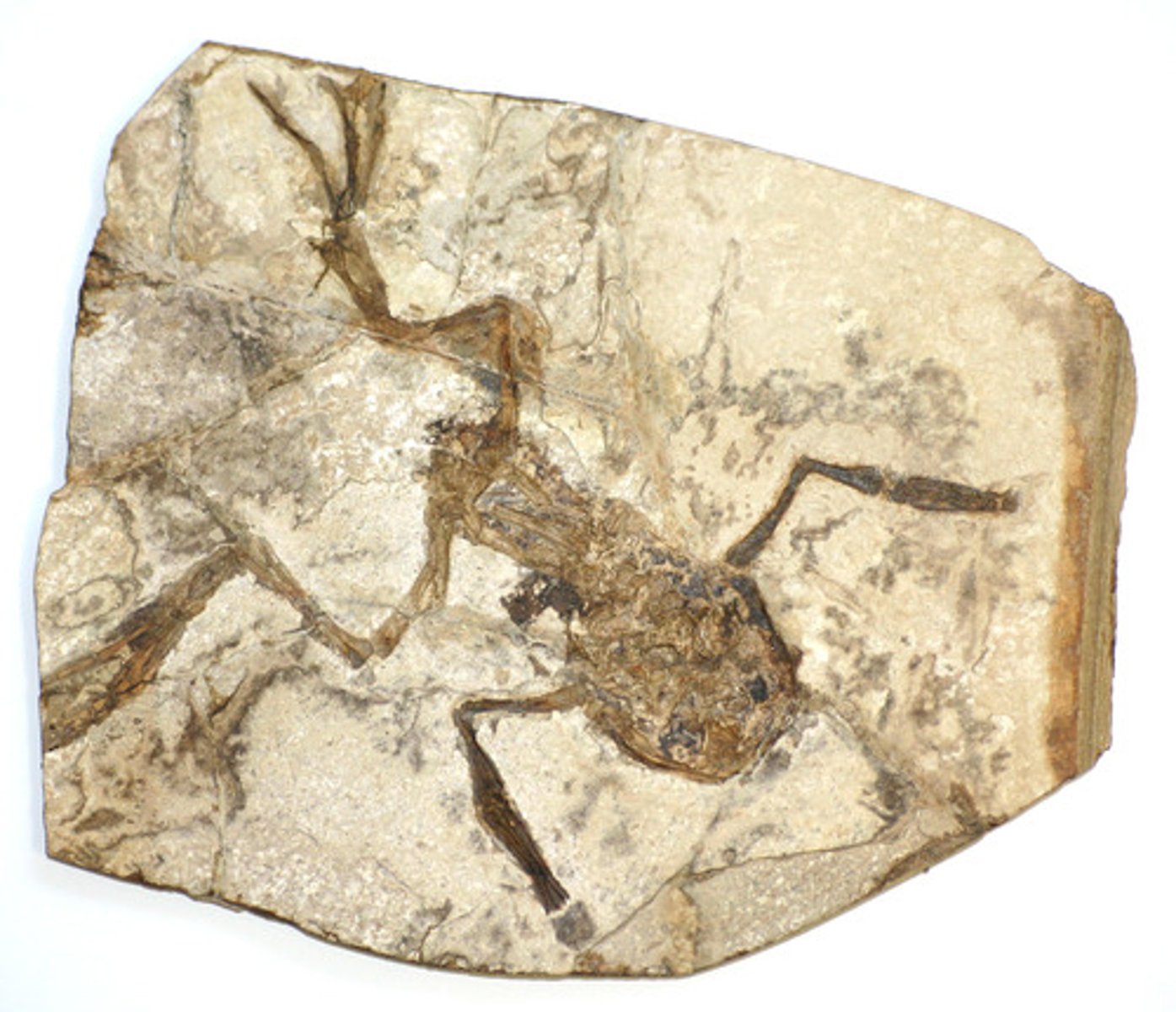

Fossil record
the information derived from fossils. The fossil record is arranged in chronological order and helps us map the history of life on Earth, placing species in the appropriate geologic time frame
Fossil succession
the principle that fossils of the same age will be in the same layer of sedimentary rock, and fossils found in a higher or lower sedimentary layer will be younger or older, respectively. Also known as faunal succession

Fossilisation
the process by which an organism becomes a fossil
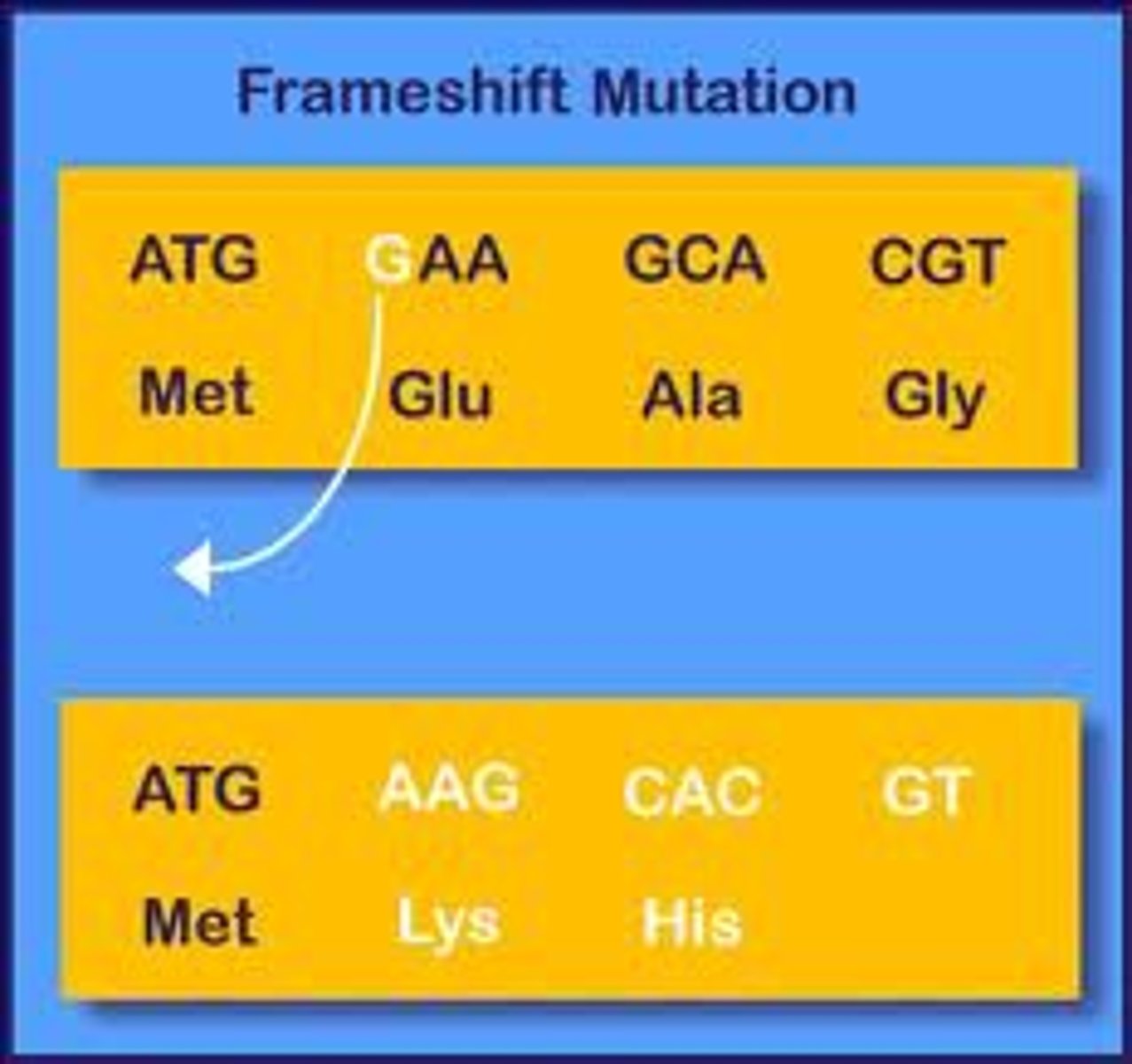
Frameshift mutation
a mutation that involves the insertion or deletion of one or two nucleotides, altering every codon from that point forward
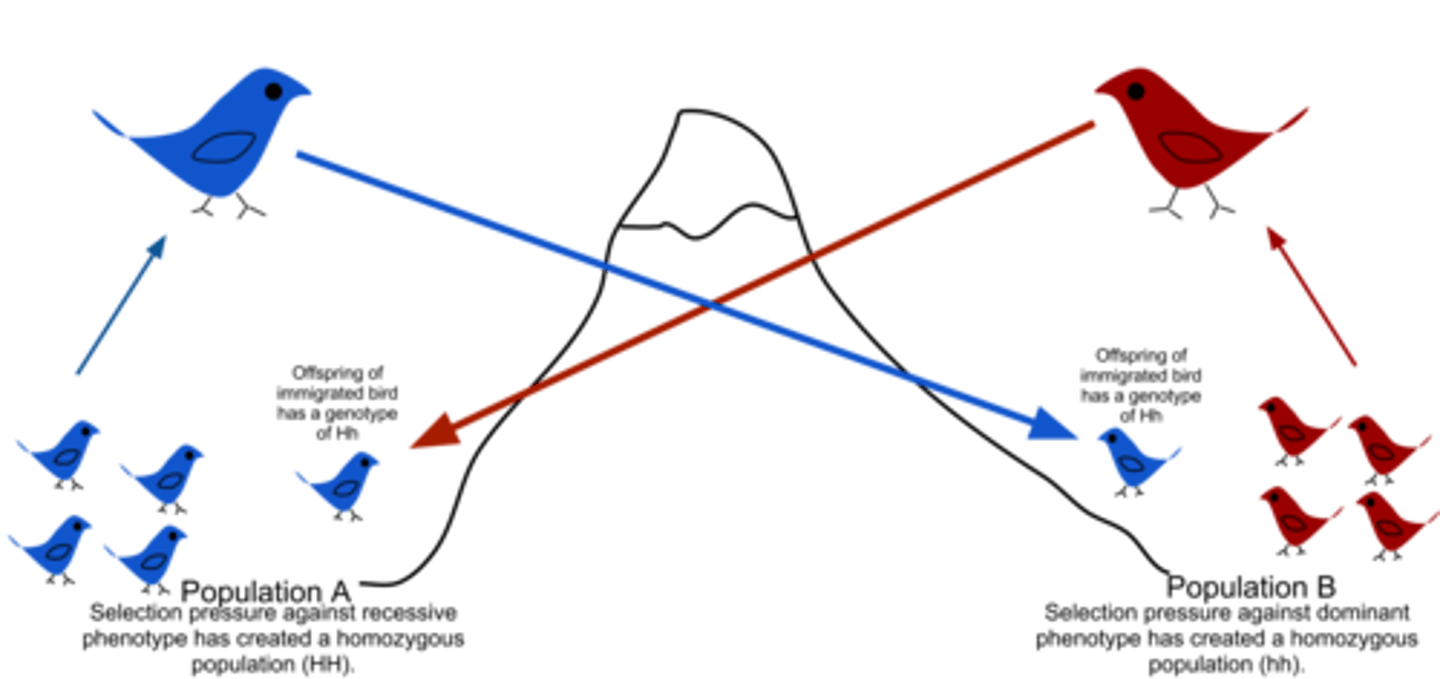
Gene flow
the flow of alleles in and out of a population due to the migration or interbreeding of individuals between two populations
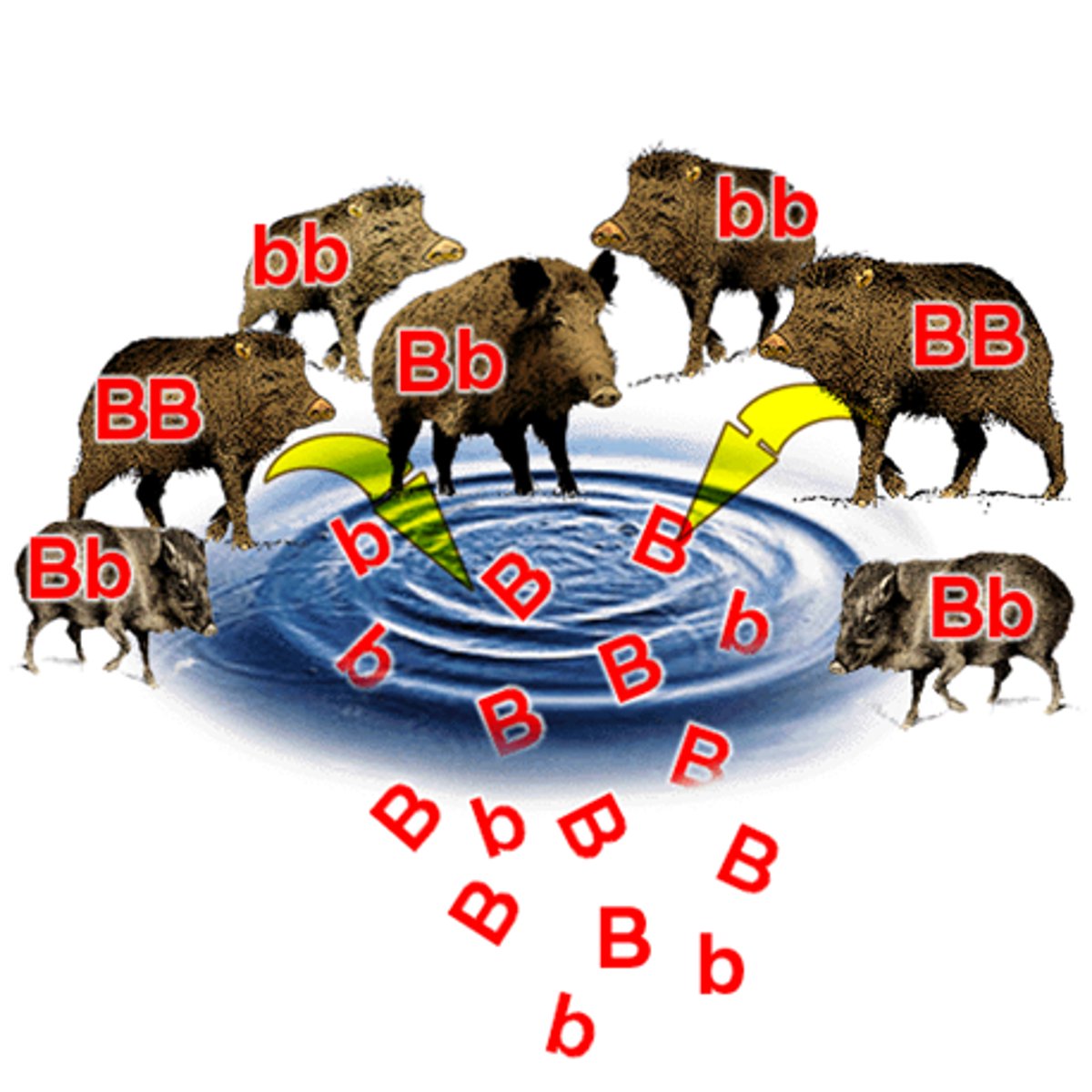
Gene pool
the complete set of alleles present within a particular population
Genetic diversity
the variation in genetic makeup or alleles within a population
Genetic drift
a random event that dramatically alters a population's gene pool
Geographic barrier
a physical factor that prevents gene flow, and thereby stops two populations from breeding together
Germline cell
a cell involved in the generation of gametes in eukaryotes
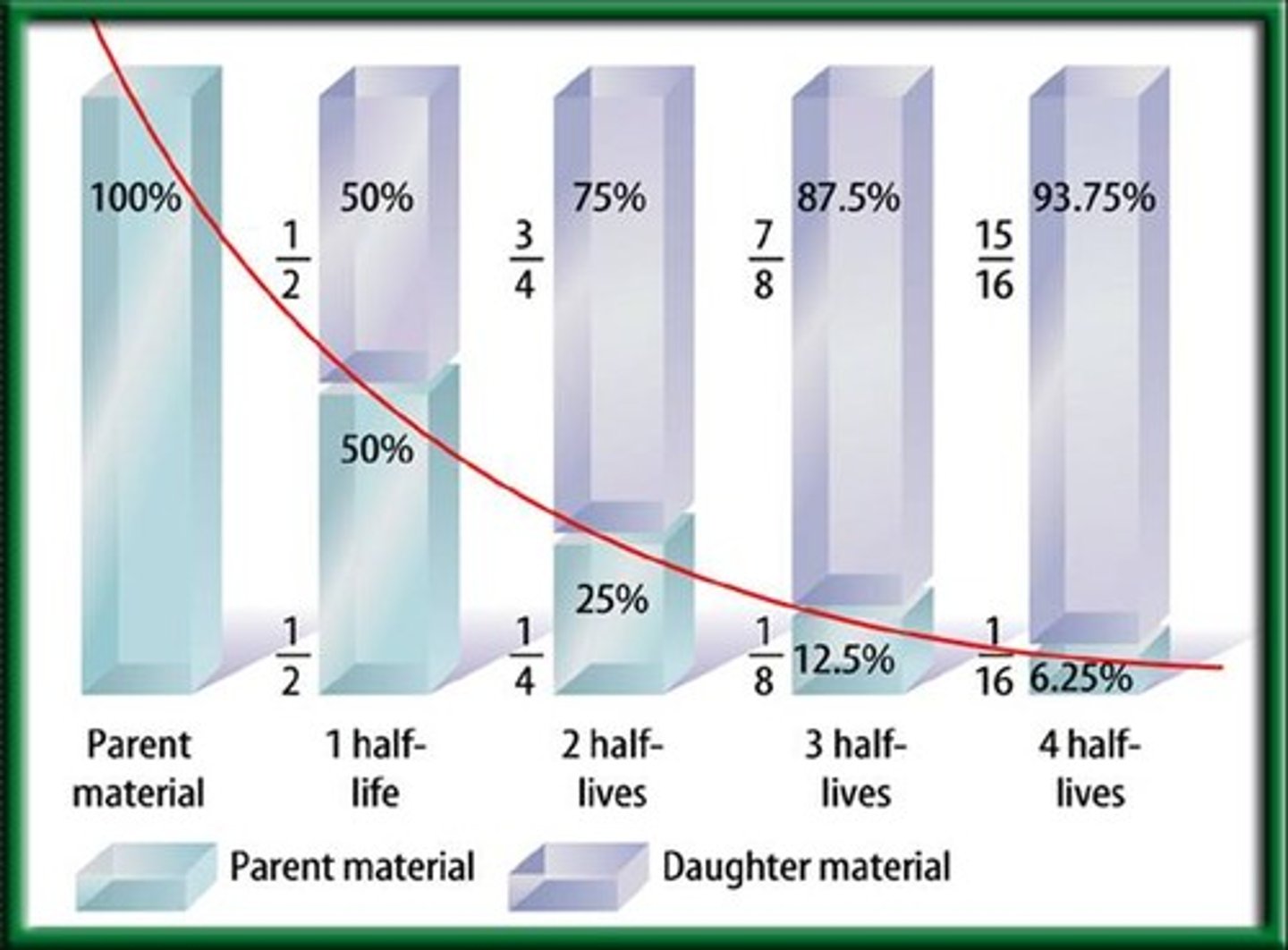
Half-life
the time taken for half the mass of a radioisotope sample to break down into its products
Heritability
the transmission from parent to offspring (i.e. encoded in genes)
Hominins
members of the taxonomic tribe Hominini that includes modern humans and our upright-walking ancestors
Hominoids
members of the superfamily Hominoidea that includes apes and humans
Homo sapiens
the species name for modern humans
Homologous structures
Structures in different species that are similar because of common ancestry.
Immigration
the movement into a population
Inbreeding
sexual reproduction between two related individuals
Index fossil
a group of widespread fossils which existed for a short period and have a known age. Can be used as a reference to easily determine the age of unknown fossils
Interbreeding
when two individuals living in different populations mate and have offspring
Leaf
the end of a branch that shows the current (or final) form of a species
Lineage
a direct sequence of species that evolved from a common ancestor
Mammals
warm-blooded vertebrates belonging to the taxonomic class Mammalia that have mammary glands, hair/fur, three middle ear bones, and one lower jawbone
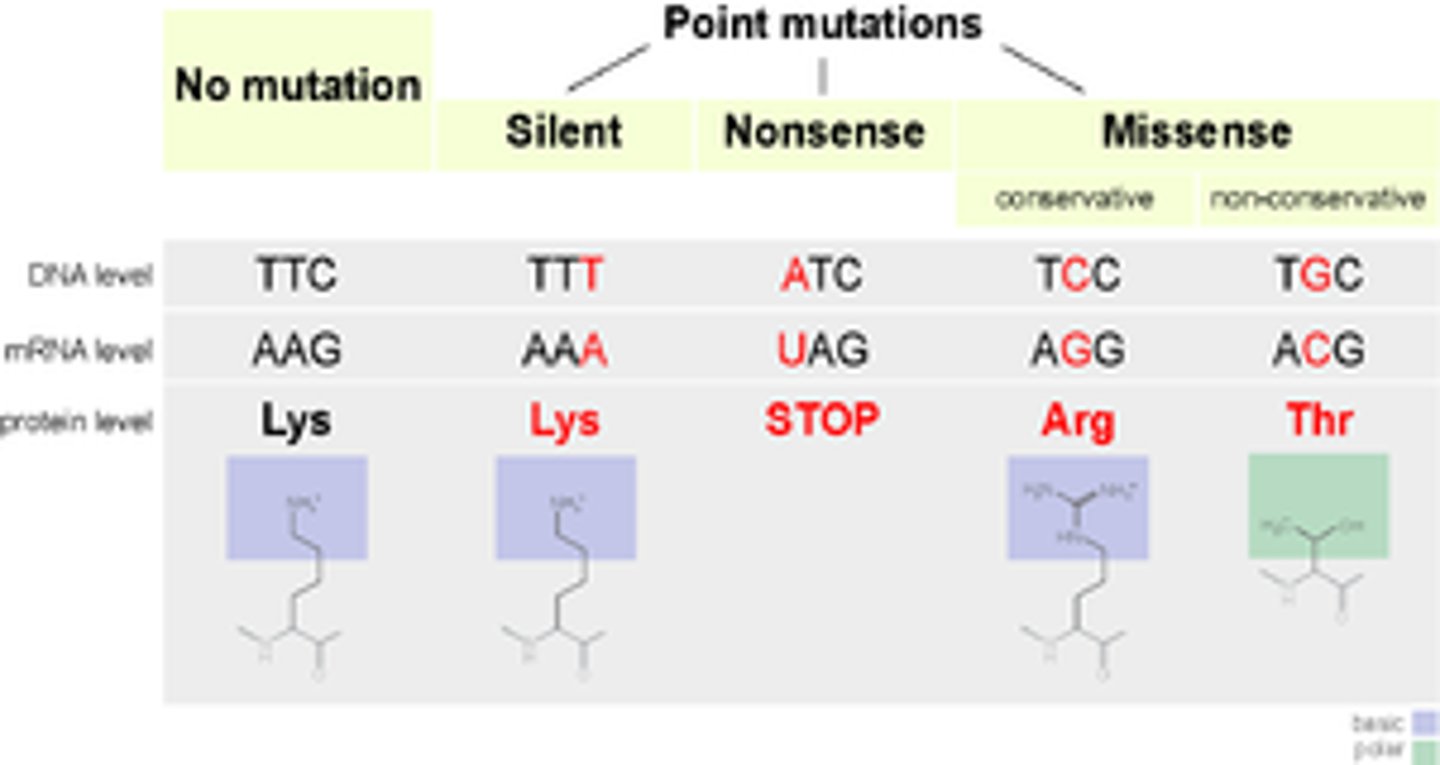
Missense mutation
a mutation in which a nucleotide is substituted for another, changing the codon and coding for a different amino acid. Therefore, there can potentially be an effect on protein structure
Moities
a two way division of society into maternal and paternal groups
Molecular homology
the study of the similarities in the nucleotide sequences of DNA or amino acid sequences in proteins between organisms to establish relatedness
Morphological clades
combinations of various physical characteristics that are unique to particular geographical regions across a wide timespan
Mould fossil
fossil formed when a living thing decomposes underneath sediment, creating a cavity in the shape of the dead organism
Multiregional hypothesis
a model for the geographical spread of Homo sapiens which suggests that separate human populations evolved independently from earlier hominins that had spread throughout Eurasia and experienced gene flow. Also known as the regional continuity model
Mutagen
an agent that can cause mutations in DNA
Mutation
a permanent change to a DNA sequence
Natural selection
a mechanism through which organisms that are better adapted to their environment have an increased chance of surviving and passing on their alleles
Node
the splitting point between two branches on a phylogenetic tree, representing a speciation event
Nonsense mutation
a mutation in which a nucleotide is substituted for another, changing the codon to a stop codon, prematurely ceasing translation of the gene's mRNA. Therefore, there is an effect on protein structure
Opposable digit
a digit (either the thumb, big toe, or both) that is able to touch all the other digits on the same appendage
Out of Africa Theory
a model for the geographical spread of Homo sapiens which suggests that humans first developed and evolved in Africa before migrating outwards and expanding their colonies, replacing the earlier hominins that had spread prior. Also known as the African replacement model
Permineralised fossil
fossil formed when mineral-rich groundwater deposits minerals like silica and calcite into organic material, creating a mineral relic
Phenotype
the physical or biochemical characteristics of an organism that are the result of gene expression and the environment
Phylogenetic tree
a diagram used to show the relatedness between organisms
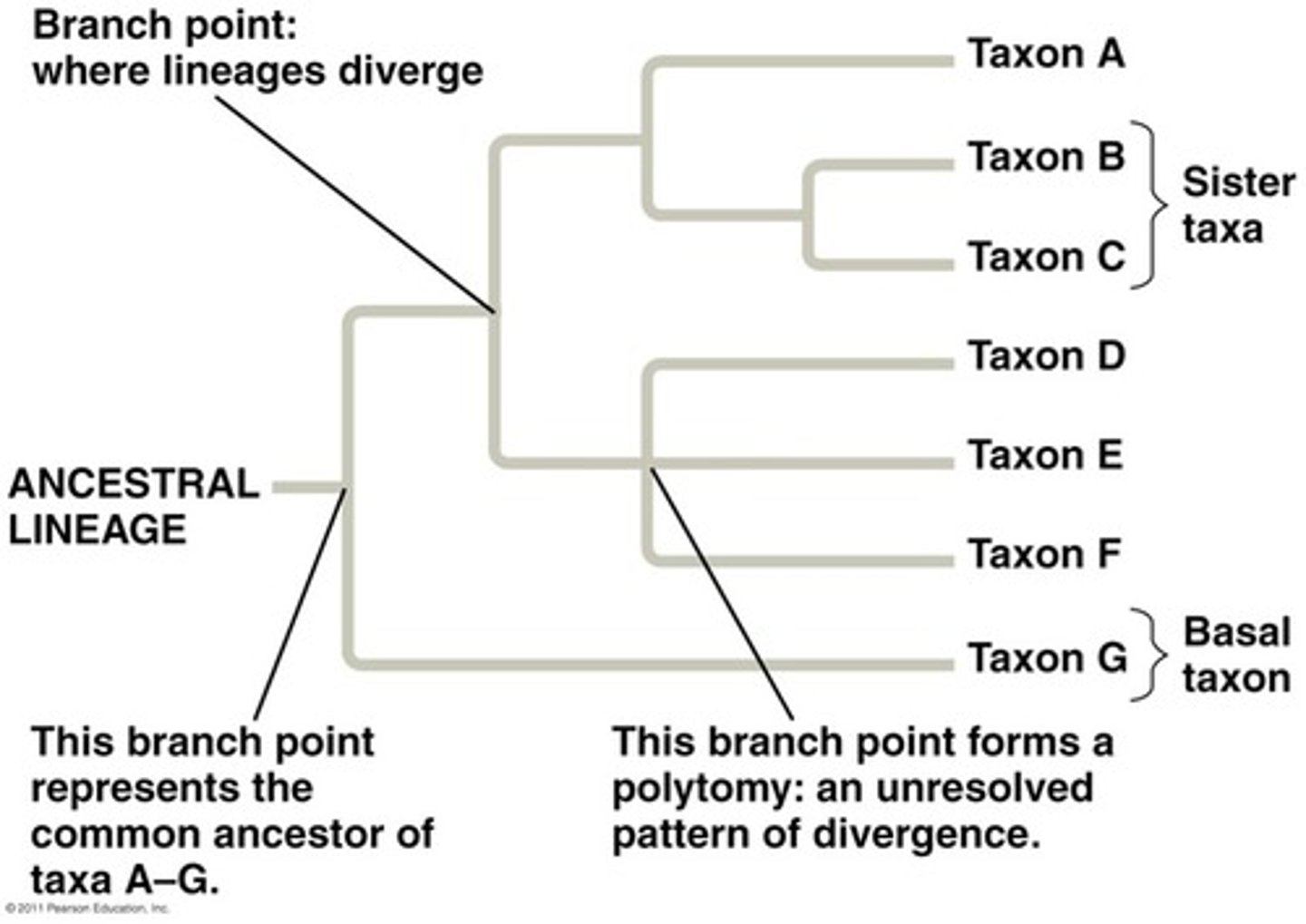
Phylogenetics
the study of evolutionary relationships among species
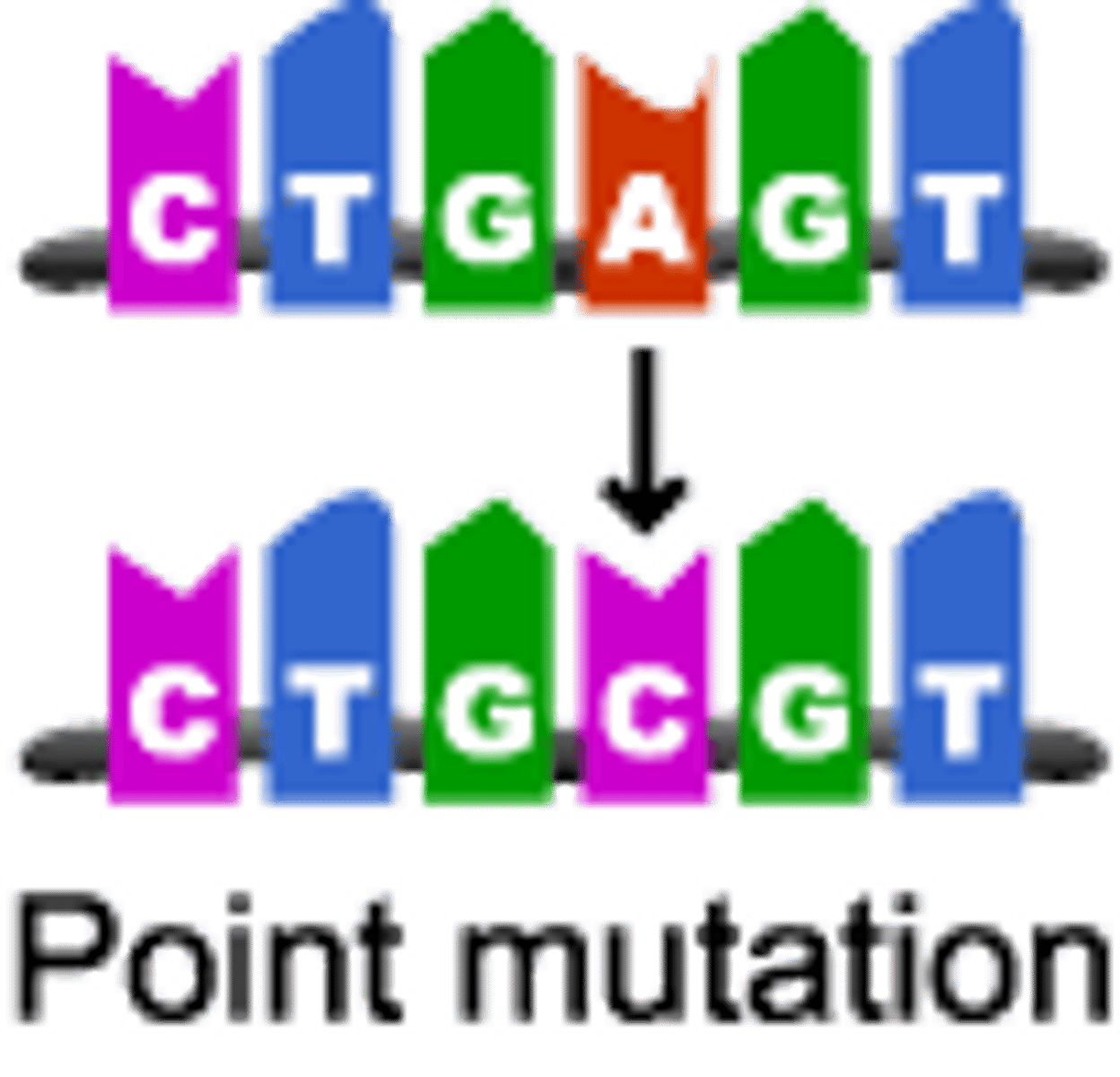
Point mutation
a mutation that alters a single nucleotide in a DNA sequence
Polyploidy
when an organism contains additional sets of chromosomes in its genome
Population
a group of individuals of the same species living in the same location
Power grip
a type of grip involving the palm and the fingers, used by primates (to varying extents) for moving and manipulating objects. The power grip generates more force due to the significant use of the palm
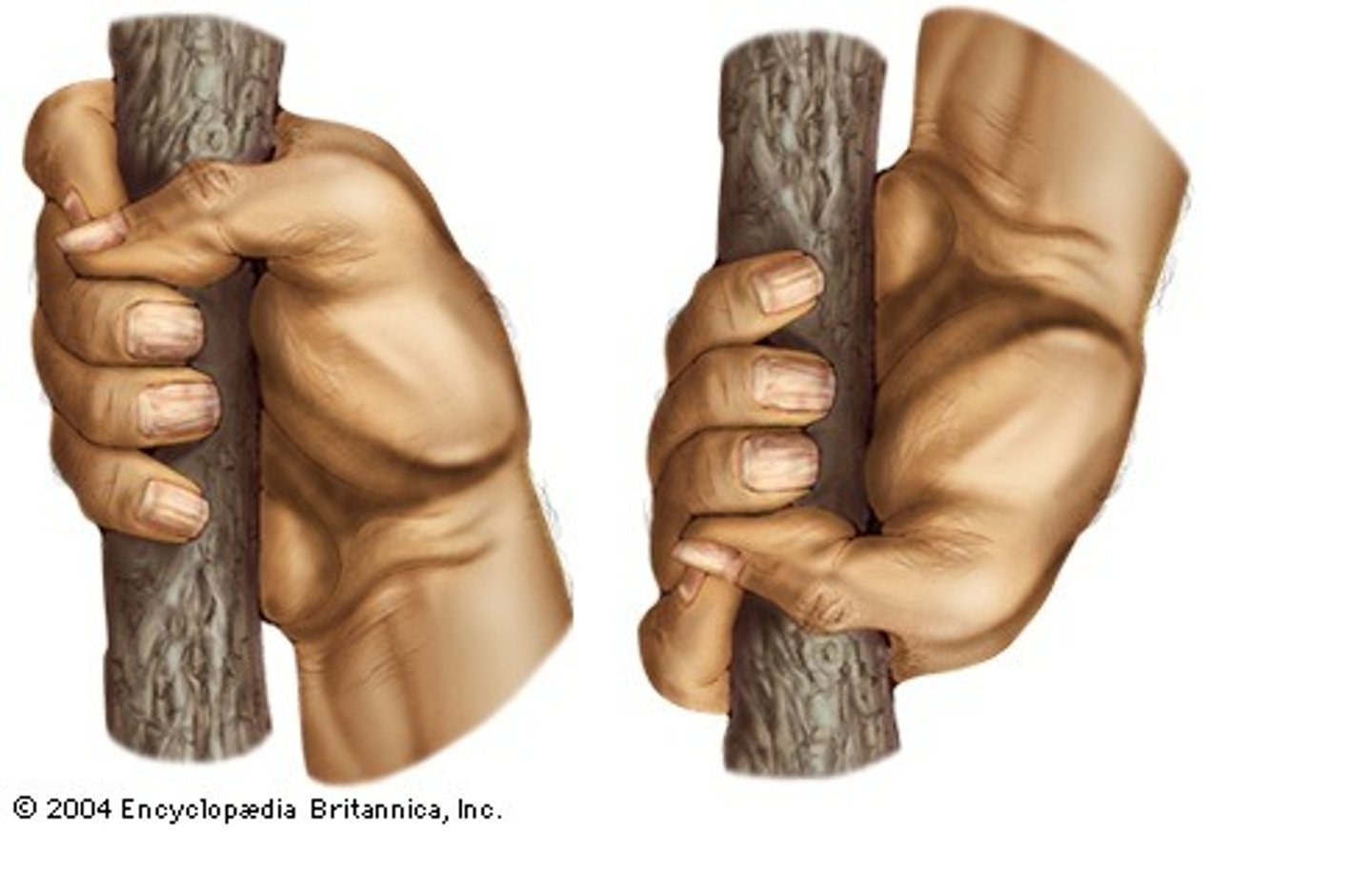
Precision grip
a type of grip involving the tips of the thumb and finger, used by primates (to varying extents) for precise manipulation of objects of various sizes
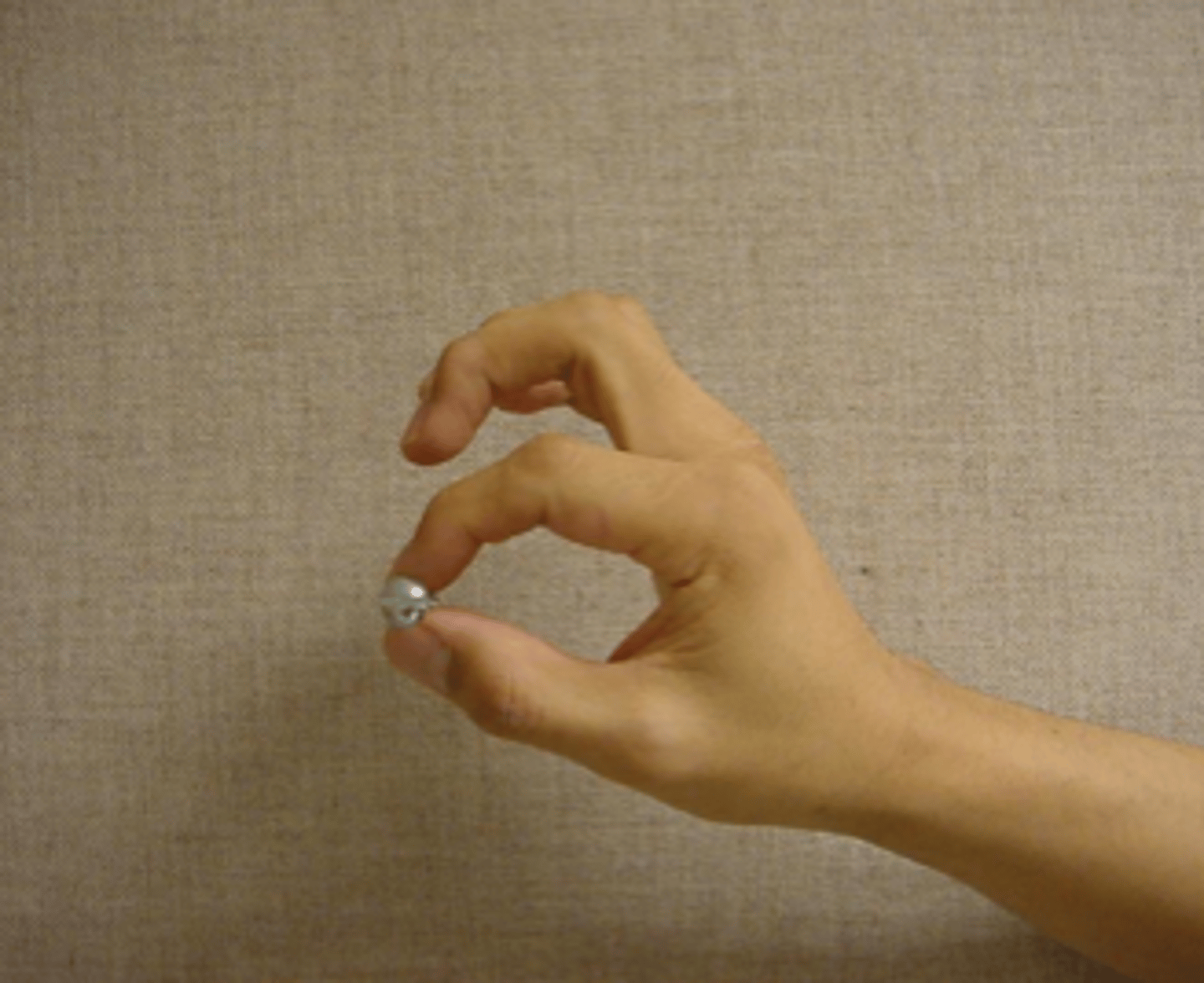
Prehensile
the ability to grasp objects
Primates
the highest order of mammals, comprised of about 400 different living species who share a number of features including opposable digits and binocular vision
Radioactive isotope
a radioactive atom of a specific element. This atom breaks down into a predictable and stable product. Also known as a radioisotope
Radiocarbon dating
a form of absolute dating used to determine the age of a fossil by measuring the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon. Also known as carbon dating and radioactive carbon dating