Dairy Cattle Industry - Exam 3
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
why are dairy cattle important in agriculture
they efficiently convert forage and feeds into high-quality human food (milk)
which animal has the highest edible product per food intake
dairy cattle (milk is 90% edible product)
what is the anual US gross revenue from the dairy industry
over $34 billion
what is the number 1 state for dairy cows & milk production
california
which areas produce the most milk in the US
midwest & pacific
why has milk production increased despite fewer cows
better genetics, nutrition, and management of cattle
what is the average milk production per cow per year in the US
~ 23,000 lbs
what is the trend of dairy cows in arkansas
a decline in dairy cows and farms
what is milk according to the FDA
the lacteal secretion which is free from colostrum that is obtained by the complete milking of one or more healthy cows
how much fat is in whole milk
3.5% fat
how much fat is in reduced fat milk
2% fat
how much fat is in low-fat milk
1% fat
how much fat is in skim milk
less than 0.2% fat
what is pasteurization
the process where raw milk is heated to kill harmful microorganisms (161°F for 15 seconds)
what is homogenization
breaking fat globules into tiny particles so that fat stays evenly mixed within the milk
how is lactose-free milk manufactured
by adding small amounts of lactase which splits up the lactose into simple sugars
what dairy product is decreasing in consumption in the US
fluid milk
what dairy products are increasing in popularity in the US
cheese and yogurt
what percentage of beef comes from dairy cattle
20-25%
what are the most important historical events in the dairy industry
1856: Condensed milk patented (Gail Borden)
1864: Pasteurization discovered (Pasteur)
1903: Milk fat testing developed (Babcock test)
1919: Homogenized milk introduced
1930s–1940s: Artificial insemination adopted
1950s–1960s: Bulk tanks & milking parlors revolutionize milk handling
1964: Plastic milk jugs introduced
how often does calving occur for cattle and why
on a year-round basis because a steady supply of calves = a reliable supply of milk & profit throughout the year
3 reasons cows are separated from dam at birth
to avoid maternal bonding
manage colostrum feeding
prevent disease
what is colostrum
the first milk produced which is rich in antibodies which protects newborn calves
what are bulls sold for
some sole as '“bucket” calves
some sold to specialized producers of veal
older calves enter stocker phase and eventually enter the feedlot phase
how does sexed semen work
farmers breed top cows to female semen to produce offspring which are better milk producers
how are heifers grown
they are weaned until they are ~ 1 month then transfered to individual housing where they are fed high quality forages + grain mix
they are expected to calf as a 2-year-old so they must reach 65% mature size + weight by 15 months
what is freshening
when a cow gives birth to a calf and begins lactating
explain the freshening graph for lactating cows
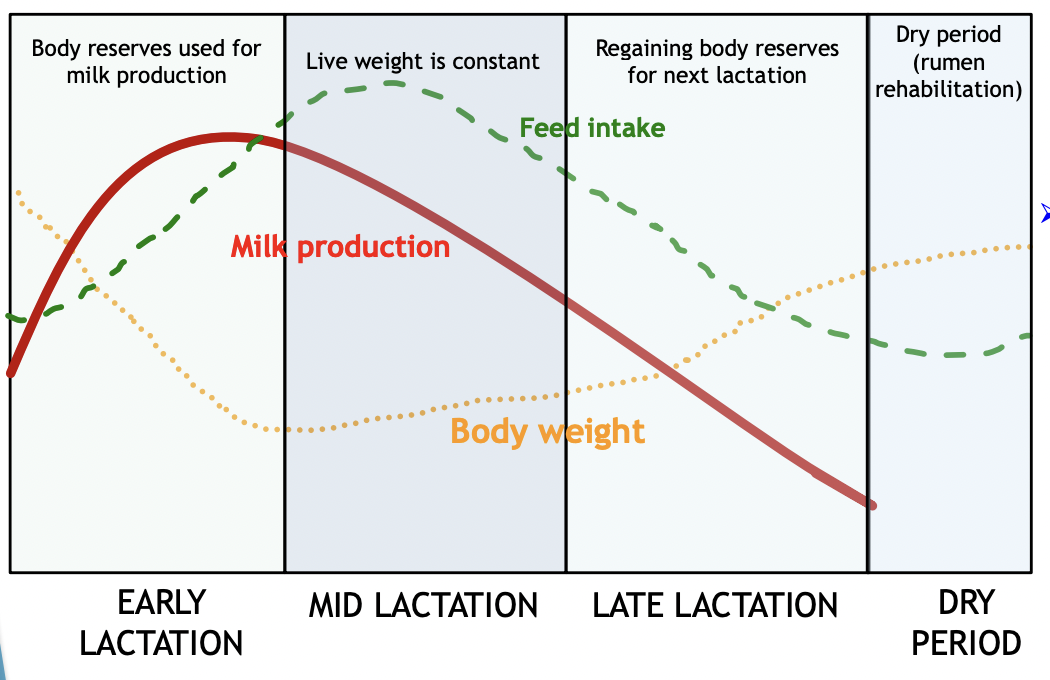
what is milk fever
a calcium deficiency which makes cows more prone to disorder and disease
what is the best way to feed milking cows
pasture + TMR
what are 3 advantages of the TMR feeding system
fewer digestive upsets with cows
less labor required to feed cows
producer has more control over total feeding
what are 2 disadvantages of the TMR feeding system
special equipment is required
doesn’t utilize pasture forages which may now require more labor to harvest and maintain fields
what is the milking system like
after calving, cows enter the milking string and are milked with semi-automated milking machines
can milk up to 100 cows at a time
what are the different grades of milk
Grade A: milk meets sanitary standards and are good for use in milk products and dairy products (class 1, 2 , 3)
Grade B: milk meets less standards and can only be used for manufactured products with FDA permission (class 3, 4))
what are the different classes of milk
class 1: beverage milk - least processed
class 2: fluid cream or soft products (yogurt, ice cream, cheese)
class 3: cream cheese and “hard” products (butter)
class 4: butter and dry milk - most processed
what is mastitis
inflammation and infection of mammary gland
the disease destroys tissue and lowers productivity of milk production
explain the lactation curve
cow reaches its peak milk production 45-60 days into lactation then milk production slowly declines
lactation lasts 305 days
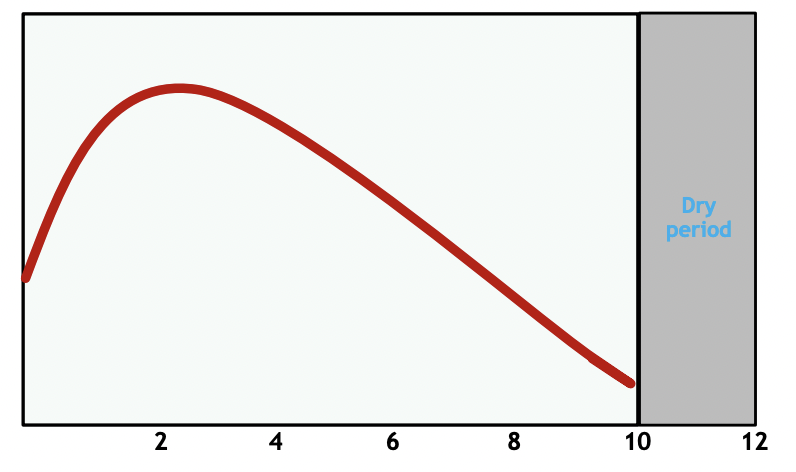
what is bovine somatotropin (bST)
a naturally occurring protein hormone which when injected can increase milk production in cows
what is the dry period in lactating cows
the end of the lactation period but also the beginning of the next lactation
cows should complete a 45-60 day dry period
what are the 3 steps to the dry period
cows removed from milking string
grain is withdrawn from diet + water supply reduced several days before dry period
udder infused with antibiotics to prevent infections