Topic 2B - Coasts
1/126
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
127 Terms
Positive feedback at coasts
Waves erode cliffs, released material helps erode more
Negative feedback at coasts
Shore is eroded, material makes wave cut platform wider, therefore it can absorb more energy and reduce impact
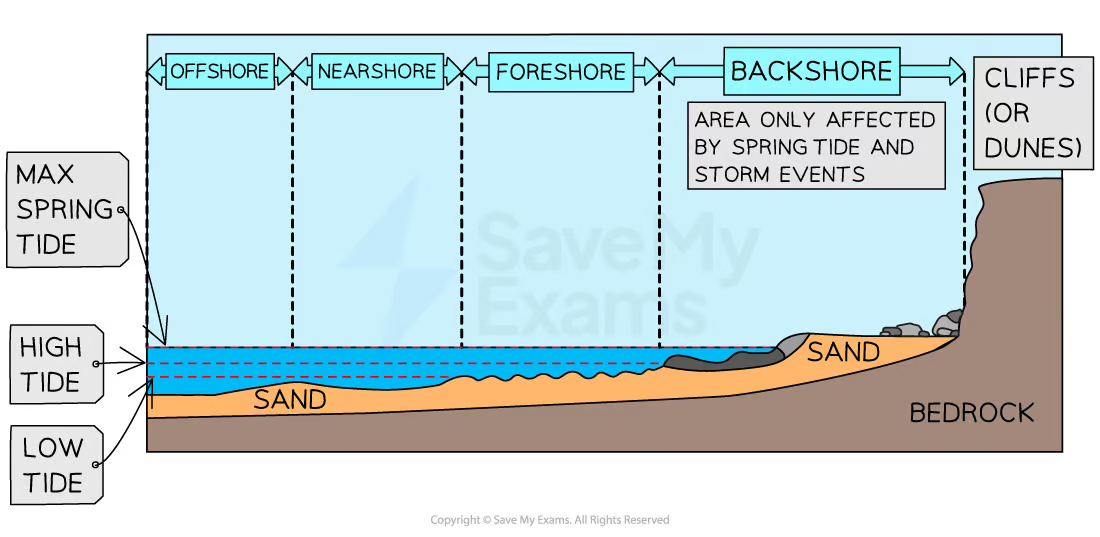
Littoral zone
The area of coasts that can be affected by wave action (dynamic zone)
4 sections of the littoral zone
Backshore
Foreshore
Nearshore
Offshore
Geology
The characteristics of the land (rock type and structure)
Concordant costaline
Rock types run parallel to the coast
Discordant coastline
Rock types run at right angles to the coast
Causes of sea level change
Global warming
Tectonic activity
Eustatic/Isostatic change
Eustatic change
Sea level itself rises
Isostatic change
Land rises or falls relative to the sea
Characteristics of high energy coasts
Destructive waves
Strong wind
Long fetches
High erosion than deposition
Rocky
Steep cliffs
Headlands
Wave cut platforms
Characteristics of low energy coasts
Constructive waves
Sheltered location
Short fetch
Higher deposition than erosion
Sandy beaches
Salt marshes
Mud flats
Gentle relief
Beaches
Spits
Coastal plains
Characteristics of rocky coasts
Cliffs
Erosion more than deposition
More resistant geology (north and west UK)
Primarily marine and sub-aerial erosion
Marine erosion
Caused by waves
Sub-aerial erosion
Weathering and mass movement
Characteristics of coastal plains
Land slopes towards sea (low relief)
Includes sandy and estuarine coastlines
Low energy (greater deposition than erosion)
Dunes, wetlands and marshes
Coastal morphology
The shape and form of the coastline, influenced by rock type and structure
Lithology
The geological structure of rocks, the way they are folded or tilted
Characteristics in lithology
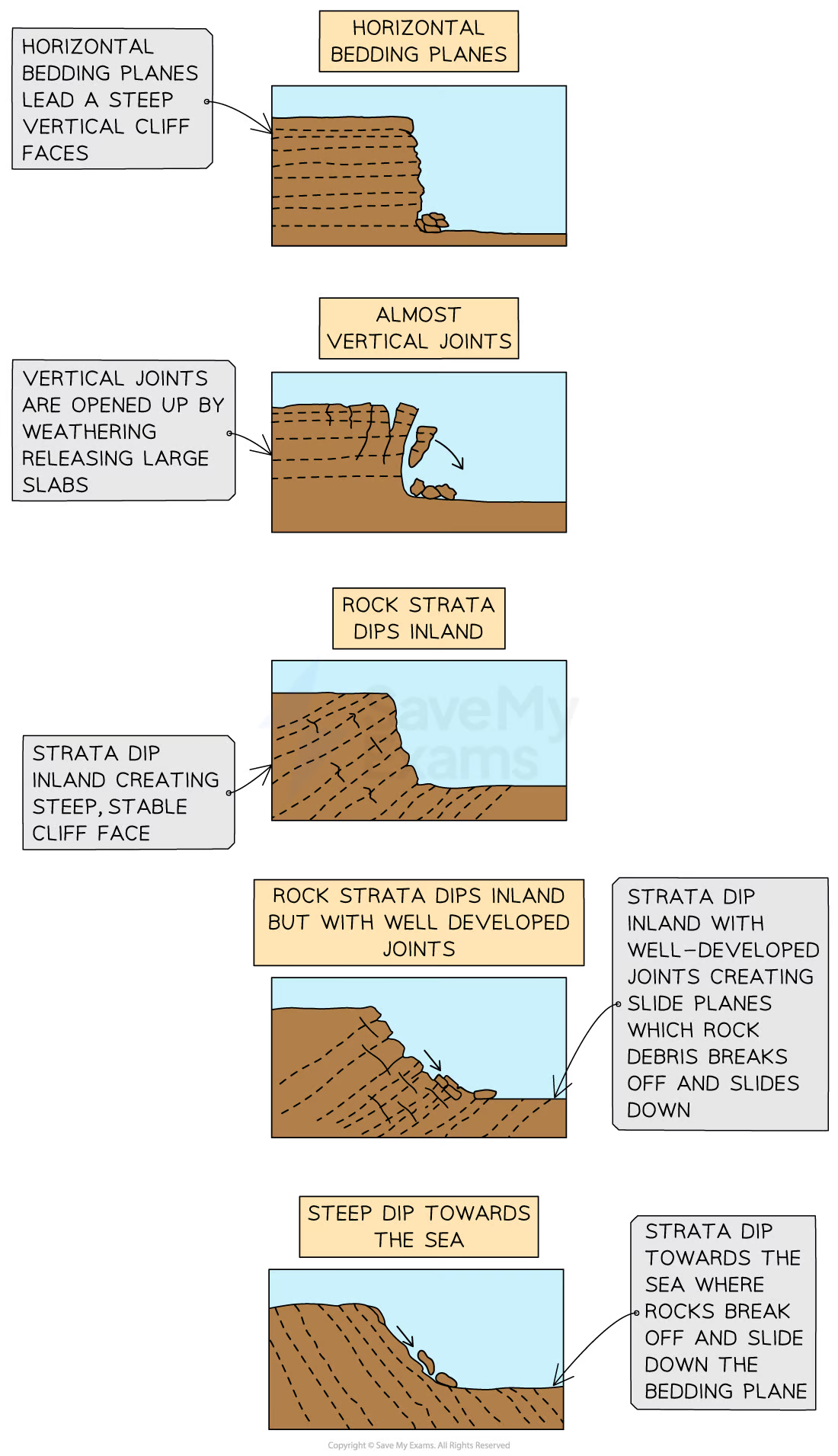
Strata - layers of rock
Bedding planes - horizontal cracks created by pauses in rock formation
Joints - vertical cracks caused by tectonic movement or contraction
Folds - the result of pressure during tectonic movement causing the rock strata to fold
Faults - the result of stress or pressure causing it to fracture
Dip - the angle of the rock strata
Cliff profile
Angle and height of the cliff face, includes other features (eg wave cut notches), is heavily influenced by lithology
Coastal recession
Retreat of the coastline inland due to multiple factors
Erosion (dependent on ithology)
Sea level rise
Submergence
Sedimentary rock
Form from pressure (compaction and cementation) AKA lithification
Examples of sedimentary rock
Shale
Sandstone
Limestone
Characteristics of sedimentary rock
Erode and weather easily (softest rock type)
Form in layers
Weak bedding planes
Heavily jointed and fractured
Metamorphic rock
Forms when sedimentary or igneous rock is altered by heat and pressure without fully melting
Examples of metamorphic rock
Slate
Marble
Characteristics of metamorphic rock
Crystalline structure
Folded and faulted
More resistant the sedimentary, less than igneous
Crystals are parallel aligned
Igneous rock
Forms when molten rock from the mantel hardens and cools
Examples of igneous rock
Granite
Basalt
Characteristics of igneous rock
Erode/weather very slowly
Two types: Intrusive (forms underground, cools slowly, big crystals) and Extrusive (forms on surface, cools quickly, smaller crystals)
Interlocking crystals
Few joints and weaknesses
Differential erosion
Changing rates of erosion of different rock types, leads to complex cliff profiles, extra prominent on discordant coastlines (headlands and bays), also affected by permeability
Vegetation at coasts
Stabilizes coastlines by helping bind soil together, reducing wind speed (therefore erosion) and adds organic matter to help form soil
Pioneer species
First plants to grow in a harsh environment, helps allow others to grow later
Sand dune formation
Windblown sand is deposited against an obstruction (eg plant)
Grows in size as more is deposited, form rows at right angles to prevailing winds
Eventually become fixed by vegetation
Sand dune succession
Embryo dune
Fore dune
Yellow dune
Grey dune
Mature dune
Embryo dune
First step, smallest dune
High pH
Little soil content
Max 1 meter
Pioneer species only
Fore dunes
Second step
Embryo dunes protect from prevailing wind
Non-pioneer species begin to grow and stabilize the dune, also add organic matter
Max height 5 meters
Yellow
Third step
Yellow-darker greyish with more organic matter
Flowering vegetation found
Max 8 meters
Grey dunes
Fourth step
Soil acidity higher
Shrubs begin to appear
Max 10 meters
Mature dune
Fifth and final stage
Most stable
Several hundred meters from shoreline
Can support trees
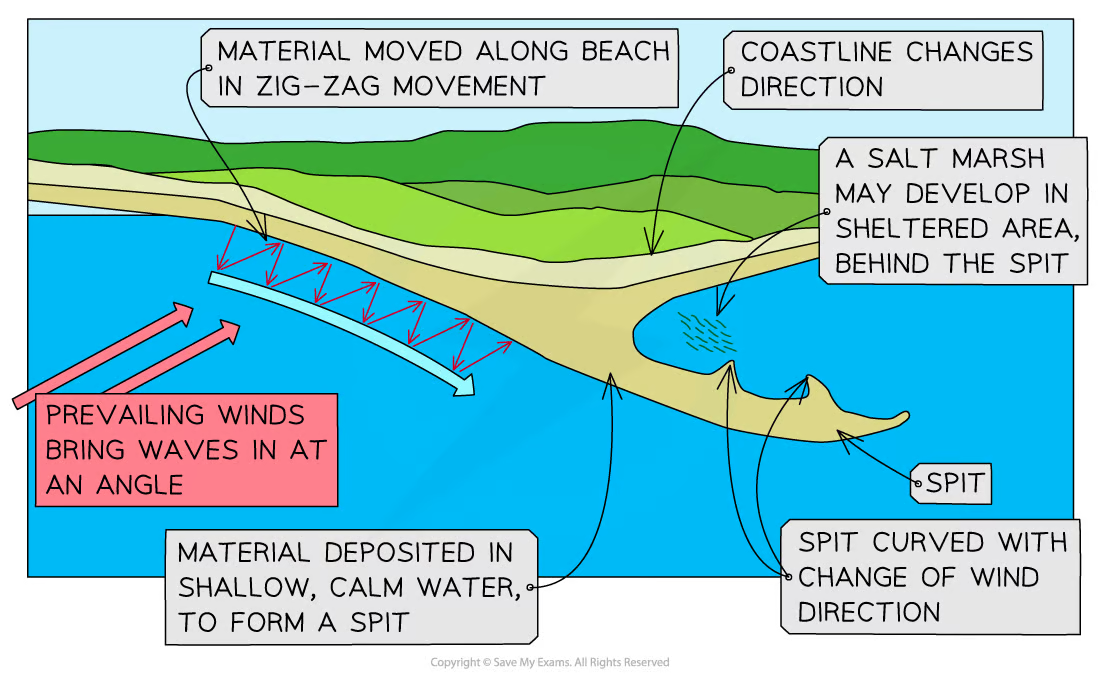
Salt marshes
Form in estuarine areas because of sediment and shelter from large waves, mix of fresh and salt water, algae helps trap sediment and bind it together, grasses start to grow
Wave fetch
Distance travelled in open water
Wave height
Distance from peak to trough
Wave length
Distance from crest to crest
Wave frequency
Number of waves that pass a point over a given time
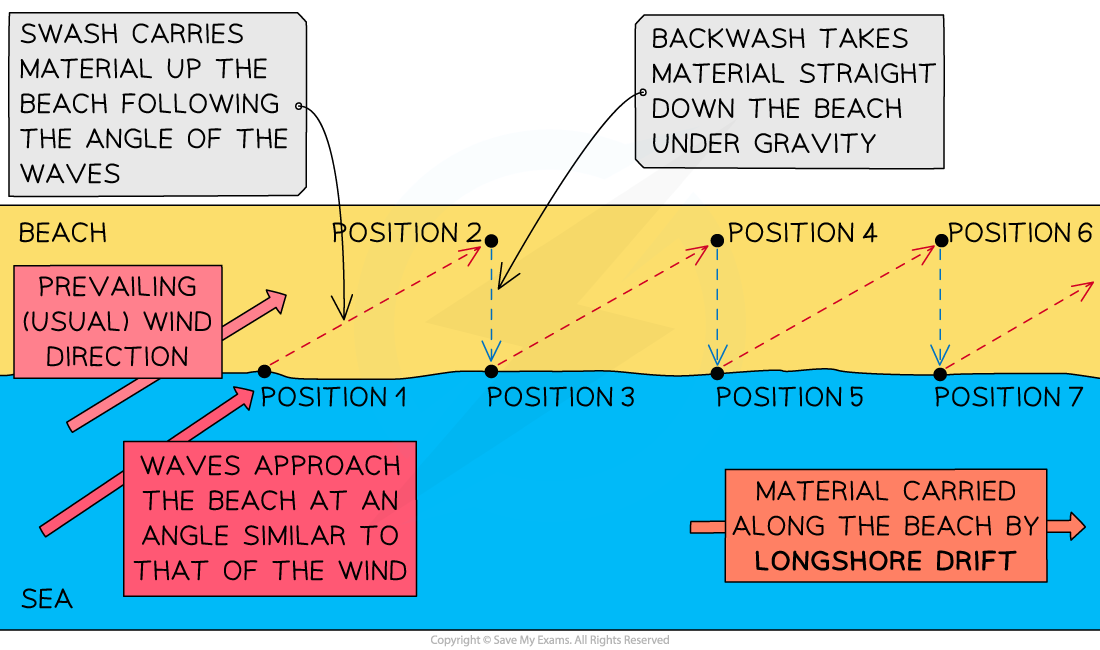
Constructive waves
Lower height
Swash stronger than backwash
Greater deposition
Destructive waves
Higher wave height
Stronger backwash than swash
Greater erosion
Abrasion (coastal)
Sediment and rock are picked up by waves and wear away at cliffs
Hydraulic action (coastal)
Force of waves forces high pressure air into crack at cliffs and weakens to rock, causing joints to expand
Corrosion (coastal)
Weak acids in water dissolve rock particles
Attrition (coastal)
Rocks bash into each other when moved by water and gradually get smaller and rounder
Factors affecting coastal erosion
Wave type
Wave size
Lithology
Traction
Large heavy material is dragged along the sea floor
Saltation
Smaller material is lifted by water and “bounces” along the floor
Suspension
Small particles are carried within the water
Solution
Smallest material is carried dissolved in water flow
Types of sediment transport
Traction
Saltation
Suspension
Solution
Longshore drift
Main process of deposition and transport along the coast
Surface currents
Formed by wind and close to surface
Deepwater current/thermohaline circulation
Caused by density differences in water, deeper under surface
Tidal range
Difference between high and low tide at a place, larger rang makes stronger tidal currents that can transport more sediment
Drift-aligned beach
Longshore drift moves sediment along the beach , often end in a spit when coastline changes direction
Swash-aligned beach
Form when energy is low, waves run parallel to shore so little sediment movement
Spits
Created because of longshore drift
When coastline changes direction the waves loose energy to carry sediment and deposit it, then builds up out to sea
Often has a curved end due to second prevailing wind
Lagoon
Small body of water is cut off from the sea
Usually behind a bar or tombolo
Way fill with sediment and from new land
Tombolo
When a spit joins the mainland to an island
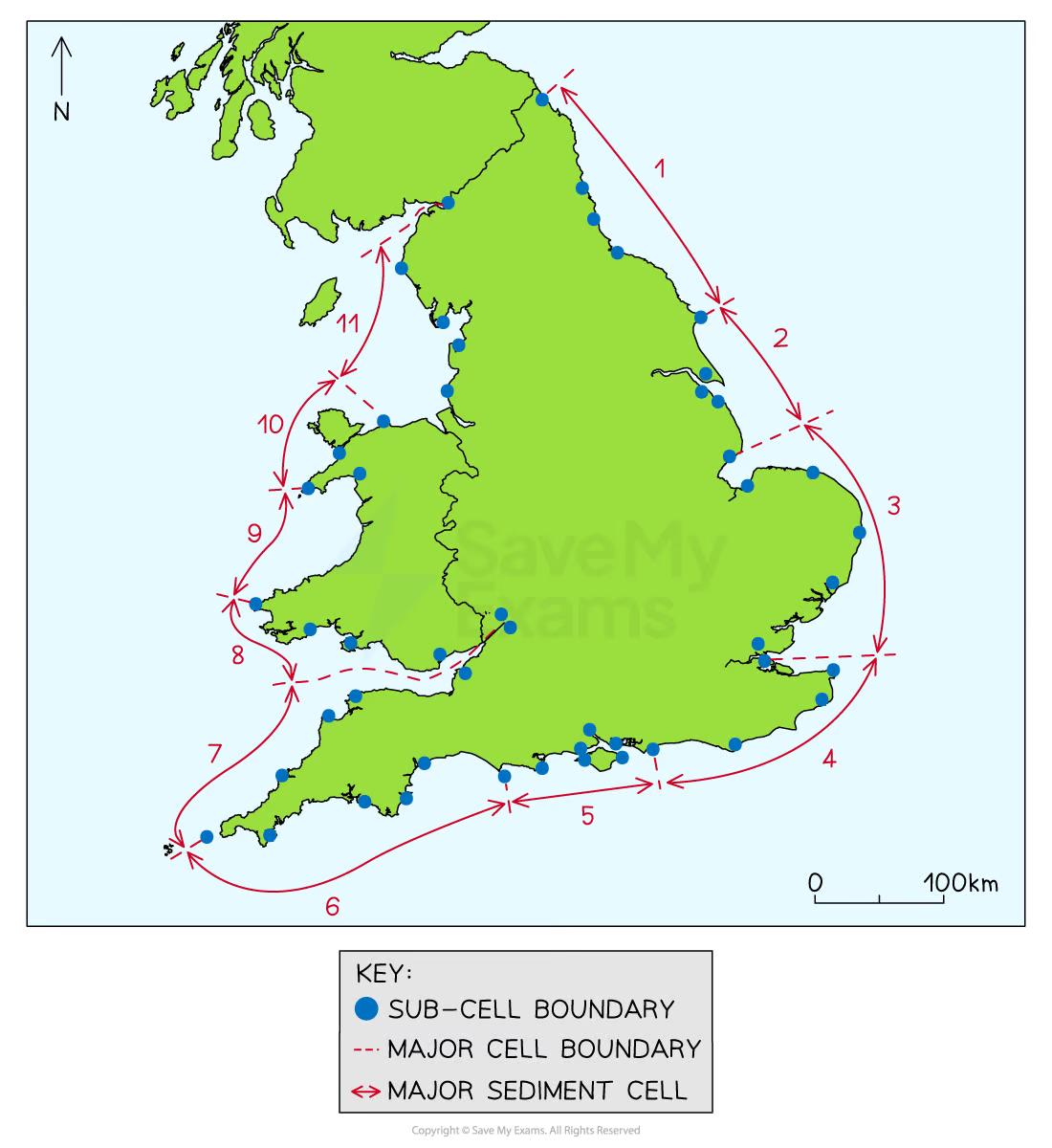
Sediment cells
Closed systems as sediment movement is contained
11 cells in the UK
Can be divided into sub-cells where inputs (sources), stores (sinks), transfers and outputs can all be identified
Sediment budget
The balance between inputs and outputs in a sediment system, should be ina. state of dynamic equilibrium but can be disturbed by human activity and climate change
Mechanical/physical weathering
When rocks breakdown without physical changes
Biological weathering
Rocks break down due to organic activity
Chemical weathering
Rocks breakdown due to a chemical reaction
Physical weathering examples
Wetting/drying
Exfoliation
Salt crystallization
Frost weathering
Chemical weathering examples
Oxidation
Hydration
Carbonation
Solution
Biological weathering examples
By vegetation
By animals
By humans
Freeze thaw
A form of physical weathering
Water collects in cracks in the rock
Water freezes and therefore expands when temps drop, widening the crack
Repeats
Mas movement
The downhill movement of material due to gravity
Factors affecting type of mass movement
Angle of slope
Nature of materials
Amount/type of vegetation
Water
Rock type/structure
Human activity
Climate
Soil creep
Soil expands due to heating or freezing
This causes it to lift at a right angle to the slope
When it shrinks it falls down
Flow
Slopes between 5-15 degrees
Between 1-15 km/year
Happens after soil has become heavily saturated
Slide
Movement of material in one group until it reaches the bottom
Fall
Steep slopes and rapid movement
Can be caused by extreme weathering, rainfall, earthquakes, and hot weather
Slumping
Weather rock types become saturated and heavy so large areas move down in one piece, leaving a curved surface behind
Can be rotational (at coasts)
Mass movement land forms
Rotational scars
Talus scree slopes
Terraced cliff profiles
Rotational scar
Curved
Un-weathered
Un-vegetated
Result of rotational slumping
Talus scree slope
Fan shaped mound of material
Made from block fall debris
Concave profile
Terraced cliff profiles
Profile of the cliff is stepped
Result of lithology and rock fractures
Causes of eustatic change
Changing amounts of ice
Thermal expansion of the sea
Tectonic changes (reduces ocean capacity)
Causes of isostatic change
Post glacial adjustment
Accretion
Tectonic activity (moves up land)
Post glacial adjustment
Heavy ice sheets in glacial period push land down, when glacial period ends the land will rebound (isostatic recovery)
Accretion
Within the sediment cell areas of high deposition cause land to build up
Emergent landforms
Can occur in isostatic recovery
Raised beaches
Fossil cliffs
Raised beaches
Emergent landform
Beaches that are high above high tide level
Very flat
Fossil cliffs
Emergent landform
Steep slope at the back of a raised beach, wave cut notches, caves and arches may be found
Submergent landforms
Happen from a relative rise in sea level, can happen when coastlines flood
Ria/drowned valley
Fjords
Dalmatian coast
Ria/drowned valley
Lower course of river valley floods
V shaped cross section
Estuarine
Most common submergent landform
Fjord
Glacial valleys flood due to eustatic change
Deeper than rias
Flat bottomed U shape
Straight profile
Can be deeper than the adjacent sea
Dredging
Removal of sediment from river or sea, changes amount of sediment being deposited at the coast
Dams and coastal recession
Construction traps sediment behind the wall (100 billion tonnes, another billion each year, which starves the coast of sediment
Reasons for changing rates of recession
Wind direction
Fetch
Tides
Seasons
Weather systems
Storms
Factors increasing flood risk
Land height
Degree of subsidence
Vegetation removal
Global sea level rise