AP Psychology: Topic 1.4 - The Brain
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

35 Terms
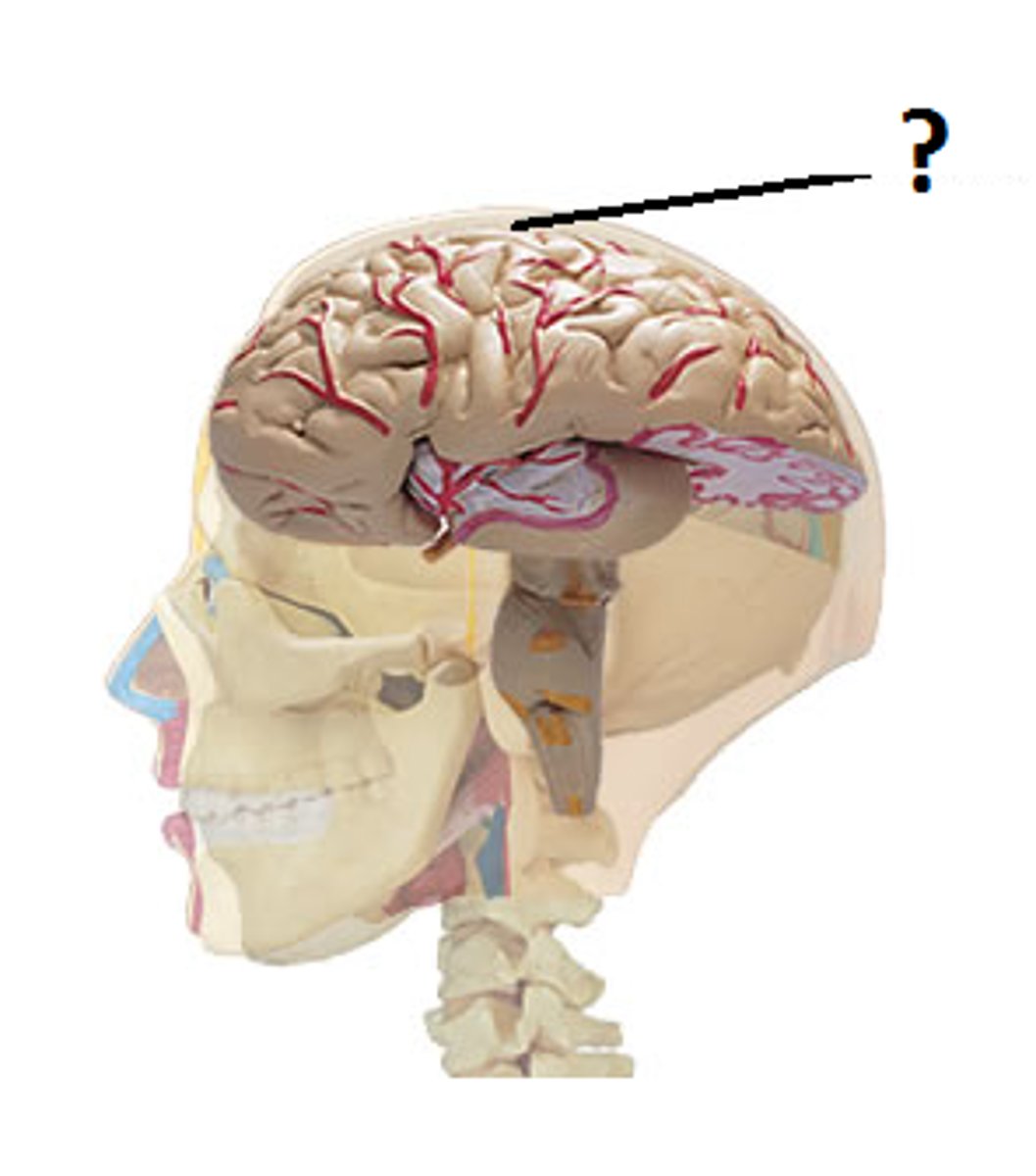
Cerebral cortex
outermost part of forebrain; controls voluntary muscular movements as well as sensation, movement, memory, emotions, and executive function
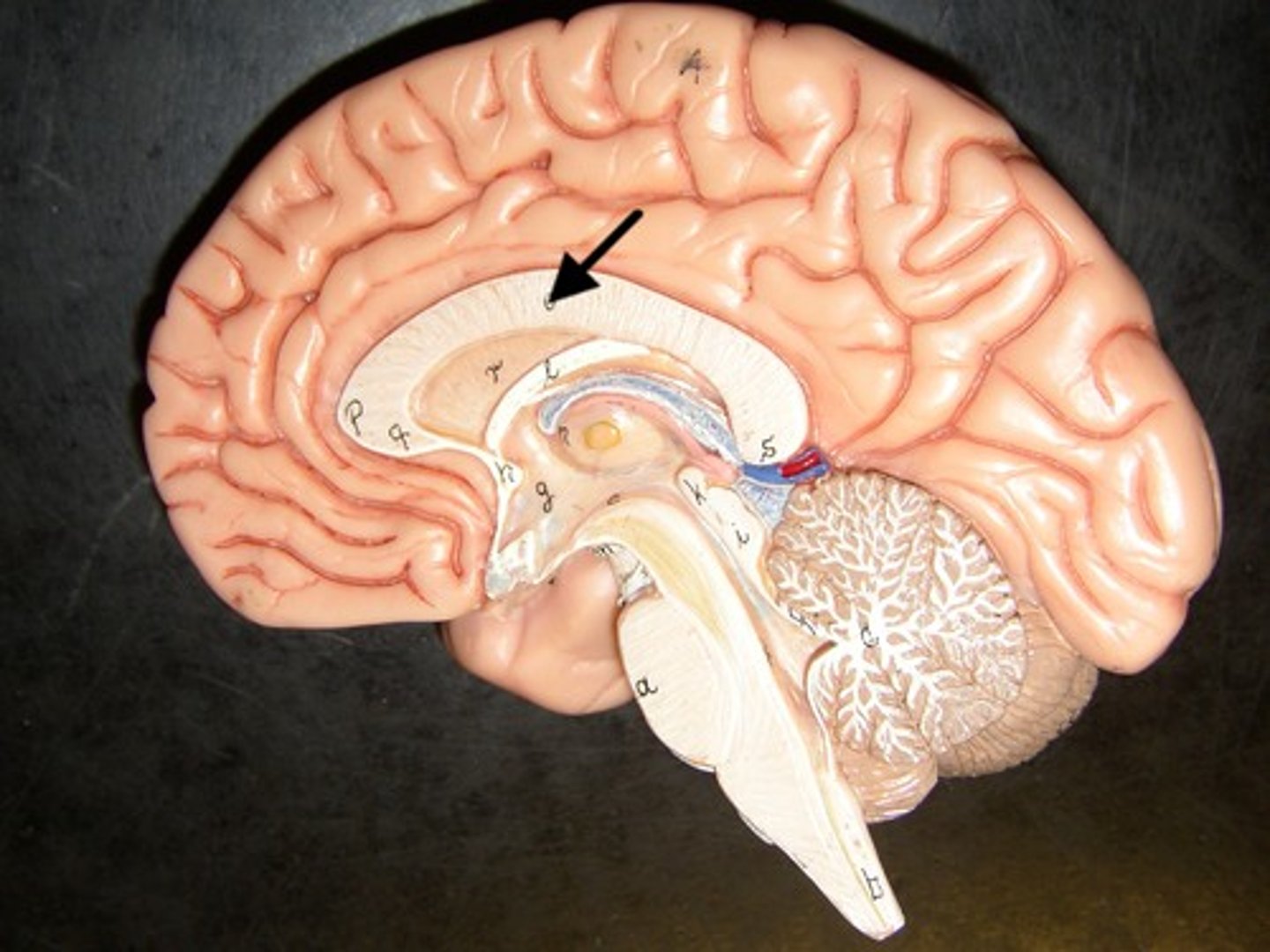
Corpus callosum
a thick band of nerve fibers that connects large areas of the cerebral cortex on each side of the brain and supports communication of information across the hemispheres
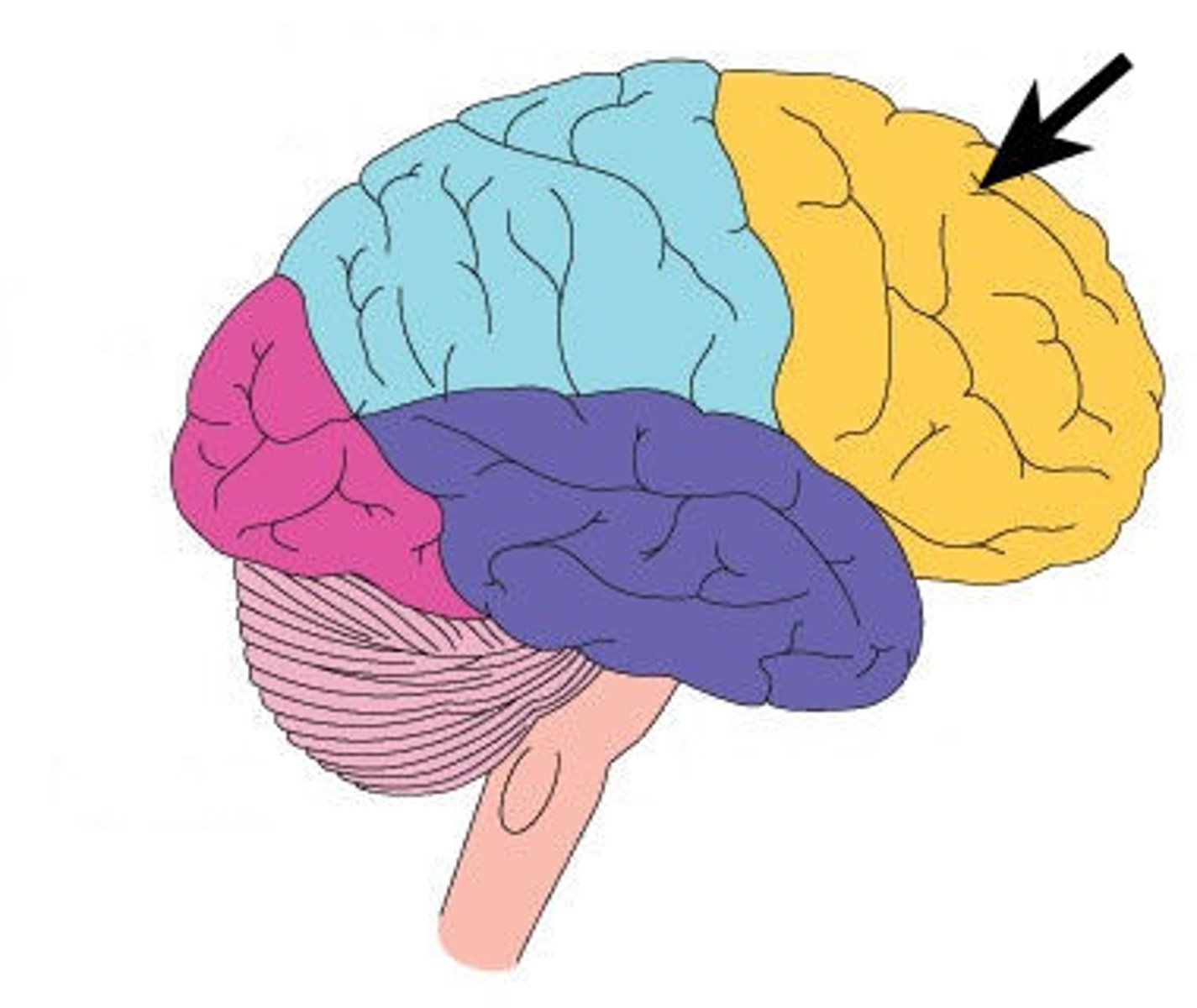
Frontal lobes
a region of the cerebral cortex that has specialized areas for movement, abstract thinking, planning, memory, and judgement
Motor cortex
an area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements
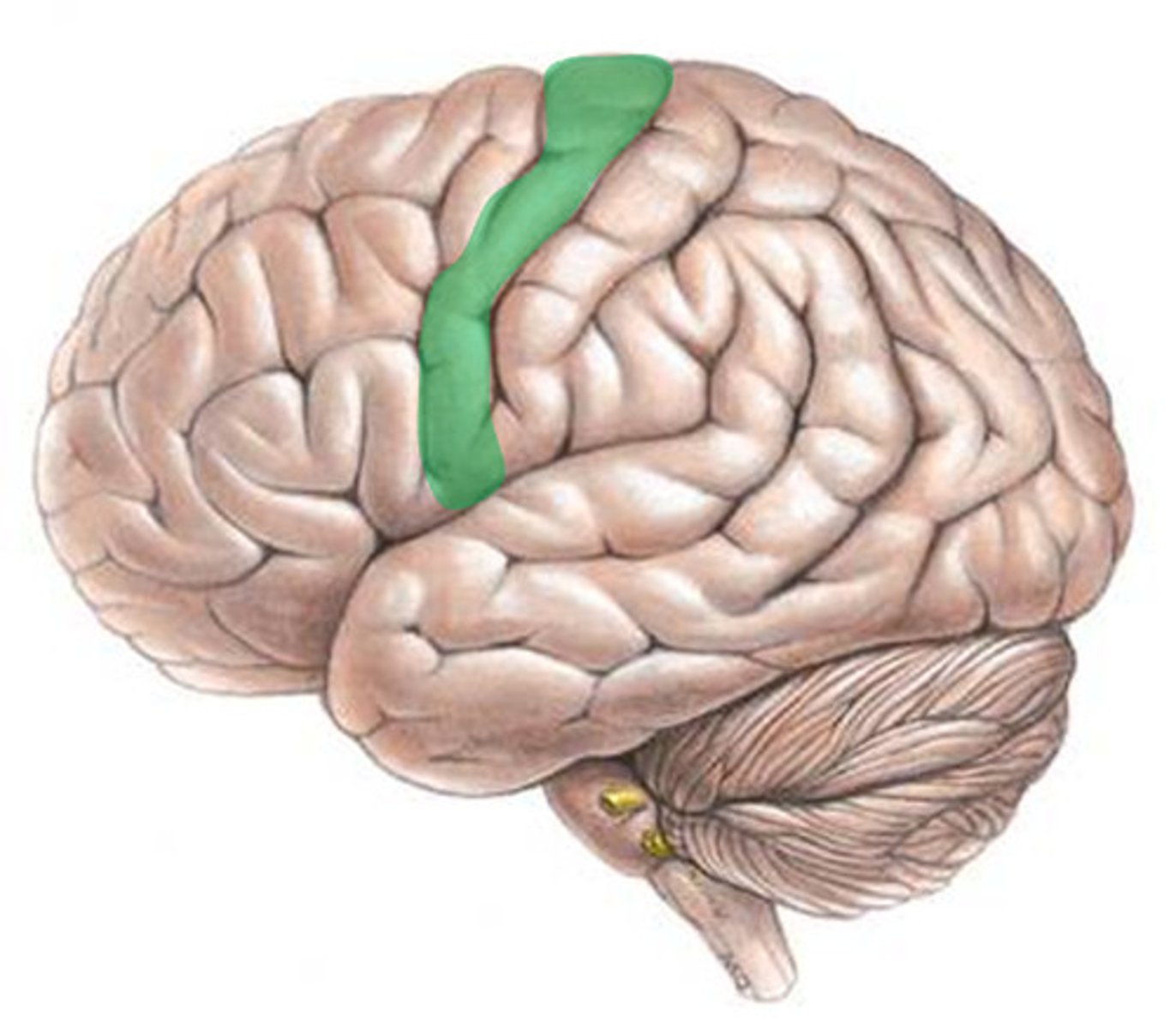
Prefrontal cortex
part of frontal lobe responsible for thinking, planning, and language
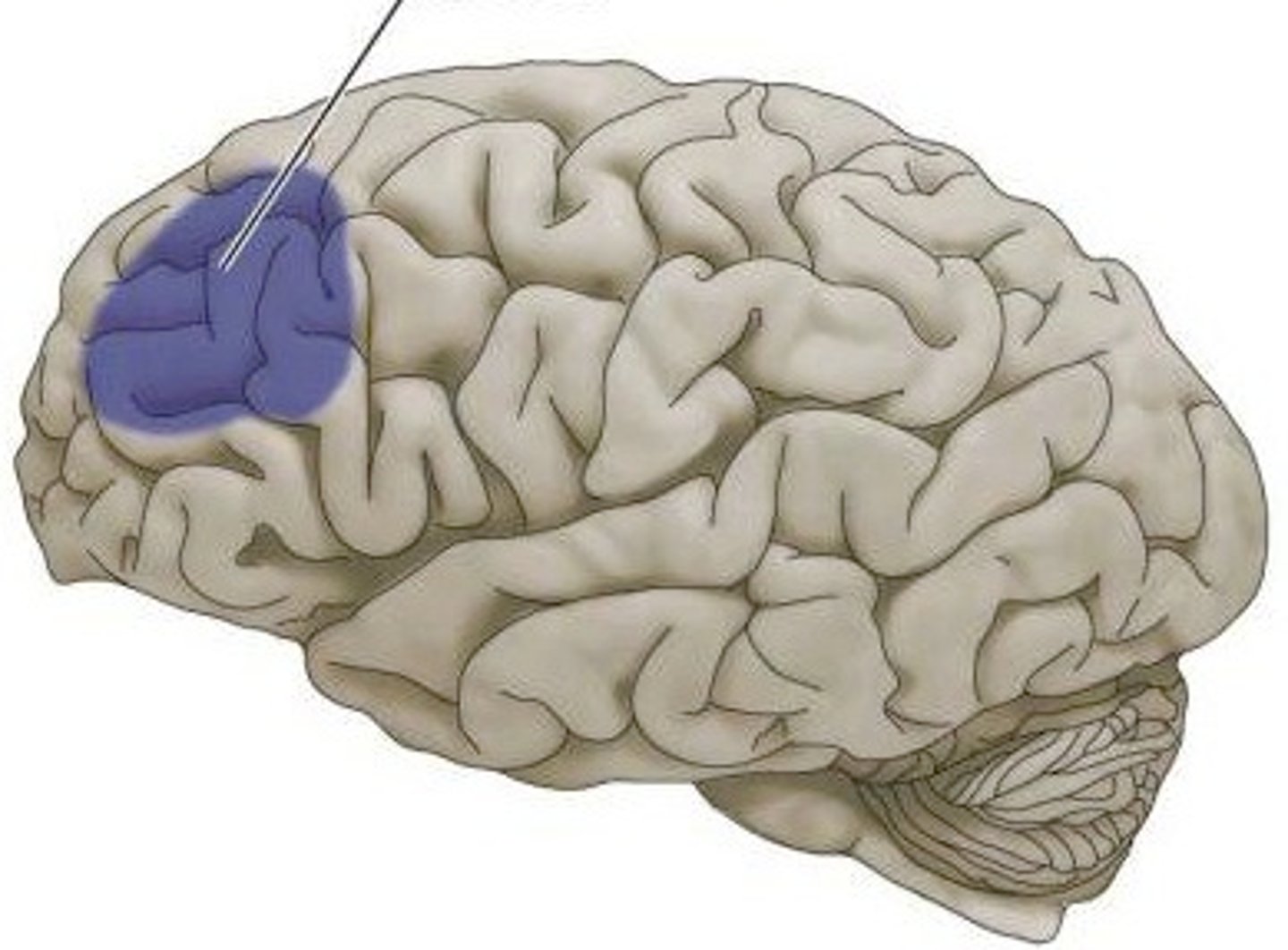
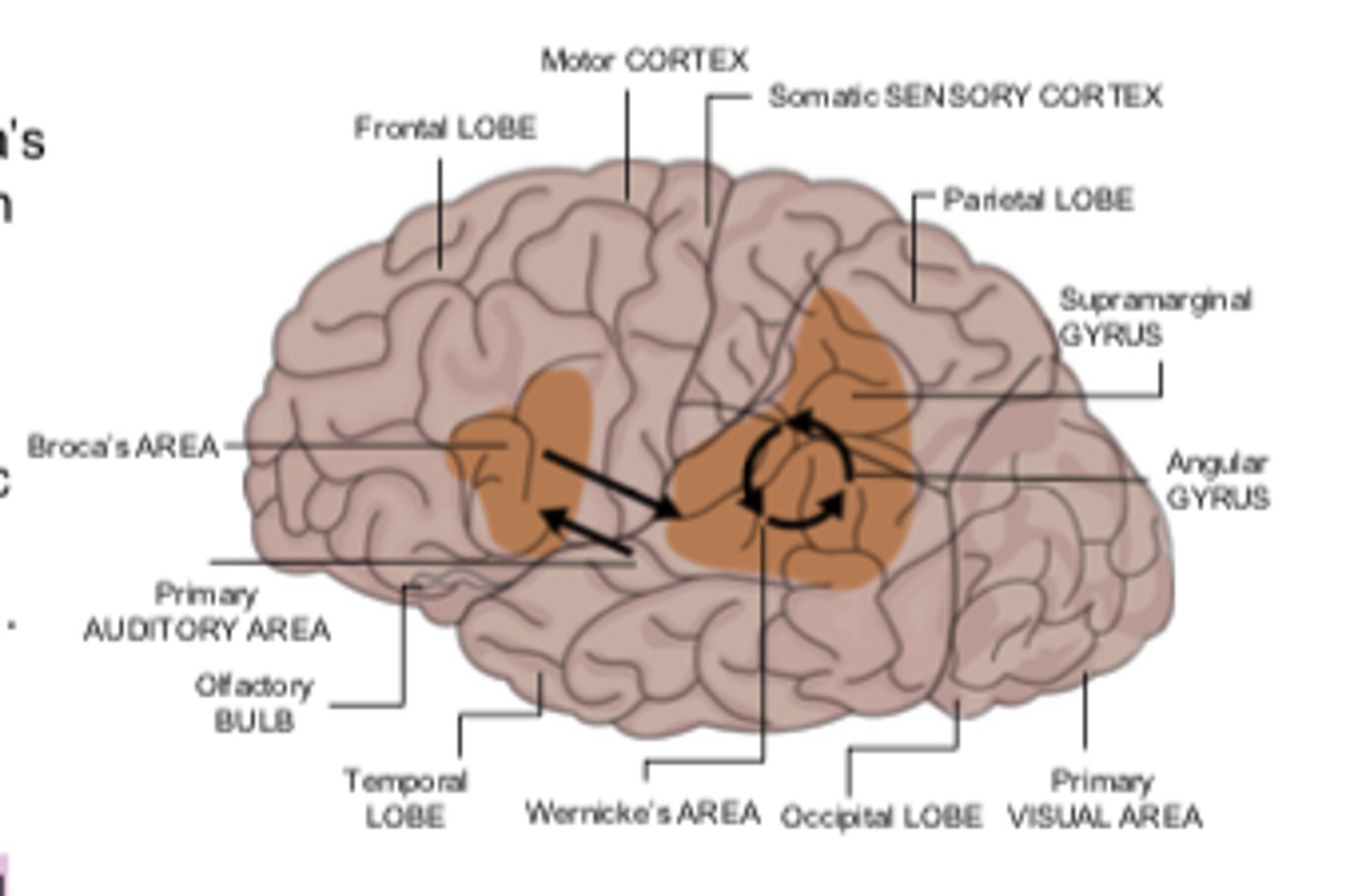
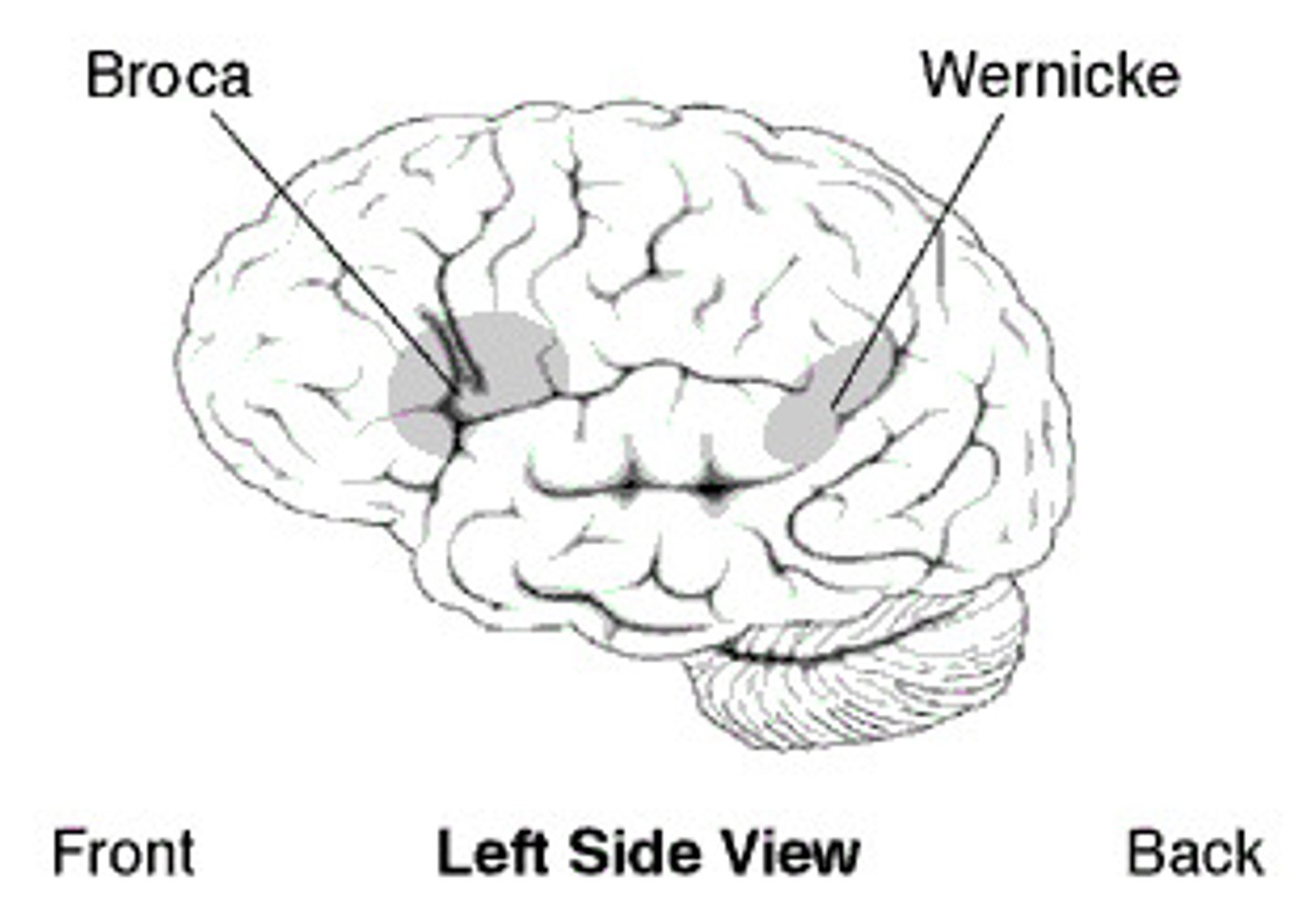
Broca's area
the language expression area in the frontal lobe (usually in the left hemisphere) that directs the muscle movements involved in speech
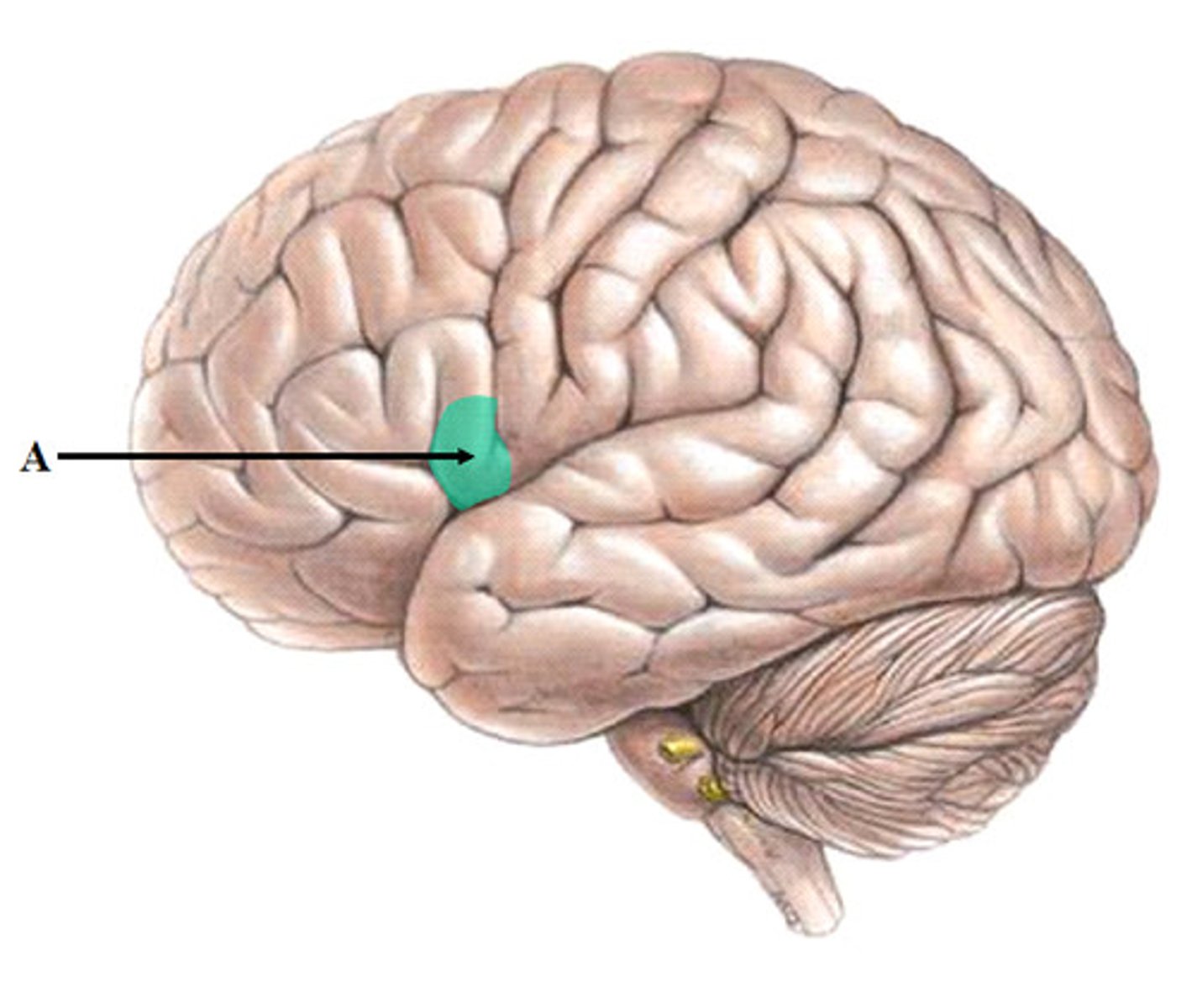
Parietal lobes
upper middle part of the cerebral cortex lying behind the frontal lobe that is specialized for touch and perception
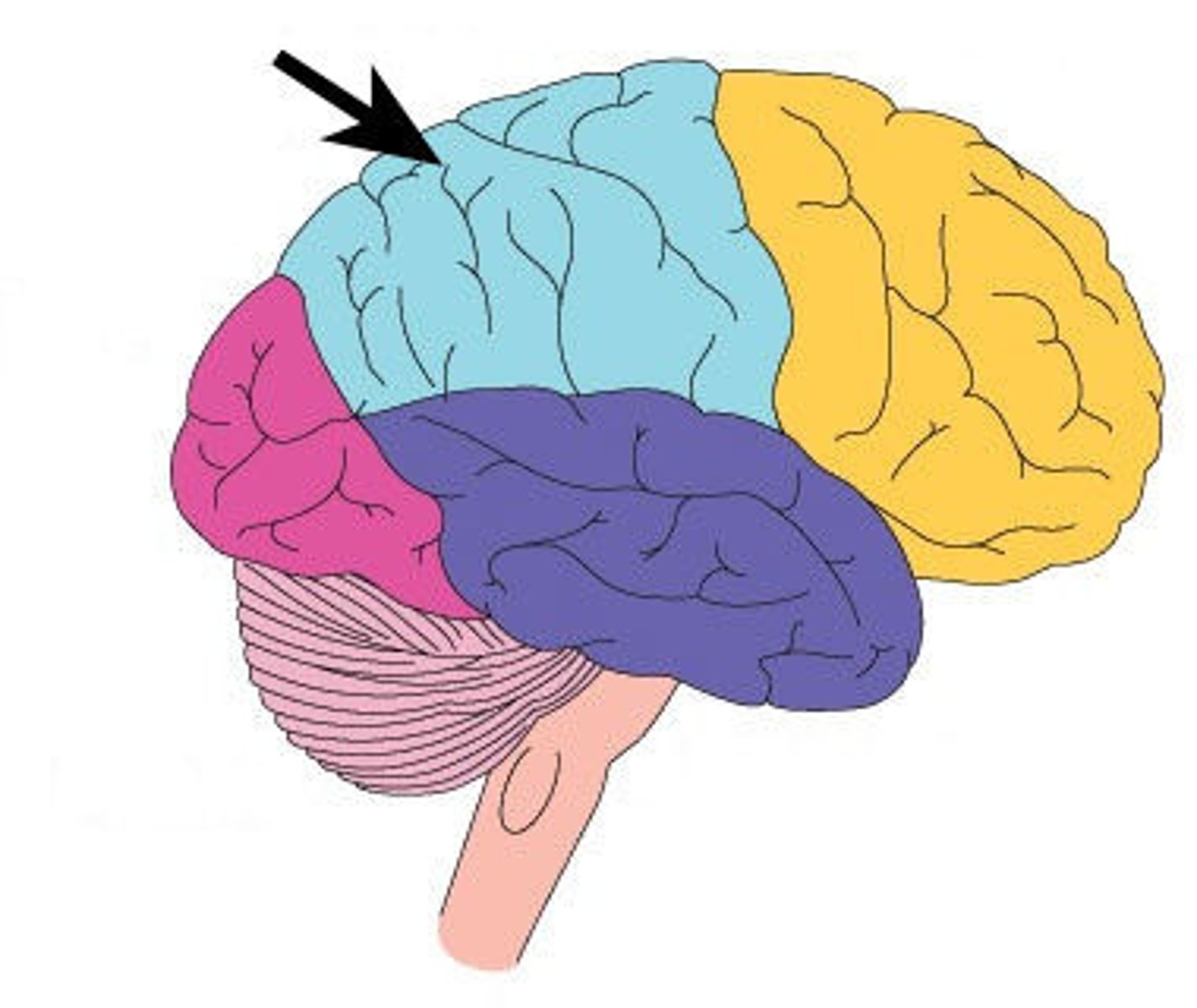
Temporal lobes
lower part of cerebral cortex involved in hearing, understanding language, and memory
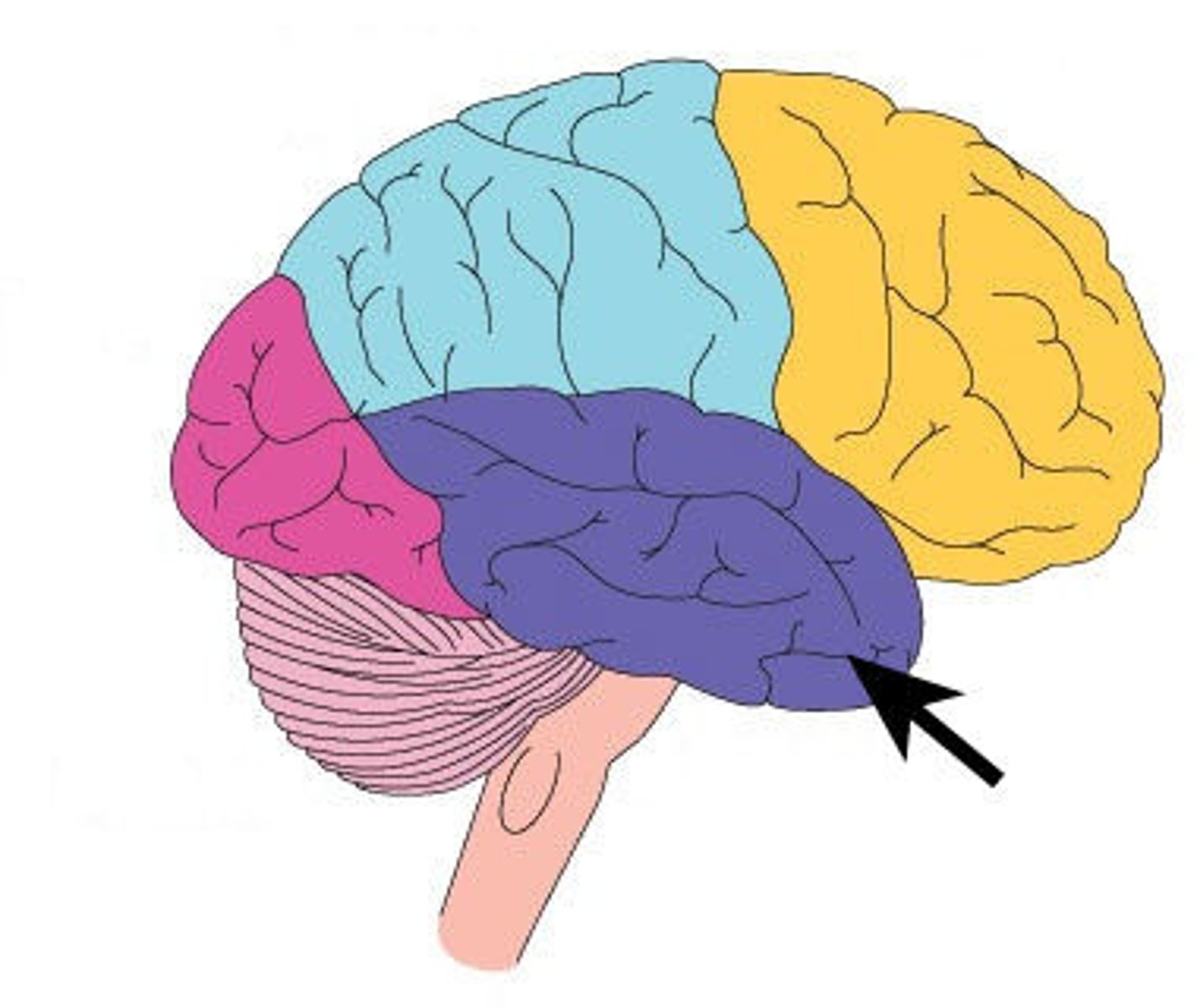
Wernicke's area
part of the temporal lobe involved in understanding speech
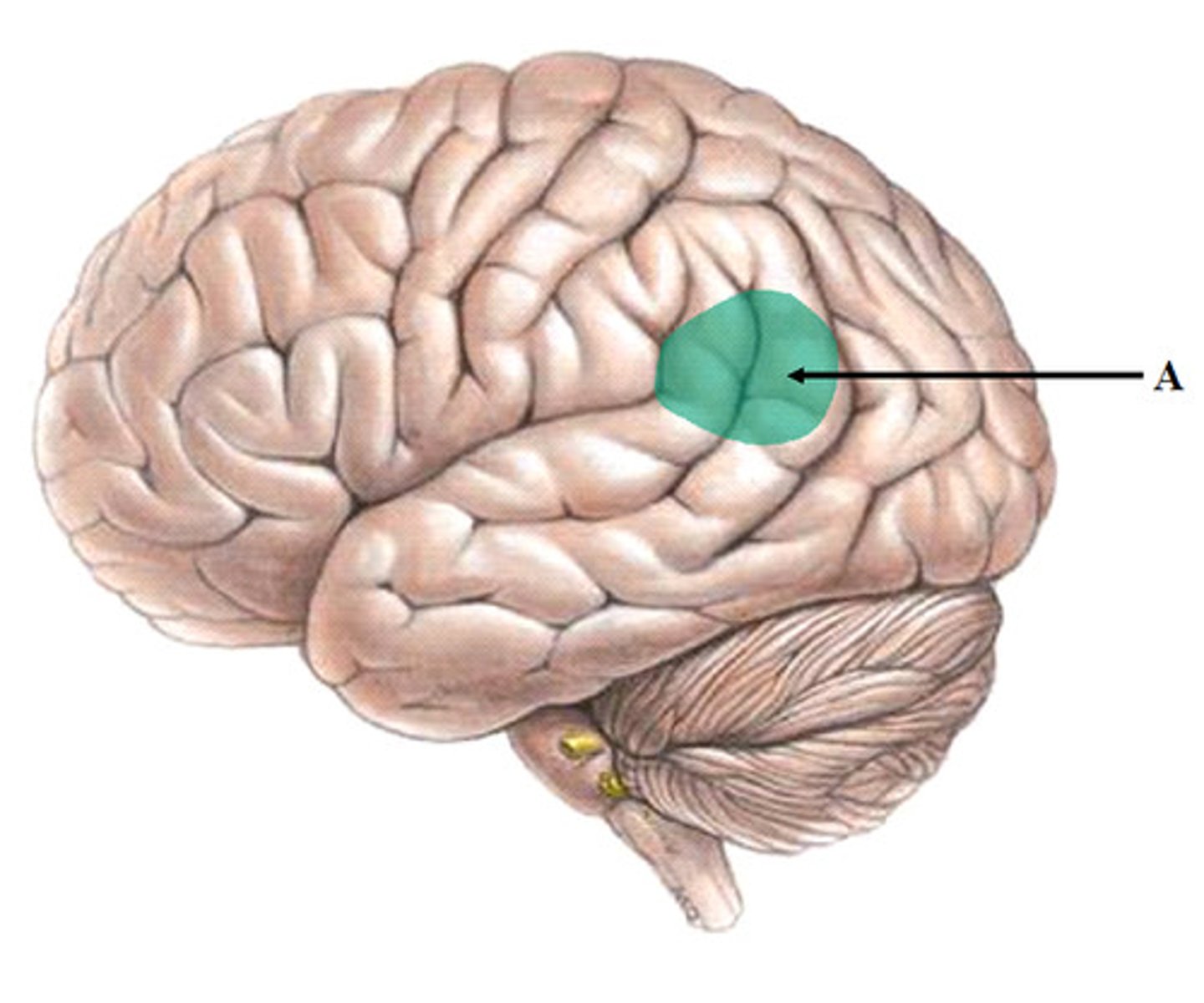
Occipital Lobes
back part of cerebral cortex specialized
for vision
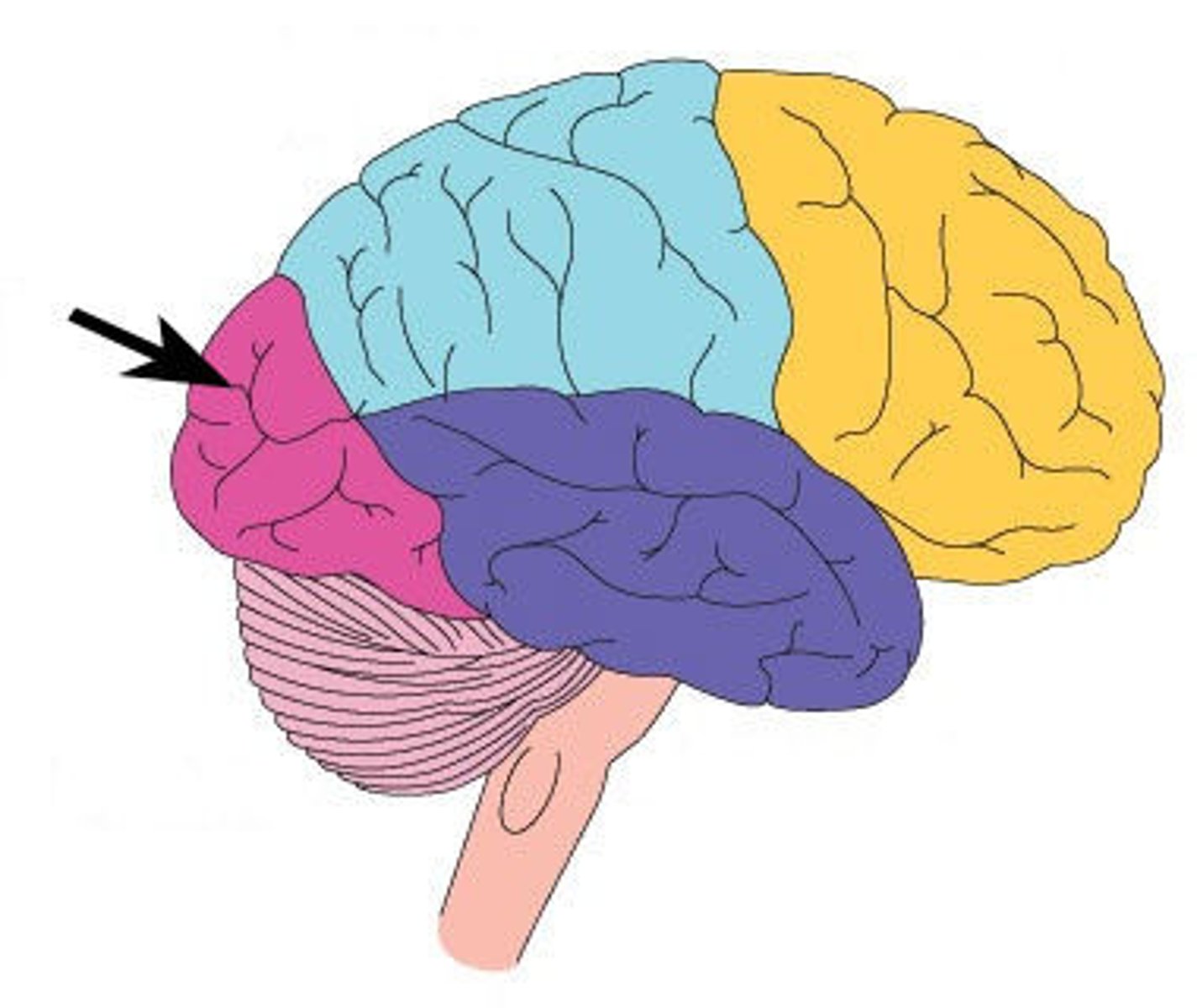
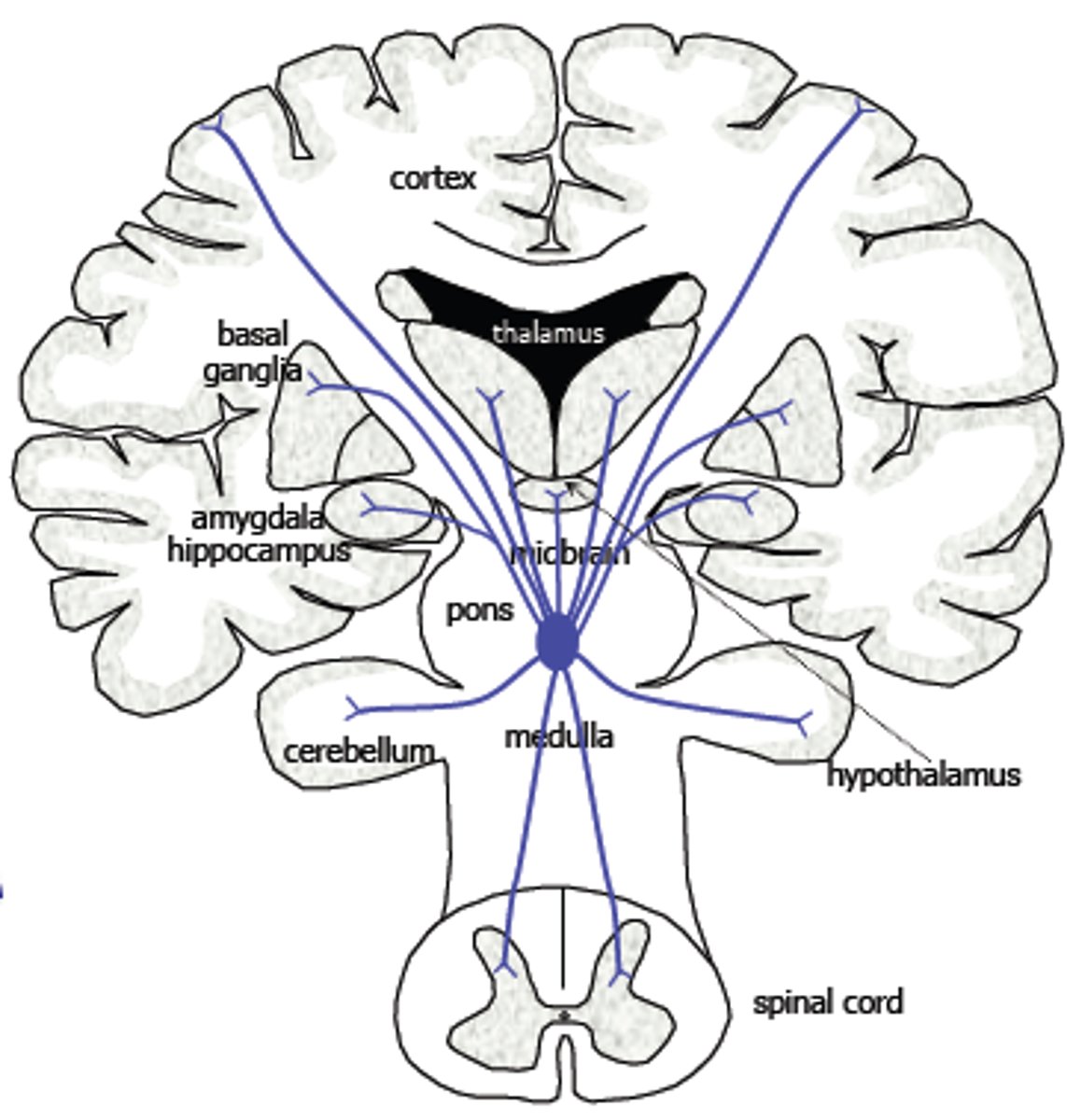
Limbic system
emotional center of brain that also plays roles in smell, motivation, and memory
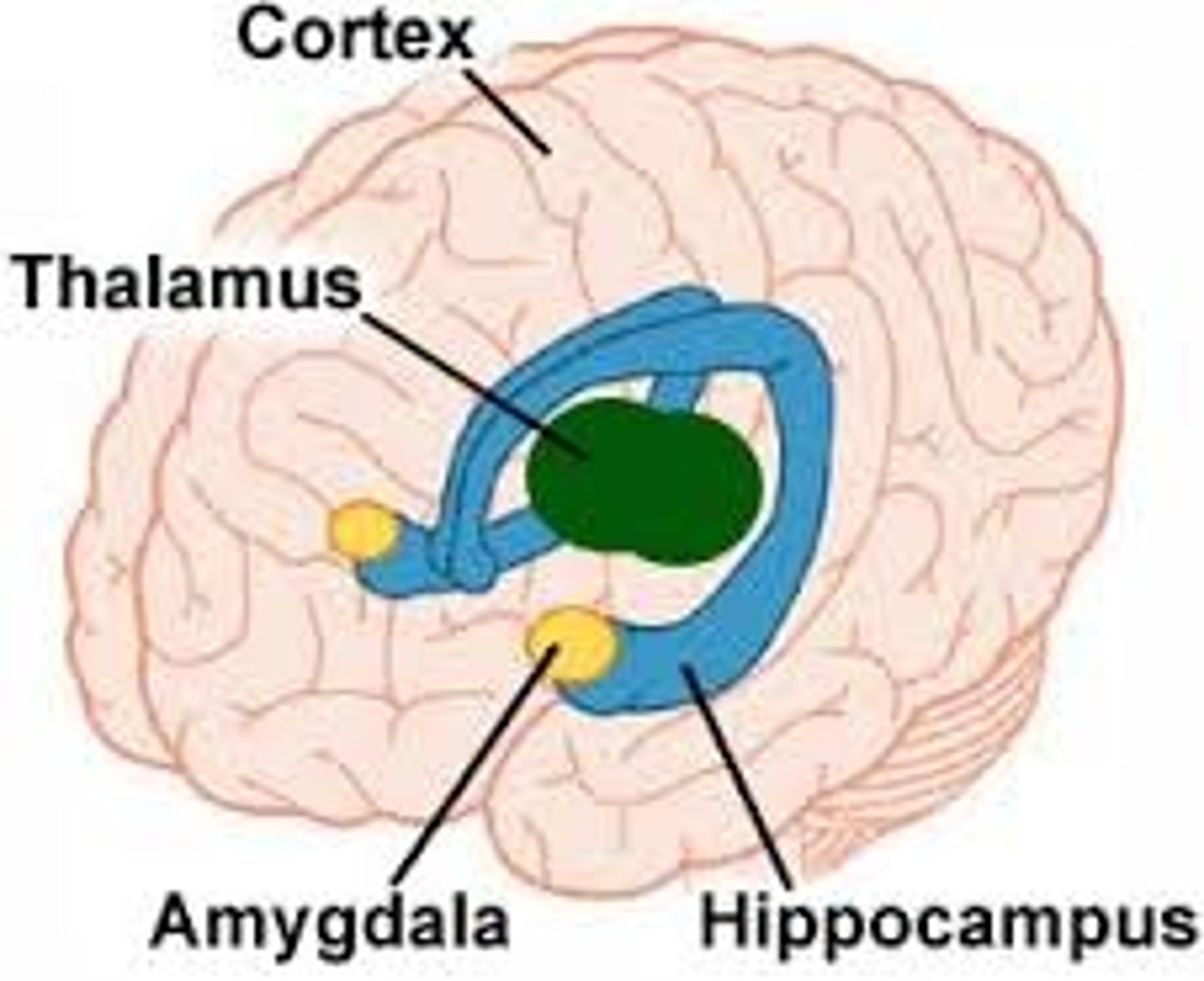
Thalamus
a forebrain structure that processes sensory information for all senses, except smell, and relays it to the cerebral cortex
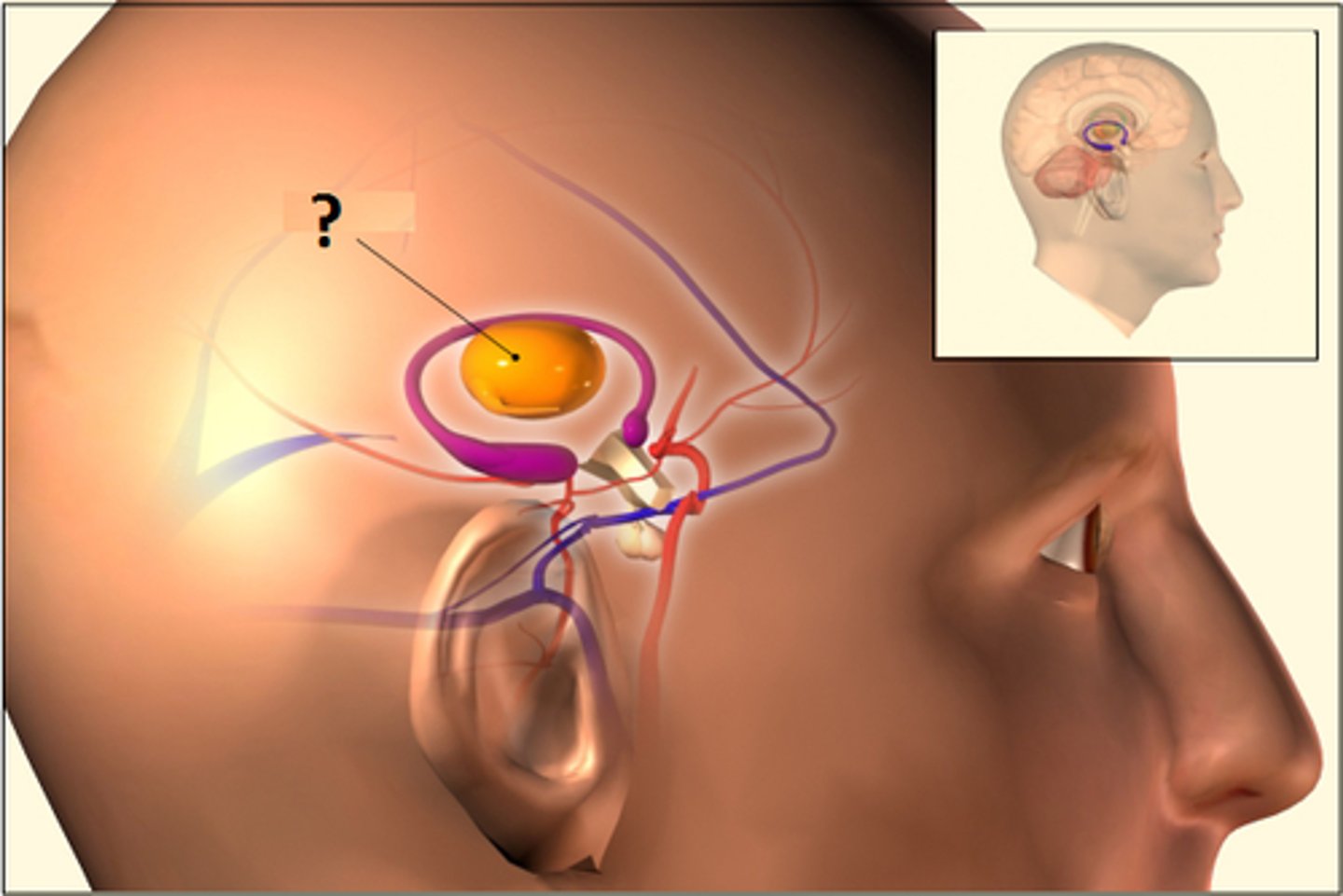
Hypothalamus
a structure below the thalamus responsible for maintaining a constant internal state
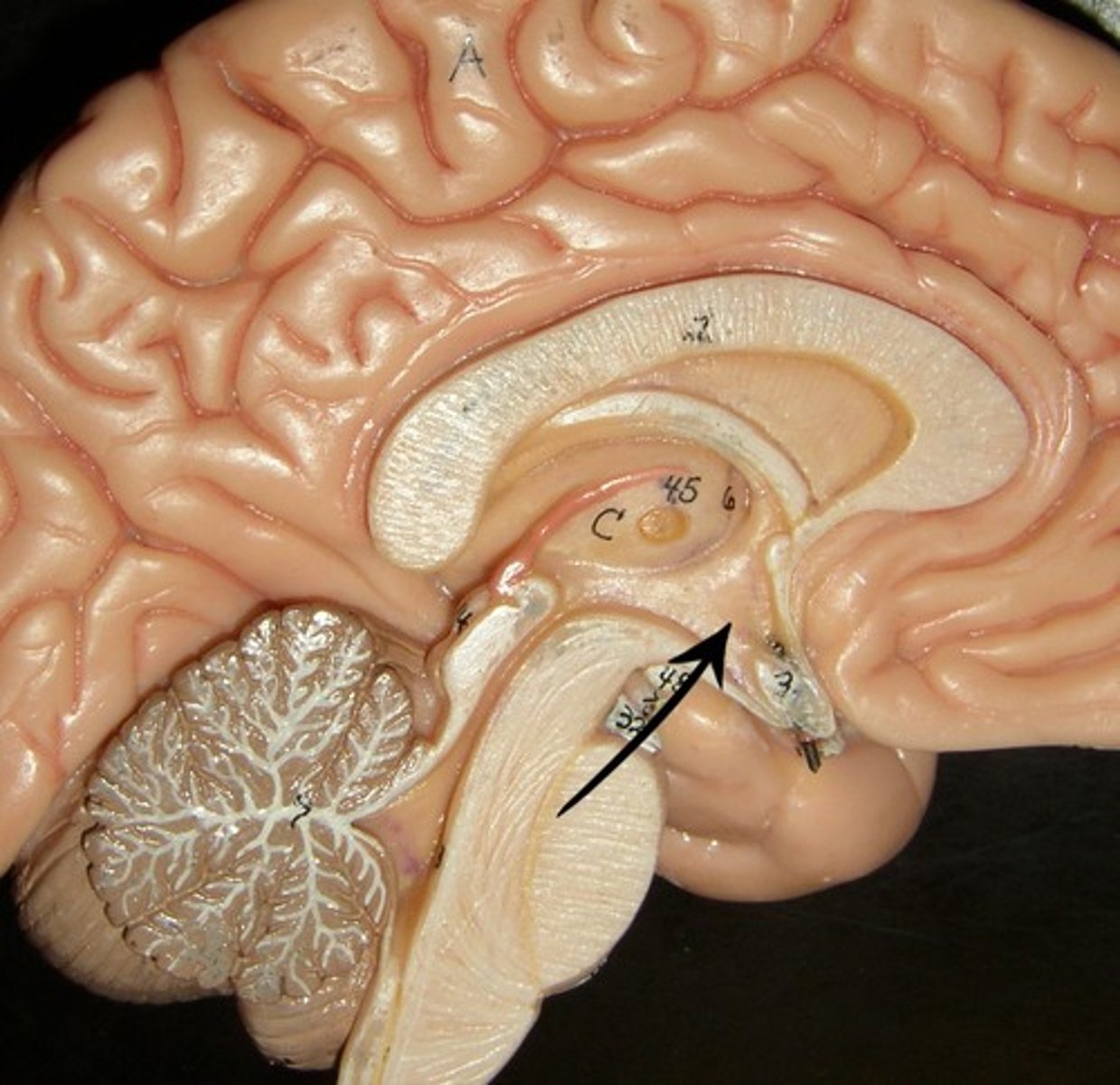
Amyglada
part of limbic system involved in
fear, excitement, and arousal
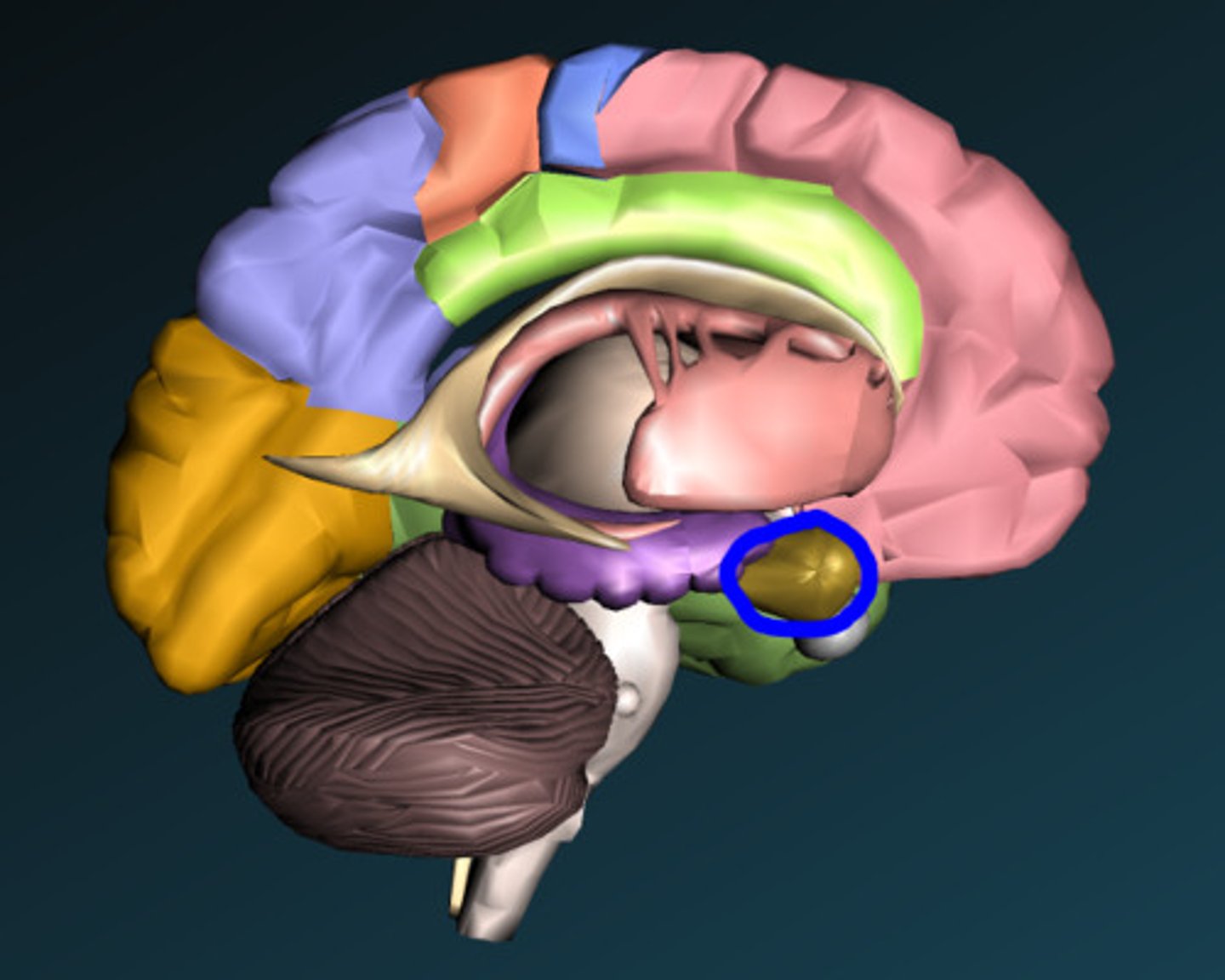
Hippocampus
part of the brain that plays a role in spatial
memory
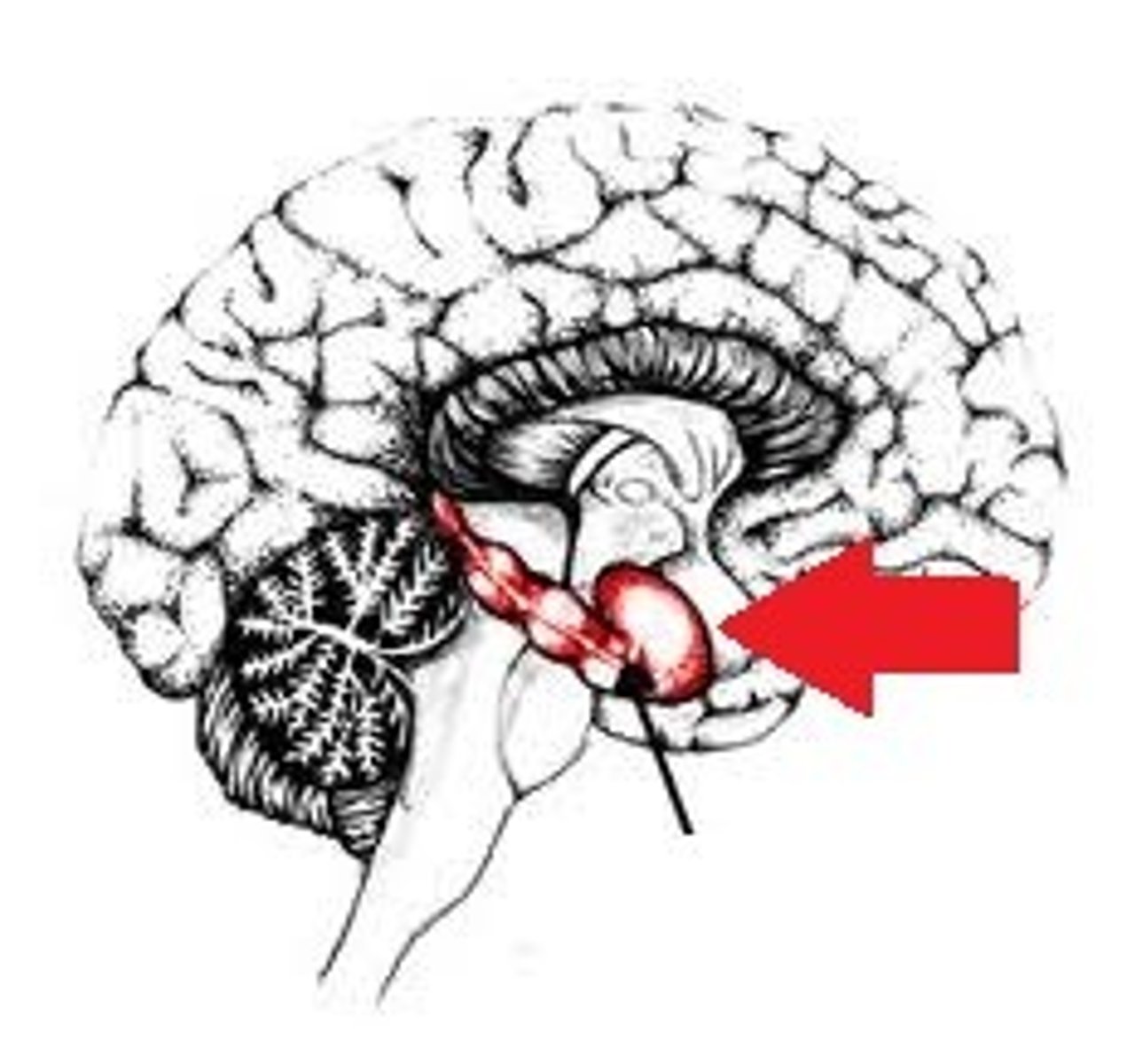
Cerebellum
part of the brain involved in balance for walking, standing, and other complex motor function
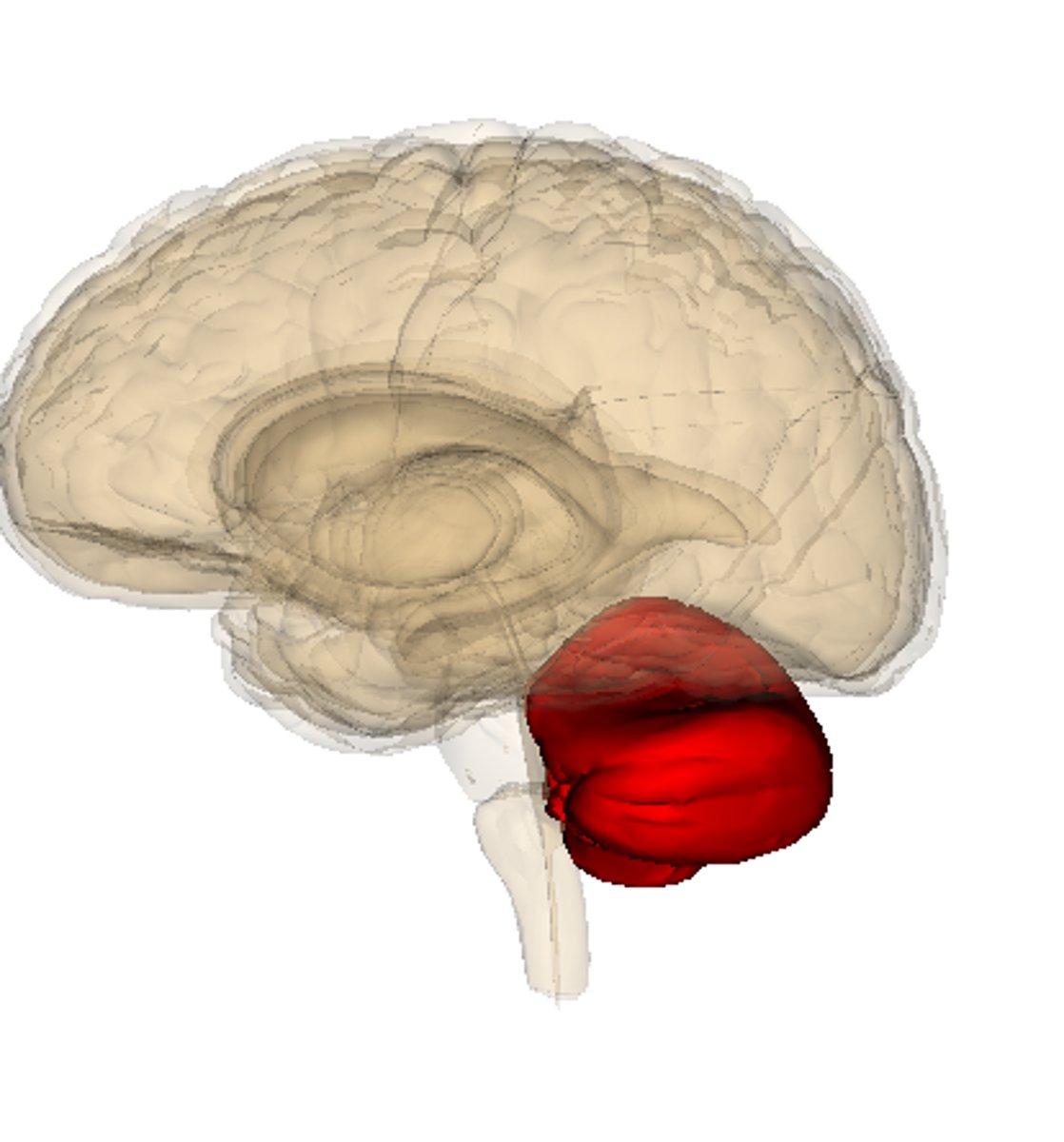
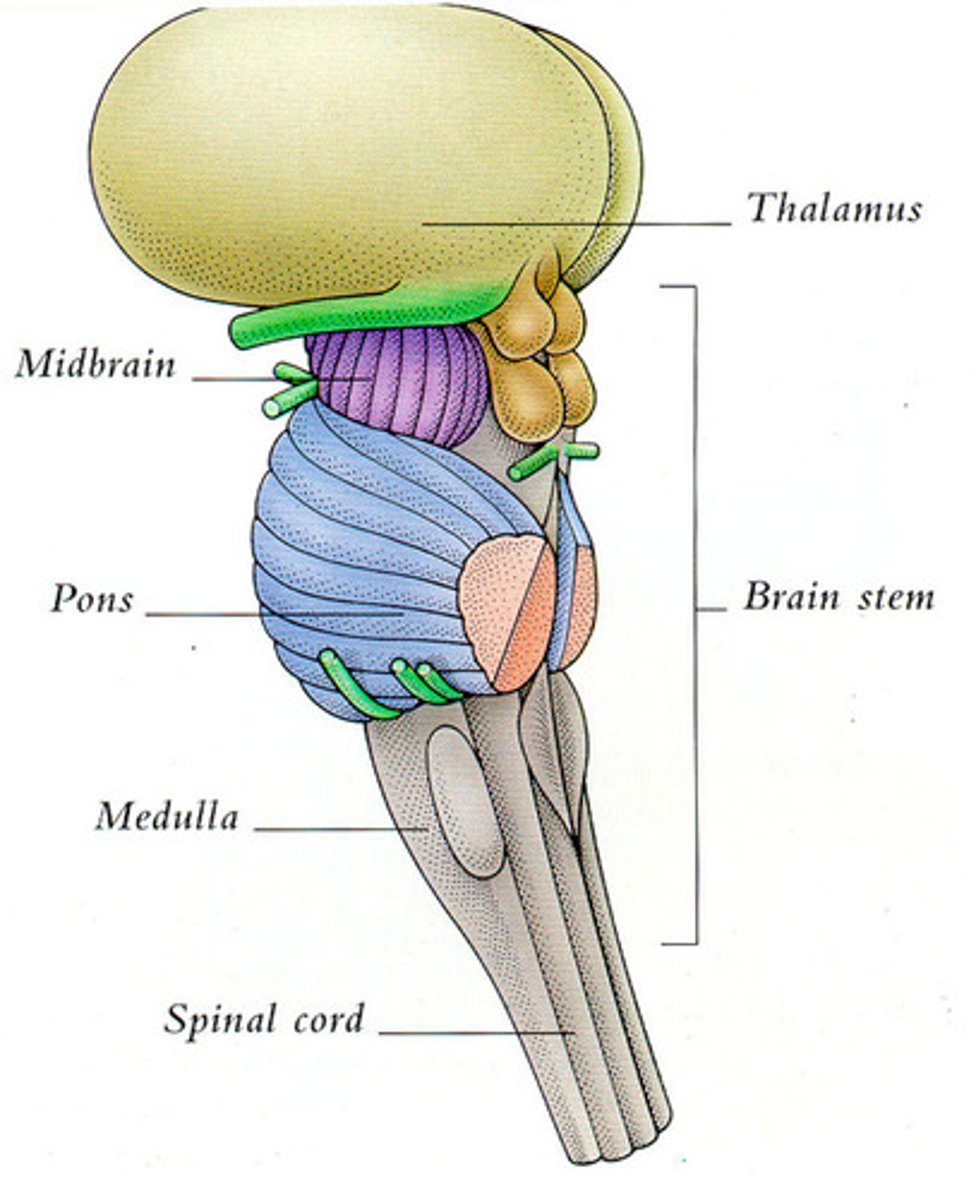
Brain stem
contains the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata; connects the cerebrum to the spinal cord and cerebellum
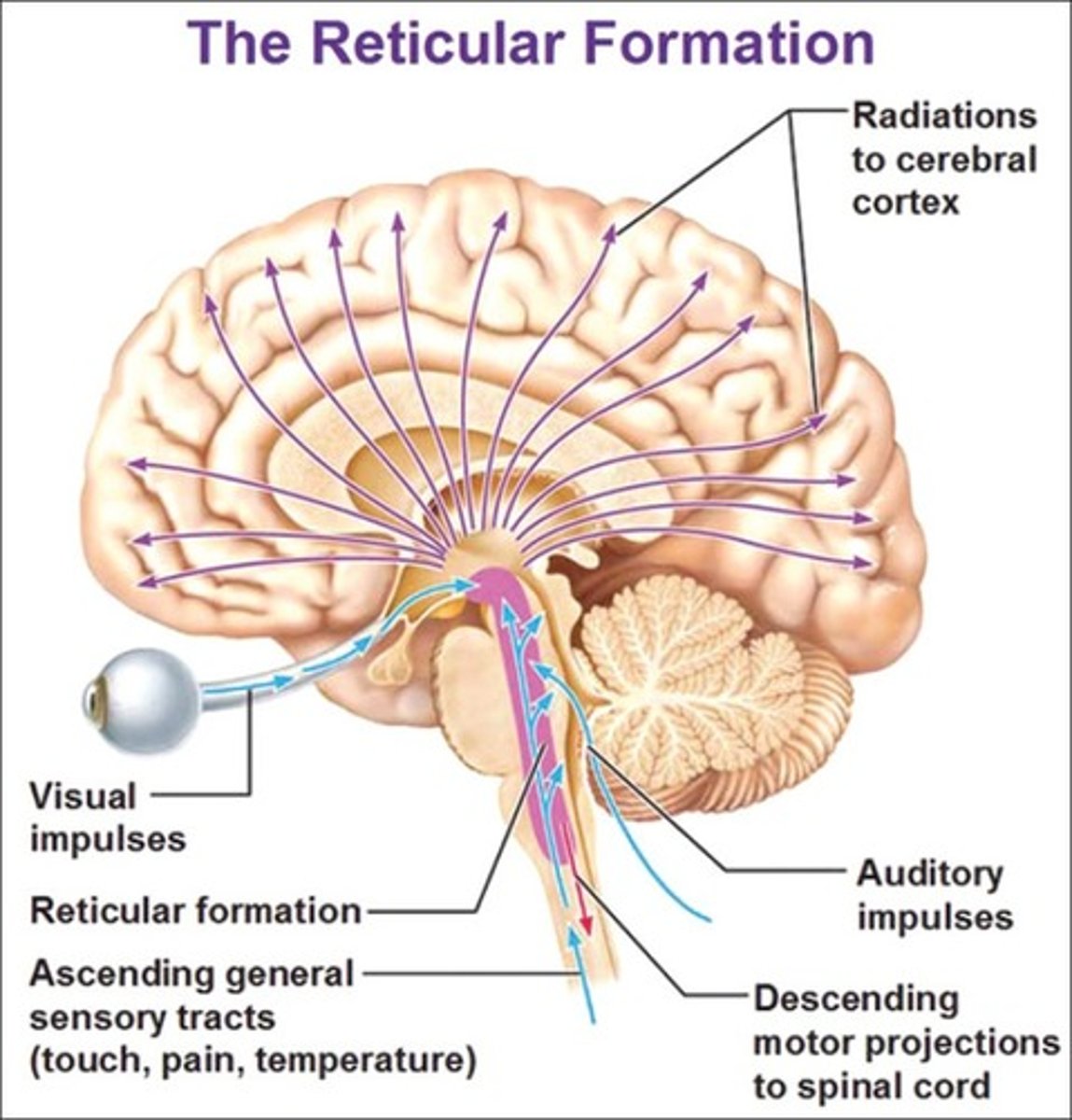
Reticular activating system (RAS)
network of neurons in the brain stem involved in mediation of behavior and arousal
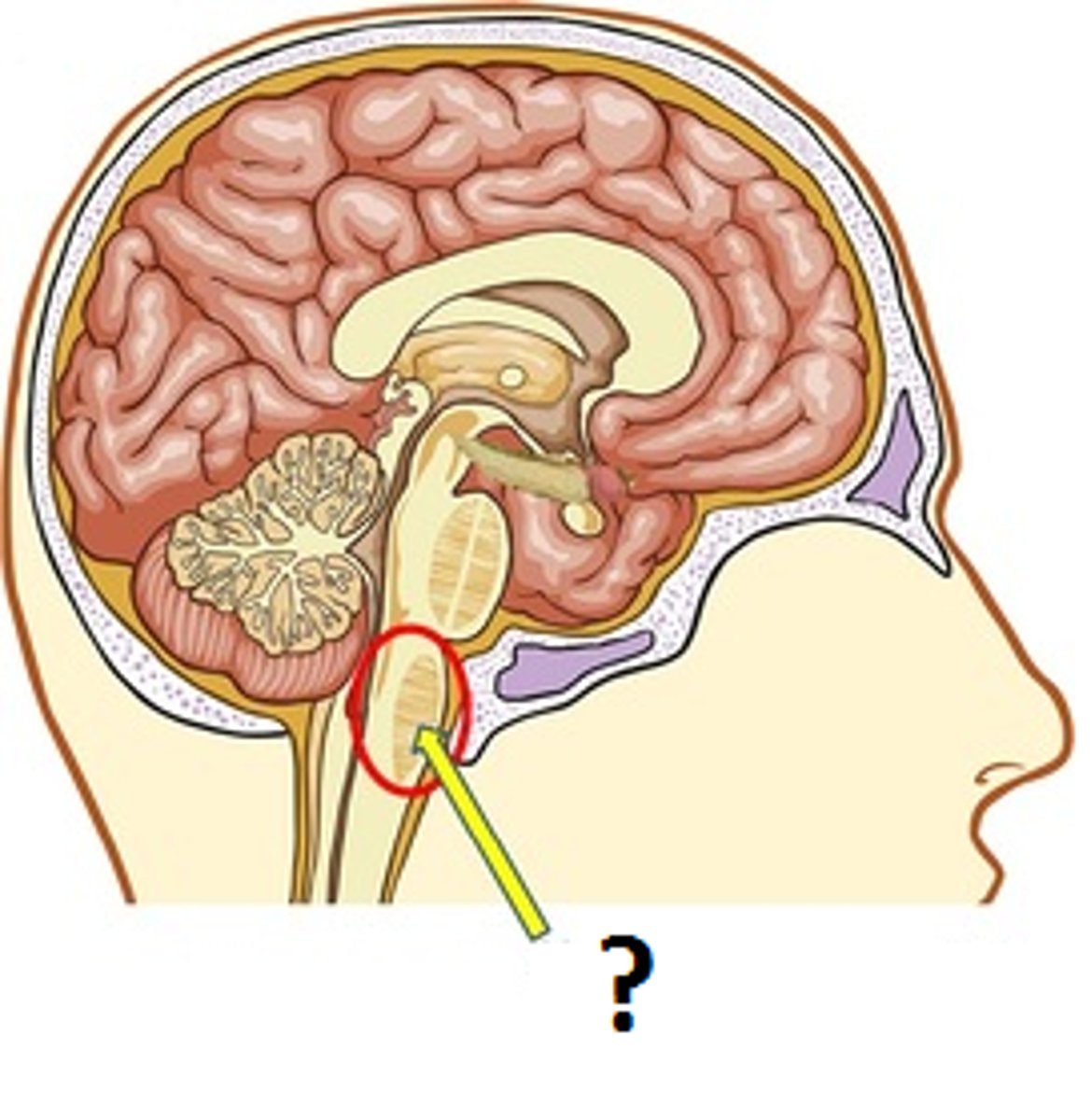
Medulla
part of brain stem involved in basic functions, such as heartbeat, breathing, and blood pressure
Pituitary gland
makes, stores, and releases several important hormones including those for growth and metabolism
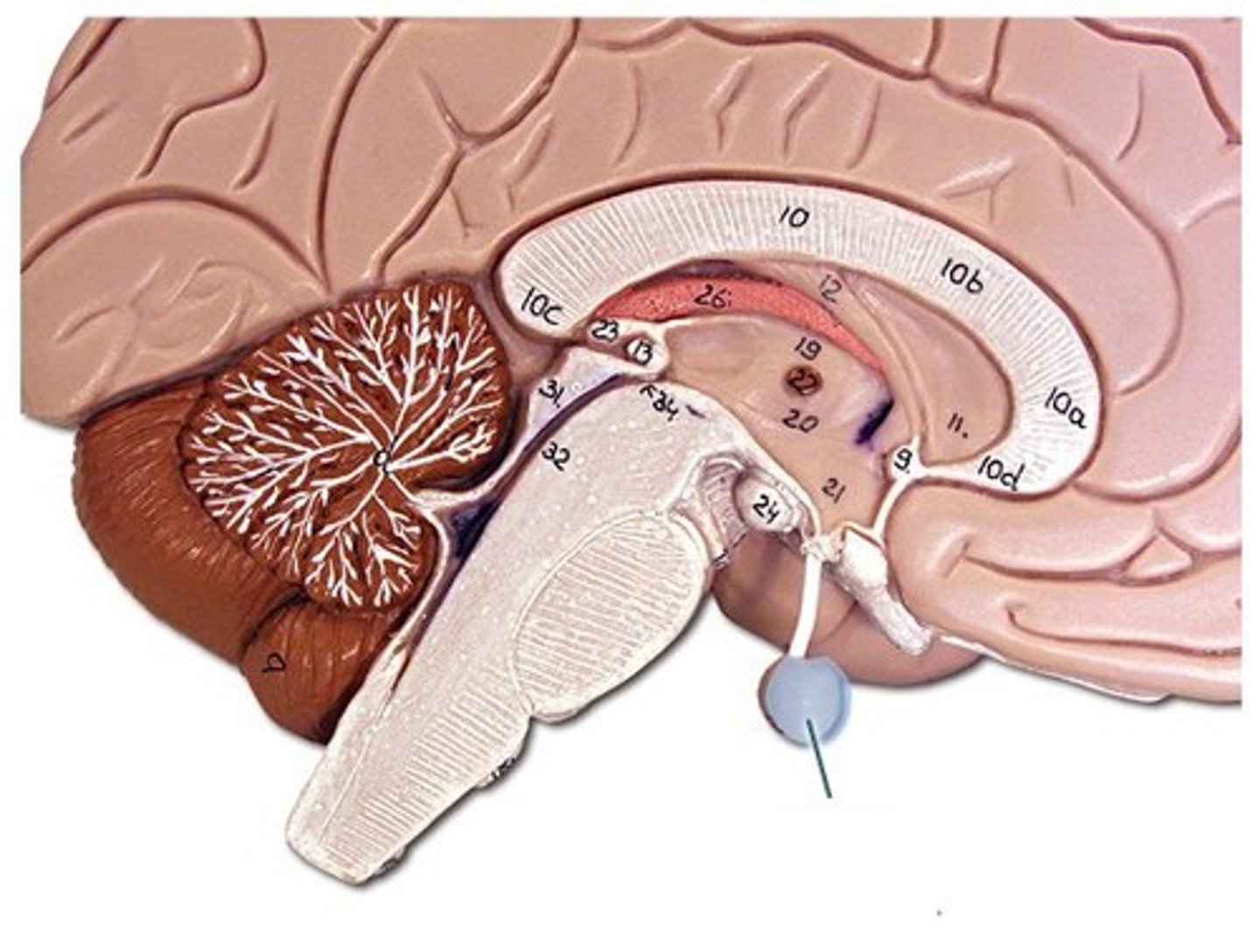
Electroencephalograph (EEG)
recording of the brain's electrical activity at the
surface of the skull
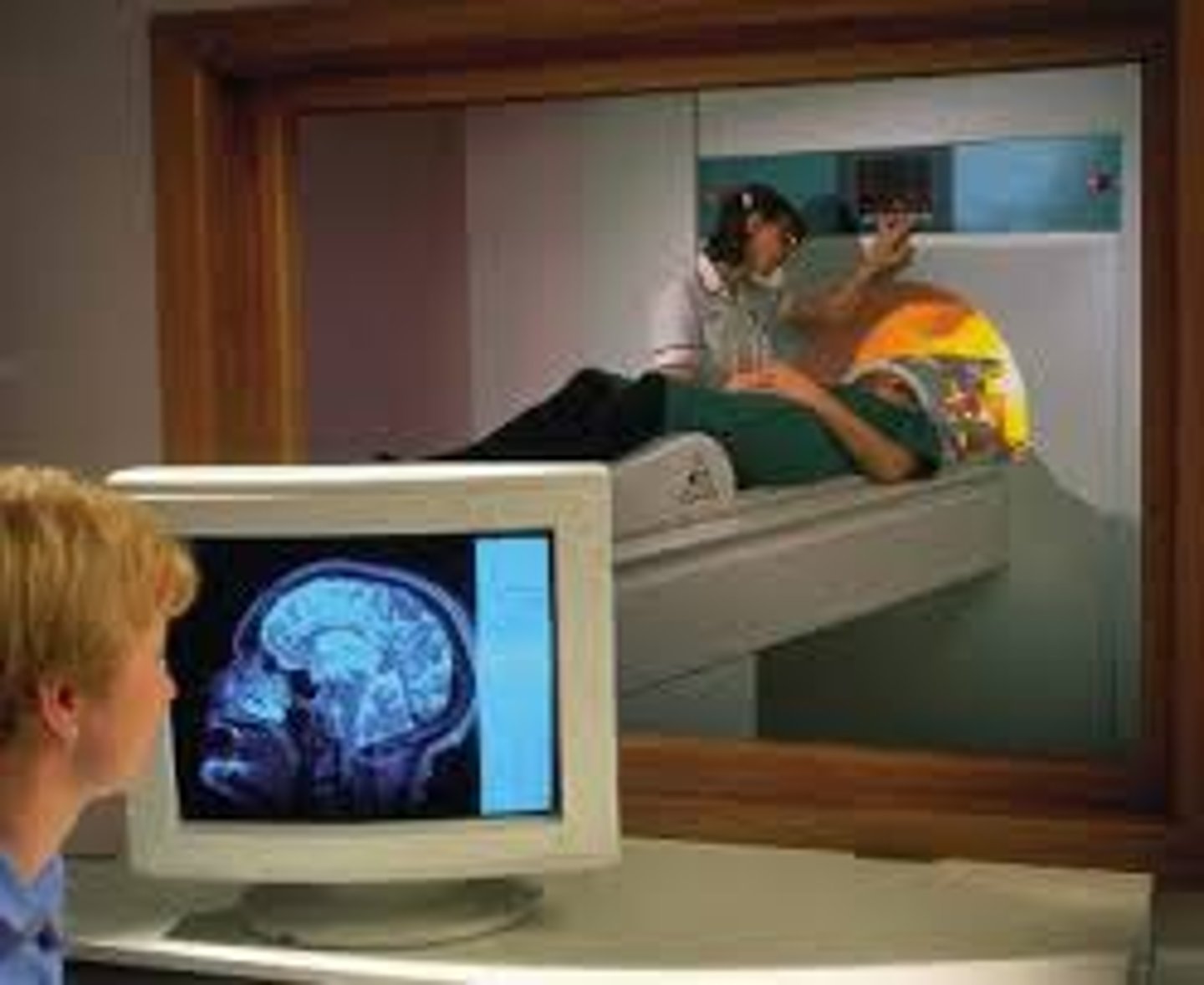
fMRI
a type of MRI scan that can show which areas of your brain are most active during specific functions
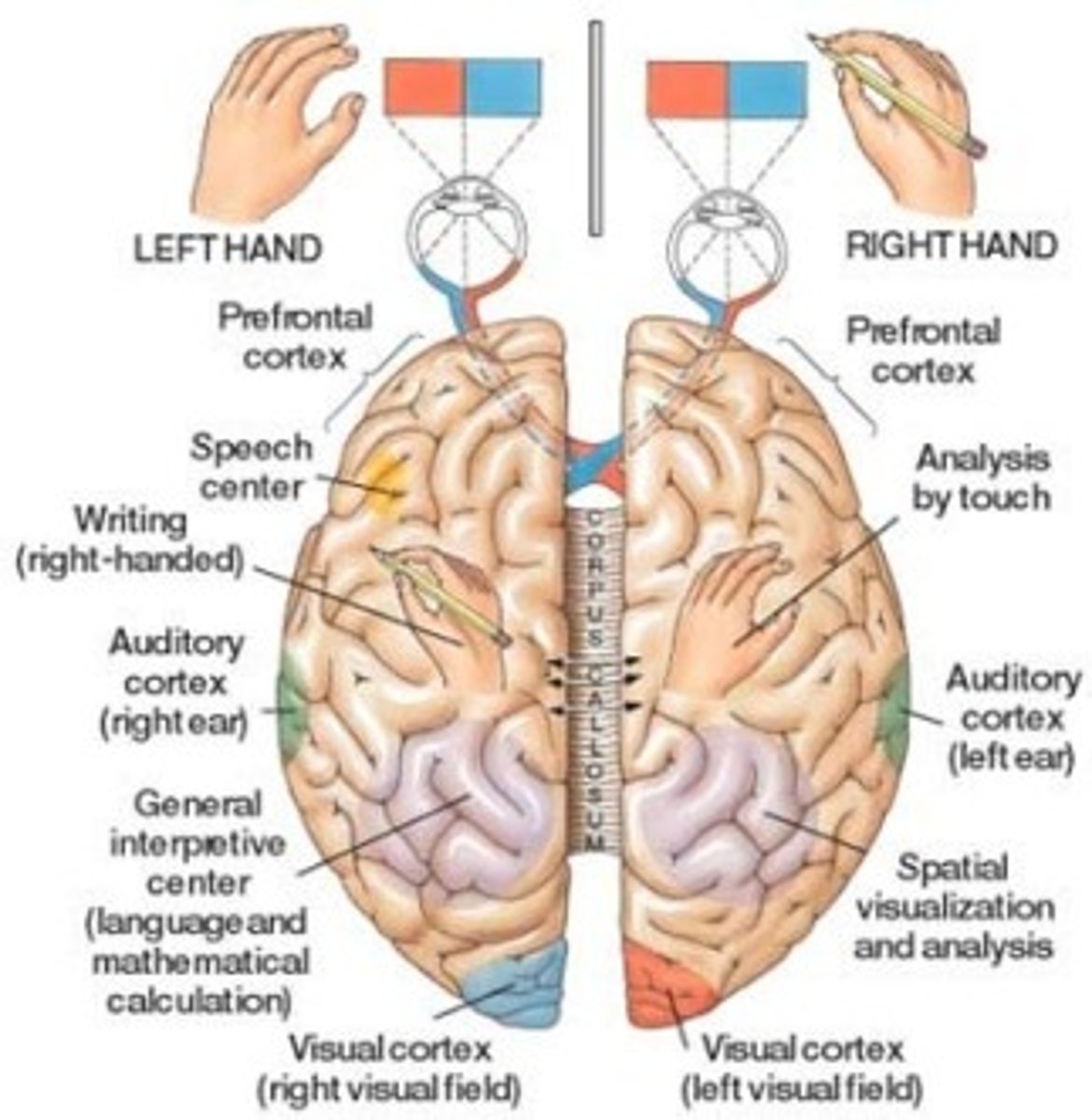
Split-brain research
study of patients with a severed corpus callosum; demonstrates right and left brain specialization; has been used to treat epilepsy
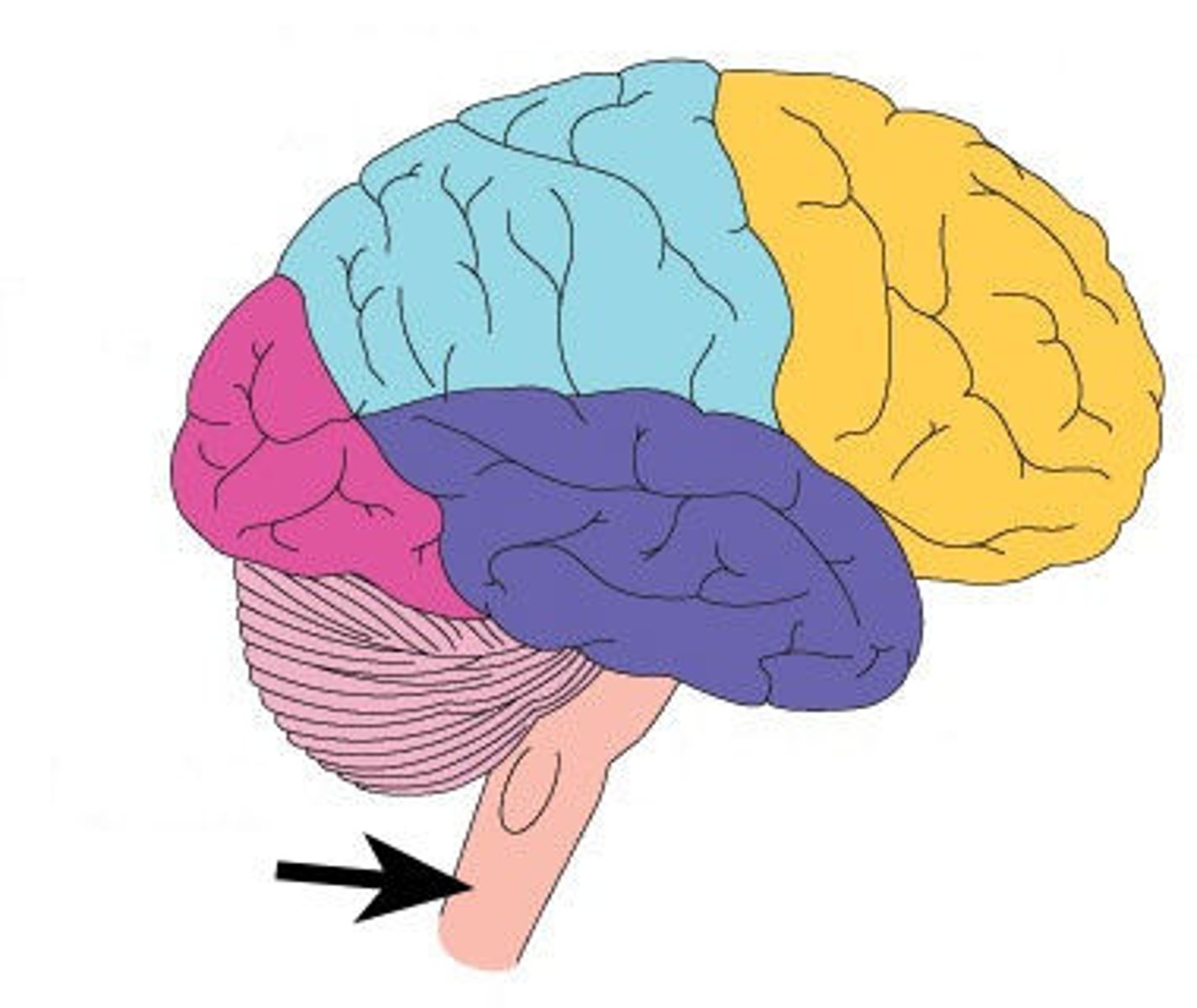
Brain stem
connection to spinal cord that filters information flow between peripheral nervous system and the rest of the brain
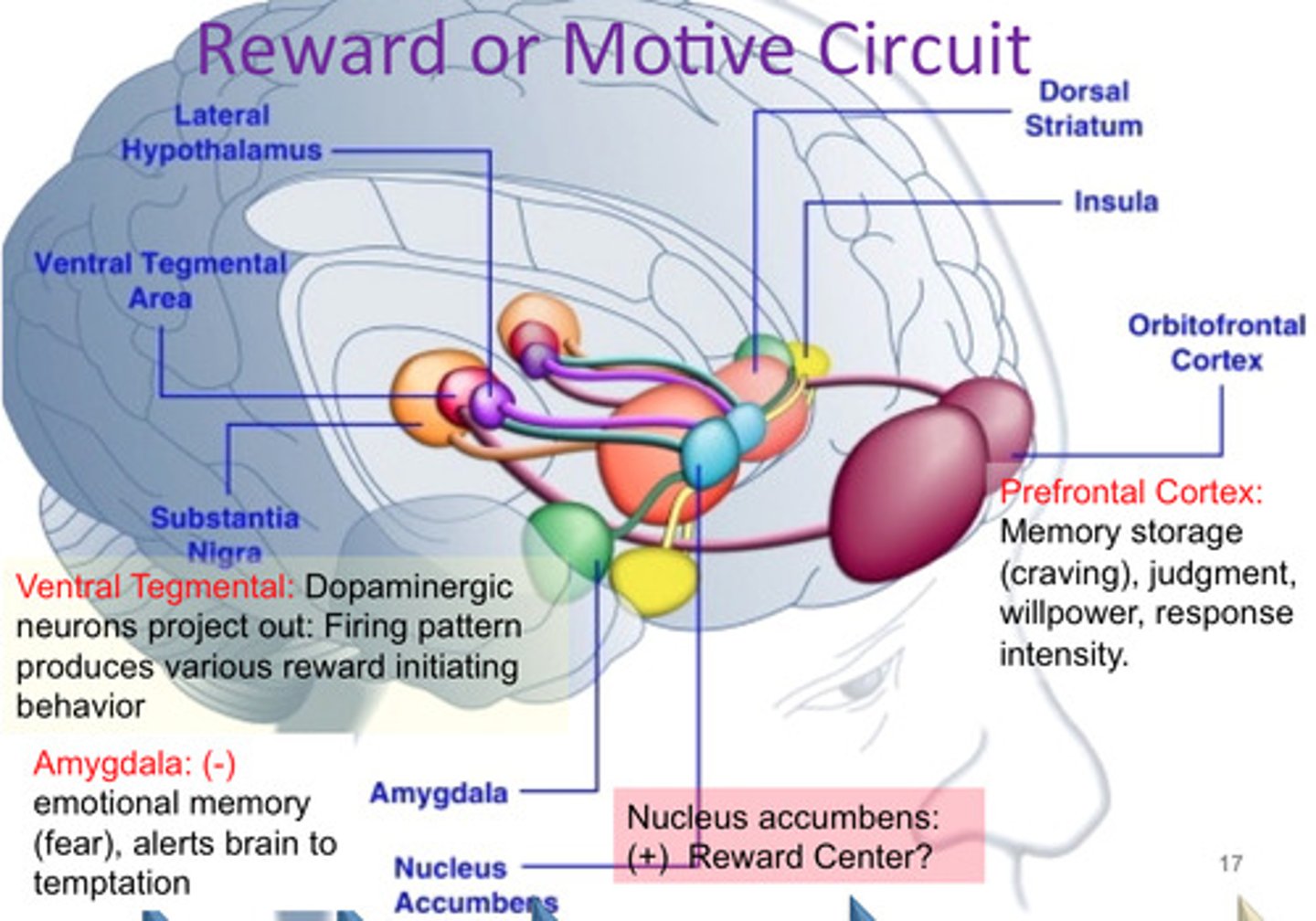
Reward center
a dopamine-rich pathway in the brain that produces feelings of pleasure when activated
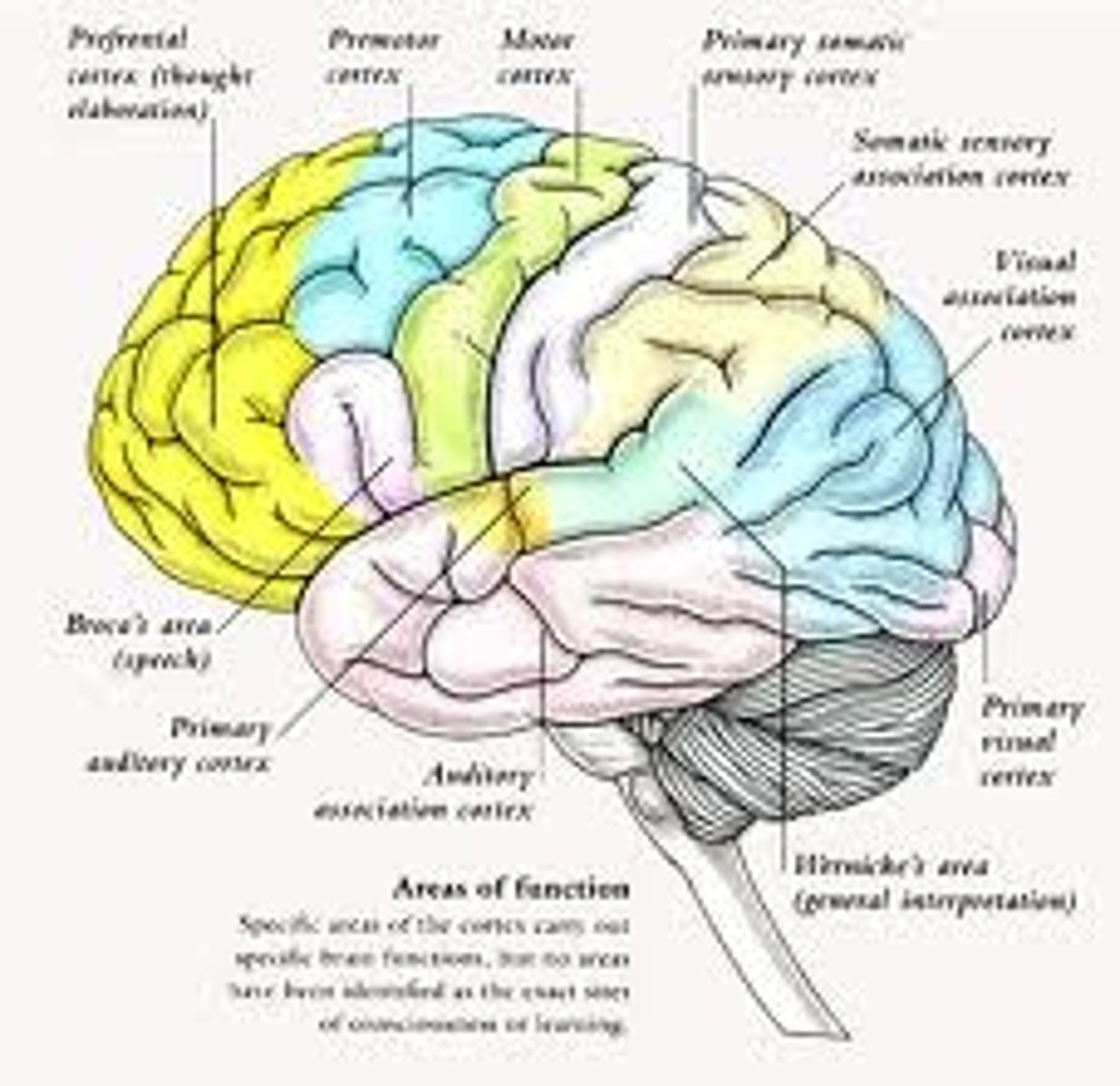
Association areas
areas of the cerebral cortex responsible for the coordination and interpretation of information, as well as higher mental processing
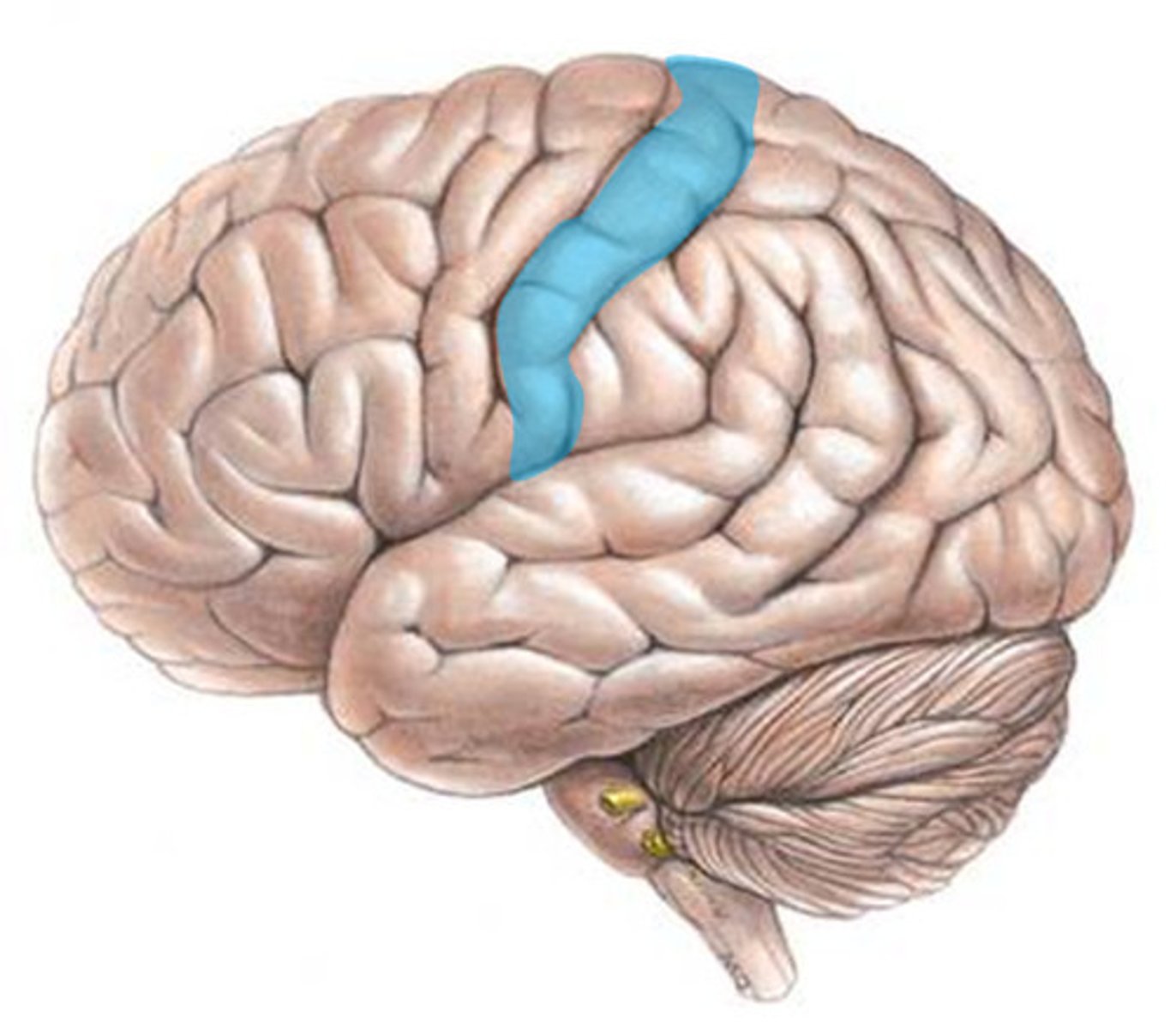
Somatosensory cortex
area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations
Linguistic processing
when language areas of the brain connect meanings of words, grammar, and rules of language to put together an utterance
Higher order thinking
includes higher cognitive skills such as problem solving, thinking, reasoning, planning, and organizing
Executive functioning
a set of mental skills that include working memory, flexible thinking, and self-control
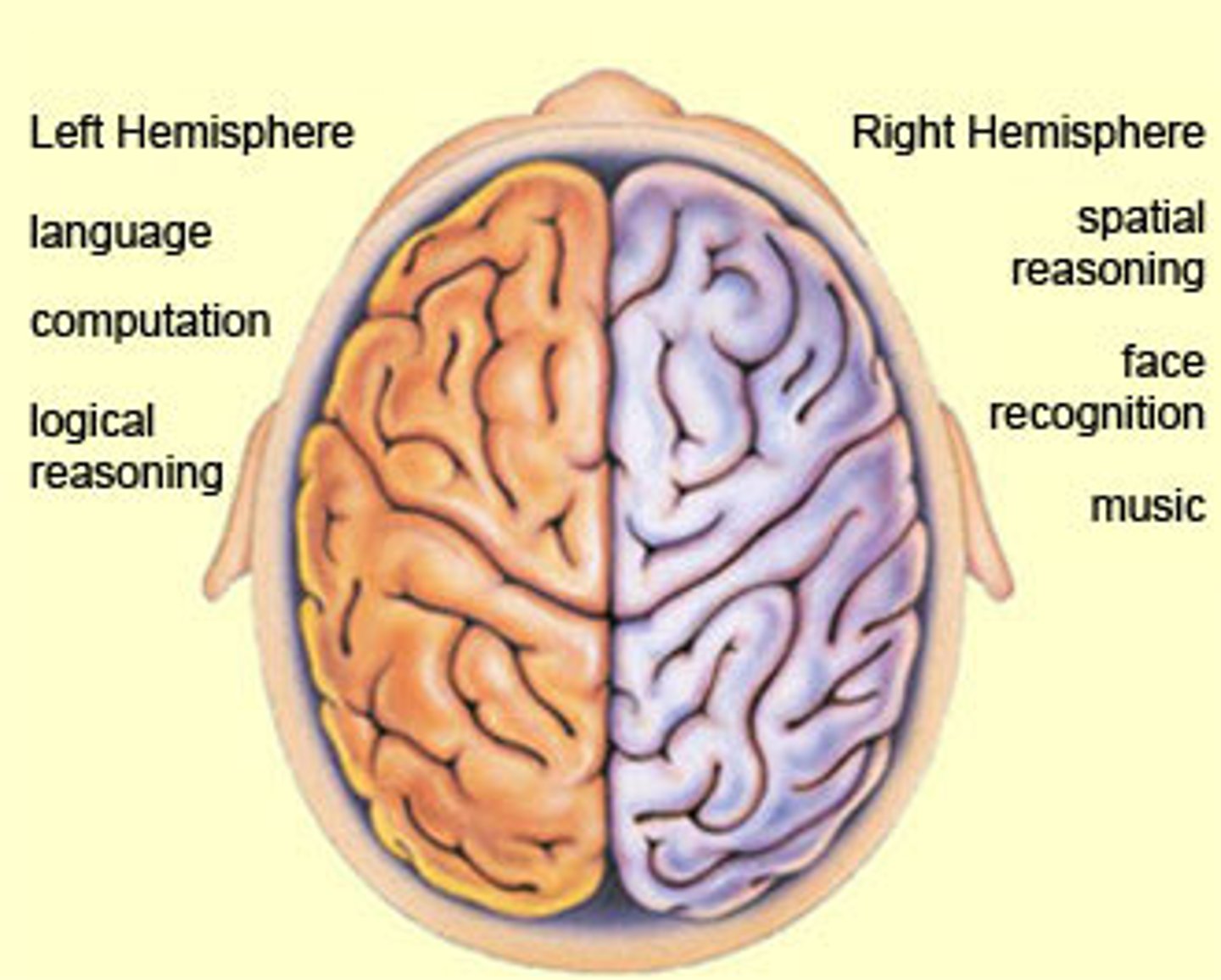
Hemispheric specialization
each hemisphere of the brain handles specific tasks (left - logic, language; right - creativity, spatial reasoning, art, emotion)
Aphasia
impairment of language, usually caused by left hemisphere damage either to Broca's area (impairing speaking) or to Wernicke's area (impairing understanding).
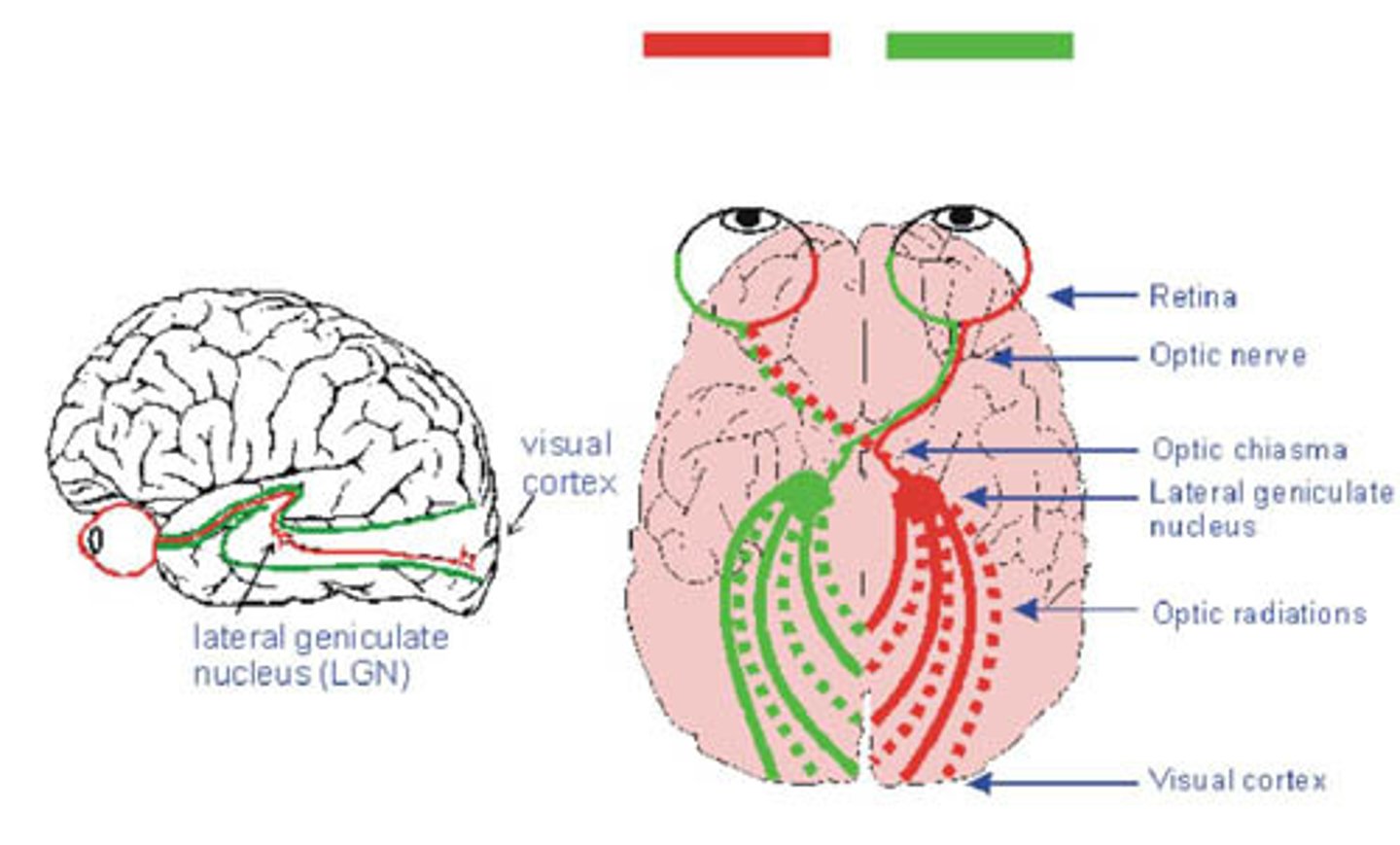
Contralateral hemispheric organization
opposite side communication between the brain and the body (the left side of the brain controls the right side and vice versa)
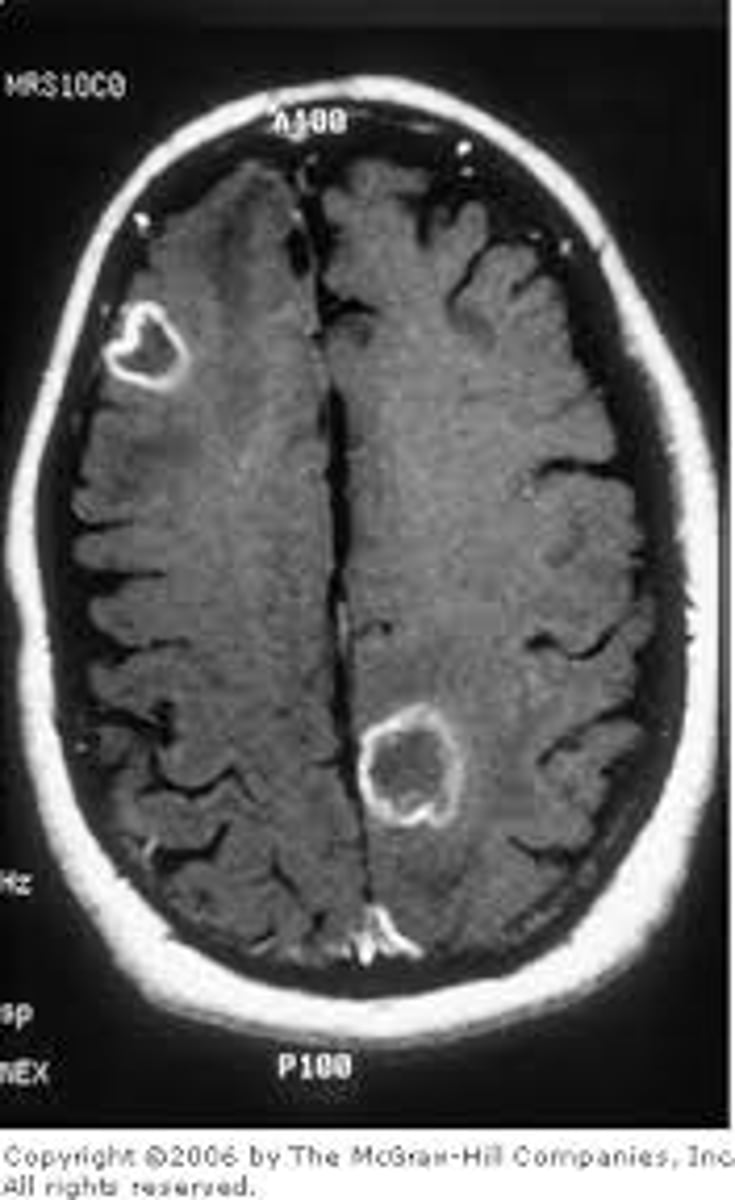
Lesioning
damage to a part of the brain that results in destruction to the neurons; can be natural (like brain injury or disease) or deliberate (surgery)
Plasticity
ability of brain tissue to modify itself and take on new functions