Toes Foot and ankle
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
An AP projection of the second toe reveals that the interphalangeal joints are not open What is the most likely cause for this radiographic outcome
Incorrect or inadequate CR centering or angle
Where is the central ray directed for an AP projection of the toes
third MTP joint
How is the patient placed for a lateral projection of the great toe and second toe
recumbent on affected side
How many degrees are the lower leg and foot rotated for the AP oblique projection of the toes in medial rotation
30 to 45 degrees
How many degrees of angulation are required to open the IP joint spaces of the toes on an AP projection
15 degrees
How many phalanges are in the great toe
Two
A patient comes to radiology for an evaluation of the longitudinal arch of the foot Which of the following projections would provide the best information about the arch
AP and lateral weight-bearing projections of foot
An AP oblique foot with medial rotation demonstrates superimposition of the third through fifth metatarsals How must the original position be changed to eliminate this problem
Decrease obliquity of the foot
An avulsion fracture of the base of the fifth metatarsal is called a ____ fracture
Jones
Extending the ankle joint or pointing the foot and toes downward is called
plantar flexion
For a lateral projection of the foot the central ray is directed to the
base of the third metatarsal
For an AP oblique projection of the foot in either medial or lateral rotation the plantar surface of the foot should form an angle of
30 degrees
How many bones are in the foot
26
How many tarsal bones are in the foot
Seven
How much CR angulation to the long axis of the foot is required for the plantodorsal axial projection of the calcaneus
40°
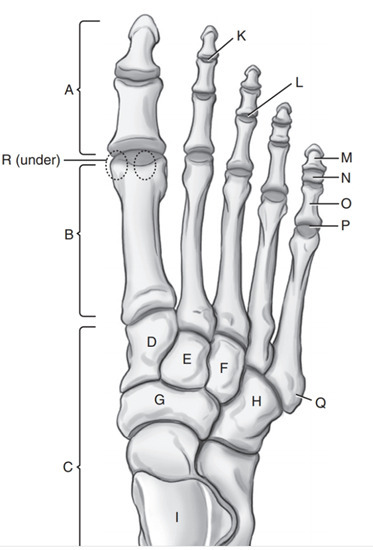
Intermediate cuneiform
E
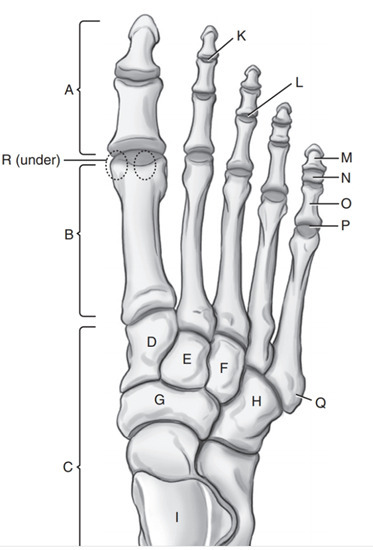
Phalanges
A
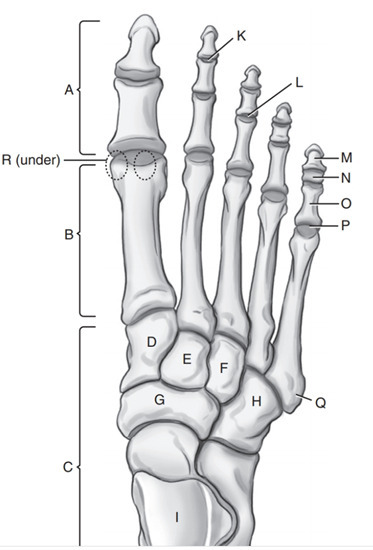
Medial Cuneiform
D
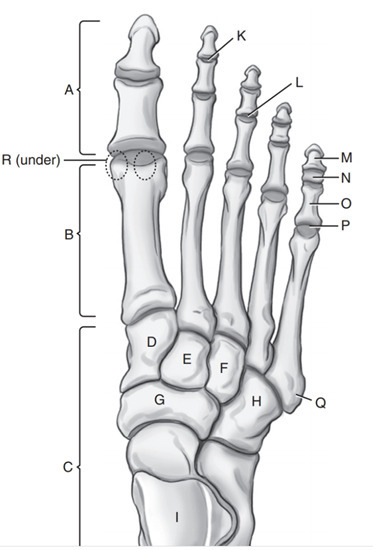
Cuboid
H
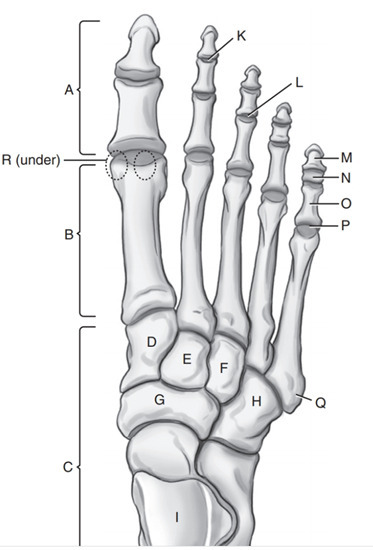
Navicular
G
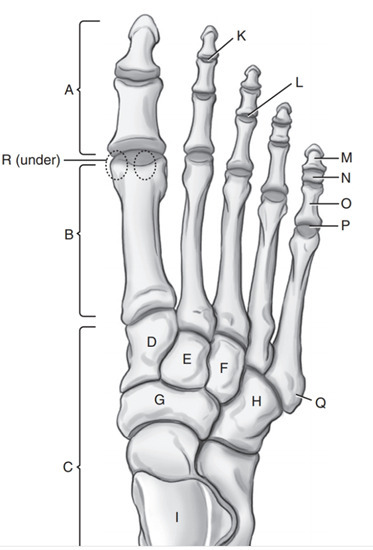
Tarsals
C
On which side of the foot does the cuboid lie
Lateral
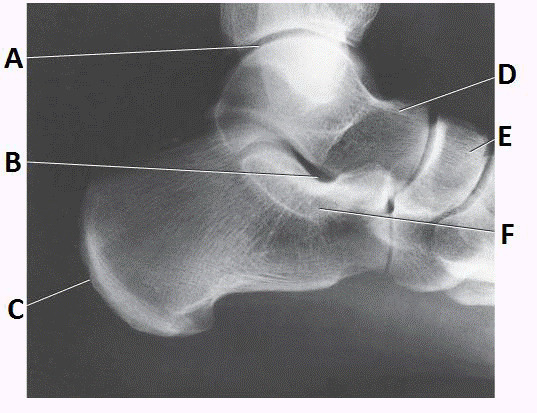
tibiotalar joint
A
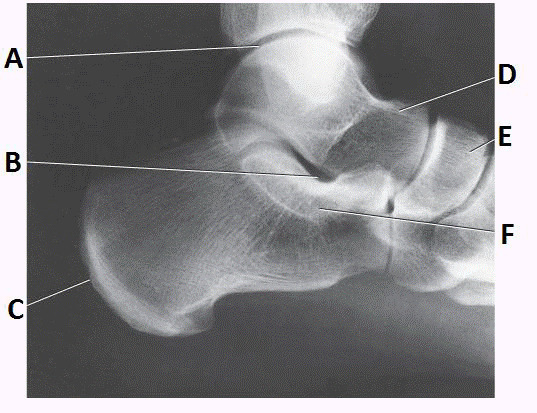
navicular
E
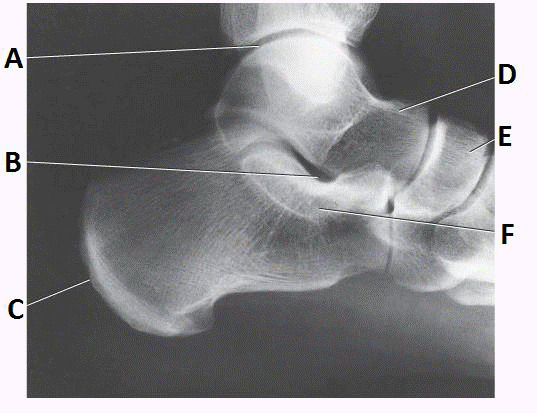
talus
D
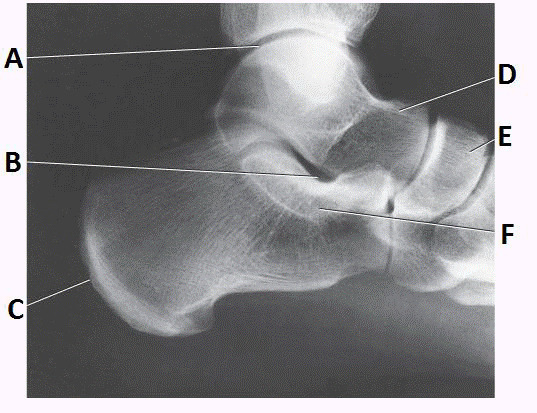
sinus tarsi
B
The central ray angulation for an AP oblique projection of the foot is
0 degrees
The central ray is directed to which of the following for an AP or AP axial projection of the foot
Base of the third metatarsal
The inferior aspect of the foot is termed the _ surface
plantar
The most commonly performed oblique projection of the foot is the oblique in
AP medial rotation
The name of the small round bones located on the plantar surface of the foot typically beneath the first MTP joint is the
sesamoids
The superior surface of the foot is termed the _ surface
dorsal
The talus articulates with how many bones
4
Which lateral projection of the foot is the most commonly performed
Mediolateral lateral recumbent position
Which foot position is performed to demonstrate the cuboid
AP oblique in medial rotation
Which of the following projections would benefit from using a compensating filter
AP foot
A correctly positioned lateral ankle will demonstrate the lateral malleolus superimposed over the posterior half of the tibia
True
Extending the ankle joint or pointing the foot and toes downward is called
plantar flexion
For a lateral projection of the ankle the central ray enters the
medial malleolus
For an AP ankle projection the central ray should be directed to enter at the
ankle joint midway between the malleoli
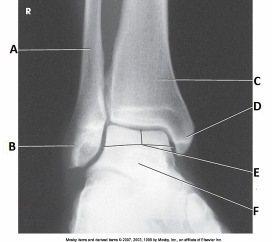
How should the lower limb be positioned to achieve the projection shown in the image below
15- to 20-degree medial rotation
The medial and lateral oblique projections of the ankle require the leg and foot to be rotated how many degrees
45
To prevent lateral rotation how should the foot be positioned for a lateral projection of the ankle
In dorsiflexion
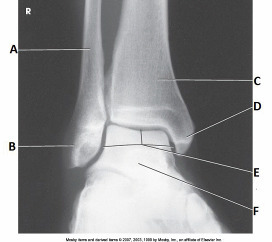
What anatomy is labeled with the letter D in the image below
Medial malleolus