NS 4410 Scurvy Lecture
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
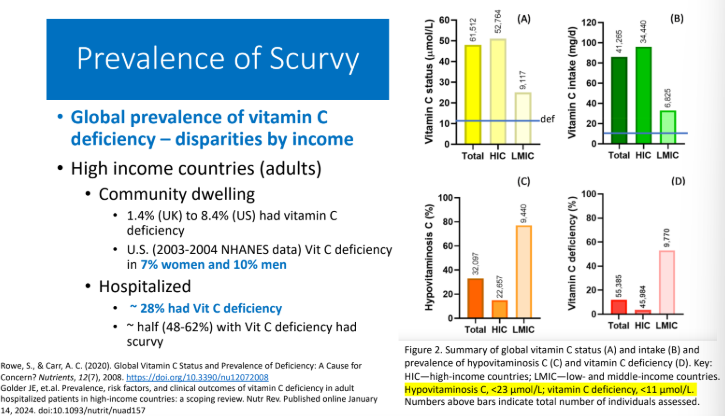
Prevalence of Scurvy
Vitamin C is ____ soluble, an _____ nutrient for humans; and it refers to family of ____ molecules
water; essential; 5
Ascorbic acid appears at ___ ph, it is the _____ form; and is it more or less stable?
acidic; protonated; more stable
What is predominant form of Vitamin C at physiologic pH (7.4)?
Ascorbate monoanion
What form of Vitamin C is 80-90% of vit c in foods?
Ascorbate monoanion
Ascorbate monoanion is what two things for many physiological reactions?
electron donor and antioxidant (reducing agent)
What is the fully oxidized form of vit c?
dehydroascorbic acid (DHA)
Dehydroascorbic acid rapidly what at physiological pH?
degrades
DHA can be reduced to _____ via recycling pathways
ascorbate
What are 3 examples of Enzymatic functions of Vit C?
Neurotransmitter (NT) and catecholamine synthesis
Collagen synthesis
Carnitine synthesis
What are 3 examples of Non-enzymatic functions of vit c?
Anti-oxidant
Non-heme iron absorption
Enhances immune function
As an electron donor, vit c maximizes activity of several enzymes involved in what 3 things?
Synthesis of catecholamines → epinephrine & norepinephrine
Synthesis of vasopressin (ADH)
Posttranslational modification of peptide hormones and neurotransmitters → TRH, GnRH,
oxytocin, CCK, gastrin, calcitonin, substance P,
neuropeptide Y
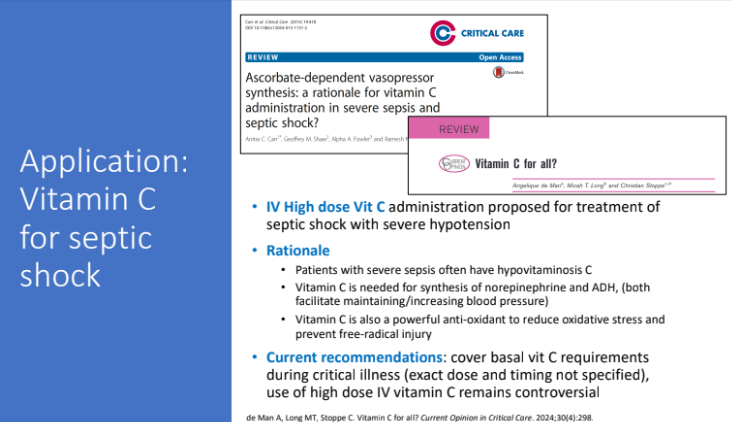
Application: Vitamin C for septic shock” What is the rationale behind this?
Patients with severe sepsis often have hypovitaminosis C
vitamin C is needed to synthesis of norepinephrine and ADH (both facilitate maintaining/increasing blood pressure)
vitamin C is also a powerful anti-oxidant to reduce oxidative stress and prevent free-radical injury
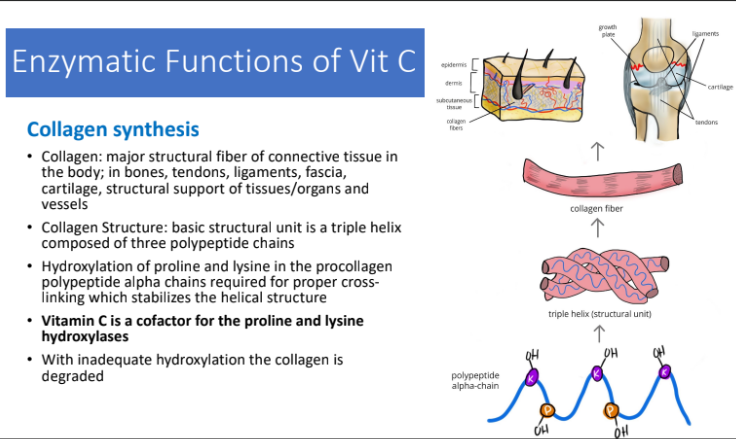
Enzymatic functions of Vit C: Collagen Synthesis: Hydroxylation of proline and lysine in the procollagen polypeptide alpha chains required for proper?
crossing-linking which stabilizes the helical structure
Vit C is a cofactor for?
the proline and lysine hydroxylases
with inadequate hydroxylation the collagen is degraded
Application: Vitamin C in wound healing: Vitamin C deficiency leads to what 3 things related to wound healing?
Impaired collagen formation
Reduced tensile strength of wounds (tear when stretched)
Increase risk of wound dehiscence (opening) and slowed healing
Vitamin C requirements may be increased with large open
wounds (pressure ulcers) to facilitate? For what reasons?
tissue regeneration
collagen formation, antioxidant properties, and possibly increased proliferation of dermal fibroblast
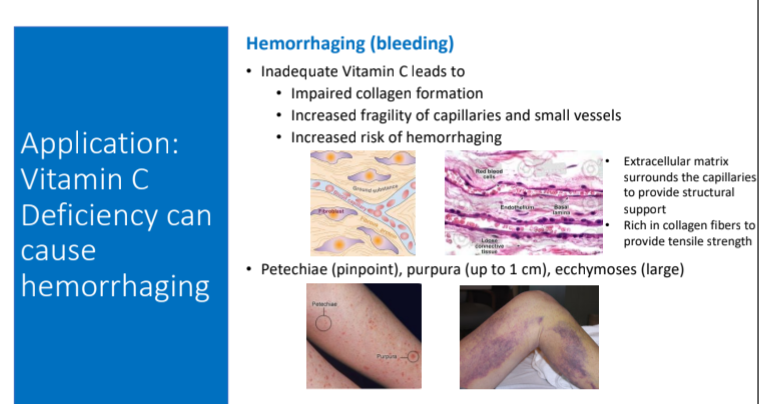
Application: Vitamin C Deficiency can cause hemorrhaging: Inadequate Vit C leads to what 2 things involved with hemorrhaging (bleeding)?
Impaired collagen formation
Increased fragility of capillaries and small vessels
^Increased risk of hemorrhaging
Enzymatic Functions of Vitamin C: Carnitine Synthesis. Vitamin C participates in two ____reactions required for the synthesis of carnitine from its amino acid precursors?
hydroxylation; lysine and methionine
What does carnitine catalyze?
the transport of long chain fatty acids from cytosol of cells into the mitochondrial matrix for subsequent B oxidation and ATP synthesis
Reductions in carnitine biosynthesis theorized to contribute to symptoms of?
fatigue with vit C deficiency
Non-enzymatic functions of Vitamin C: It is a powerful biological antioxidant and free radical scavenger. Which form acts as a electron donor to free radicals, neutralizing them?
Ascorbate
Vit C protects against ______associated with inflammation
oxidative damage
Who has increased inflammation and therefore increase needs for vit c
Smokers → in conditions with high levels of inflammation observe lower levels of vit c and increases the need
How does Vit C increase non-heme iron absorption?
in the gut lumen, ascorbic acid reduces ferric form (Fe3+) to ferrous form (Fe2+) that can be absorbed
Fatigue is a common symptom in scurvy. Impairment of which of the following functions of vitamin C could result in fatigue when vitamin C is deficient?
i. Collagen synthesis
ii. Carnitine synthesis
iii. Catecholamine synthesis
iv. Biological antioxidant
v. Non-heme iron absorption
ii, v
Vit C is a water-soluble essential micronutrient because humans lack what needed for synthesis of vit c?
gluconolactone oxidase (GULO)
There is a limited ability to store vit c. What is the total body pool?
~1500 mg (need nearly daily intake to maintain tissue stores)
The RDA for vit c is higher than amount needed for prevention of?
deficiency, set at levels adequate to support antioxidant and physiologic functions
What populations have an increased need of vit c? What is the upper limit and why?
Infants, pregnancy, lactation, smokers
2000 mg/day for adults, due to GI side effects of nausea, cramping, diarrhea

Are Current Vit C Recommendations Adequate?Collagen related pathologies and Vitamin C requirements: Recent re-analysis of data from depeletion/repletion studies suggest HIGHER intake (95 mg/day) vit c needed to prevent and treat?
collagen related pathologies (Weak scar strength) for 97.5% of the population
Bleeding tendency and Vit C requirements: Gingival bleeding and retinal hemorrhages occur at low or high plasma ascorbic acid levels which are above the plasma level for?
low'; diagnosis of scurvy
Food Sources of Vitamin C: Vit c is very unstable; lost in cooking due to? and in storage due to? It is best preserved in?
Lost in cooking due to heat sensitivity and water soluble
Storage → oxygen and light exposure
Best preserved in acidic pH (most stable form)
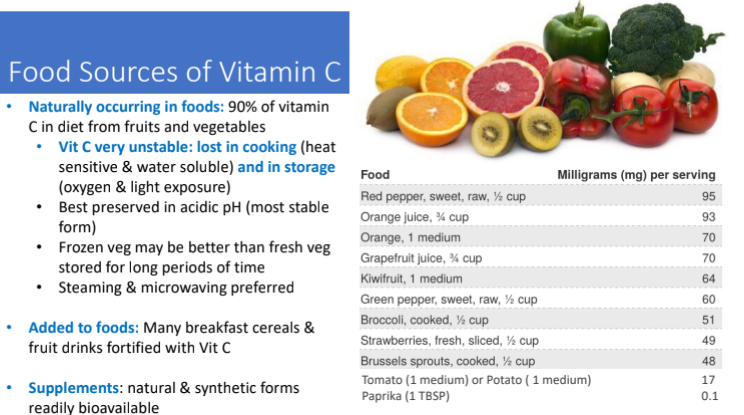
10 mg of vit c may be adequate to?
prevent overt symptoms and signs of frank scurvy but fails to maximize health
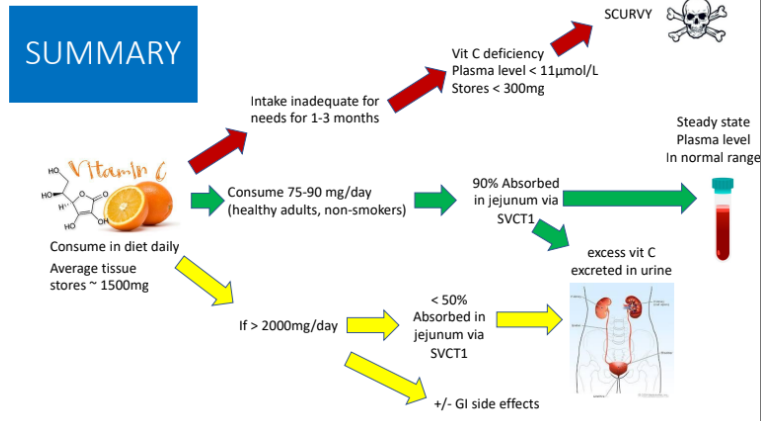
Absorption and Bioavailability of Vitamin C: Ascorbate and dehydroascorbic acid are absorbed in?
jejunum; absorption near complete with typical dietary intake
>90 % of typical dose (up to ___ mg) of vit c is absorbed in healthy persons
200 mg
At higher doses, we see less bioavailability; What are the absorption rates with 500 mg and 1250 mg?
500 mg → 70%
1250 mg → 50%
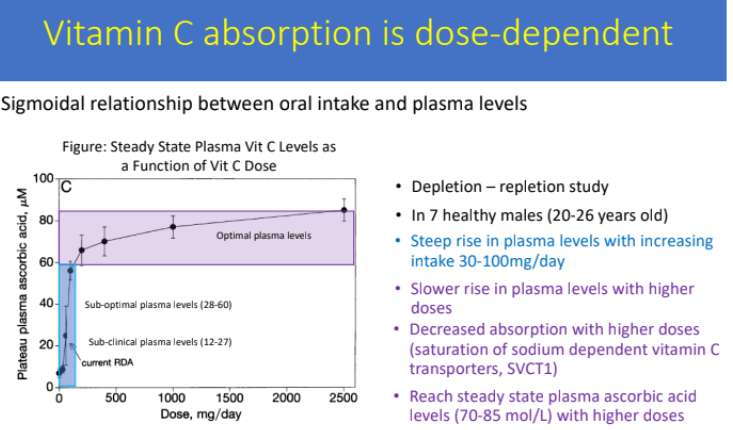
Vitamin C absorption is dose-dependent: There is what type of relationship between oral intake of vit C and plasma levels?
sigmoidal
steep rise in plasma levels with increases intake 30-100 mg/day
SLOWER rise in plasma levels with higher doses
Reach steady state plasma ascorbic acid levels (70-85 mol/L) with higher doses
There is decreased absorption with higher doses. Why?
Sodium dependent vit c transporters (SVCT1) gets saturated
Plasma Vit C levels tightly controlled. Single doses (over 200 mg) produce what in plasma level?
transient peak in plasma level
vitamins C plasma concentrations tightly controlled
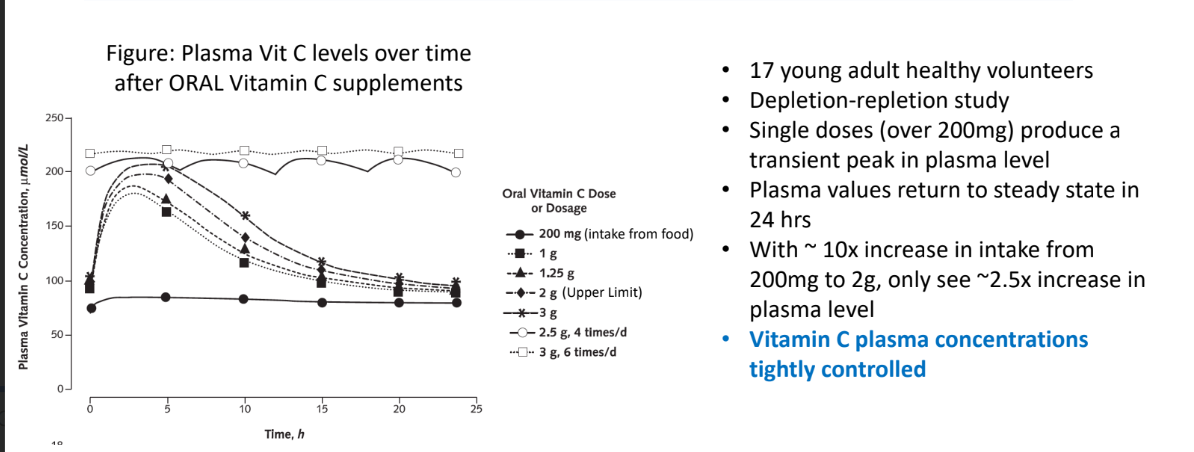
What are the 2 ways the could body maintain a steady state Vit C plasma level with increasing oral doses above 200mg?
Decrease absorption of vit C from the GI tract
Increase excretion of vit C (via the kidney, in the urine)
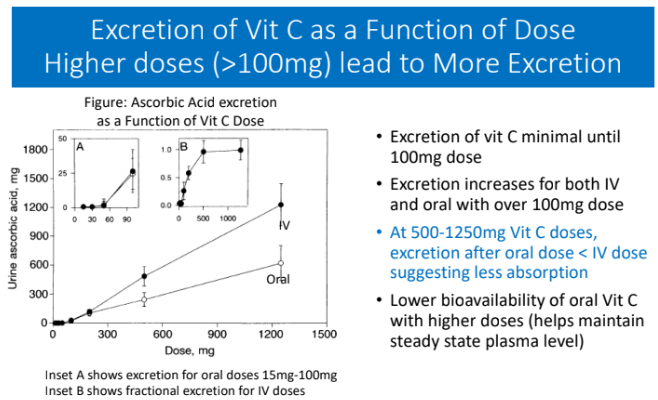
Excretion of Vit C as a Function of Dose Higher doses (>100mg) lead to More Excretion: Excretion of vit C minimal until 100 mg dose; Excretion increases for BOTH IV and and oral over 100 mg dose. Why is urinary excretion of vitamin C lower after a 500–1250 mg oral dose compared to the same IV dose?
Because high oral doses exceed the gut’s absorption capacity (saturation of SVCT1 transporters), so less vitamin C is absorbed into the bloodstream than with IV administration.
Lower bioavailability of oral Vit C with higher doses helps maintain?
steady state plasma level
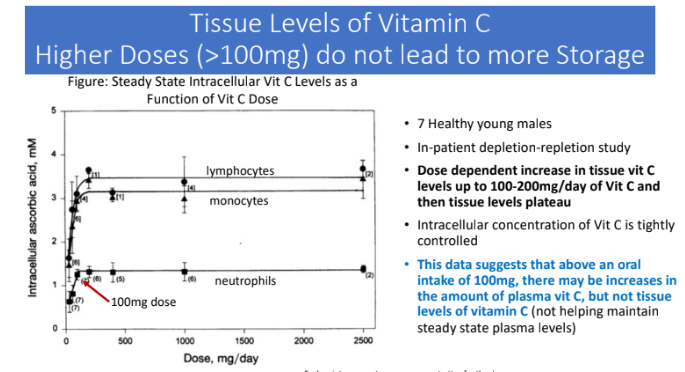
Tissue Levels of Vitamin C Higher Doses (>100mg) do not lead to more Storage: Dose dependent increase in tissue vit C levels up to _____ mg/day of Vit C and then?
200; tissue levels plateau
Intracellular concentration of Vit C is?
tightly controlled
This data suggests that above an oral intake of 100 mg, there may be?
increases in the amount of plasma vit C, but not tissue levels of vit C (not helping maintain steady state plasma levels)
Vitamin C transported into cells via?
Sodium dependent Vit C Transporters
SVCT1 and SVCT2
What does SVCT1 mediate?
systemic homeostasis
absorption in the GI tract (jejunum)
reabsorption in the kidney
What does SVCT2 control?
local demands
widely expressed in all organs
mediates movement INTO tissues
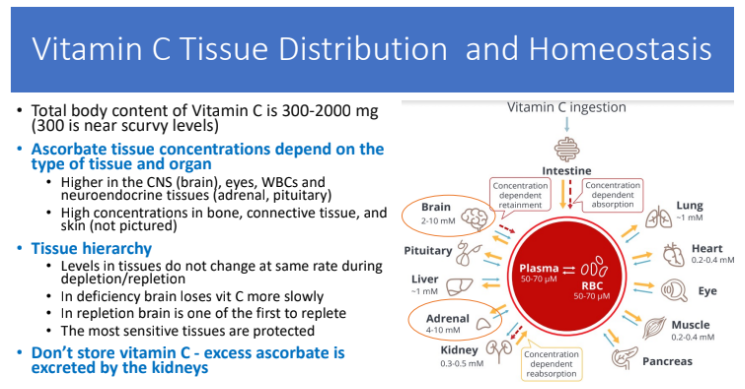
Vitamin C Tissue Distribution and Homeostasis: Total body content of Vit C is ?
300-2000 mg
300 is near scurvy levels
Ascorbate tissue concentrations depends on?
tissue and organs
There are higher ascorbate tissue concentrations where?
Higher in CNS (brain), eyes, WBCs and neuroendocrine tissues (adrenal, pituitary)
High concentrations in bone, connective tissue, and skin
Describe the tissue hierarchy
levels in tissues do NOT change at the same rate during depletion/repletion
in deficiency brain loses vit C more slowly
in repletion brain is one of the first to replete
the most sensitive tissues are protected
Don’t store vit C: What happens to excess ascorbate is?
excreted by the kidney
Summary
Scurvy Etiology: Inadequate Vitamin C
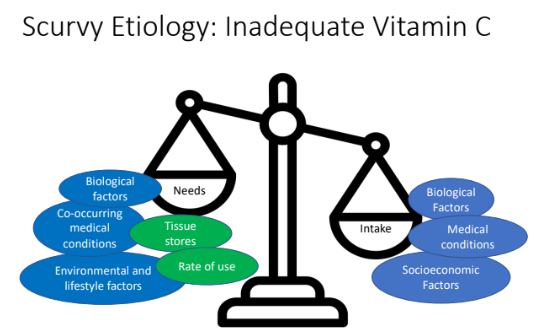
Etiology of Scurvy: What are the 4 causes of scurvy?
Increased needs
Decreased absorption
Increased excretion
Inadequate intake
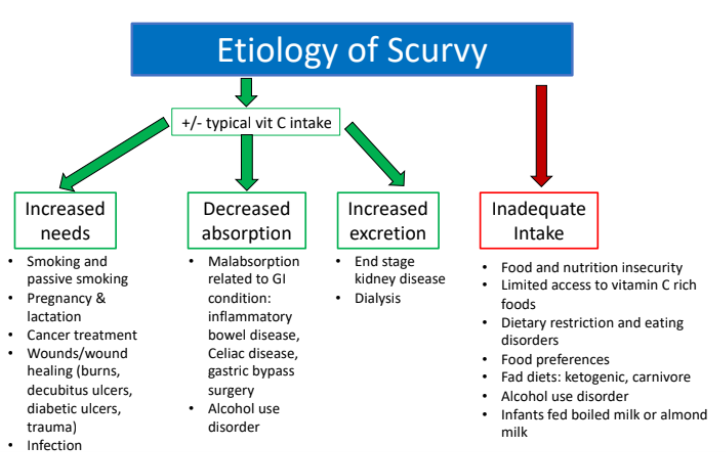
Clinical Presentation of Scurvy: Variable & Depends on length of time deficient in Vit C
Clinical Presentation: Symptoms/signs appear progressively because of?
tissue hierarchy
What are 3 early symptoms/signs?
Fatigue
Malaise
Lethargy (enzymatic functions)
What are 4 late symptoms and signs?
Cognitive changes
Confusion
Depression
Cognitive impairment
Time to development of deficiency depends on?
baseline vit c intake

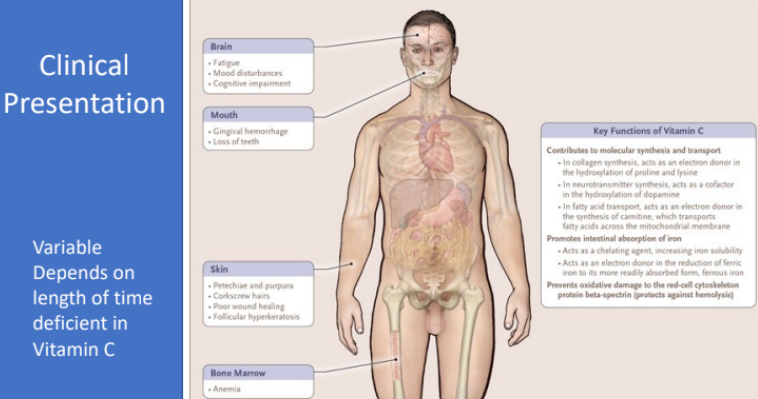
What are 7 clinical manifestations of scurvy?
Ecchymosis (large bruised areas)
Purpura and Petechiae (red dots)
Perifollicular hemorrhages and corkscrew hairs
Malaise/fatigue & myalgias
Follicular hyperkeratosis
Splinter hemorrhages
Bleeding swollen gums (loose teeth)
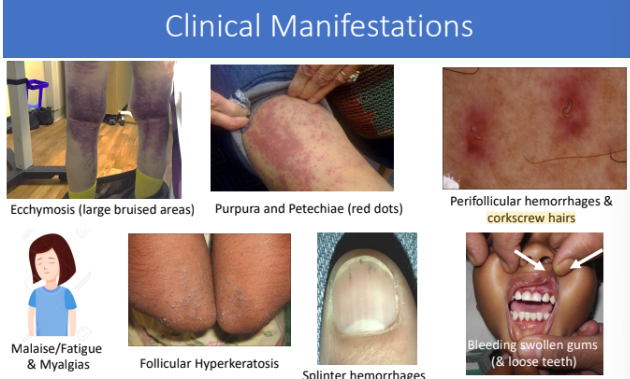
About 90% of matrix of mature bone is ____ & hence a lack of it will have severe effect on bone
collagen
How does lack of collagen affect children?
altered endochondral bone formation- leads to poor bone growth, bone lesions and fractures, pseudo paralysis
How does lack of collagen affect adults?
joint pain, related to hemarthrosis, subperiosteal hemorrhages
Depression and Asthenia (lack of energy) is associated with low?
serum/plasma levels of ascorbic acid
Observed in experimental depletion studies and cross
sectional studies
Reversible with repletion of Vitamin
Association of cognitive impairments with lower?
plasma ascorbic acid levels (<11-28 umol/L) as compared to those with higher levels
cross sectional studies
Pathophysiology of Scurvy

Pathophysiology: Disrupted ____ bond formation and disrupted ___ formation leads to?
disulfide; keratin
Impaired hair growth
Coiled corkscrew hairs (pathognomonic)
broken hairs
Scurvy reduces iron absorption in the GI tract which can cause?
Iron deficiency anemia
Which of the following clinical manifestations observed in the case study is correctly paired with its pathophysiology?
A. Petechiae: carnitine deficiency
B. Bleeding gums: decreased iron absorption
C. Corkscrew hairs: catecholamine synthesis
D. Ecchymosis: decreased collagen synthesis
D. Ecchymosis: decreased collagen synthesis
We can diagnose scurvy with history and physical findings alone

What are the 6 reasons for inadequate vit c intake?
Alcohol use disorder or substance use
Autism spectrum disorder
Institutionalization or those without housing
Limited food access, nutrition insecurity (children, older, adults)
Poor dentition (impacts foods consumed)
Food preferences

Clinical presentation in order for scurvy

Laboratory tests: Plasma Ascorbate Levels
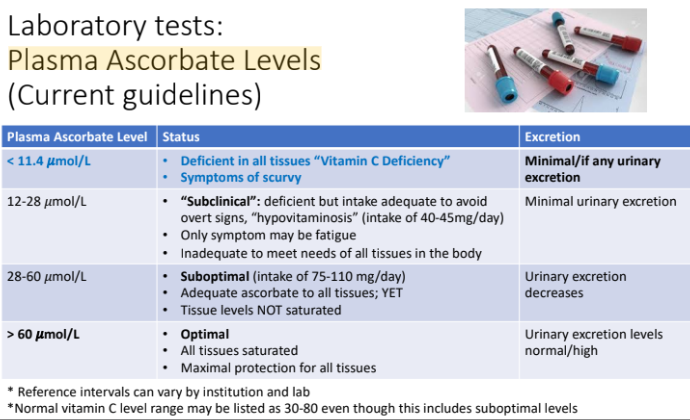
Plasma ascorbate (vitamin C) concentration plasma levels reflect what?
recent dietary intake; concentration in plasma can be a POOR indicator of tissue levels
With Vit C intake more than 100 mg/day the levels plateaus at ~70-80 umol/l due to?
decreased absorption rates and increased renal excretion
Laboratory Tests: WBC ascorbate (vit c) con; is a more ____ measure of tissue stores; correlates with? BUT is not routinely measured in the clinic
accurate; longer term dietary intake
Lab Test: Urinary excretion of ascorbic acid after IV
ascorbic acid administration is reliable indicator of?
tissue stores; not used clinically
Treatment: Supplemental Vit C: dose and timing individualized: Describe the difference between infants and children
Infants and children: 100-300 mg/day to start
Adults: 500-1000mg/day (divided doses!) to start
Duration: supplementation until full recovery (1-3 months)
Which type of supplementation is preferred?
oral supplementation over injection or intravenous
Use injection or intravenous when oral intake not possible, GI malabsorption, and/or unable to take adequate oral intake
Treatment: Increase dietary intake of Vit C rich foods
Education: Foods, storage, preparation
Address barriers to access