B5 PPC/OMM
1/423
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
424 Terms
RUQ
In which anatomical quadrant are the following abdominal structures:
-liver
-gallbladder
-pylorus
-duodenum
-pancreas head
-R adrenal
-R kidney (upper pole)
-end of ascending colon
-beginning of transverse colon
LUQ
In which anatomical quadrant are the following abdominal structures:
- liver L lobe
-spleen
-stomach
-pancreas body
-L adrenal
-L kidney (upper pole)
-end of transverse and beginning of descending colon
RLQ
In which anatomical quadrant are the following abdominal structures:
- R kidney lower pole
-cecum
-appendix
-beginning of ascending colon
-R ureter
-R ovary
-R fallopian tube
-R spermatic cord
-uterus (if enlarged)
-bladder (if enlarged)
LLQ
In which anatomical quadrant are the following abdominal structures:
- L kidney lower pole
-sigmoid colon
-end of descending colon
-L ureter
-L ovary
-L fallopian tube
-L spermatic cord
-uterus if enlarged
-bladder if enlarged
true
T/F: the chief complaint (CC) should be in the patient's own words
abdominal disease
Sx of _________ include:
•Pain
•Nausea & Vomiting
•Rectal bleeding
•Abdominal distention
•Change in bowel movements
•Early satiety
•Jaundice
•Pruritus
pain
What can result from
mucosal irritation
smooth muscle spasm
peritoneal irritation
capsular swelling
direct nerve stimulation?
acute pain
What type of pain:
-acute perforation, inflammation, or torsion of an organ
referred pain
What type of pain:
-pain originates in areas supplied to somatic nerves entering the spinal cord at the same segment as the sensory nerves from the organ responsible for the pain
on exam!!
gastric ulcer perforation
What cause of pain presents as a "burning" type of pain?
dissecting aneurysm
What cause of pain presents as a "tearing" type of pain?
intestinal obstruction
What cause of pain presents as a "gripping" type of pain?
pylonephritis
What cause of pain presents as a "dull" type of pain?
nephrolithiasis/renal colic
What cause of pain presents as a "crampy" type of pain?
hollow viscera
(hollow viscera/peritoneal irritation) pain presents as crampy, paroxysmal, often poorly localized, related to peristalsis, and presents w/ pt writhing on table
peritoneal irritation
(hollow viscera/peritoneal irritation) pain presents as steady/constant, often localized, and presents w/ pt lying in a fetal position
substernal
Where is the referred area of pain for a patient with esophagitis?
shoulder
Where is the referred area of pain for a patient with sub-phrenic abscess of the diaphragm?
epigastric
Where is the referred area of pain for a patient with a gastric ulcer of the stomach?
epigastric
Where is the referred area of pain for a patient with a duodenal ulcer of the duodenum?
epigastric
Where is the referred area of pain for a patient with cholecystitis of the gallbladder?
epigastric
Where is the referred area of pain for a patient with hepatitis of the liver?
epigastric or midback
Where is the referred area of pain for a patient with pancreatitis?
right scapula
Where is the referred area of pain for a patient with biliary colic of the biliary tract?
midback
Where is the referred area of pain for a patient with aortic dissection?
periumbilical
Where is the referred area of pain for a patient with obstruction of the small intestine?
hypogastrium
Where is the referred area of pain for a patient with diverticulitis or ulcerative colitis of the colon?
sacrum
Where is the referred area of pain for a patient with proctitis or abscess of the rectum?
vomiting
What can be caused by irritation of the peritoneum, perforation of an organ, obstruction of the bile duct/ureter/intestine, or toxins?
Note: extra-abdominal conditions that may cause this are CNS conditions, pregnancy, MI, or drug toxicity
hepatocellular disease, pregnancy, and metastatic disease
When is nausea without vomiting seen?
Meniere's disease
Vomiting (emesis) with hearing loss and tinnitus may be seen with ________
bright red blood (hematochezia)
What type of rectal bleeding is associated with:
-tumors, diverticular disease, UC
red blood mixed w/ stool
What type of rectal bleeding is associated with:
-IBD, tumors, or hemorrhoids
black tarry stools (melena)
What type of rectal bleeding is associated with:
-bleeding from above the small bowel caused by stomach tumors or ulcer disease
silver colored stools (acholic)
What type of rectal bleeding is associated with:
-duodenal cancer w/ sloughing off of tissue
tenesmus
What type of rectal bleeding is associated with:
-painful, continued straining during stooling caused by lesion in distal rectum or anus
jaundice
what is caused by liver disease or obstruction to bile flow in which there is decreased excretion of conjugated bilirubin into bile?
generalized itching
What type of itching is associated with chronic renal or liver disease, thyroid disease, and, in the elderly, winter itch/dry skin?
intense generalized itching
What type of itching is associated with lymphoma, Hodgkin's disease, cancer of GI tract (esp. distal pancreas), primary biliary cholangitis?
rectal itching (pruritis ani)
What type of itching is associated with fistulas, parasites, psoriasis, or diabetes?
appendicitis
What disorder has a classic pain pattern of:
-diffuse periumbilical pain and anorexia early
-pain localized to RLQ as peritonitis develops
-low grade fever, n/v may not be present
-XRAYs and other tests (-)
-can be diagnosed w/ CT
on exam!!!
acute cholecystitis
What disorder has a classic pain pattern of:
-localized or diffuse RUQ pain
-radiation to R scapula
-vomiting, constipation, low grade fever
on exam!!!
acute renal colic
What disorder has a classic pain pattern of:
-severe flank pain
-radiates to groin
-vomiting and urinary Sx
-blood in urine
on exam!!!
true
T/F: when doing a physical exam, you should examine the area of pain last with the pt supine, abdomen fully exposed, arms at sides and legs flat
renal or biliary colic
What disorder may have a pt writhing in the room?
peritonitis
What disorder may have a pt lying perfectly still in the room?
shock
What disorder may have a pt pale and sweating in the room?
peritonitis, bleeding, obstruction
What disorder may increase respirations?
cirrhosis
What disorder can cause large lunula of the hands/nail beds?
peutz-jeghers syndrome
What disorder can cause pigmented macules around the mouth from melanin deposits?
osler-weber-rendu syndrome
What disorder can cause telangectasias of the lips from melanin deposits?
cushing's syndrome
What disorder is associated with a round puffy face?
Hint: long term use of glucocorticoids
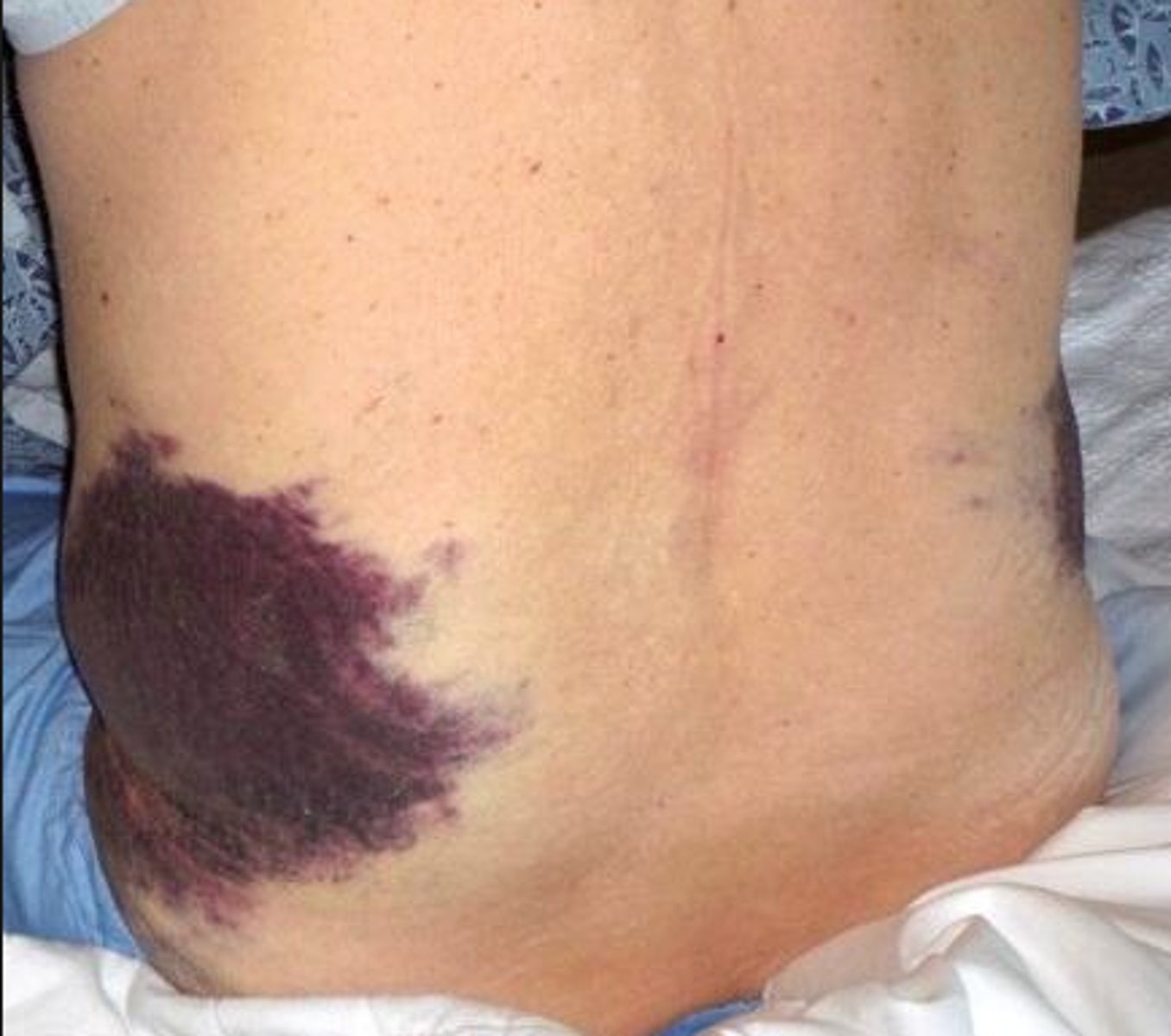
grey turner's sign
What is massive ecchymosis noted on the flanks from pancreatitis?
grey turner's sign
ID
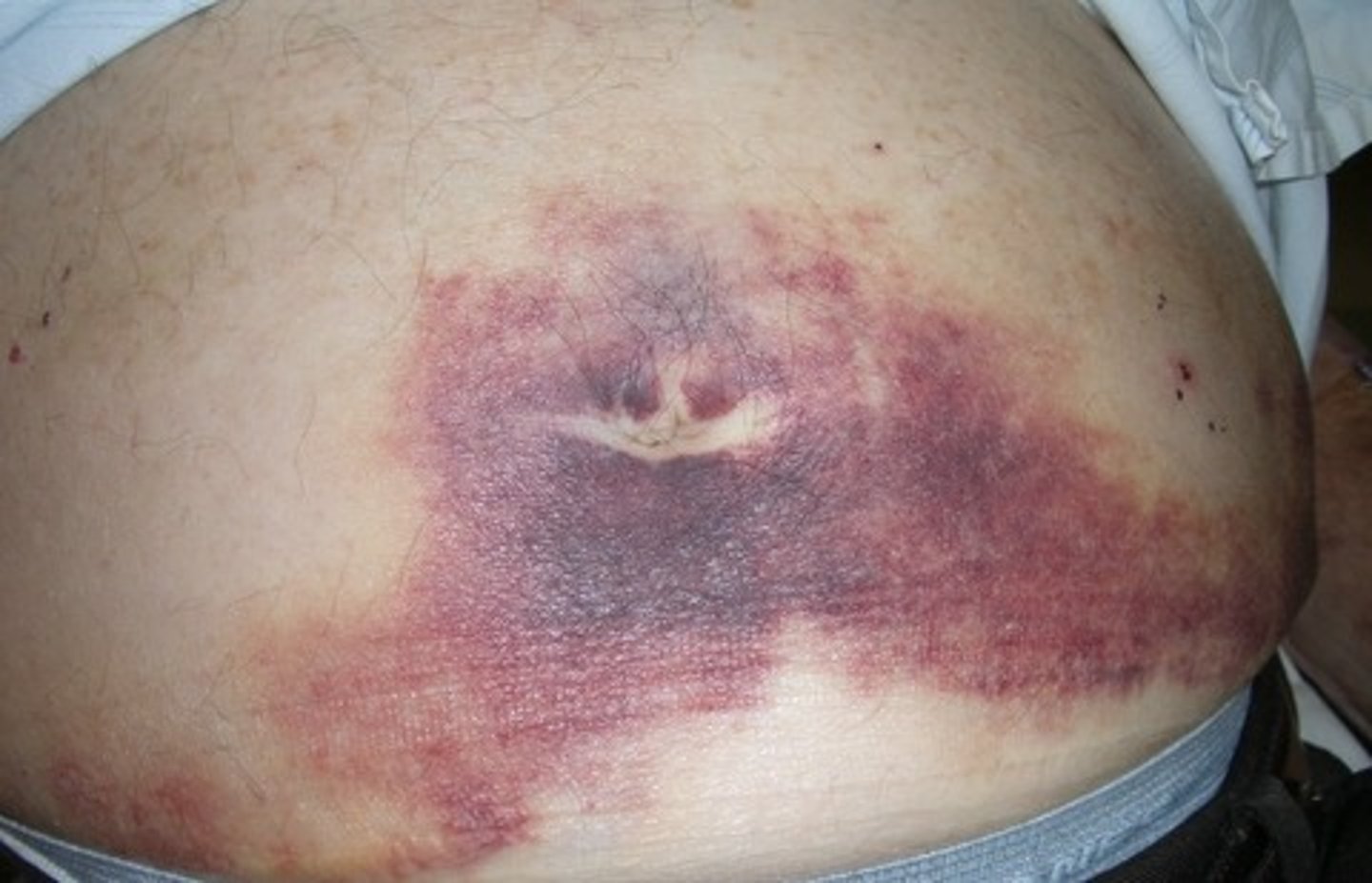
cullen's sign
what is bluish discoloration of the umbilicus from hemoperitoneum?
cullen's sign
ID
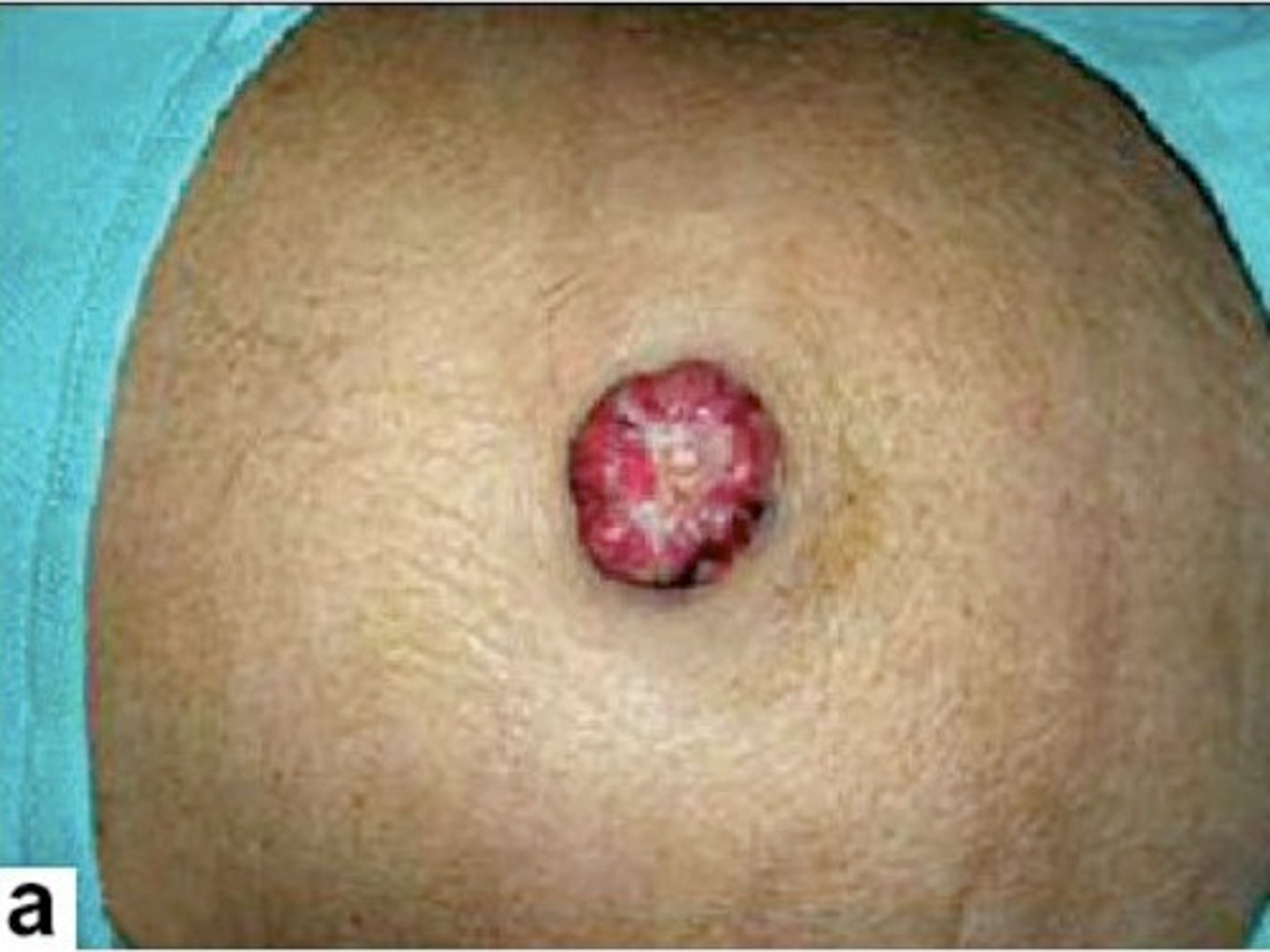
sister mary joseph nodule
What is a cutaneous metastasis localized to the umbilicus?
sister mary joseph nodule
ID
abdominal distension
What can occur from increased gas in the intestine or ascites (gas from malabsorption, irritable colon, or air swallowing, ascites from cirrhosis, CHF, portal HTN, peritonitis, or neoplasia)?
hernia
What is a protrusion of the peritoneal cavity that can include omentum, intestine, and/or bladder wall?
aortic or iliac aneurysm
What should you be concerned about if you can feel a pulsatile mass in the abdomen?
ileus
You should listen for up to 2 minutes in each quadrant until bowel sounds are heard. If no sounds after 2 minutes, "absent bowel sounds" may be from ________
borborygmi
Are are low pitched rumbling bowel sounds?
ascites
When a pt has _________:
-ID area of tympany (gas) and dullness (disorder)
-have pt change position and dullness will shift to dependent position
Shifting dullness:
•Patient’s hand indents subcutaneous adipose tissue to prevent impulse transmission
•Examiner taps one flank while palpating the other
•Detection of a fluid wave indicates
•May see false positive in obese patients
•May see bulging flanks if enough fluid is present to push flanks outward
false
T/F: when palpating the abdomen, you should use fingertips
true
T/F: when palpating the abdomen, you should use flat part of hand or finger pads
light
(light/deep) palpation of the abdomen is used to ID muscle spasm + tenderness
rigidity
What is involuntary spasm of abdominal wall (does not relax w/ expiration) and indicates diffuse or localized peritoneal irritation?
hyperesthesia
What is an area of increased sensitivity that may be noted w/ a light stroking of the abdomen?
C1-C2
What spinal levels affect:
-R pancreas, liver, gallbladder, small intestine, ascending colon
-L esophagus, stomach, duodenum
-Hint: associated w/ C2 and temporal bone restrictions, CN X
S2-S4
What spinal levels affect:
-L half of transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, rectum
celiac ganglion
Which splanchnic ganglion is associated with the foregut?
Hint: receives fibers from T5-T9 and is located at the mid epigastric below xiphoid process
superior mesenteric ganglion
Which splanchnic ganglion is associated with the midgut?
Hint: receives fibers from T8-T12, located at the midline along linea alba above umbilicus
inferior mesenteric ganglion
Which splanchnic ganglion is associated with the hindgut?
hint: receives fibers from T10-L2 via 3 lumbar splanchnic nerves and is located at the midline linea alba above the umbilicus
esophagus
What organ is associated with palpable tissue texture changes on the R T3-T6 region?
stomach
What organ is associated with palpable tissue texture changes on the L T5-T10 region?
duodenum
What organ is associated with palpable tissue texture changes on the R T6-T8 region?
pancreas
What organ is associated with palpable tissue texture changes on the BL T5-T9 region?
gallbladder
What organ is associated with palpable tissue texture changes on the R T5-T10 region?
small intestine
What organ is associated with palpable tissue texture changes on the BL T8-T10 region?
appendix
What organ is associated with palpable tissue texture changes on the R T9-T12 region?
cecum and ascending colon
What organ is associated with palpable tissue texture changes on the R T11-L1 region?
descending colon
What organ is associated with palpable tissue texture changes on the L L1-L3 region?
deep
(light/deep) palpation:
-Used to estimate organ size and detect masses
-Bottom hand flat with upper hand exerting force with fingertips
-May wish to have patient flex knees to relax muscles
-Guarding is any voluntary muscle spasm (cold hands)
-Rebound tenderness (referred) = Peritoneal irritation caused by palpating deeply and slowly in an area away from the suspected area of inflammation, the palpating hand is quickly removed, and a sensation of pain is felt at the area of inflammation
-Rovsing’s Sign = Pain produced in RLQ when palpating the LLQ
true
T/F: A non-palpable liver does not rule out hepatomegaly but makes it less likely to have an enlarged liver
true
T/F: spleen is NOT palpable under normal conditions
McBurney's point
What special test:
-pain produced @ 1/3 distance from ASIS to umbilicus
iliopsoas test
What special test:
-pt lies on unaffected side and extends other leg against examiner's hand
-(+) = pain
obturator test
What special test:
-pt is supine and examiner flexes pt's thigh at hip w/ knee bent and rotates leg internally and externally at the hip
-(+) = pain, likely due to inflammation adjacent to the muscle
dermatomal
______ pain arises directly from compression on a peripheral nerve, particularly at its root (e..g, single-nerve compression)
sclerotomal
______ pain is described by patients as "deep, dull, and toothache-like." pain patterns are frequently overlooked because they may project some distance from their pain generators and are often due to irritation by chemical or mechanical stimuli. pain is "experienced" as originating from all of the tissues that are innervated by the same nerve
myotomal
______ pain is poorly localized, and the patient may describe symptoms located at a substantial distance from the actual lesion. Patients typically describe this pain as "crampy" or "stiff," with the pain suddenly "grabbing" them during a particular motion
L T5-T9
What spinal level correlates with the stomach?
Note: specifically talking about spinal reflex levels
R T10
What spinal level correlates with the duodenum?
Note: specifically talking about spinal reflex levels
R T9
What spinal level correlates with the gallbladder?
Note: specifically talking about spinal reflex levels
R T5-T9
What spinal level correlates with the liver?
Note: specifically talking about spinal reflex levels
BL T6-T9
What spinal level correlates with the pancreas?
Note: specifically talking about spinal reflex levels
corresponding side T10-L1
What spinal level correlates with the kidney & ureters?
Note: specifically talking about spinal reflex levels
corresponding side T10-L1
What spinal level correlates with the ovaries and testes?
Note: specifically talking about spinal reflex levels
T10-L1
What spinal level correlates with the adrenals?
Note: specifically talking about spinal reflex levels