ap psych unit 2 quiz 1 vocab
1/40
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
bottom-up processing
analysis of the stimulus begins with the sense receptors and works up to the level of the brain and mind
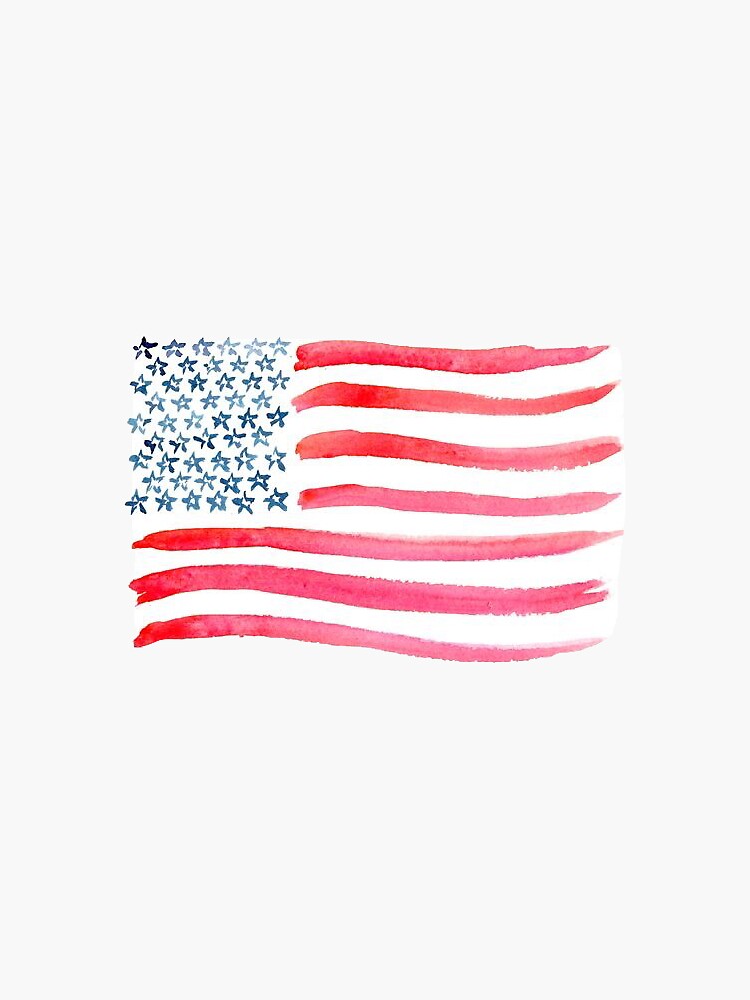

top-down processing
information processing guided by high level mental processes as we construct perceptions drawing on our experience and expectations

schema
a concept or framework that organizes and interprets information.
perceptual set
a mental predisposition to perceive one thing and not another.
gestalt psychology
an organized whole. gestalt psychologists emphasized our tendency to integrate pieces of information into meaningful wholes.
closure
the idea that your brain will fill in the missing parts of a design or image to create a whole

figure & ground
the organization of the visual field into objects that stand out from their surroundings.

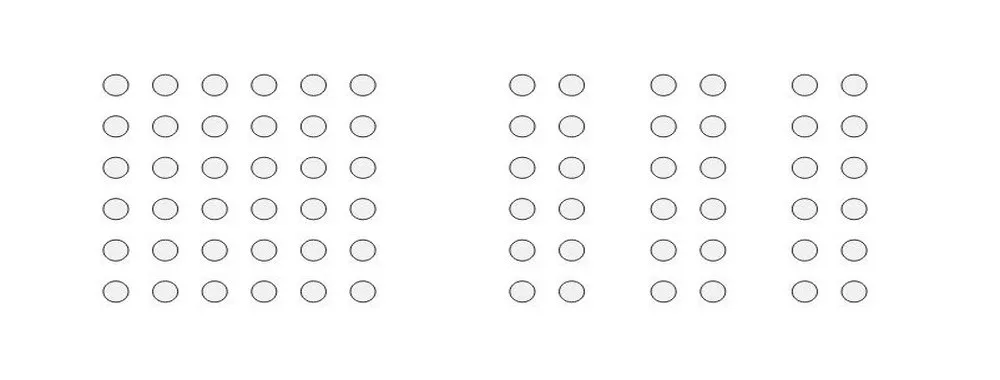
proximity
refers to how close elements are to one another. the strongest proximity relationships are those between overlapping subjects, but just grouping objects into a single area can also have a strong proximity effect
similarity
similar elements are visually grouped (color, shape, size, etc) regardless of their proximity to each other
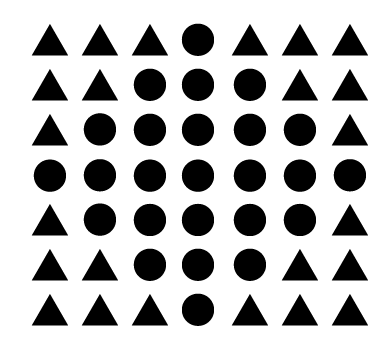
attention
focusing on one thing while ignoring other things that may be going on at the same time
selective attention
focusing conscious awareness on a particular stimulus.
cocktail party effect
the ability to focus one's attention on a particular stimulus while filtering out a range of other stimuli
inattentional blindness
failing to see visible objects when attention is directed elsewhere.
change blindness
failing to notice changes in the environment; a form of inattentional blindness.
binocular depth cues
depth perception, size, & distance through two eyes
retinal disparity
a binocular cue for perceiving depth. by comparing retinal images from the two eyes, the brain computes distance - the greater the disparity (difference) between the two images, the closer the object.
convergence
a cue to nearby objects’ distance, enabled by the brain combining retinal images.
monocular depth cues
a depth cue, such as interposition or linear perspective, available to either eye alone.
relative clarity
a monocular cue that helps people judge the distance of objects by their apparent sharpness and detail
relative size
a perceptual clue which allows you to determine how close objects are to an object of known size
texture gradient
indistinct (fine) texture signals increasing distance
linear perspective
parallel lines like railroad tracks, appear to converge with distance. the more the lines converge, the greater their perceived distance
interposition
objects that occlude (block) other objects tend to be perceived as closer
apparent movement
the sensation of seeing movement when nothing actually moves in the environment
prototypes
a mental image or best example of a category. matching new items to a _____ provides a quick and easy method for sorting items into categories.
assimilation
interpreting our new experiences in terms of our existing schemas.
accommodation
in developmental psychology, adapting our current schemas (understandings) to incorporate new information.
algorithms
a methodical, logical rule or procedure that guarantees solving a particular problem. contrasts with the usually speedier — but also more error-prone — use of heuristics.
heuristics
a simple thinking strategy—a mental shortcut — that often allows us to make judgments and solve problems efficiently; usually speedier but also more error-prone than an algorithm.
representativeness heuristic
judging the likelihood of events in terms of how well they seem to represent, or match, particular prototypes; may lead us to ignore other relevant information.
mental set
a tendency to approach a problem in one particular way, often a way that has been successful in the past.
priming
the activation, often unconsciously, of particular associations in memory.
framing
the way an issue is posed; how an issue is framed can significantly affect decisions and judgments.
gambler’s fallacy
a cognitive bias that adheres to the ideas that if something hasn’t happened recently it soon will
sunk-cost fallacy
a cognitive bias that makes you stay in a situation despite losing resources or benefits
executive functions
cognitive skills that work together, enabling us to generate, organize, plan, and implement goal-directed behavior.
creativity
the ability to produce new and valuable ideas.
divergent thinking
expanding the number of possible problem solutions; creative thinking that goes in different directions.
convergent thinking
narrowing the available problem solutions to determine the single best solution.
functional fixedness
tendency to think of only the familiar or typical functions for objects
availability heuristic
judging the likelihood of events based on their availability in memory; if instances come readily to mind (perhaps because of their vividness), we presume such events are common.