Biology I-Semester 2 Final 22-23
4.8(5)
4.8(5)
Card Sorting
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Covers LTs. 4.3: Explain the process of bacterial reproduction, 5.1: Model the process of meiosis and discuss how it begins, and how this process leads to genetic variation, and 6.2: Model how organisms make proteins from their genetic code (Transcription & Translation).
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
1
New cards
What is sexual reproduction of bacteria called?
Conjugation
2
New cards
Is binary fission sexual or asexual?
Asexual
3
New cards
Does asexual reproduction make identical or genetically different cells?
Identical
4
New cards
Bacteria do mitosis, true or false?
False
5
New cards
Conjugation creates more cells, true or false?
False
6
New cards
What is the name of the structure that is built to another cell during conjugation?
Pilus
7
New cards
What do binary fission and mitosis have in common?
Identical cells, makes two cells
8
New cards
What are two advantages of asexual reproduction?
Fast, less energy
9
New cards
What shape is the bacterial chromosome?
Circular
10
New cards
How many cells are created in binary fission?
Two
11
New cards
How many cells are created in conjugation?
Zero
12
New cards
What two processes do bacteria do to reproduce?
Binary fission and conjugation
13
New cards
What is one thing that conjugation and binary fission have in common?
Bacteria do it
14
New cards
What type of reproduction creates 4 daughter cells?
Sexual reproduction
15
New cards
When homologous chromosomes are being separated, what phase is that?
Anaphase I
16
New cards
When does crossing over occur?
Prophase I
17
New cards
What process that involves egg and sperm eventually will happen to create a diploid organism?
Fertilization
18
New cards
If diploid is a full set of chromosomes, what is haploid?
Half the chromosomes/one set of chromosomes
19
New cards
When homologous pairs are separated, and the cell membrane is beginning to pinch together, what phase is that?
Telophase I
20
New cards
When homologous chromosomes swap pieces of DNA, what is that called?
Crossing over
21
New cards
When there are two genetically identical daughter cells, is that sexual or asexual reproduction?
Asexual reproduction
22
New cards
When sister chromatids are being separated, and there are two cells present, what phase is that?
Anaphase II
23
New cards
What is a picture of all the chromosomes in a cell called?
Karyotype
24
New cards
If a karyotype has sex chromosomes, is that sexual or asexual reproduction?
Sexual reproduction
25
New cards
How many cells are made at the end of meiosis?
Four
26
New cards
What is the scientific term for sex cells?
Gametes
27
New cards
If the haploid number of chromosomes is 14, what is the diploid number?
28
28
New cards
What is the entire purpose of meiosis?
Create genetically different cells/offspring
29
New cards
What is a pair of replicated, similar chromosomes from mom and dad called?
Homologous pair
30
New cards
Does meiosis create genetically different or genetically identical offspring?
Different
31
New cards
What is it called during Metaphase I when homologous chromosomes line up randomly?
Independent assortment
32
New cards
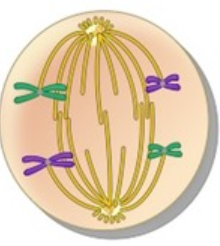
What phase is this?
Anaphase 1
* homologous pairs are being pulled apart
* homologous pairs are being pulled apart
33
New cards
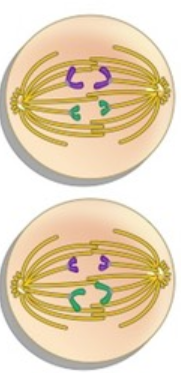
What phase is this?
Anaphase II
* sister chromatids are being pulled apart
* sister chromatids are being pulled apart
34
New cards
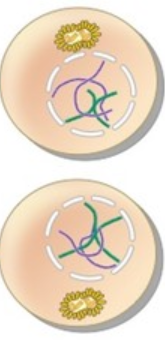
What phase is this?
Cytokinesis I
* two cells are finally separated -nucleus is reforming
* two cells are finally separated -nucleus is reforming
35
New cards
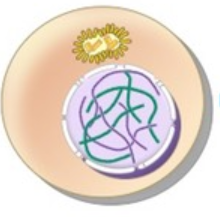
What phase is this?
Interphase
* DNA is in chromatin form -The nucleus is fully intact
* DNA is in chromatin form -The nucleus is fully intact
36
New cards
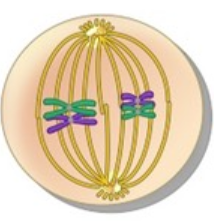
What phase is this?
Metaphase I
* Homologous pairs are lined up in the middle of the cell
* Homologous pairs are lined up in the middle of the cell
37
New cards
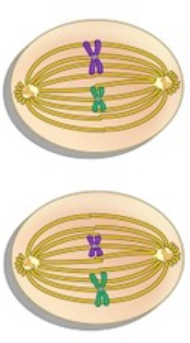
What phase is this?
Metaphase II
* Sister chromatids are lined up in the middle of the cell
* Sister chromatids are lined up in the middle of the cell
38
New cards
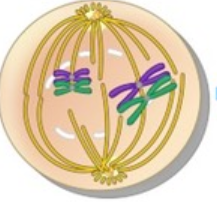
What phase is this?
Prophase I
* DNA is condensing to chromosomes
* Crossing over happens
* Spindle fibers are forming
* Nucleus is going away
* DNA is condensing to chromosomes
* Crossing over happens
* Spindle fibers are forming
* Nucleus is going away
39
New cards
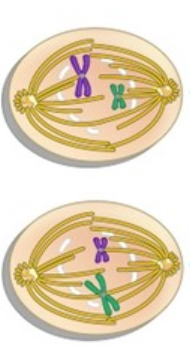
What phase is this?
Prophase II
* Nucleus is going away
* DNA is condensing to chromosomes
* Nucleus is going away
* DNA is condensing to chromosomes
40
New cards
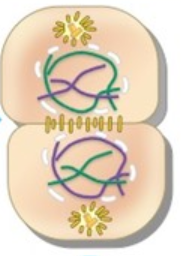
What phase is this?
Telophase I
* Cells are starting to split
* 1 cell going to 2
* Can see a cleavage furrow
* Cells are starting to split
* 1 cell going to 2
* Can see a cleavage furrow
41
New cards
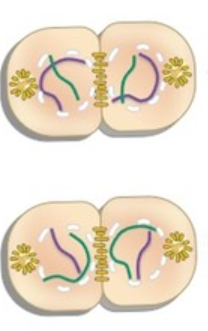
What phase is this?
Telophase II
* Cells are starting to split
* 2 cells going to 4
* Can see a cleavage furrow
* Cells are starting to split
* 2 cells going to 4
* Can see a cleavage furrow
42
New cards
If a DNA strand is TAC what will the mRNA strand be?
AUG
43
New cards
Which happens first, transcription or translation?
Transcription
44
New cards
What is the end product of transcription?
mRNA
45
New cards
What is a codon?
A group of 3 nucleotides on mRNA
46
New cards
Where does translation occur?
Cytoplasm
47
New cards
What does tRNA do?
Brings in amino acids
48
New cards
What is the end product of translation?
Protein
49
New cards
What molecule has an anticodon?
tRNA
50
New cards
How can you tell the beginning of a gene on DNA?
TAC
51
New cards
Where does transcription occur?
Nucleus
52
New cards
TRUE OR FALSE Methionine (Met) signals the end of an mRNA sequence.
FALSE- it codes for the start
53
New cards
What are the types of RNA that participate in translation?
mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
54
New cards
Why can't DNA leave the nucleus?
Could get damaged
55
New cards
What is the final product of translation?
Protein
56
New cards
What structure does mRNA leave through after transcription?
Nuclear pore
57
New cards
What is the name of the tool you use to find the amino acid based on the mRNA codon?
Codon table
58
New cards
What is responsible for reading the mRNA strand?
A ribosome (rRNA)
59
New cards
What two processes is mRNA involved in?
Transcription, Translation
60
New cards
Going from DNA to mRNA is what process?
Transcription
61
New cards
Going from mRNA to a protein is what process?
Translation
62
New cards
What is the monomer of a protein?
Amino Acids