BSC 181 Lab Quiz 1
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
ocular lens
eyepiece of a microscope that have a magnification factor of 10
nosepiece
Holds the objectives and can be rotated to change the magnification
objective lenses
these are found on the nosepiece and range from low to high power
Scanning lens
shortest lens, typically 4X, only lens you can use the course adjustment nob on (40 with ocular)
Low power lens
10x magnification, (100 with ocular)
High power lens
40x magnification, "High and dry lens" (400 with ocular)
adjustment knobs
moves the stage up and down in order to focus on a specimen
Course asjust
Larger of the two. moves objective lens up an down in order to focus. ONLY used with scanning lens
Fine adjust
Smaller of the two. Can safely be used with the low power and scanning lenses
stage
supports the slide being observed
stage adjustment knobs
used to move the slide on a mechanical stage in vertical(Away) and horizontal (right) directions
arm and base
the backbone of the microscope, attaches the body to the base and used to transport it
parafocal scopes
when you focus at one magnification, the image stays mostly in focus as you move to the next level.
transverse
Divides body into upper and lower parts
frontal
divides the body into anterior and posterior sections
sagittal
divides the body into left and right sections
midsaggital
divides the body into right and left sides in half
cervical
neck region
acromial
point of shoulder
sternal
breastbone
axillary
armpit
mammary
pertaining to the breast
brachial
arm
antecubital
anterior surface of elbow
ante brachial
forearm
carpal
wrist
palmar
palm
pollux
thumb
digital
fingers, toes
umbilical
belly button
pelvic
pelvis region
inguinal
groin area
coxal
hip
femoral
thigh
patellar
front of knee
crural
lower leg
fibular (or peroneal)
side of leg
tarsal
ankle region
metatarsal
top of foot
hallux
big toe
occipital
back of head
olecranal
back of elbow
metacarpal
back of hand
popliteal
back of knee
sural
calf of the leg
calcaneal
heel of foot
plantar
bottom of foot
scapular
shoulder blade
vertebral
spinal column
lumbar
lower back
sacral
area between hips
perineal
region between the anus and external genitalia
frontal
forehead
orbital
eye
mental
chin
Otic
ear
Superior
toward the head
inferior
away from the head
anterior
front of the body
posterioir
toward the back
lateral
away from the midline, towards the sides
medial
toward the midline
proximal
Closer to the point of attachment
distal
away from the point of attachment
superficial
near the surface
deep
away from the surface
mitosis
cell division in which the nucleus divides into nuclei containing the same number of chromosomes
DNA is doubled within the nucleus to prepare for cell division, NOT part of mitosis
what happens during interphase?
interphase, mitosis, cytokinesis
What are the three stages of the cell cycle?
cells divide into two new nuclei
what happens in mitosis?
interphase
what phase of the cell cycle is pictured here
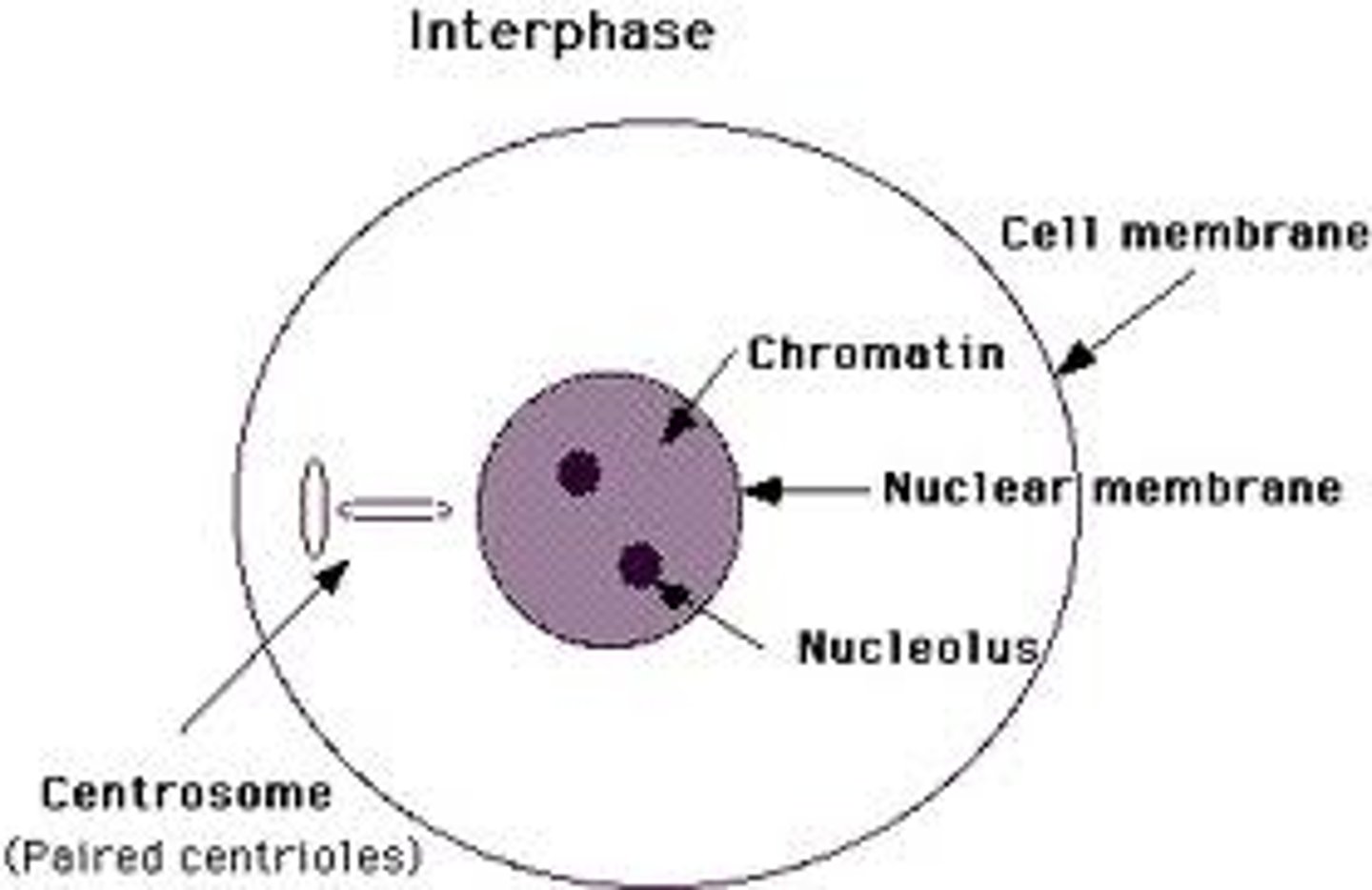
prophase
what phase of the cell cycle is pictured here
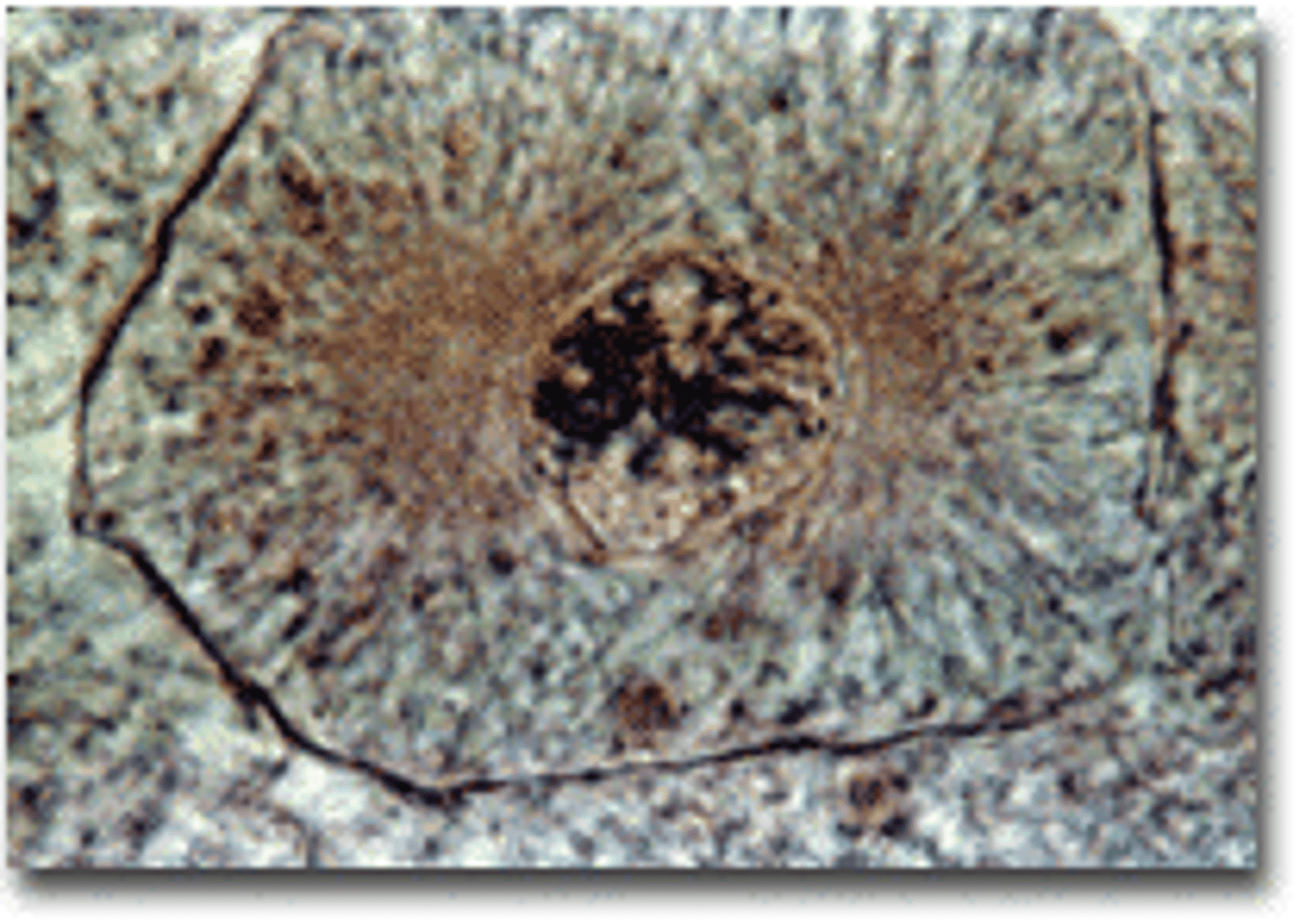
metaphase
what phase of the cell cycle is pictured here
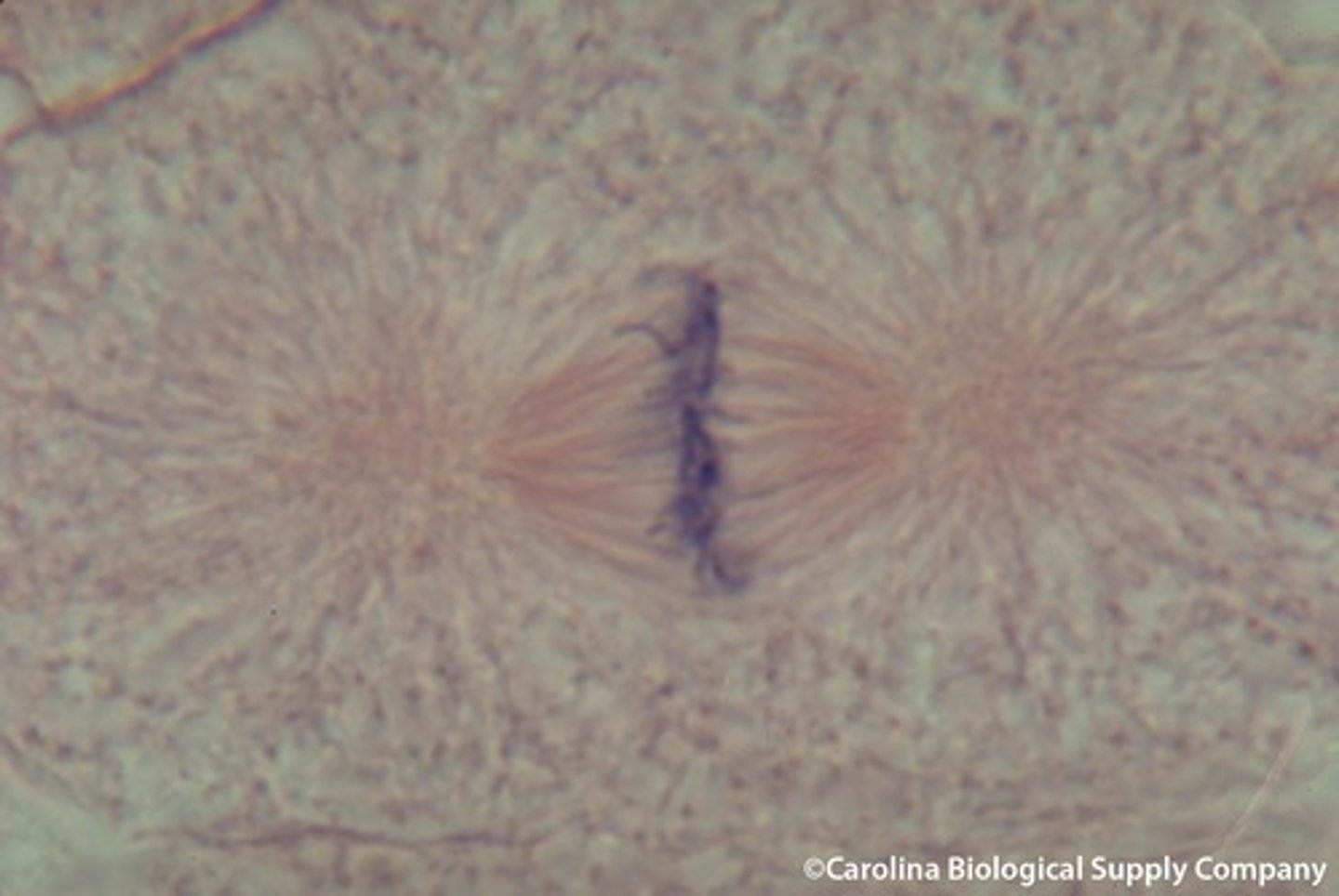
anaphase
what phase of the cell cycle is pictured here
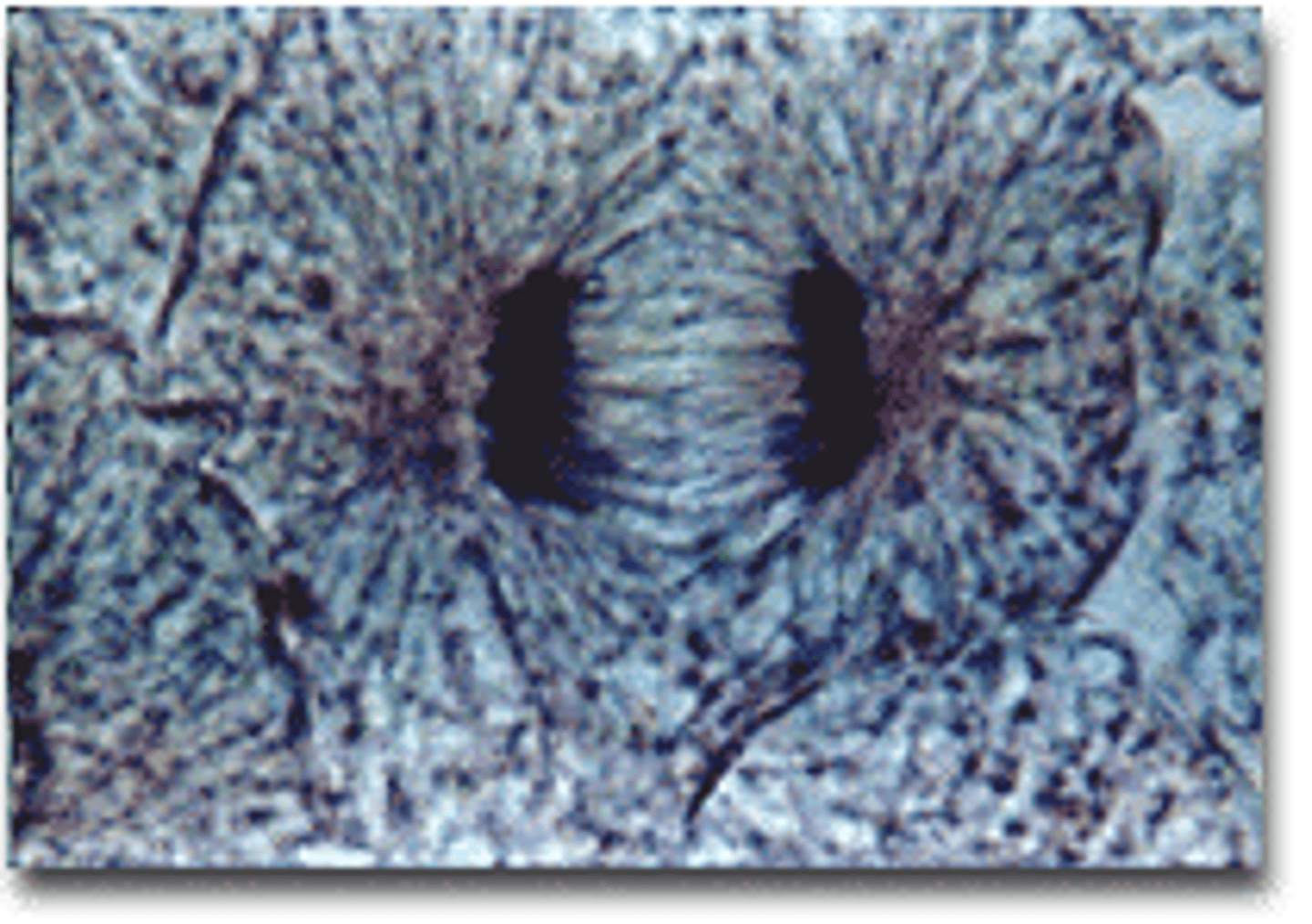
telophase
what phase of the cell cycle is pictured here
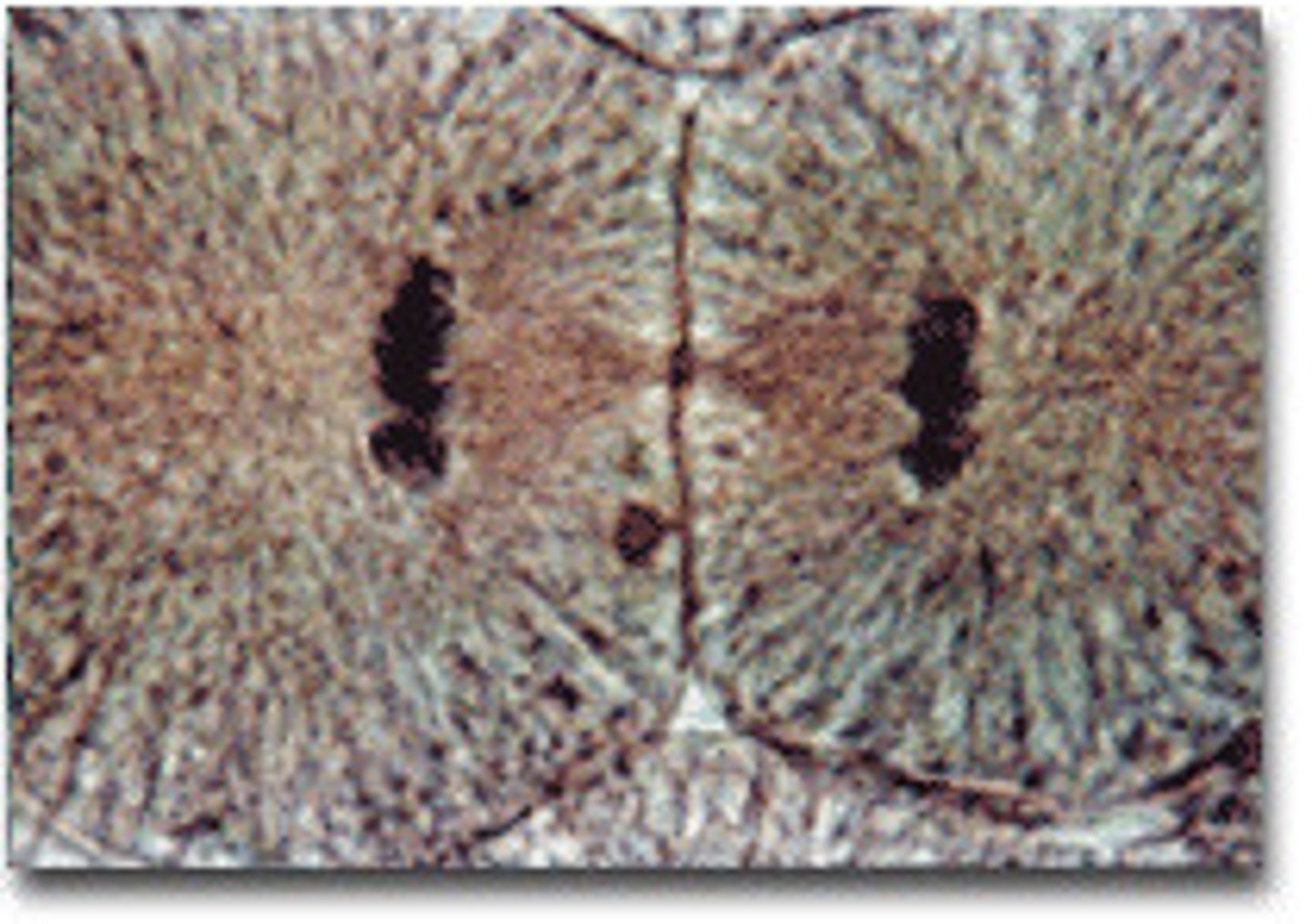
Chromatin condenses into chromosomes, nucleus is already broken down and the chromatin has all condensed into chromosomes. spindel fibers are formed and centrioles have moved to poles of cells
what happens during prophase?
What happens during metaphase?
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
what happens during anaphase?
The chromosomes separate and move along spindle fibers to opposite ends of the cell
what happens during telophase?
Chromosomes uncoil, spindle microtubules break down, nuclear envelope reforms.
homologous chromosomes
Pair of chromosomes that are the same size, same appearance and same genes.
2 sister chromatids, each made with chromatin & containing genes, attached in the middle by a centromere
what is the structure of a chromosome?
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase
What are the 4 stages of mitosis?
3 events that make up cell cycle
interphase, mitosis, cytokineseis
spindle fibers
help pull apart the cell during replication and are made up of microtubules. separate genetic material
chromatin
loose, uncoiled form of DNA with the nucleus of a cell consisting of DNA wrapped around proteins call histones (working form of DNA)
Chrmosomes
a threadlike structure of nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells, carrying genetic information in the form of genes.
What is the point of mitosis
to create 2 identical cells
simple squamous tissue, in the lungs
what is this type of tissue and where is it found?
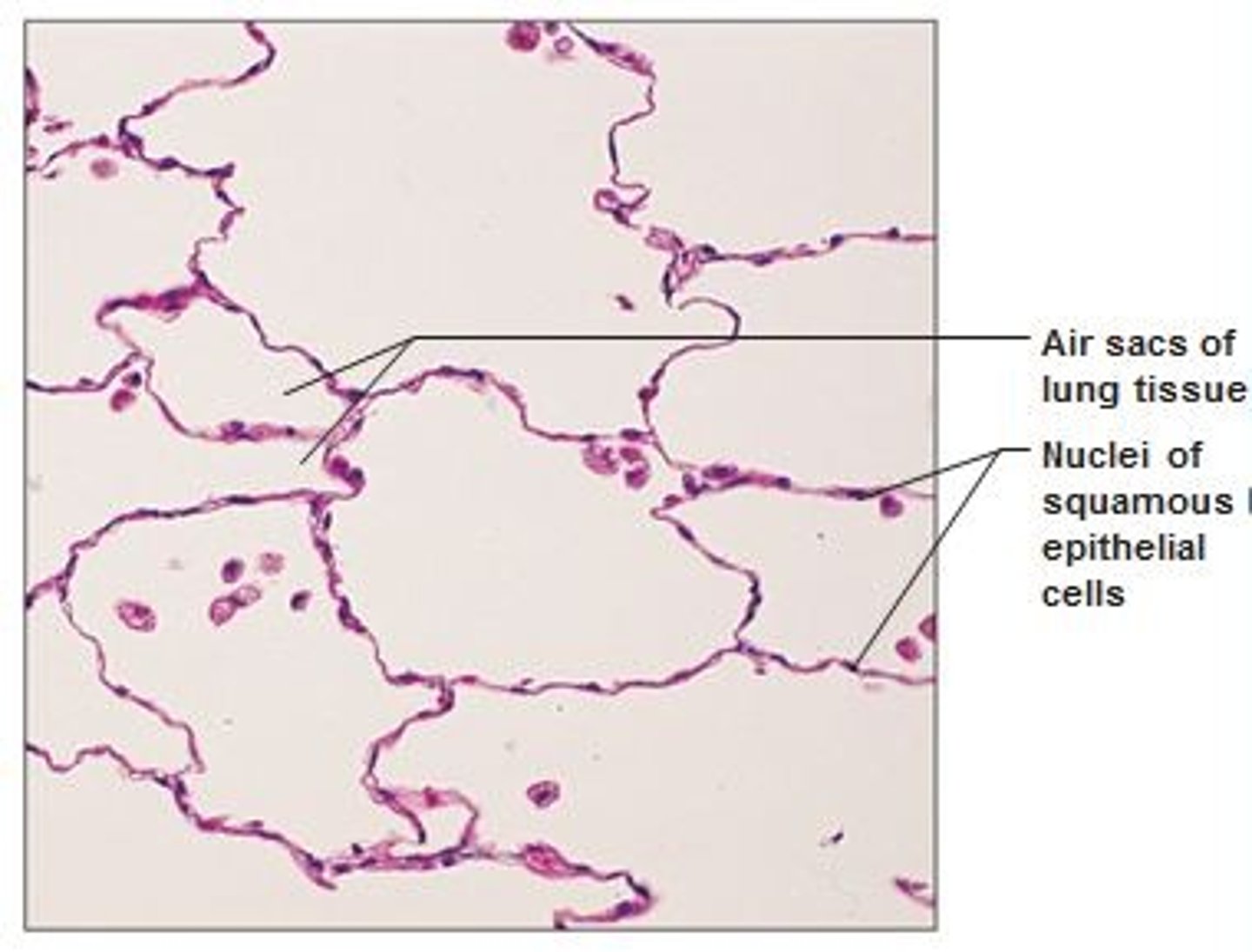
simple squamous epithelium
single layer of flattened cells found in lungs
simple cuboidal, in the kidney
what is this type of tissue and where is it found?
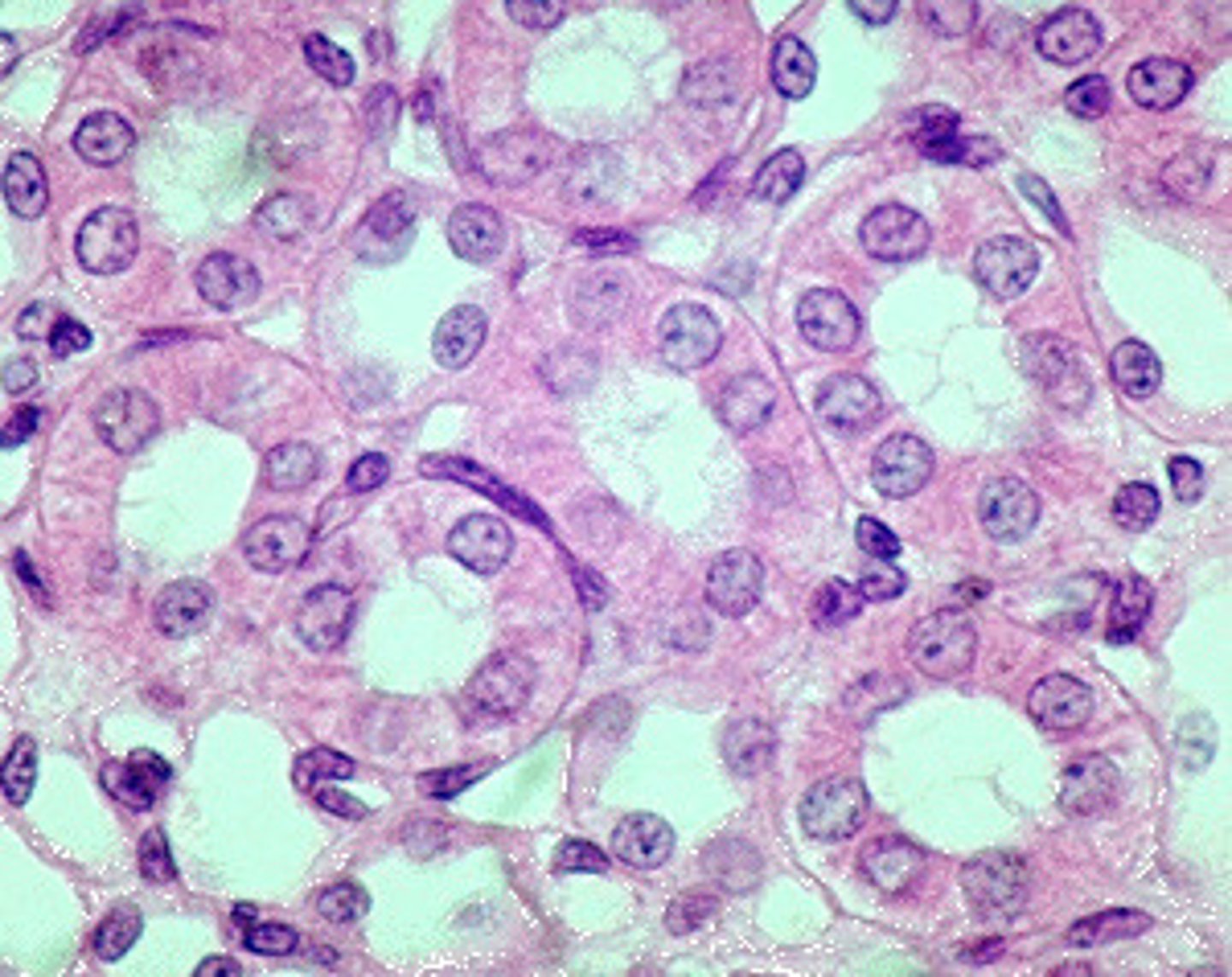
Simple cuboidal
single layer of cube shaped cells, nuclei located in center of cell
simple columnar, in the duodenum
what is this type of tissue and where is it found?
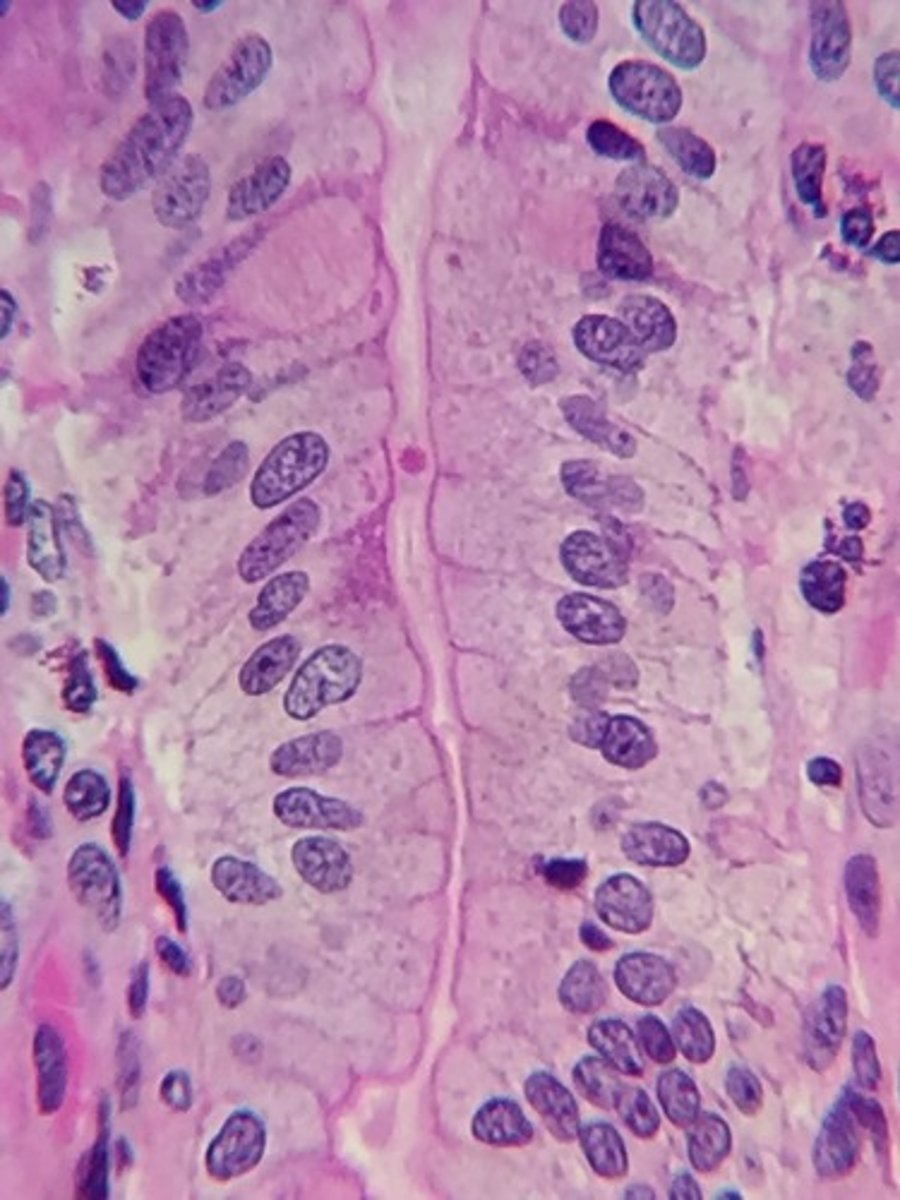
simple columnar
Single layer of tall cells, round or oval nuclei near basement membrane
pseudo stratified epithelium, in the trachea
what is this type of tissue and where is it found?
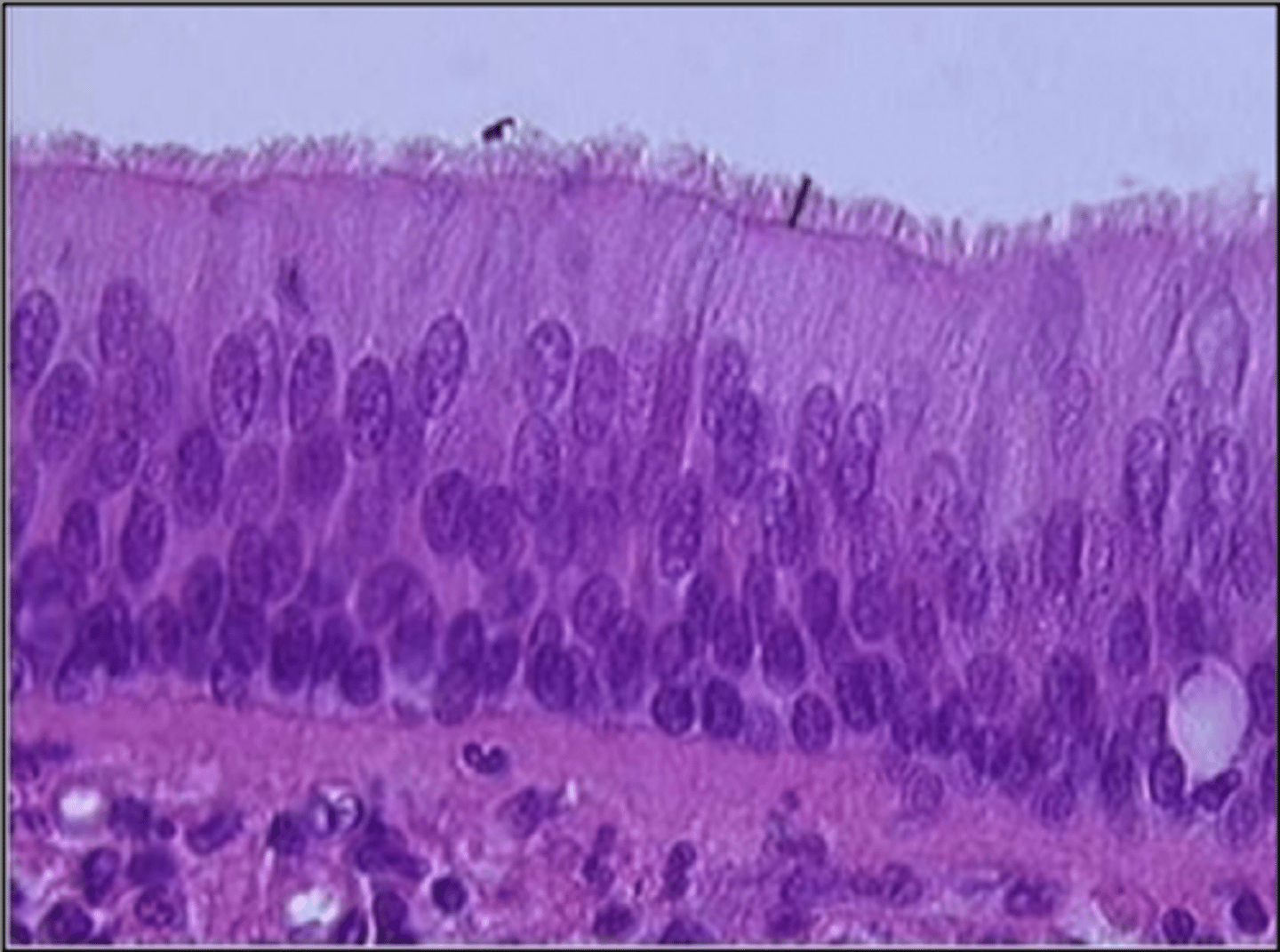
Pseudostratified epithelium
Multiple layers due to difference in cell height, but are really one layer.
they only have one layer of cells
how can you tell what is a simple tissue
stratified squamous epithelium, on the skin
what is this type of tissue and where is it found?
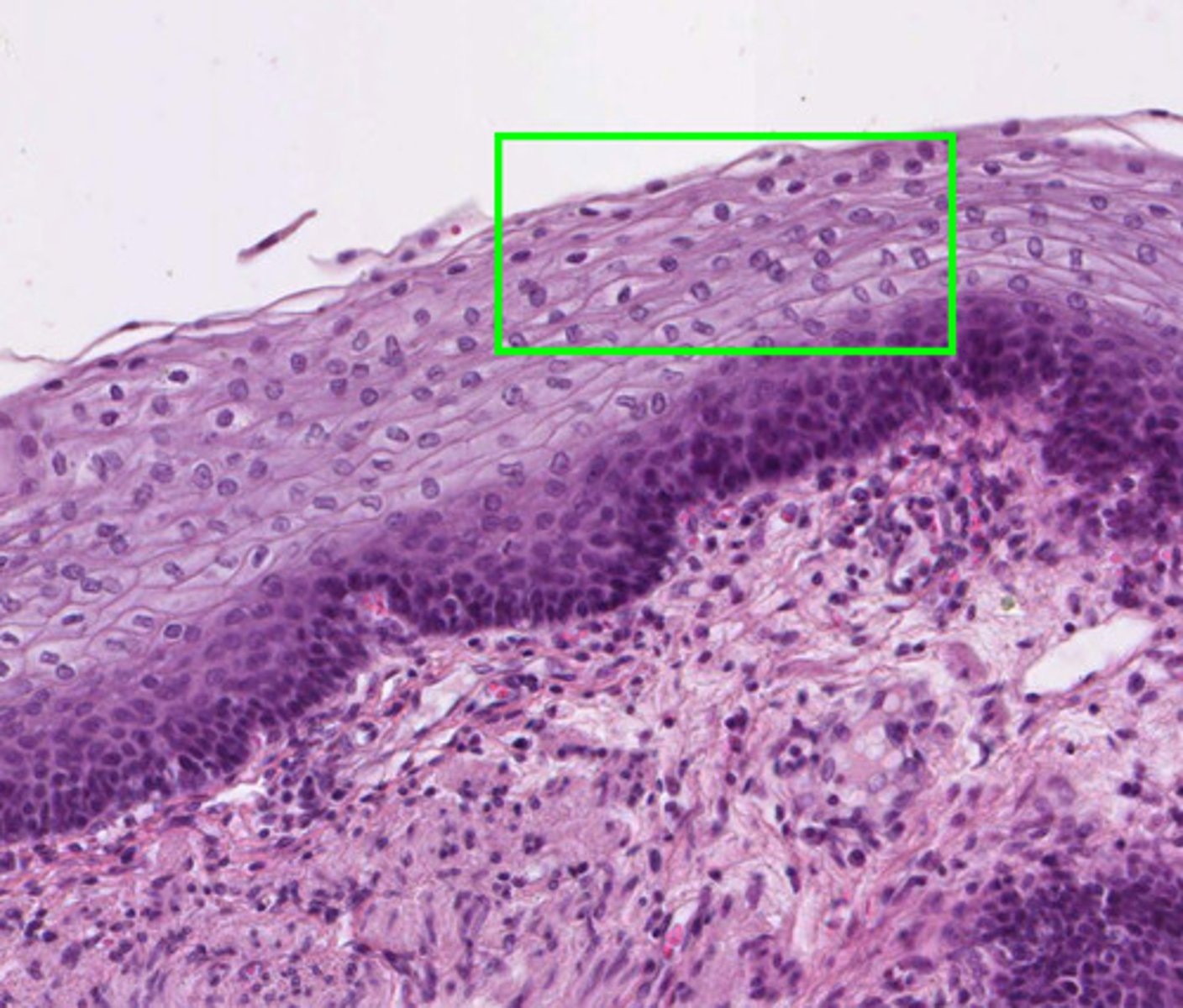
stratified squamous epithelium
has multiple layers, protects underlying tissues in areas subjected to abrasion
transitional epithelium, urinary bladder
what is this type of tissue and where is it found?
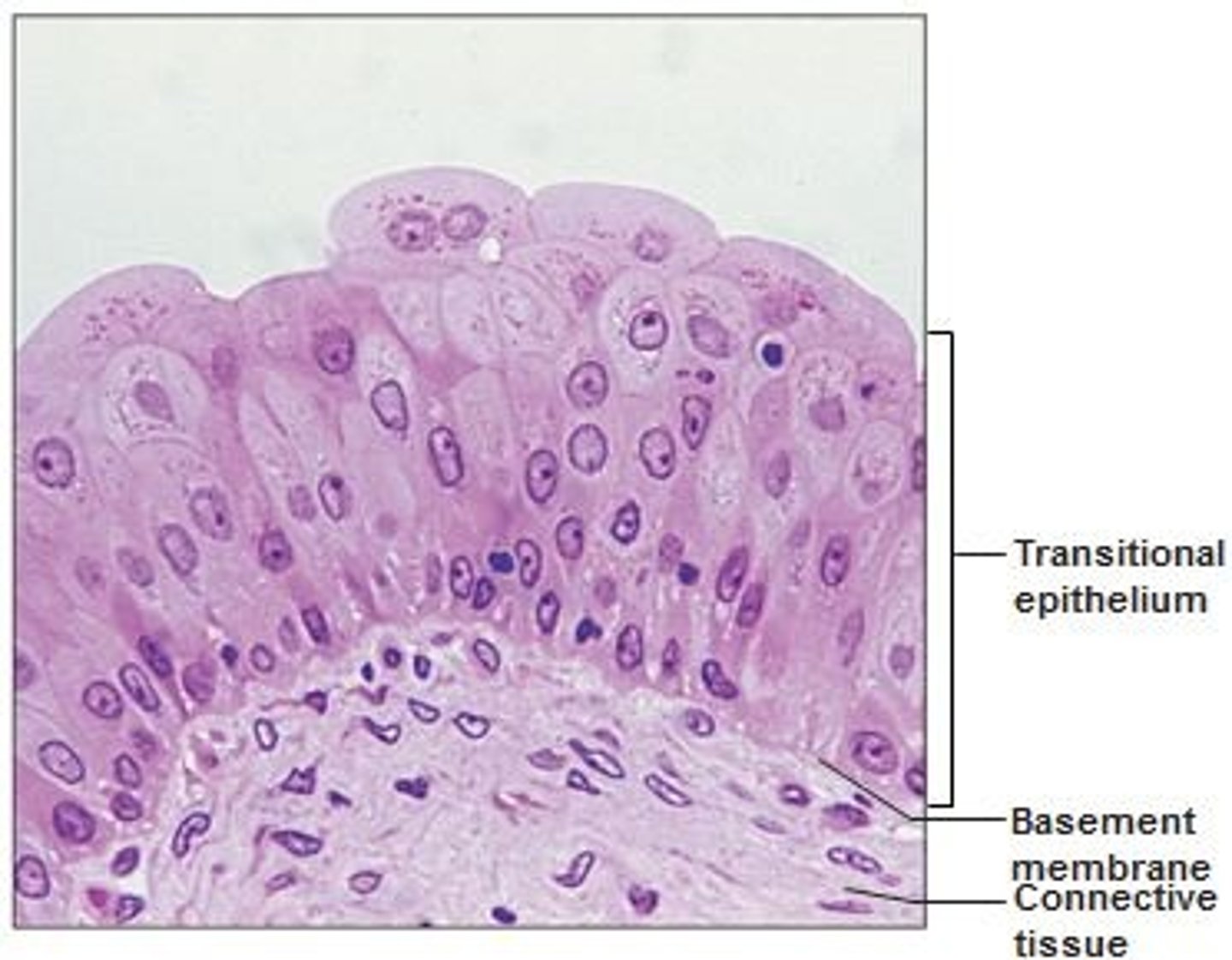
transitional epithelium
function: stretches readily and permits distension of urinary organ by contained urine
Location: lines the ureters, urinary bladder, and part of the urethra