Cnidaria part 2- Invertebrate zoology
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
what do all cnidaria have?
stinging cells
what conditions do anthozoa like to live in?
shallow to abyss, temperate, tropical, and polar regions
what is the lifespan of anthozoa?
some species can live 1,000 years or more
what is actinopharynx?
Tube that projects into gastrovascular cavity
what is siphonoglyphs?
Ciliated groove in gastrovascular cavity
what is Mesenteries?
Radially arranged sheets of tissue that extend from the body wall into the actinopharynx
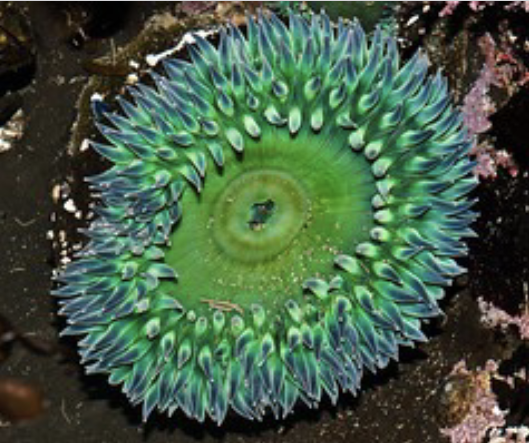

what is this ?
Siphonoglyph
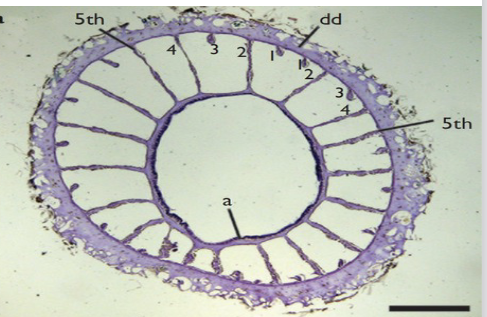
what is this?
Mesenteries
what does anthozoa stand for?
flower animal
what subclasses are anthozoa divided into?
Hexacorallia and Octocorallia
how many layers of cells do anthozoa have?
2, endotherm and ectotherm
what is a polyp
tubelike sac, single opening which serves as both
mouth and anus
what are Cnidocytes?
stinging cells used in prey capture, defense, and intraspecific competition
what are the 3 types of cnidae
Nematocysts, Spirocysts, Ptychocysts
are anthozoa predatory?
yes
characteristics of nematocysts
venomous. found in all anthozoans
characteristics of spirocysts
non-venomous, sticky, hexacorallia
characteristics of Ptychocysts
used in tube construction, Ceriantharia only
are anthozoans colonial, clonal, or solitary?
Can be all types, depending on the species.
what can anthozoa skeletons be made of?
water (hydrostatic), protein, octorallia, and scleractinia
are anthozoa sexual or asexual?
both
definition of a genet
genetically identical group of individuals
how an corals produce fragmentation?
storms and wave action
definition of fragmentation
a piece of the parent colony becomes detached and forms a new, genetically identical colony
what kind of reproduction uses gametes?
Sexual reproduction
are anthozoa gonochoristic or hermaphroditic
can be both
what do anthozoa eggs develop into?
planula larvae
where are anthozoa found?
all oceans
do deep or shallow corals live in groups?
shallow corals often live in groups.
what are deep sea examples of coral that live in deep water?
coral gardens and forests
do corals need a host?
yes, they are host obligate
diet of anthozoa
amphipods, copepods, chaetognaths, polychaetes
can coral drown?
yes
how long can black coral live?
up to and over 4,000 years
what can coral skeletons be used for?
to study past ocean chemistry
why would a deep sea fish be red?
because red is one of the first colors to disappear in deep water, making them less visible to predators.
why would deep sea fish have bigger eyes?
to help them see in the low-light conditions of deep water
do corals compete against each other?
yes, intraspecific competition
how do corals compete/ avoid predators?
mucus and nematocysts
what does bamboo coral use for defense and feeding?
sweeper tentacles
what coral produces toxins to deter predation, but also uses the same toxins as sperm-attractants
octocorals
what is mtDNA
mitochondrial DNA
what can chemicals from corals be used for?
HIV inhibitor, cytotoxic, anticancer, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial
do anthozoa have fast sequences of evolution?
no, they evolve at a slow rate
what are some reasons anthozoa evolve slower?
low metabolic rate, significant bottleneck, mismatch repair genes
what is anthozoans place in the ToL
one of the earliest branches of metazoans
wat is anthozoans sister group?
bilateria
do hydrozoans have a simple life cycle?
no, it is complex
what do hydrozoans alternate bewteen?
being asexual (benthic poly) and sexual planktonic medusae
do hydrozoans always have a polyp and medusae faze?
no, they can be absent
do hydrozoans prefer freshwater?
they can prefer both marine and freshwater
what are limiting factors of hydrozoan distribution?
temperature and salinity
what is a hydrozoan that is invasive?
cordylophora caspia
what do some hydroids host?
dinoflagellates (like millepora and myrionema)
what do green hydra host?
green algae
what do genetics reveal about the life-cycle of hydrozoans
dependent of gene loss, gene replication, and horizontal gene transfer
what is HGT
transfer of genes between species
what kind of gene transfer happens between parent and offspring?
Vertical gene transfer
cnidaria is made up of 2 monophyletic clades, what are they?
Medusozoa and Anthozoa
what is a sister group?
when a single ancestral lineage gives arise to two daughter lineages
what forms a clade that is sister to hydrozoa?
scyphozoa