Final Exam ECE Digital Devices
1/284
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
285 Terms
Convert the following 8-bit fixed precision unsigned binary value to decimal % 1010 1101
173
Convert the following 8-bit fixed precision unsigned binary value to decimal % 0110 1010
106
Convert the following decimal number into 8-bit fixed-precision unsigned binary value: 141
%10001101
Convert the following decimal number into 8-bit fixed-precision unsigned binary value: 173
%10101101
Convert the following binary value into 12-bit fixed-precision unsigned hex value
%1001 1011 1110
$9BE
Convert the following 12-digit fixed-precision unsigned hex value to binary: $67D
0110 0111 1101
Convert the following decimal number into 8-bit fixed-precision unsigned hex value: 76
$4C
Convert the following decimal number into 8-bit fixed-precision unsigned hex value: 84
$54
Convert the following 2-digit fixed-precision unsigned hexadecimal value to decimal: $4E
78
Convert the following 2-digit fixed-precision unsigned hexadecimal value to decimal: $42
66
Conversion from decimal to binary
Use successive division – dividing by 2, keeping track of your remainder.
The converted number is all of the remainders (first division is the least
significant bit). Pad the value with enough zeros to have the correct fixed
precision.
Conversion from decimal to hexadecimal
Use successive division – dividing by 16, keeping track of your remainder.
The converted number is all of the remainders (first division is the least
significant digit). Pad the value with enough zeros to have the correct
fixed precision
Conversion from binary to decimal
Use Positional notation to determine the decimal equivalent. Each bit
represents a power of 2, with the least significant bit representing 2 to the
0th power or 1.
Conversion from hexadecimal to decimal
Use Positional notation to determine the decimal equivalent. Each bit
represents a power of 16, with the least significant bit representing 16 to
the 0th power or 1.
Conversion from binary to hexadecimal
Starting at the LSB working left, group the bits by 4s. Padding of 0s can
occur on the most significant group. Convert each group of 4 into the
equivalent HEX valu
Conversion from hexadecimal to binary
Convert each HEX digit to the equivalent four-bit binary grouping
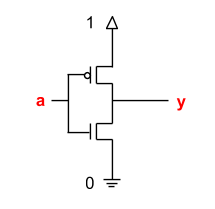
Given the following transistor diagram, what is y when a is 0?
1
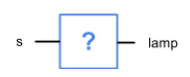
Indicate which one logic gate is best suited to implement the desired system functionality.
A sensor detects sunlight (s = 0 means no sunlight, s = 1 means sunlight). Based on that sensor, a lamp should turn on (lamp = 1) only at night.
NOT
A digital system has the following inputs and outputs:
Inputs: d: door is open, w: window is open, e: alarm is enabled, n: time-of-day is night
Output: s: sounds alarm
Select the Boolean equation that describes the indicated goal.
Goal: Sound alarm if alarm is enabled, and also the window is open or the door is open.
s = e(w+d)
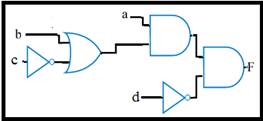
Given the function (F), choose the correct schematic/circuit diagram.
F = a (b + c’) d’
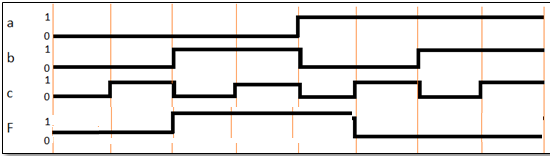
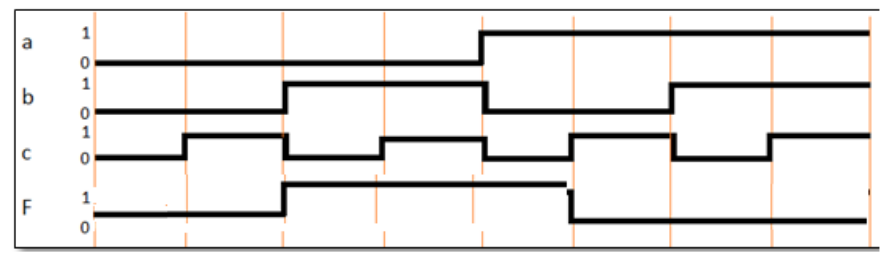
Given the timing diagram below, write the Boolean function equation for “F(a,b,c)”:
F = a’bc’ + a’bc + ab’c’
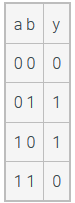
Consider the following truth table. An SOP equation will be y = ___ + ___. Which is one of the minterms in the equation?
a’b
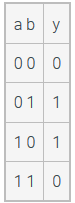
Consider the following truth table. An POS equation will be y =( +)*( +). Which is one of the MAXterms in the equation?
a+b
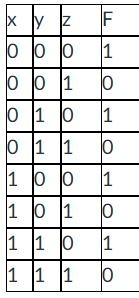
Given the truth table, write the equation of the function F in minterm notation decimal format:
F = ∑m(0,2,4,6)
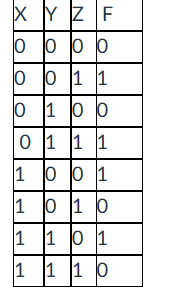
Write the equation for F in MAXterm notation decimal format.
F(X,Y,Z) = ∏M(0,2,5,7)
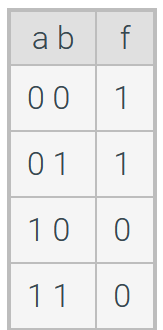
Enter the following truth table in POS form.
(a'+b)(a'+b')
Write the following truth table in minterm notation decimal format.
f(a,b,c) = ∑m(2,3,4)
Following the example 2.1.6 in Zybooks, determine the simplification for the following equation using what is called the absorption property
f(a,b,c,d) =a'b + b + bc' + bcd'
f(a,b,c,d) = b
Using the absorption property,
f(x,y) = xy + x
can be simplified to
f(x,y) = x
Using Zybooks participation activity 2.1.6 as an example, determine what the following equation would be simplified to. This theorem is also listed on the Boolean Algebra theorems sheet as theorem 16a.
f(x,y) = x'y' + y
f(x,y) = x' + y
Using the factoring methods of boolean algebra, simplify the following equation.
f(a,b,c) = a'bc' + a'b'c'
f(a,b,c) = a'c'
Simplify the following equation using boolean adjacency and idempotent axiom (can or additional terms matching what is already there).
f(a,b,c) = ab'c' + a'b'c' + a'b'c
f(a,b,c) = b'c' + a'b'
Apply DeMorgan's law twice to determine the inverse of the following function
(a + bc')'
Put your equation in SOP form.
a'b' + a'c
Apply DeMorgan's law 3 times to determine inverse of the following:
(a'b' + cd)'
(a+b)*(c'+d')
Use the identity axiom for OR to expand the following term to Maxterm canonical form
f(a,b,c) = (a + b)*(b' + c)
f(a,b,c) = (a + b + c')*(a + b + c)*(a' + b' + c)*(a + b' + c)
Given the following function, determine the minimum SOP equation.
F(A,B,C,D) = B'D'
Given the following function, determine the minimum SOP equation.
F(A,B,C,D) = C'D'
Given the following function, determine the minimum SOP equation.
F(A,B,C,D) = B'
Given the following function, determine which of the following equations would be minimum SOP equation.Mark all choices that are minimum SOP.
F(A,B,C,D) = A'B'C' + A'BD + ABC + ACD' , F(A,B,C,D) = A'B'C' + A'C'D + BCD + ACD' , F(A,B,C,D) = A'B'C' + A'BD + BCD + ACD'
Given the following function, determine the minimum SOP equation.
F(A,B,C,D) = B' + D'
Given the following function, determine the minimum SOP equation.
F(A,B,C,D) = B'D'
Given the following function, determine the minimum SOP equation.
F(A,B,C,D) = C'D'
Given the following function, determine the minimum SOP equation.
F(A,B,C,D) = B'
Given the following function, determine which of the following equations would be minimum SOP equation.Mark all choices that are minimum SOP.
F(A,B,C,D) = A'B'C' + A'BD + ABC + ACD' , F(A,B,C,D) = A'B'C' + A'C'D + BCD + ACD', F(A,B,C,D) = A'B'C' + A'BD + BCD + ACD'
Given the following function, determine the minimum SOP equation.
F(A,B,C,D) = B' + D'
Given the following equation:
a(w,x,y,z) = ∑m(1,4,11,13)
determine the correct minimum SOP equation
a(w,x,y,z) = (w'x'y'z) + (w'xy'z') + (wx'yz) + (wxy'z)
Given the following equation:
b(w,x,y,z) = ∑m(5,6,11,12,14,15)
determine the correct minimum SOP equation
b(w,x,y,z) = (w'xy'z) + (xyz') + (wxz') + (wyz)
Given the following equation:
c(w,z,7,z) = ∑m(2,12,14,15)
determine the correct minimum SOP equation
c(w,x,y,z) = (wxy) + (w'x'yz') + (wxz')
Given the following equation:
d(w,x,y,z) = ∑m(1,3,.7,10,15)
determine the correct minimum SOP equation
d(w,x,y,z) = (w'x'y'z) + (w'xy'z') + (xyz) + (wx'yz')
Given the following equation:
e(w,x,y,z) = ∑m(1,3,4,6,7,9)
determine the correct minimum SOP equation
e(w,x,y,z) = (w'z) + (w'xy') + (x'y'z)
Given the following equation:
f(w,x,y,z) = ∑m(1,2,3,7,13)
determine the correct minimum SOP equation
f(w,x,y,z) = (w'x'z) + (w'x'y) + (w'yz) + (wxy'z)
Given the following equation:
g(w,x,y,z) = ∑m(0,1,7,12)
determine the correct minimum SOP equation
g(w,x,y,z) = (w'x'y') + (w'xyz) + (wxy'z')
Write the equation for the output SUM for a half adder. The inputs are named A, B. Make a truth table if necessary.
Sum(A,B) = A'B + AB'
Write the equation for the output C( or CarryOut) for a half adder, Make a truth table if necessary.
C(A,B) = AB
A half Adder creates an arithmetic circuit that adds _________ single bit inputs.
2
Write the SOP equation for the output SUM for a full adder. Hint: Make a truth table.
Sum(A,B,Cin) = AB(Cin) + A'B'(Cin) + A'B(Cin)' + AB'(Cin)'
Write the SOP CANONICAL equation for the output C( or CarryOut) for a full adder. Hint: Make a truth table if necessary.
C(A,B,Cin) = AB(Cin) + AB(Cin)' + AB'(Cin) + A'B(Cin)
Write the minimum SOP equation for the output C( or CarryOut) for a full adder. Make a kmap from your truth table.
C(A,B,Cin) = AB + A(Cin) + B(Cin)
A full Adder creates an arithmetic circuit that adds _________ single bit inputs.
3
A 4-bit adder can be made from four full adder circuits by cascading them together. The carryout of each full adder becomes the carry in of the next adder. To use four full adders, the least significant adder must have cin tied to _________.
ground (0)
A half adder can be used as a(n) ________________ circuit, which adds 1 to a number.
incrementor
A four bit incrementer can be built from four half adders by cascading them together. The carryout of each half adder becomes the b input of the next adder. To use four half adders as a 4-bit incrementer, the least significant half adder must have input b tied to _______________.
High(1)
A 2:4 decoder outputs exactly how many "1"s for a given set of inputs. In other words, if I1I0 = "00", how many outputs are equal to 1. If I1I0 = "11", how many outputs are equal to 1, ...
one
A 2:4 decoder has how many outputs.
four
Some decoders have an additional input called an enable input that when 0 sets all outputs to ____.
0
Some decoders have an additional input called an enable input that when 0 sets all outputs to ____, and when 1 enables the decoder for normal behavior..
0
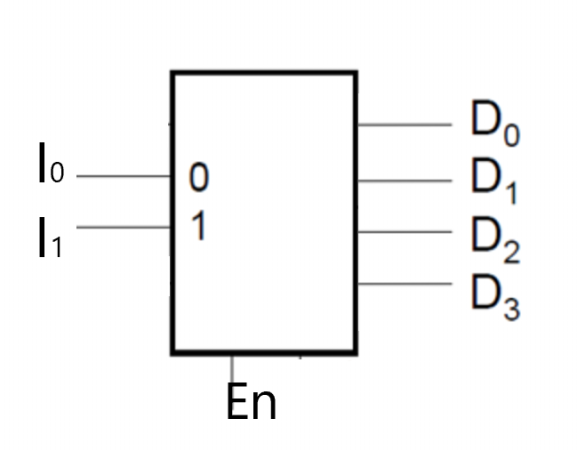
Give the equation for the output D1 for the following decoder
D1 = En * I1’ * I0
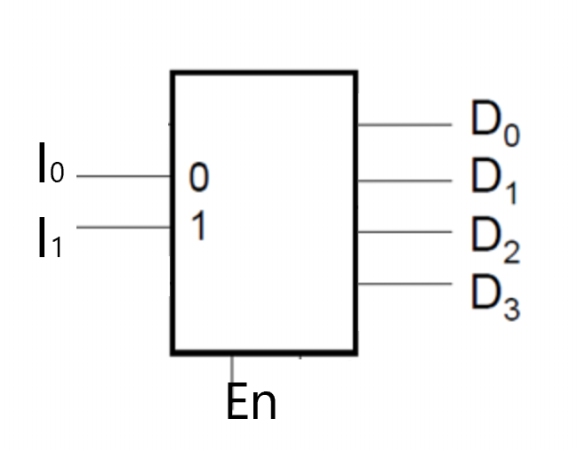
Give the equation for the output D2 for the following decoder
D2 = En I1 I0'
A decoder is an n-to-2n device that generates all of the _____________ of a function. (Hint: think about which output is 1 for any given set of inputs. 2:4, 3:8, 4:16, 5:32, etc...; think about what term we learned with kmaps that were associated with a row being 1).
minterms
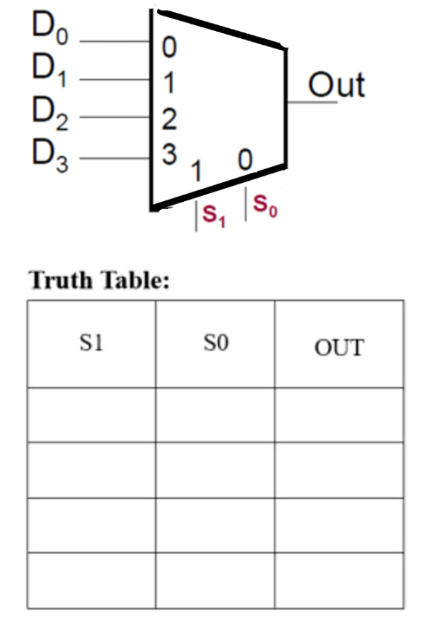
Select which of the following equations implement a 4:1 Multiplexer. HINT: Write the truth table for the select inputs for a 4:1 Mux to determine the circuit implementation.
Out = S1'S0'D0 + S1'S0D1 + S1S0'D2 + S1S0D3
A multiplexor is a combinational circuit that passes one of multiple data inputs through to a single output. Additional inputs are the controls that determine which input is selected. The control inputs are called______________ inputs.
police
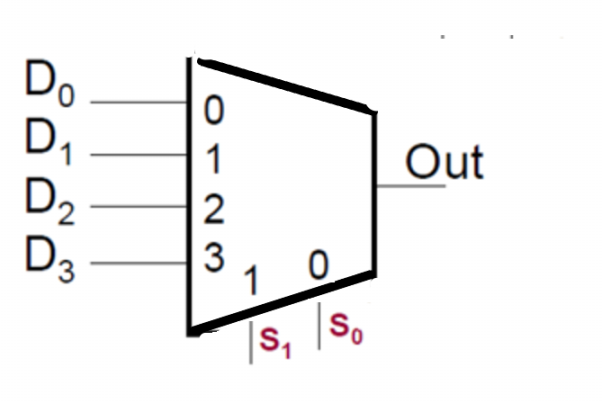
Shown is a 4:1 Multiplexer. What values of S1S0 select D1 to pass through to the output.
S1S0 = "01"
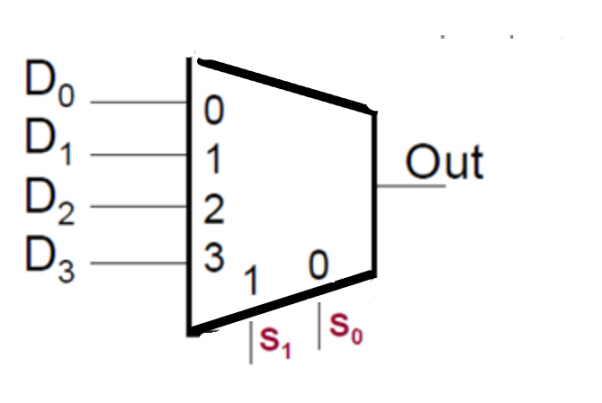
Shown is a 4:1 Multiplexer. If the values of S1S0 select D1 to pass through to the output, and D1 = "0", then the output, OUT =
OUT = 0
Just like the Analogy: Due to road construction, four lanes (the data inputs) may be reduced to a single lane (the single output). A policeman (the select inputs) selects which one lane currently passes through by blocking the other lanes. Just as sometimes the police have one lane open, but no cars are coming through at that time, when the input for the data input selected =0, the output = __________.
0
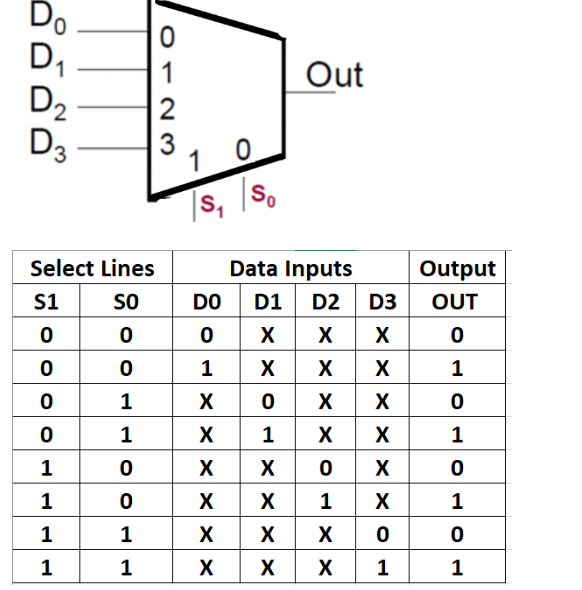
To make a truth table for a mux, we could only write the rows where a specific input is selected, and the other inputs as DON'T CARES. For a 4:1 Multiplexer, for what is the product term associated with D3 where the output OUT = 1.
Out = S1S0D3
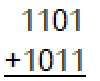
Add the following 4-bit, fixed-precision, 2s complement numbers and give the 4-bit sum along with the overflow result.
1000, overflow did not occur
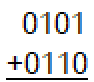
Add the following 4-bit, fixed-precision, 2s complement numbers and give the 4-bit sum along with the overflow result.
1011, overflow occurred
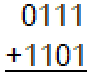
Add the following 4-bit, fixed-precision, 2s complement numbers and give the 4-bit sum along with the overflow result.
0100, overflow did not occur
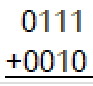
Add the following 4-bit, fixed-precision, 2s complement numbers and give the 4-bit sum along with the overflow result.
1001, overflow occurred
Add the following 8-bit, fixed-precision, 2s complement numbers and give the 8-bit sum along with the overflow result.
1101 1110
1011 0101
1001 0011, overflow did not occur
Add the following 8-bit, fixed-precision, 2s complement numbers and give the 8-bit sum along with the overflow result.
0111 1110
1011 0101
0011 0011, overflow did not occur
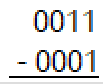
Subtract the following 4-bit, fixed-precision, 2s complement numbers and give the 4-bit result along with the overflow result.
0010, overflow did not occur
Subtract the following 4-bit, fixed-precision, 2s complement numbers and give the 4-bit result along with the overflow result.
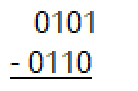
1111, overflow did not occur
Subtract the following 4-bit, fixed-precision, 2s complement numbers and give the 4-bit result along with the overflow result.
1010, overflow occurred
Subtract the following 8-bit, fixed-precision, 2s complement numbers and give the 8-bit result along with the overflow result.
0101 1110
- 1111 0101
0110 1001, overflow did not occur
Subtract the following 8-bit, fixed-precision, 2s complement numbers and give the 8-bit result along with the overflow result.
0101 1110
- 1000 0101
1101 1001, overflow occurred
For a subtractor built from an adder, the adder is configured to subtract by setting the adder's cin bit to ___
high(1)
A 4-bit subtractor can be made from a 4-bit adder along with 4 inverters into input B[3:0] and setting Cin to 1. This can be written algebraically as
A - B = A + (-B)
Because two's-complement representation performs subtraction by complementing and adding, a single adder circuit can perform either addition or subtraction, thus saving circuit size. What device must be placed in the circuit to select between addition or subtraction.
4 2:1 Muxes
The select line each of the muxes which chooses between B and inverted B is also connected to the ___________ input of the adder.
cin
To do normal addition on the adder/subtractor, the input sub must equal ____________.
0
To do subtraction on the adder/subtractor, the input sub must equal ____________.
1
Configure the adder/subtractor to do the following arithmetic. 5 - 4
a3a2a3a0 = 0101 b3b2b3b0 = 0100 sub = 1
For a 4-bit right shifter with a control input sh = 0, if inputs (i3,i2,i1,i0) = 1011 and in = 0, then outputs (q3,q2,q1,q0) = ____?
1011
For an 8-bit left shifter with a control input sh = 1, if inputs (i7,i6,i5,i4,i3,i2,i1,i0) = 11101110 and in = 0, then outputs (q7,q6,q5,q4,q3,q2,q1,q0) = ________?
11011100
Give the output for q[3:0] given the following inputs.
1111