Week #7-Science AIR Vocabulary
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
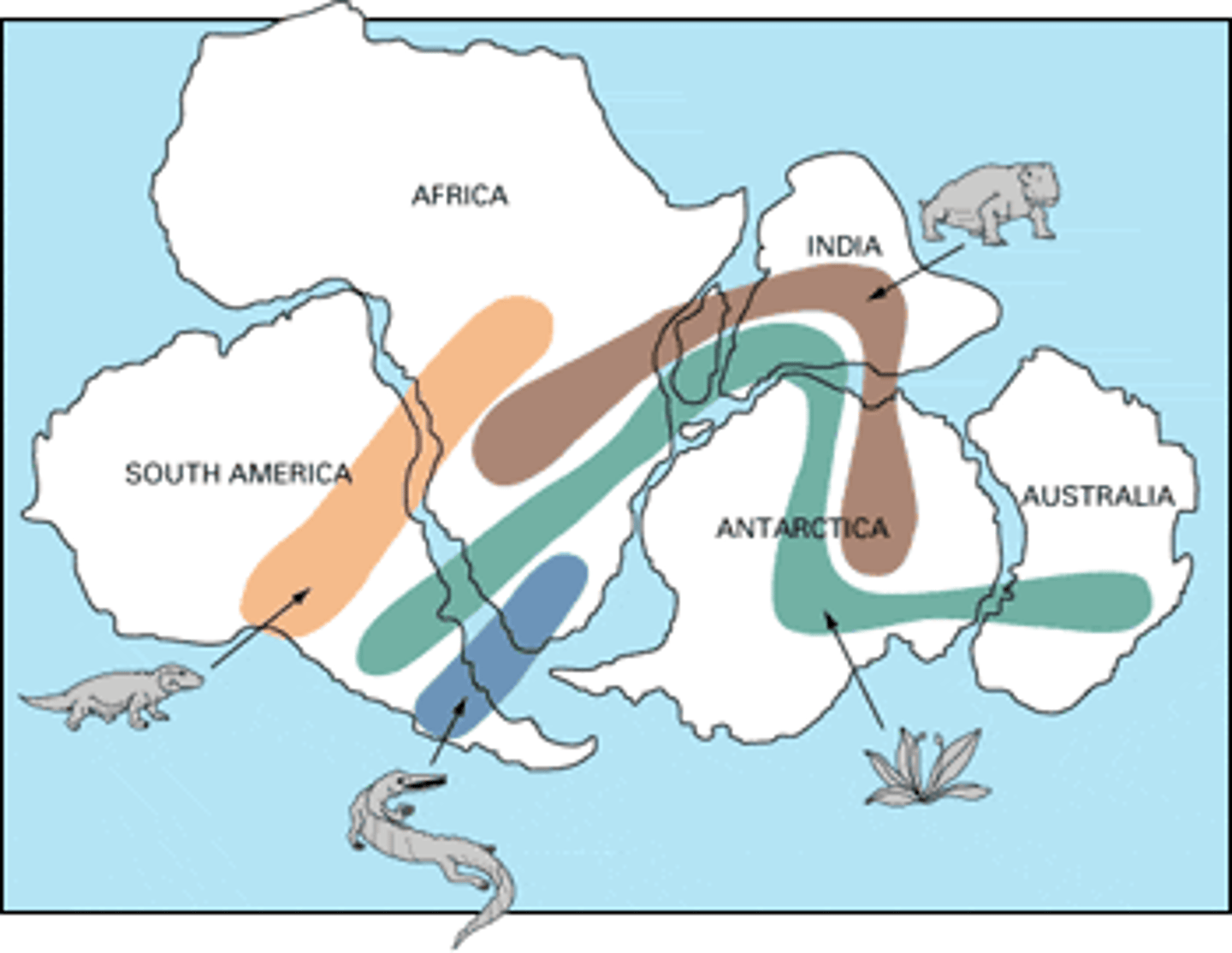
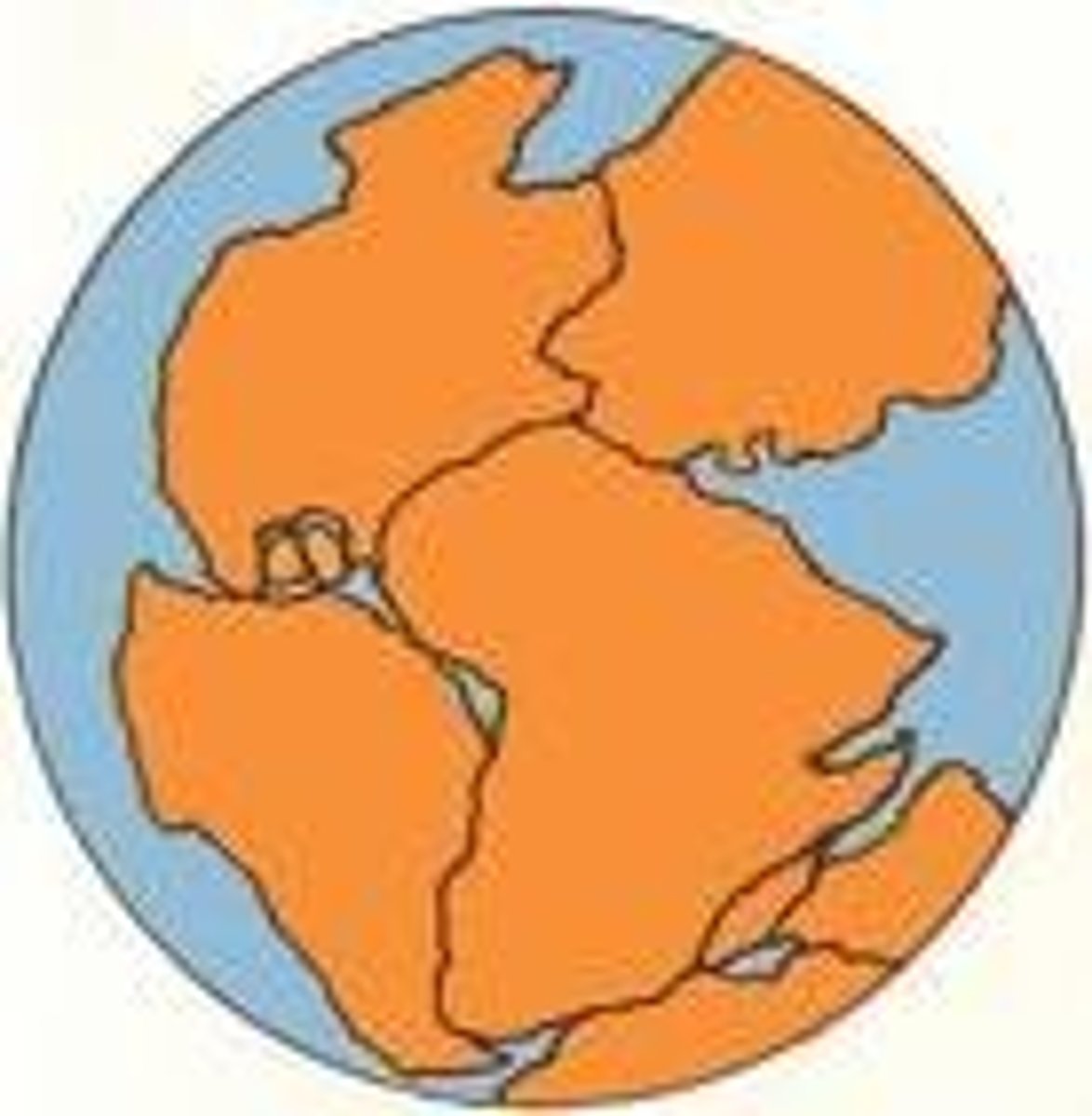
continental drift
The hypothesis that a single large landmass broke up into smaller landmasses to form the continents, which then drifted to their present locations; the movement of continents.
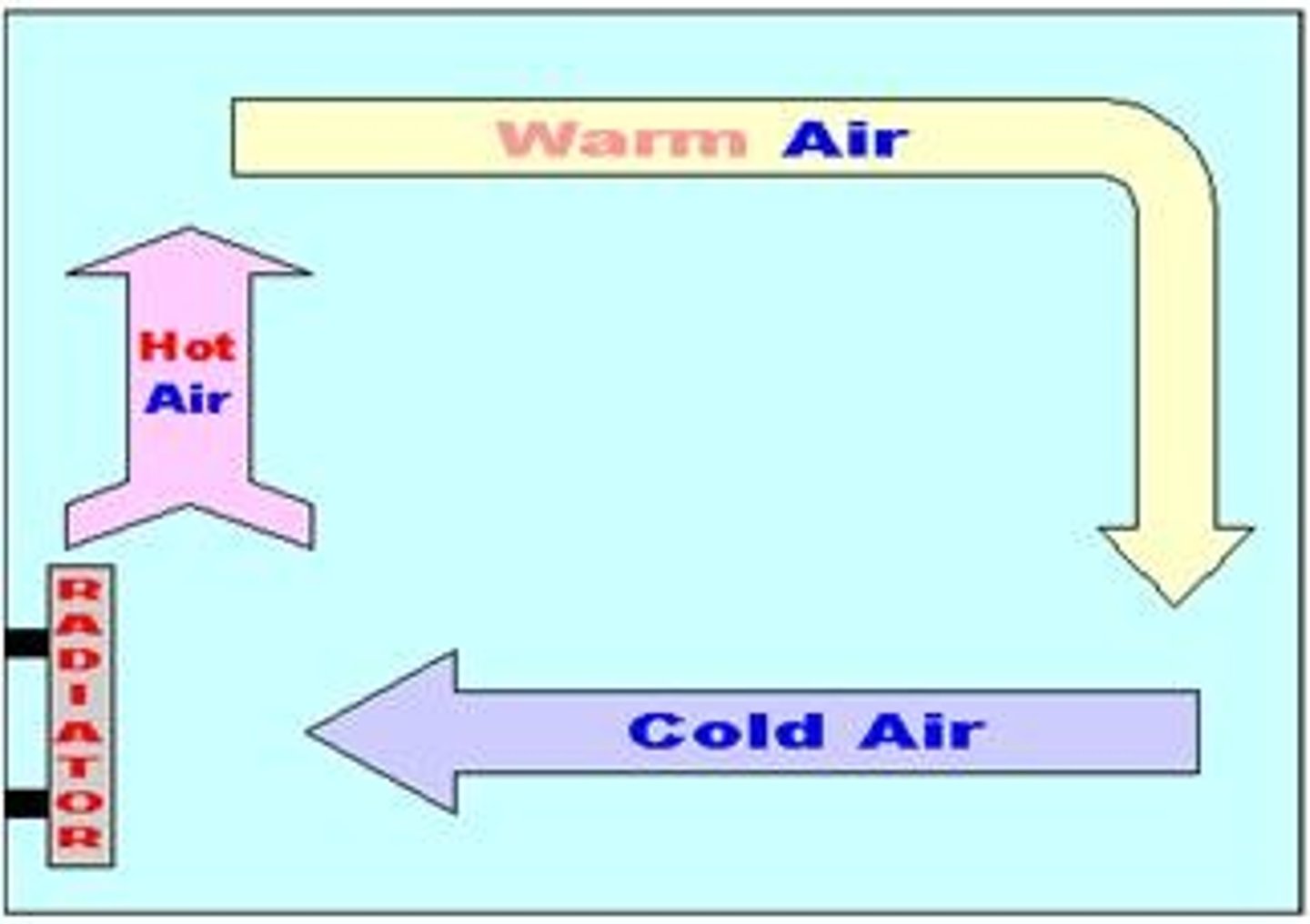
convection
The movement of matter due to differences in density; the transfer of energy due to the movement of matter.
sea floor spreading
The process by which new oceanic lithosphere (sea floor) forms when magma rises to Earth's surface at mid-ocean ridges and solidifies, as older, existing sea floor moves away from the ridge.
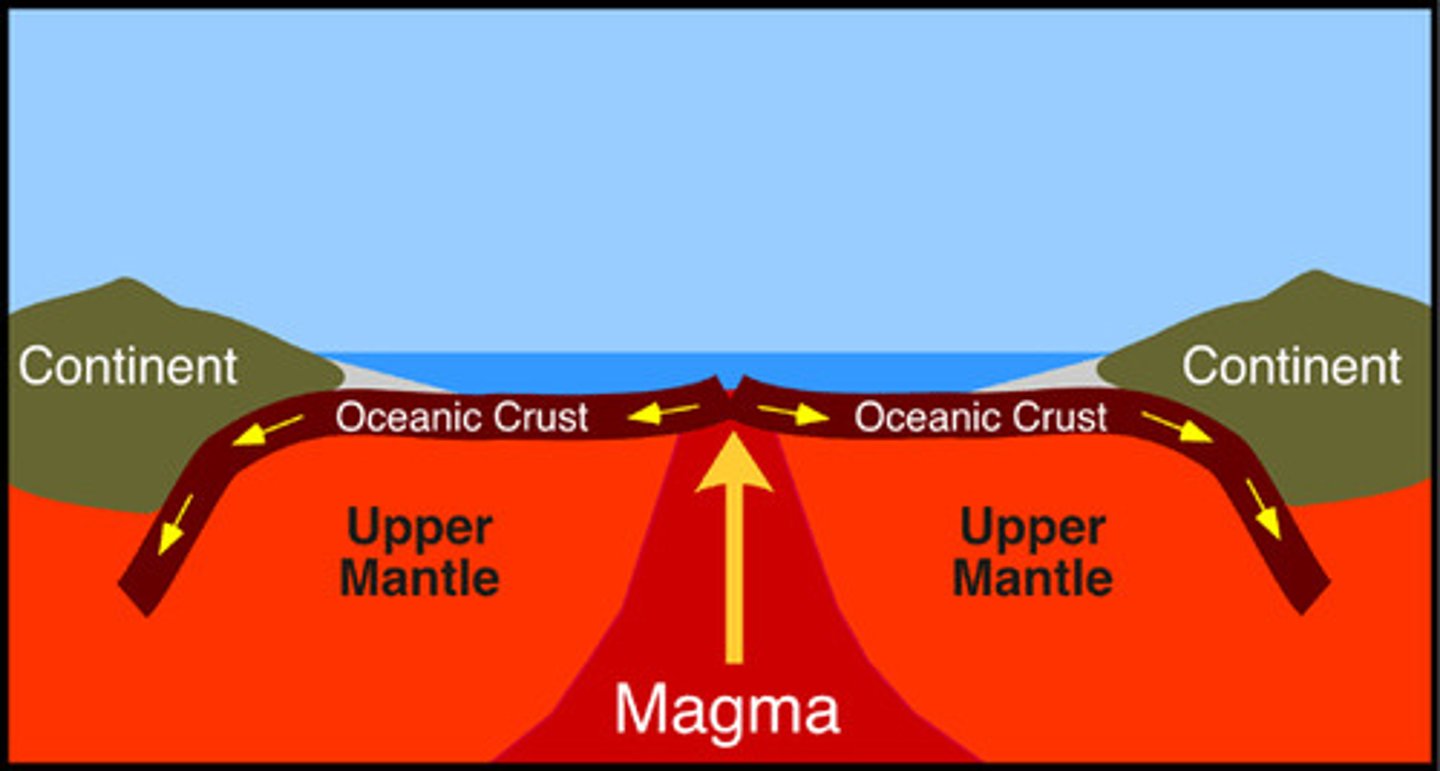
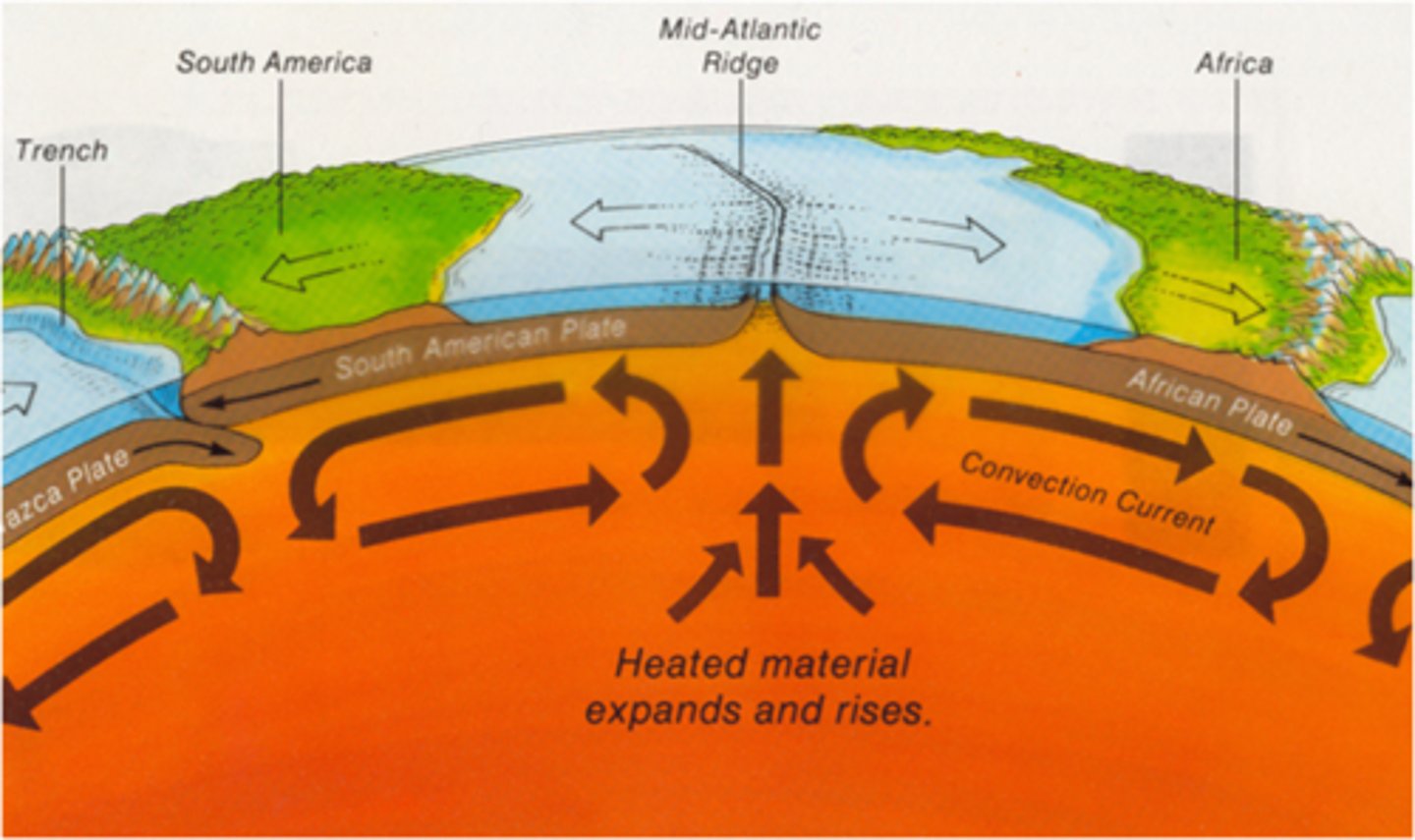
plate tectonics
The theory that explains how large pieces of the lithosphere, called plates, move and change shape.
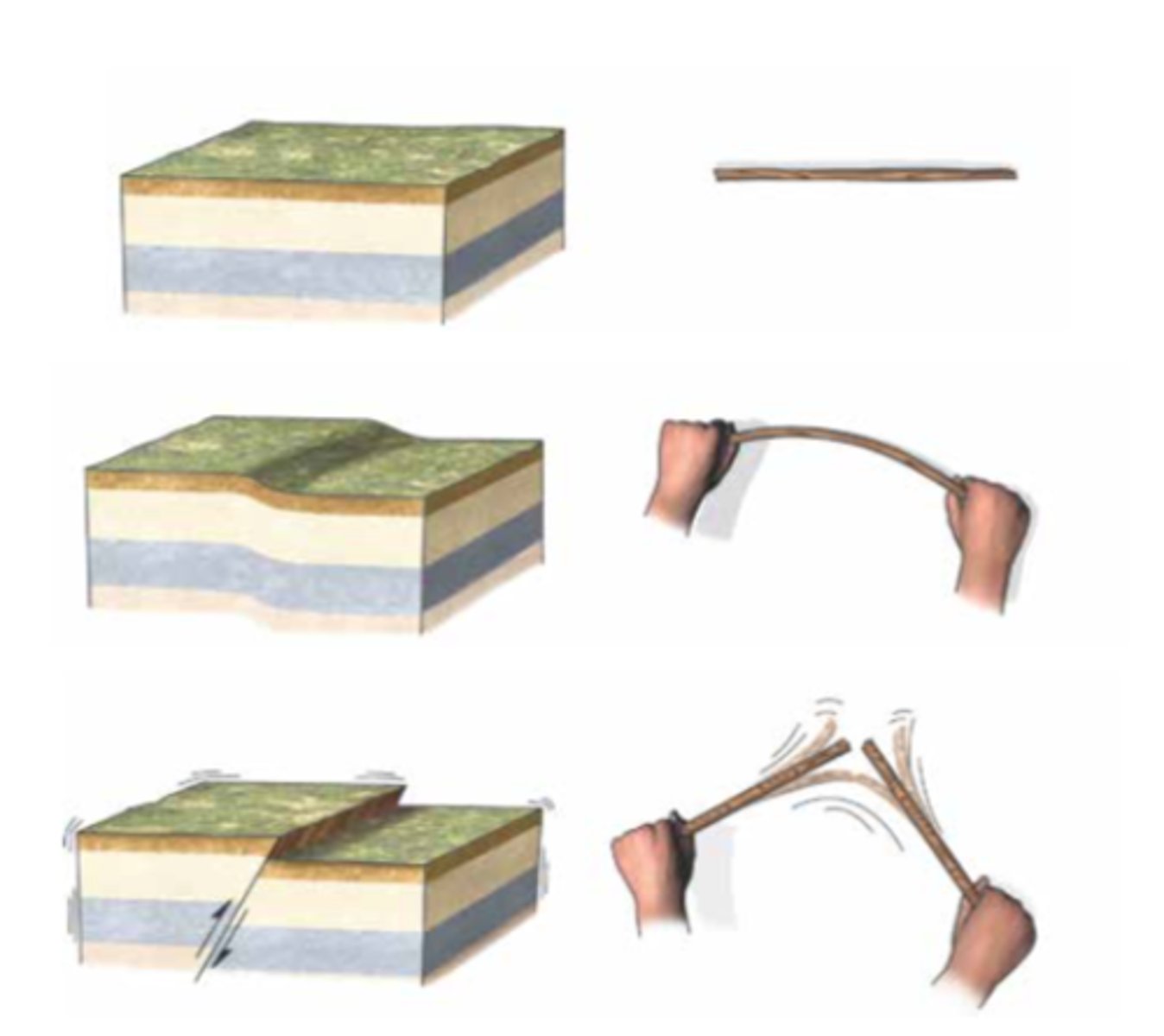
elastic rebound
The sudden return of elastically deformed rock to its undeformed shape.
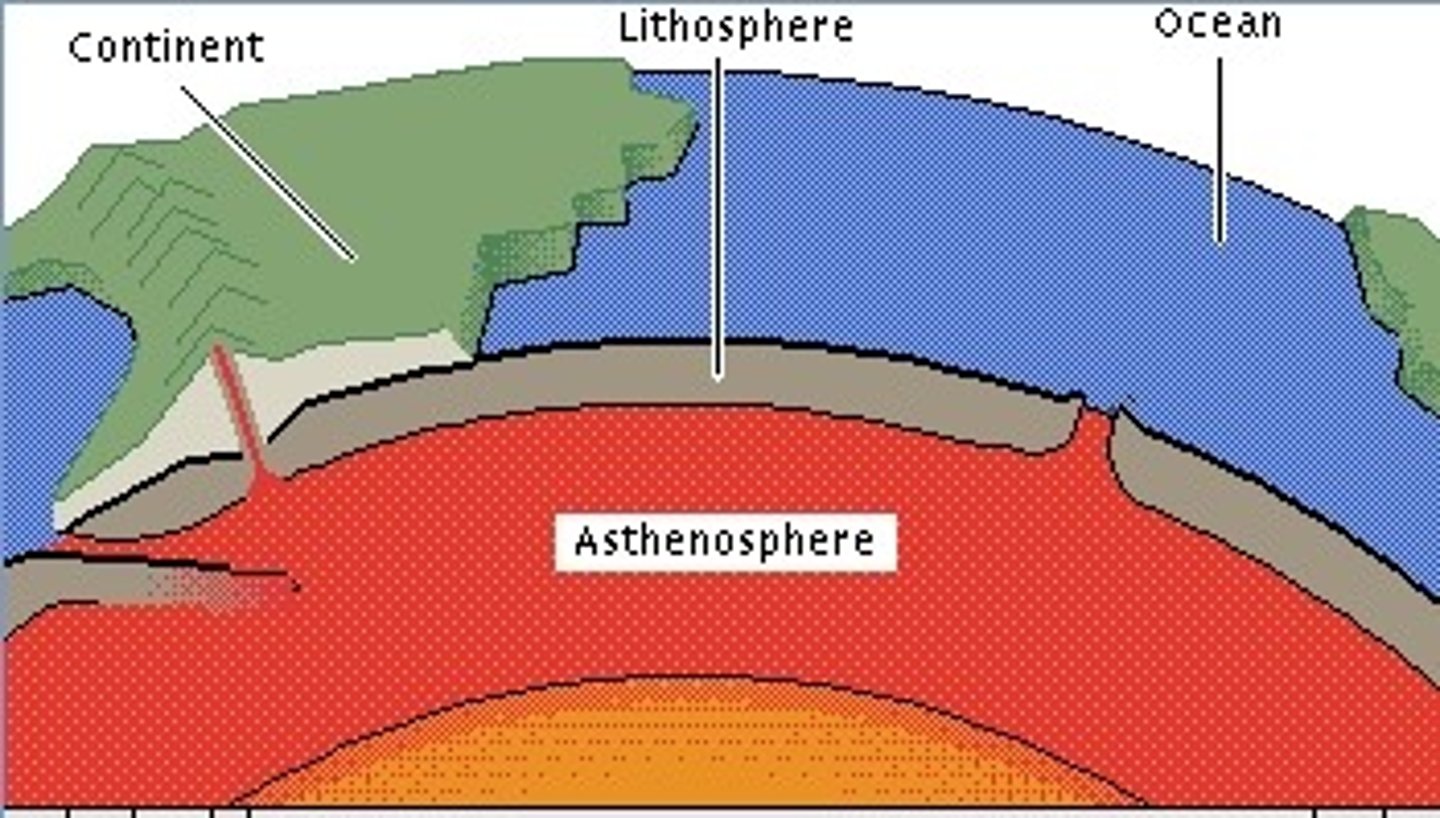
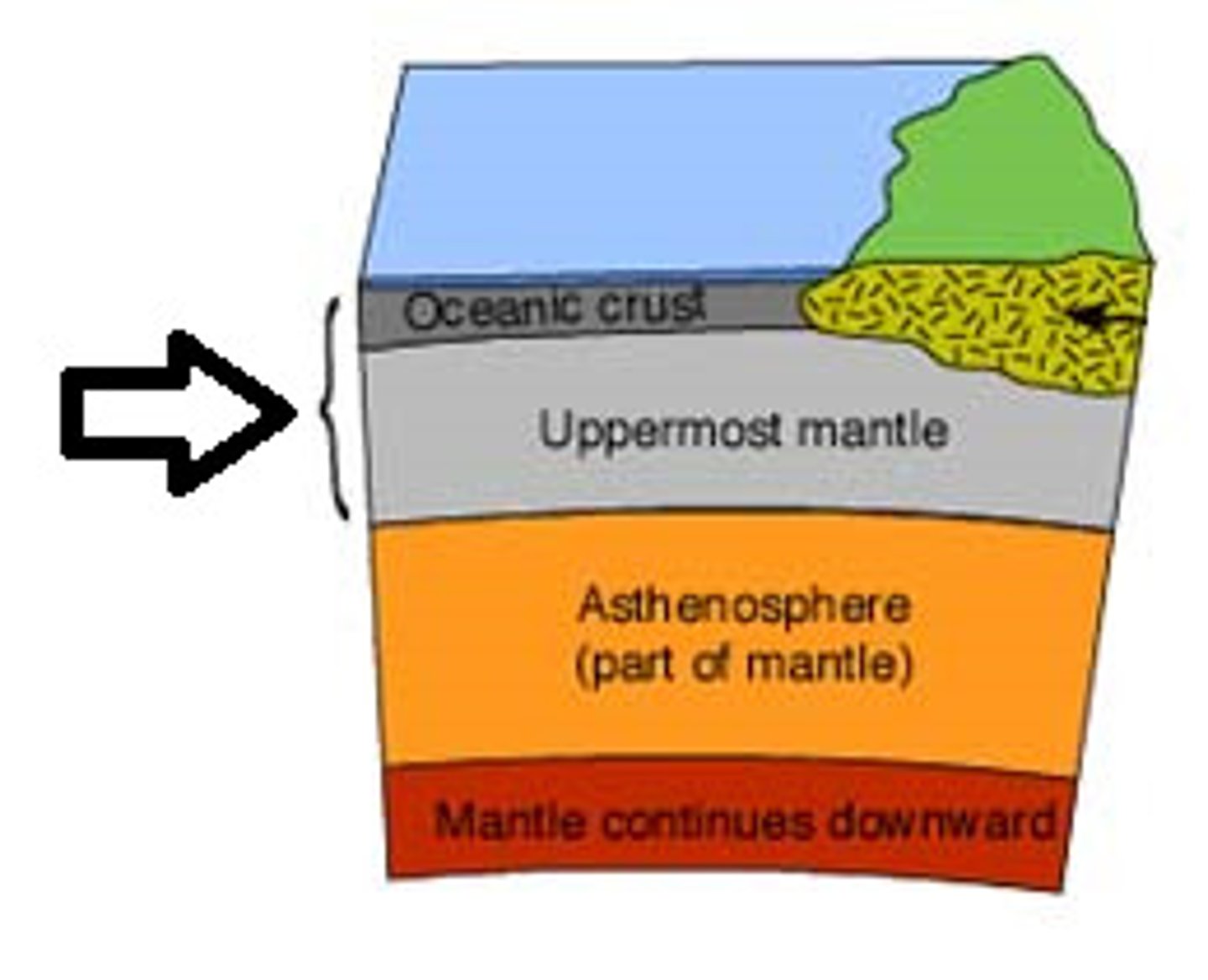
athenosphere
The soft layer of the mantle on which the tectonic plates move.
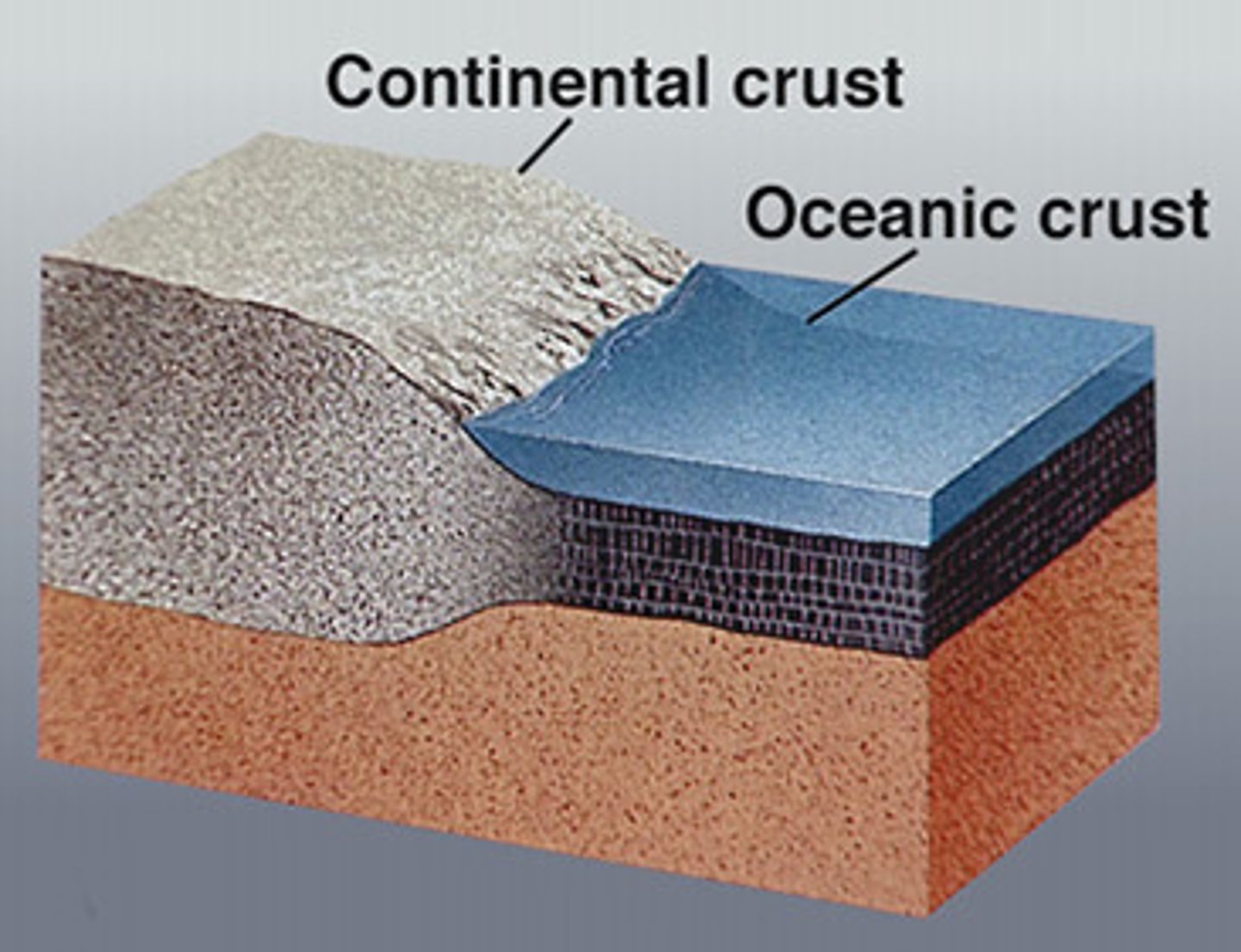
continental crust
The thin and solid outermost layer of Earth above the mantle.
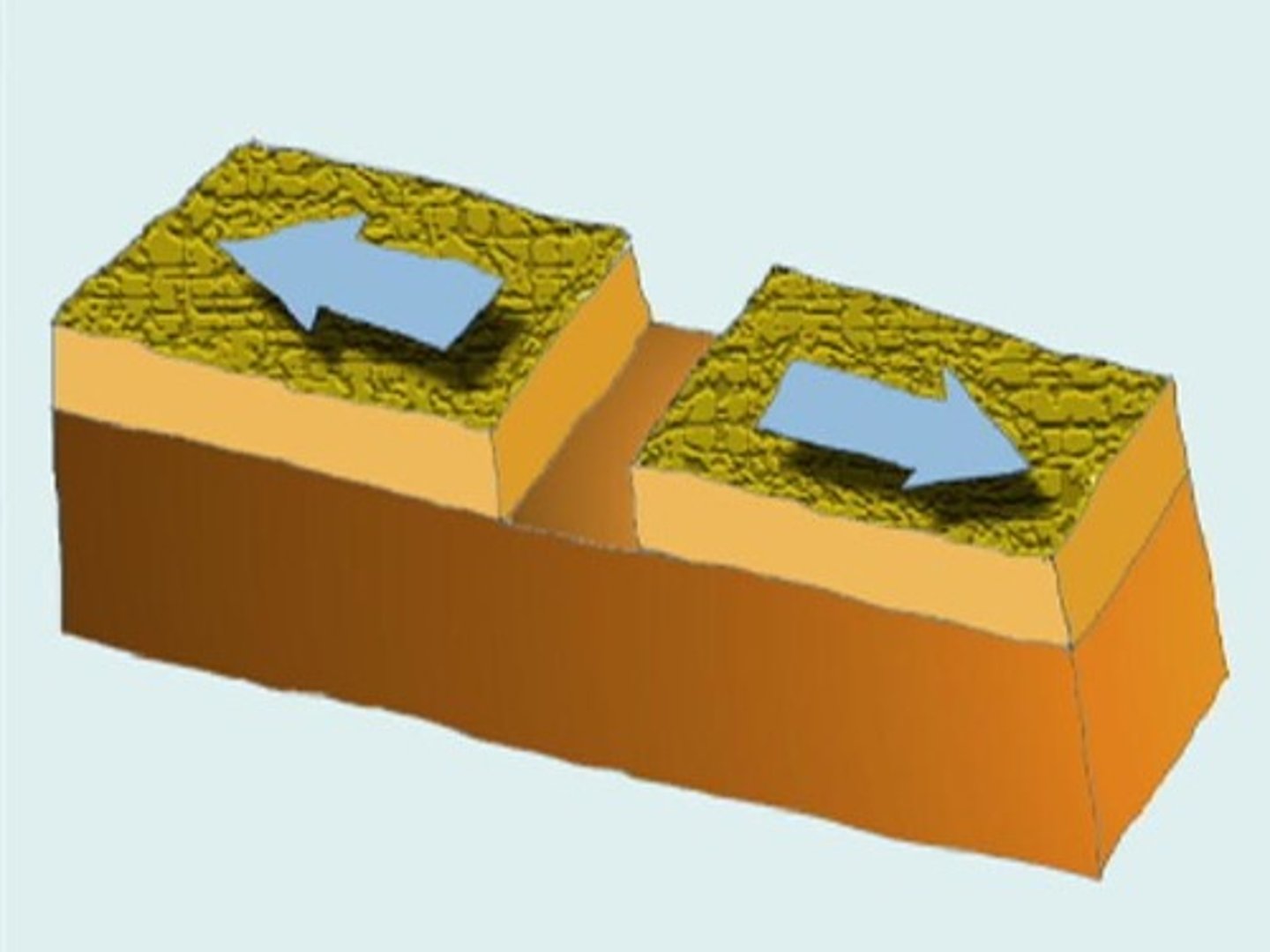
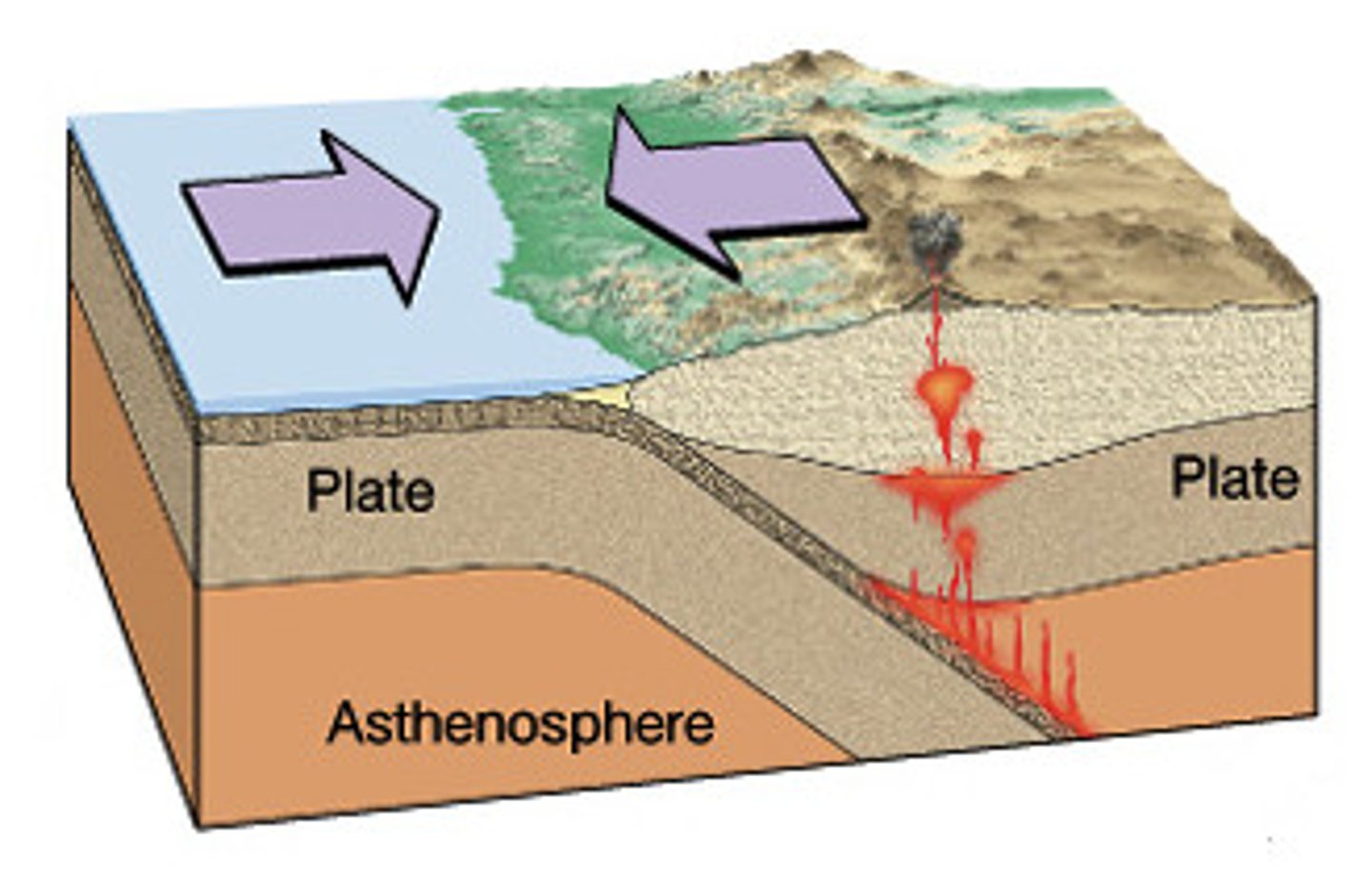
divergent boundary
The boundary between two tectonic plates that are moving away from each other.
convergent boundary
The boundary between tectonic plates that are colliding.
lithosphere
The solid, outer layer of Earth that consists of the crust and the rigid upper part of the mantle.
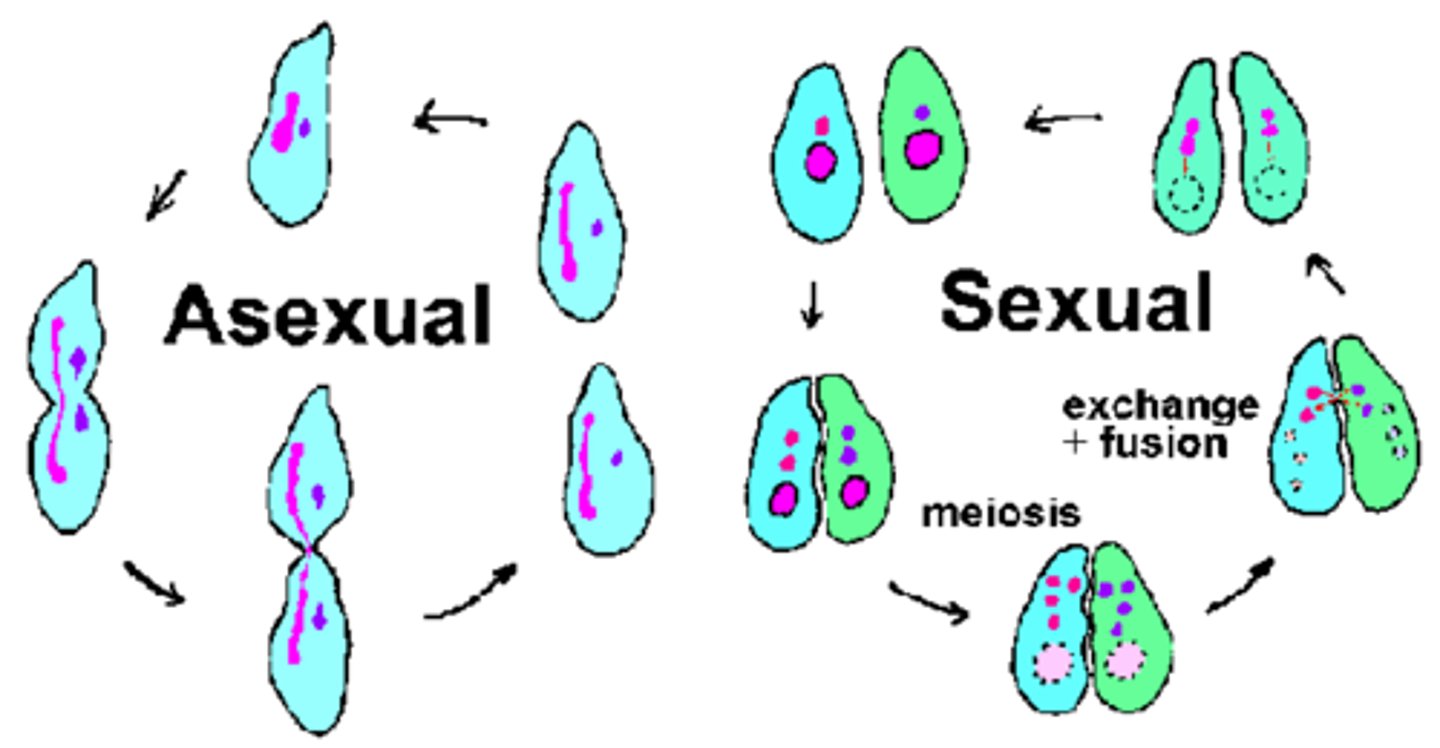
asexual reproduction
Reproduction that does not involve the union of sex cells and in which one parent produces offspring that are genetically identical to the parent.
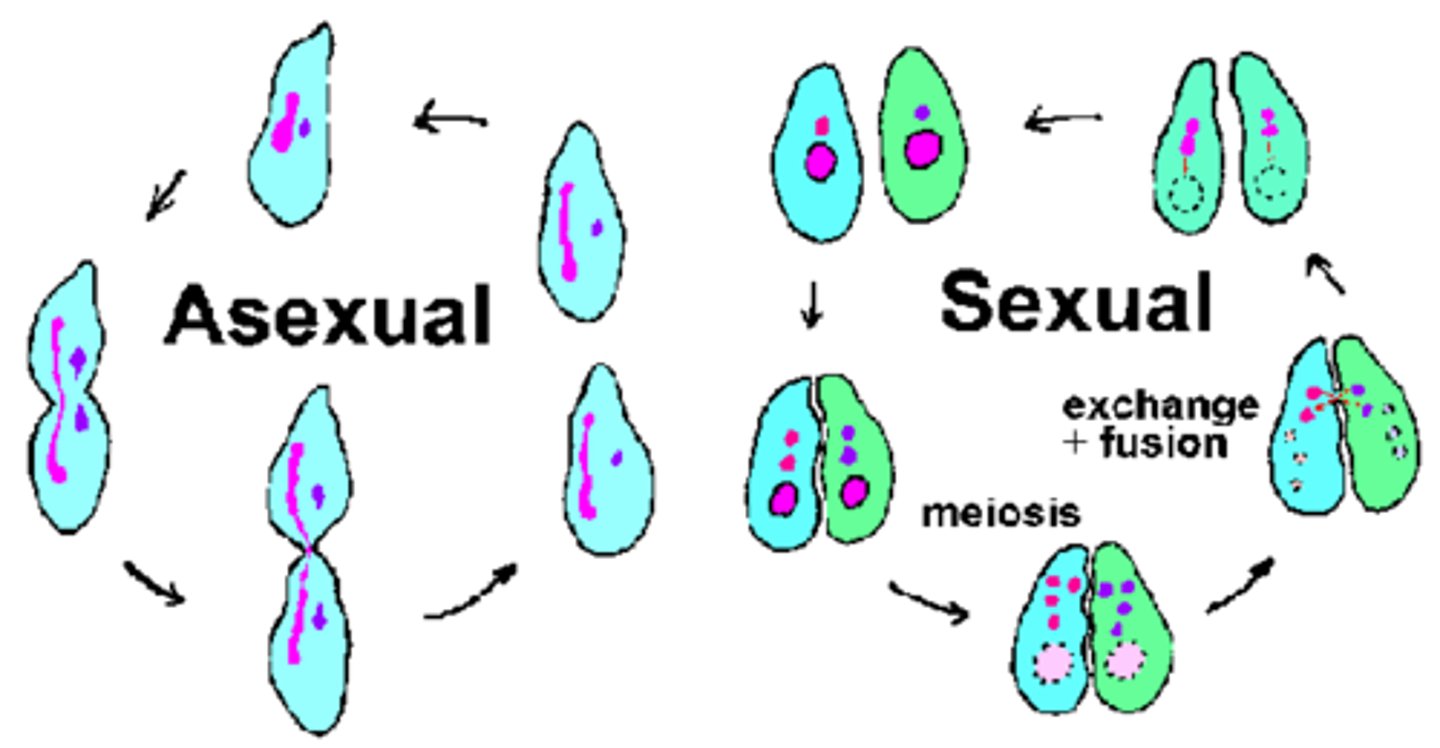
sexual reproduction
Reproduction in which the sex cells from two parents unite to produce offspring that share traits from both parents.
genetics
The study of heredity and the variation of inherited characteristics.

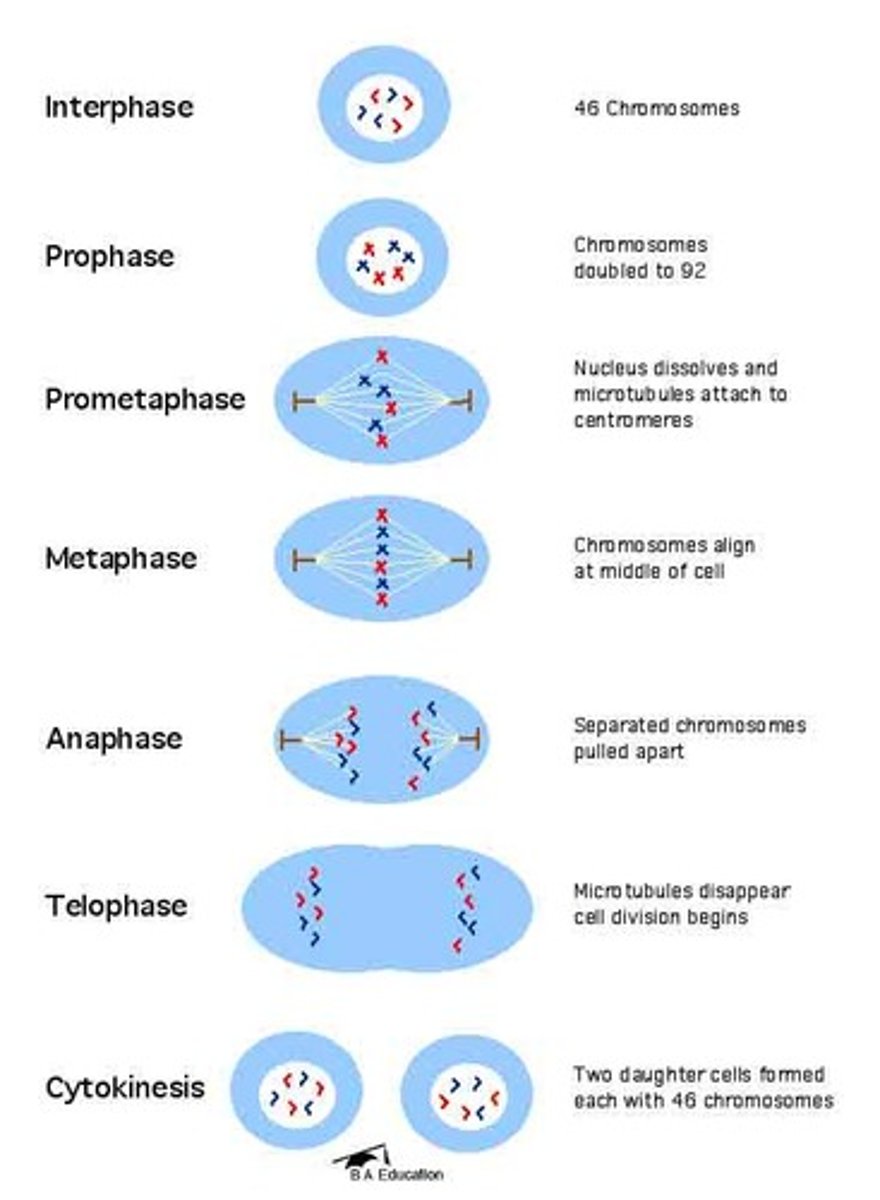
mitosis
In eukaryotic cells, a process of cell division that forms two new nuclei, each of which has the same number of chromosomes.
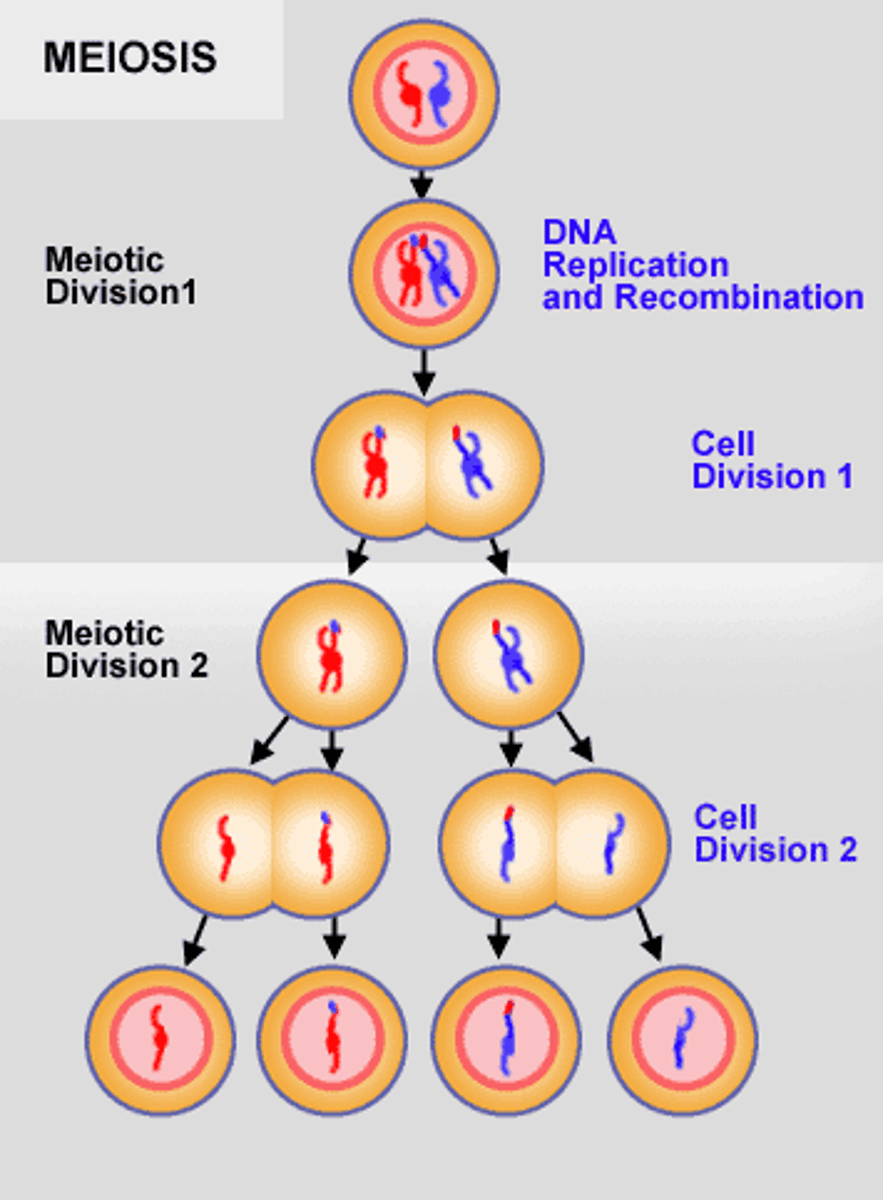
meiosis
A process in cell division during which the number of chromosomes decreases to half the original number by two divisions of the nucleus, which results in the production of sex cells (gametes or spores).
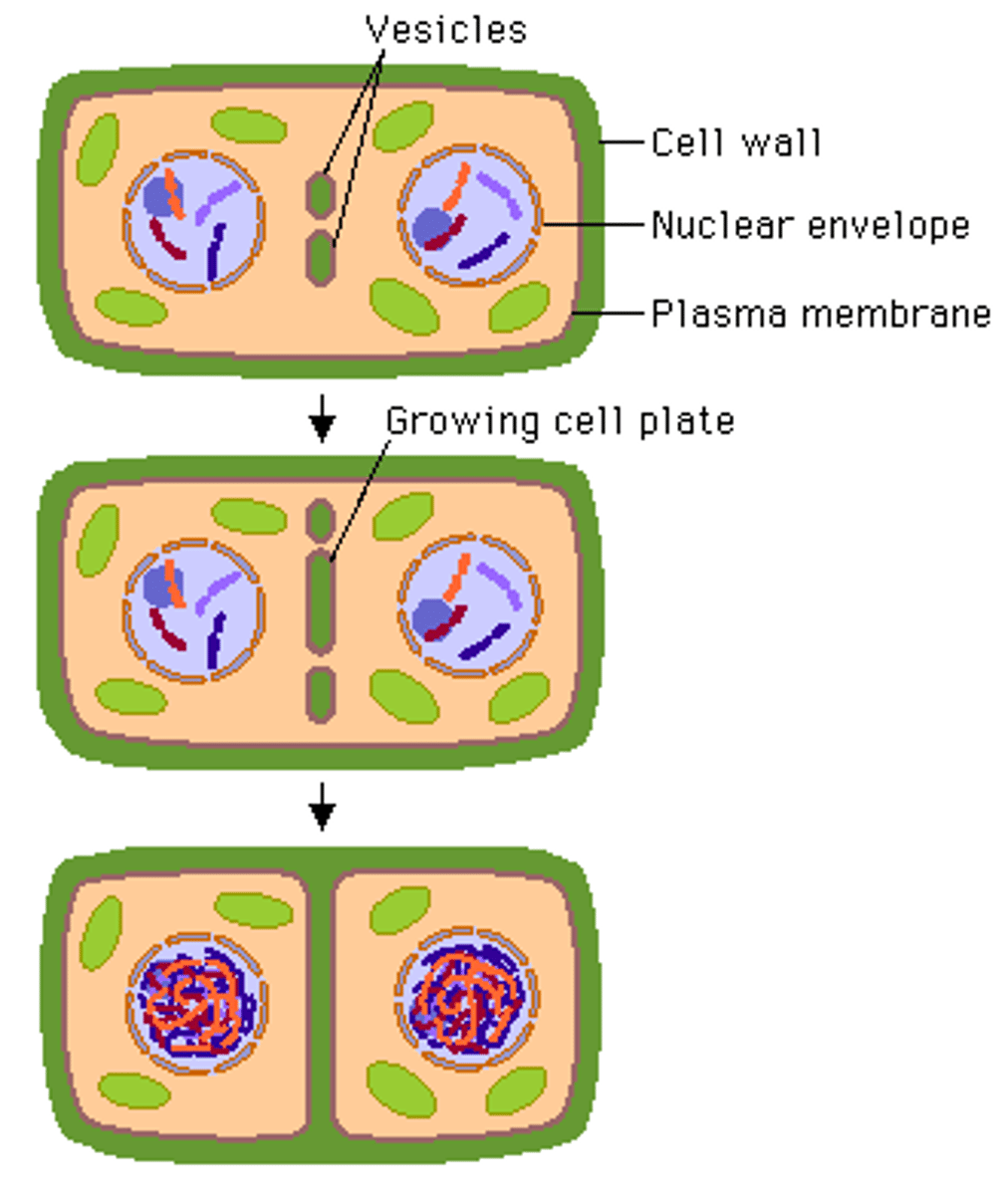
cell plate
A structure that forms in the cells of plants while they are undergoing cell division.
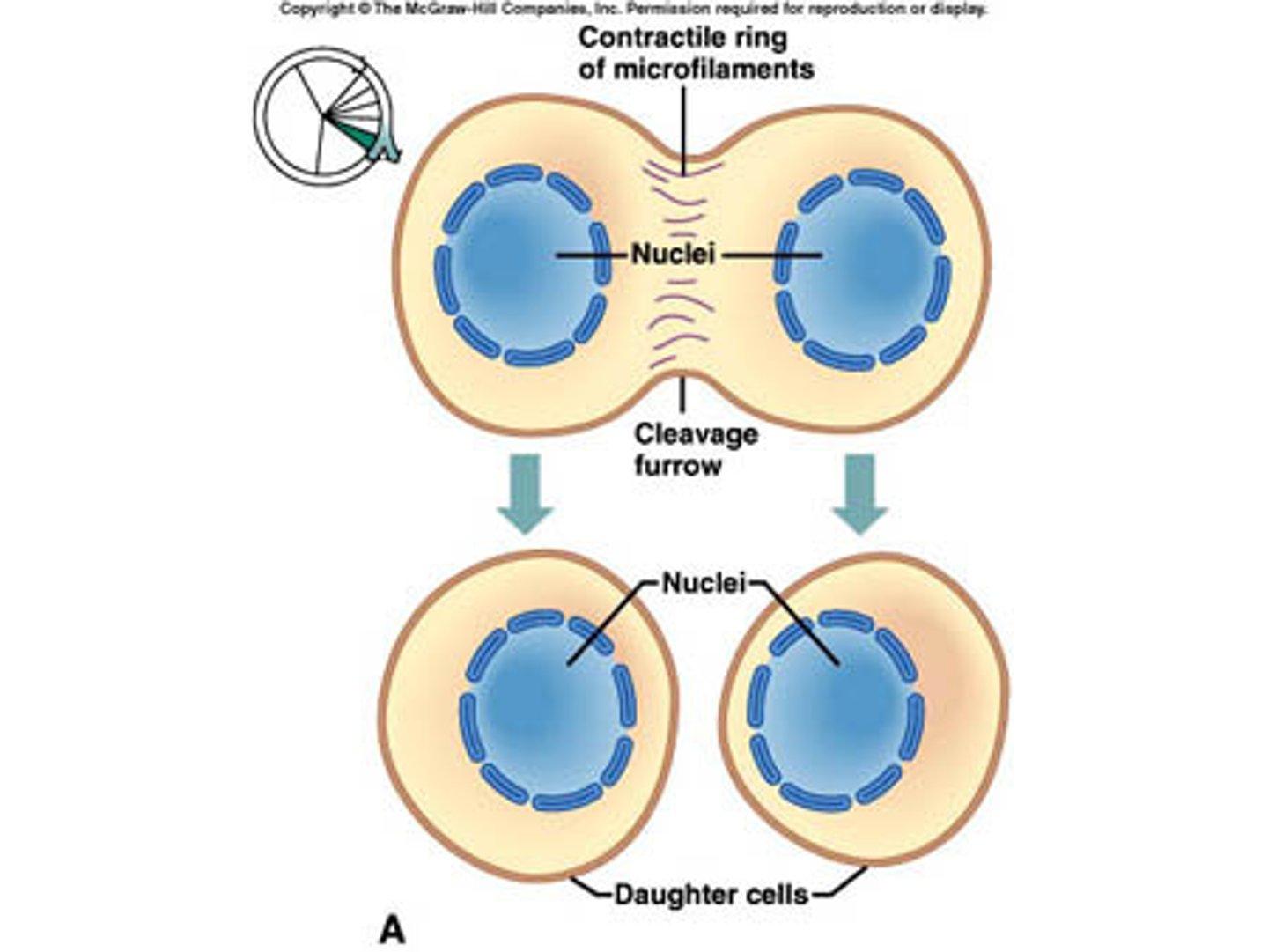
furrow
A new membrane that forms in an animal cell during cell division, that pinches the cytoplasm into two new cells.
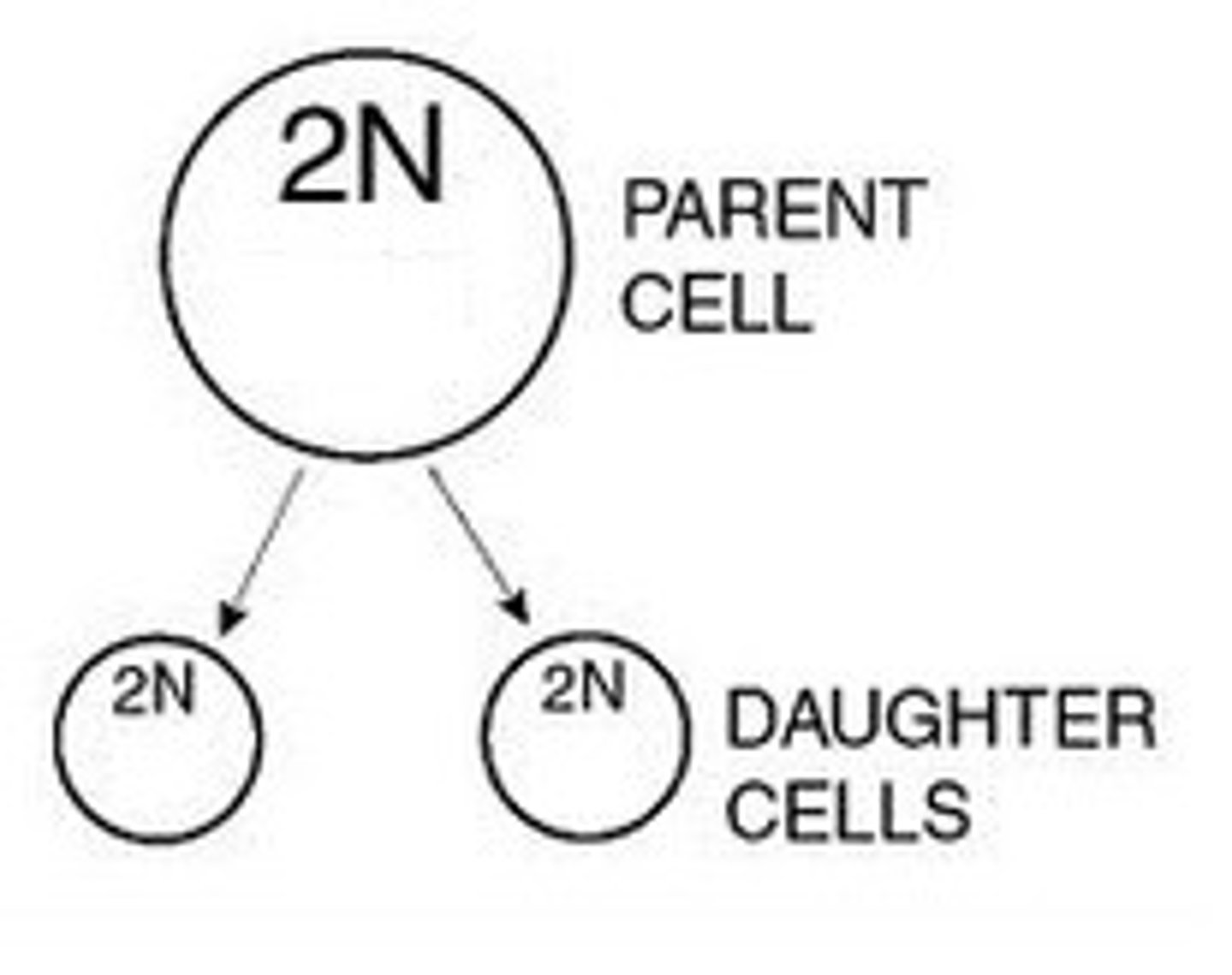
parent cell
The original cell that divides to produce two or more new cells called daughter cells.
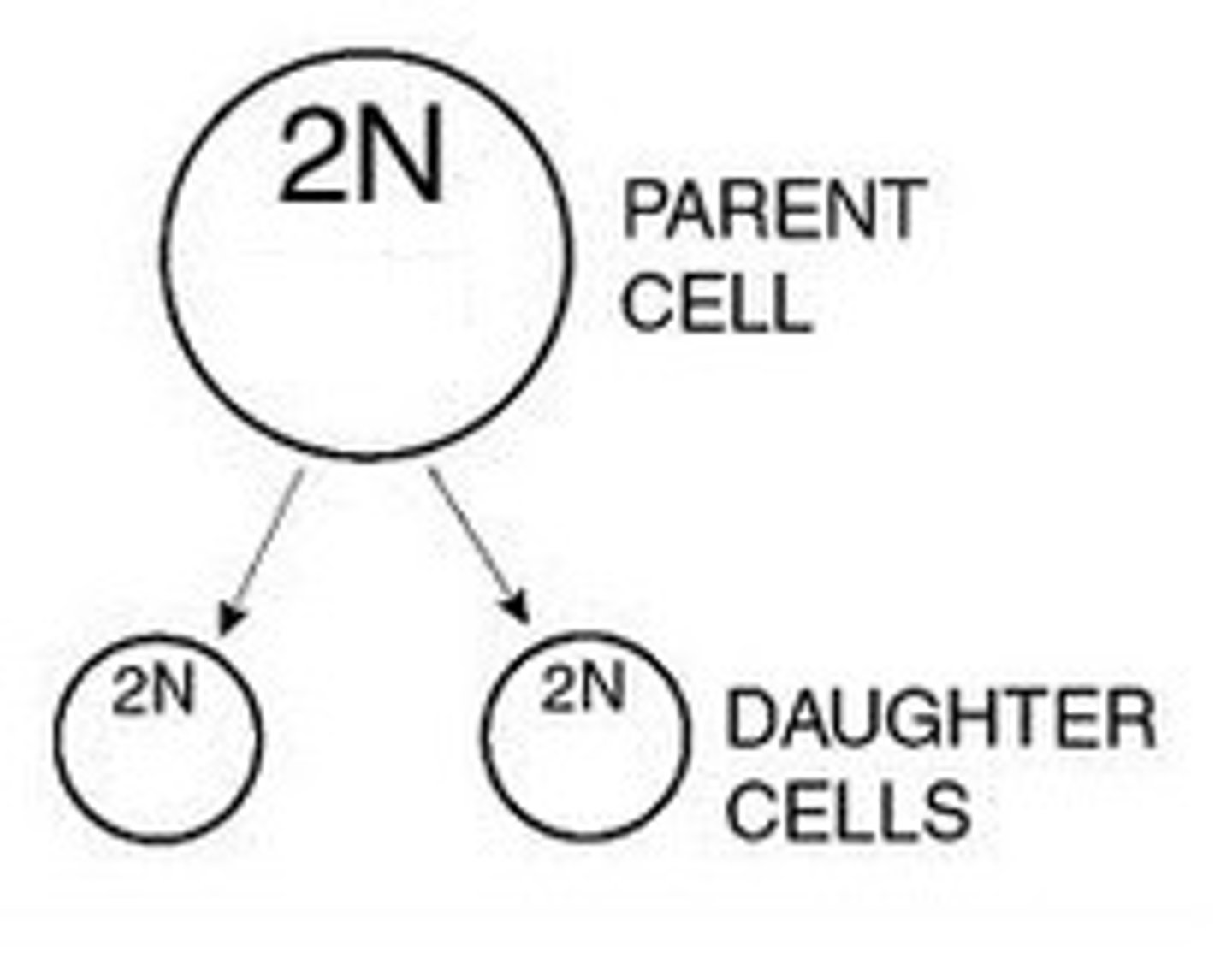
daughter cell
The new cells produced as a result from the division of a single parent cell. They are produced by the division processes of mitosis and meiosis.
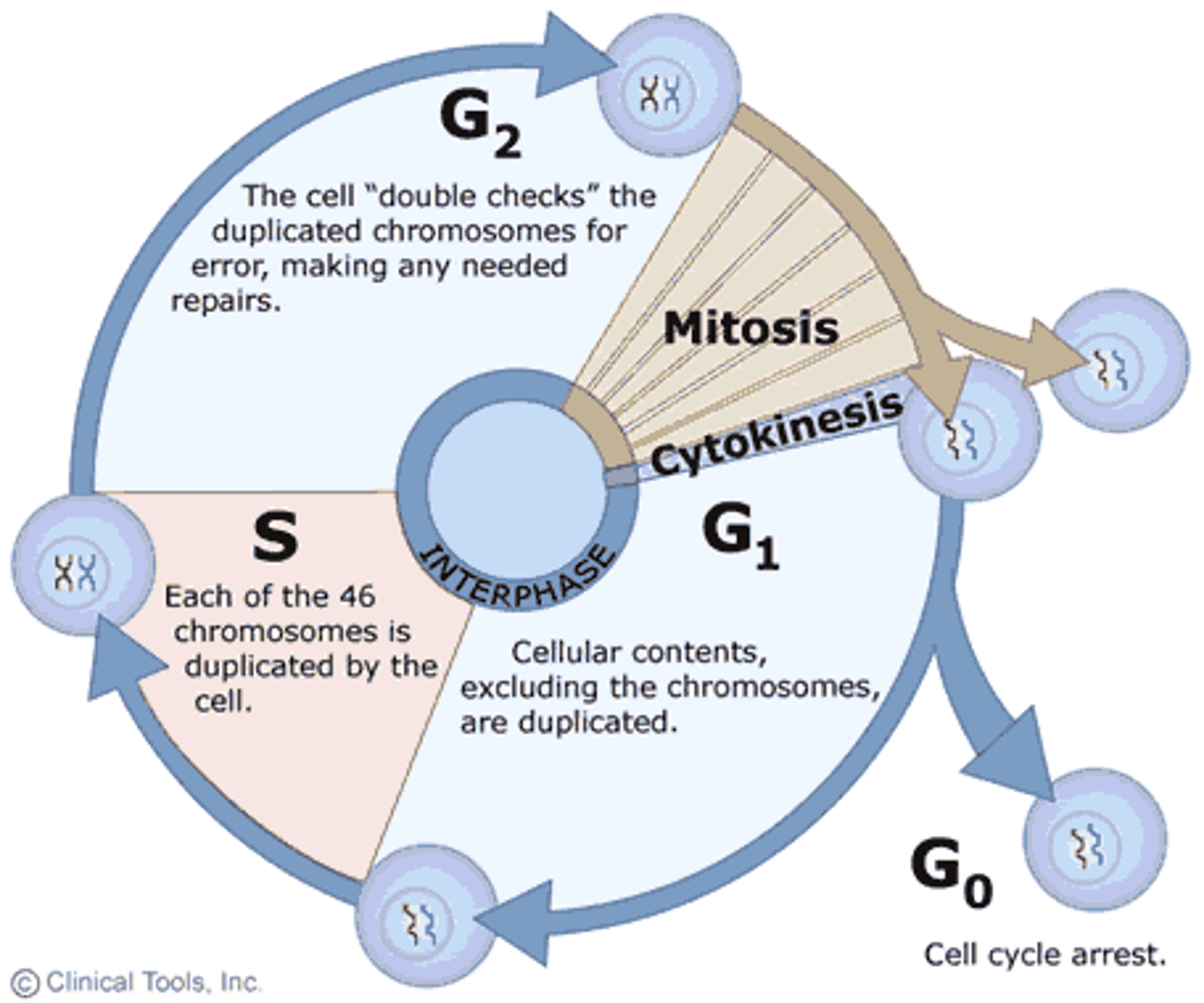
cell cycle
The life cycle of a cell.
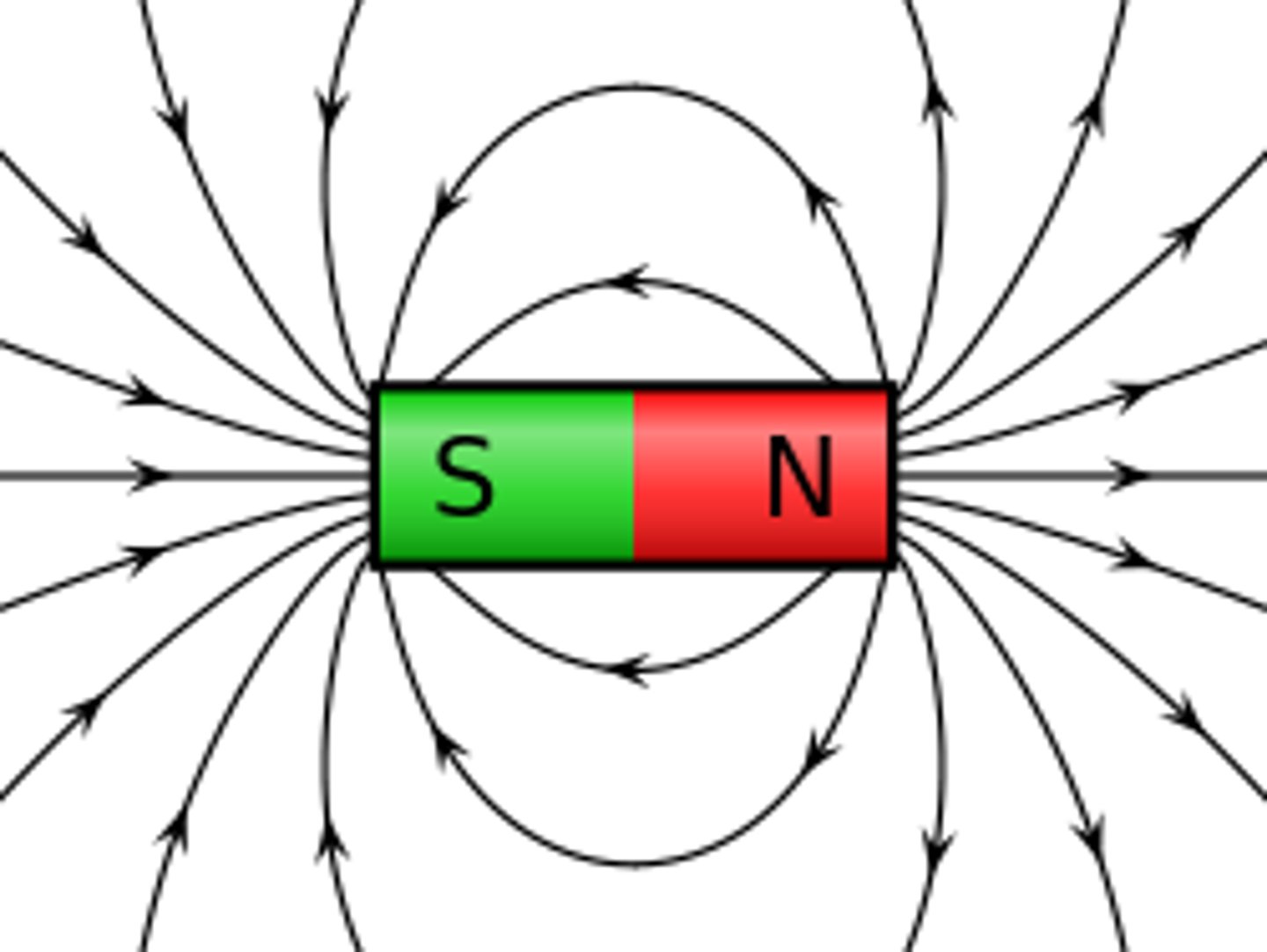
magnetic field
A region where a magnetic force can be detected.
force
A push or a pull exerted on an object in order to change the motion of the object; force has size and direction.
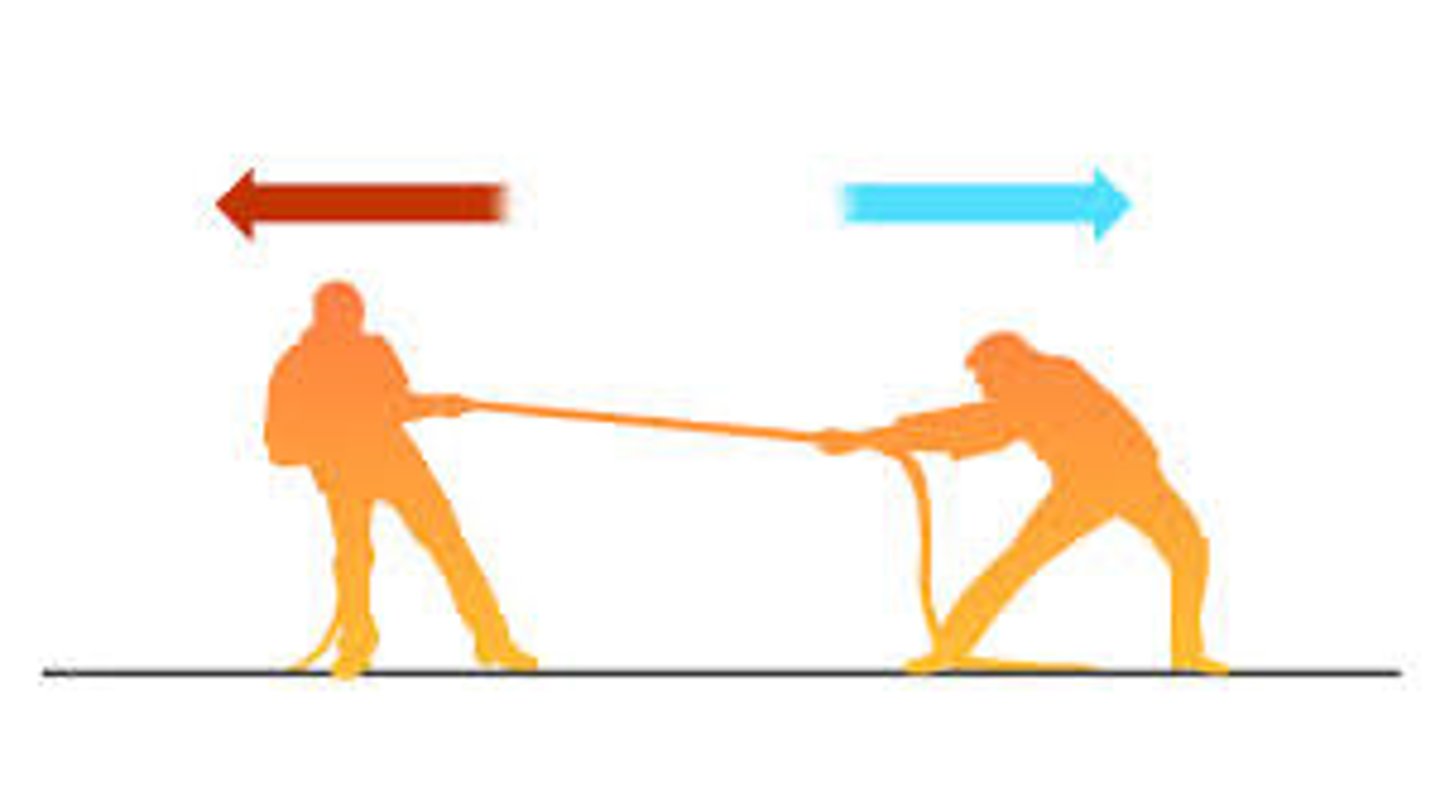
motion
An object's change in position relative to a reference point.
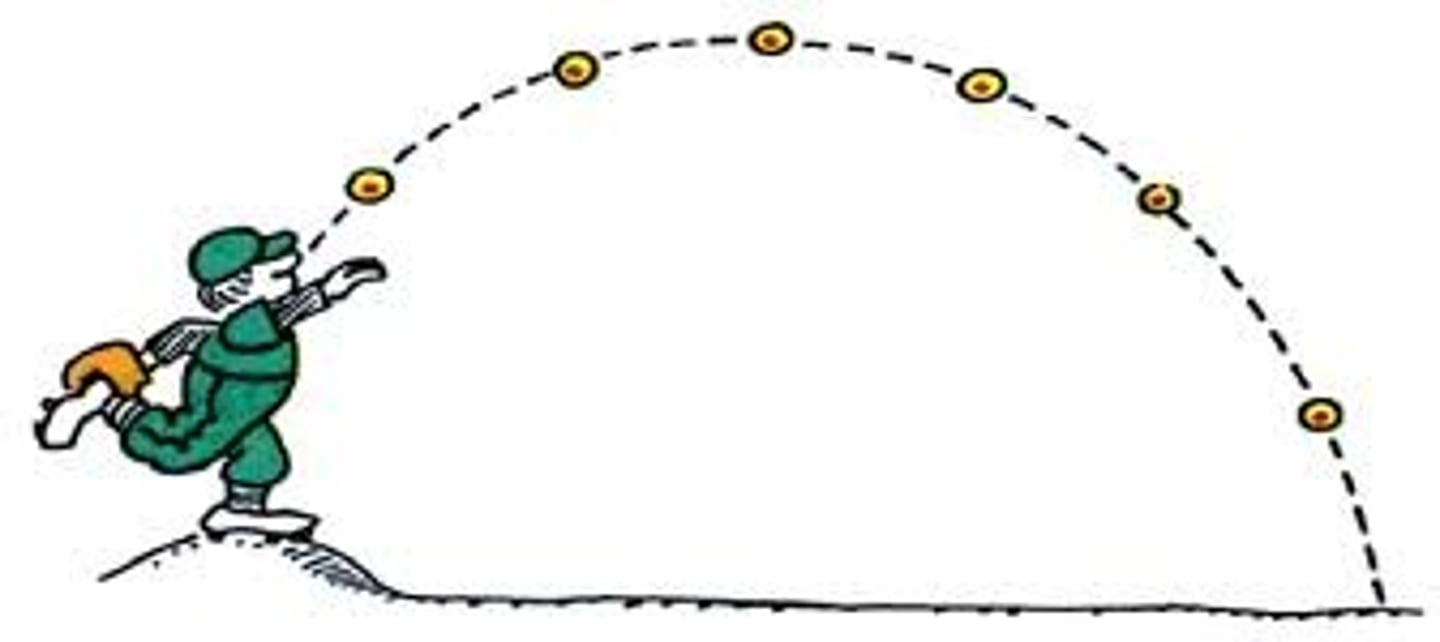
mass
A measure of the amount of matter in an object.

acceleration
The rate at which velocity changes over time; an object accelerates if its speed, direction, or both change.
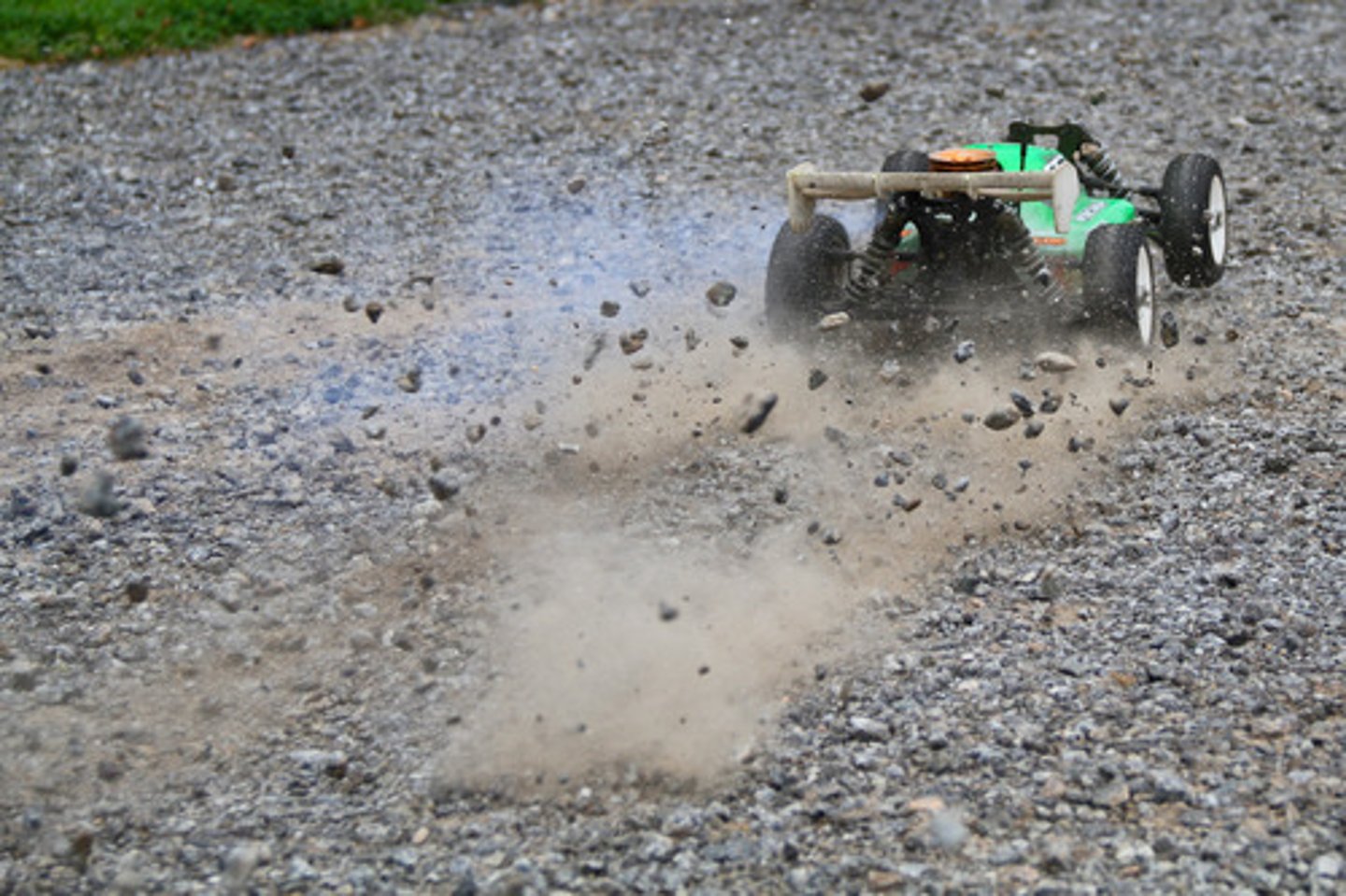

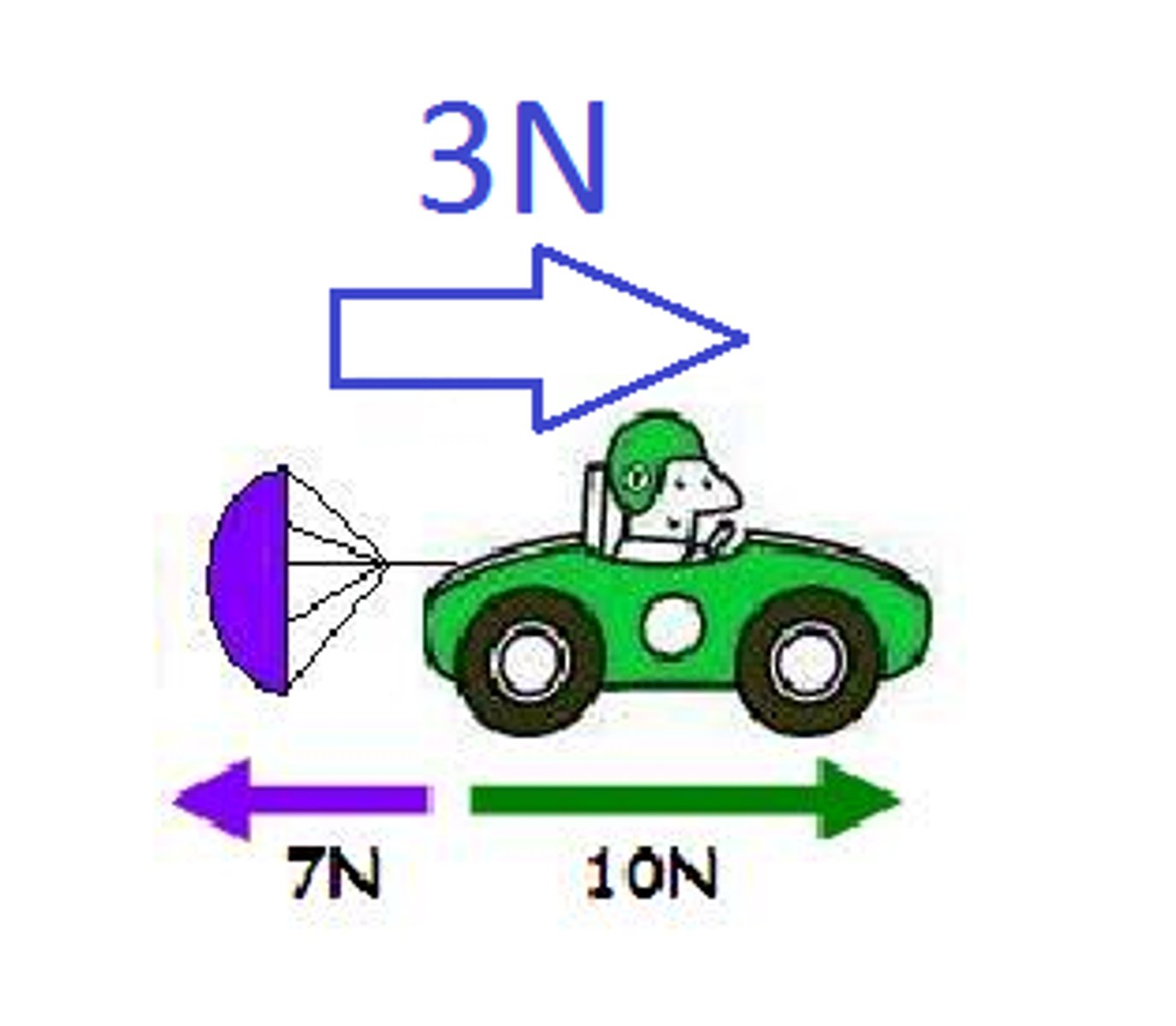
net force
The combination of all of the forces acting on an object.
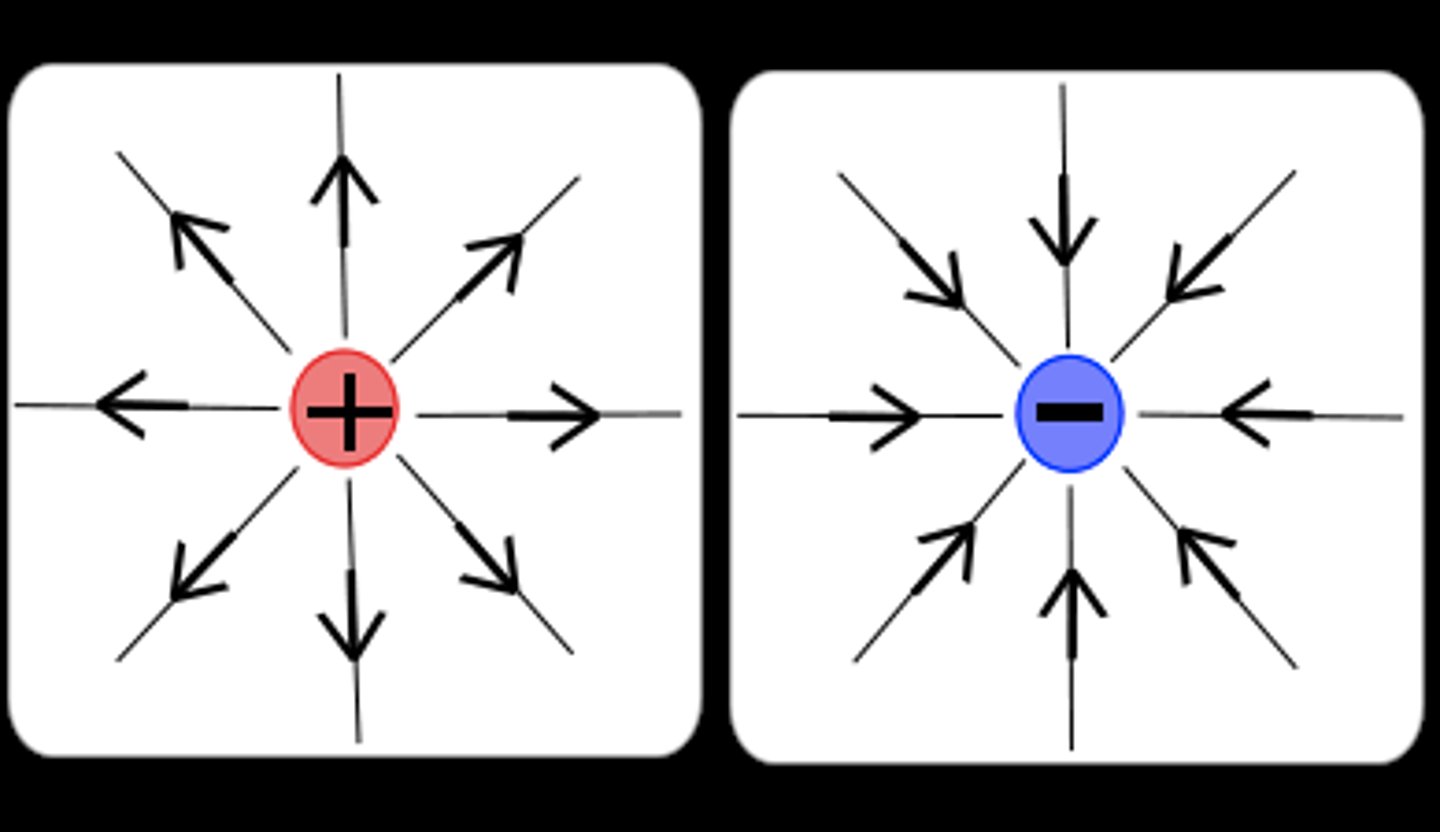
electric field
A region around a charged particle or object within which a force would be exerted on other charged particles or objects.
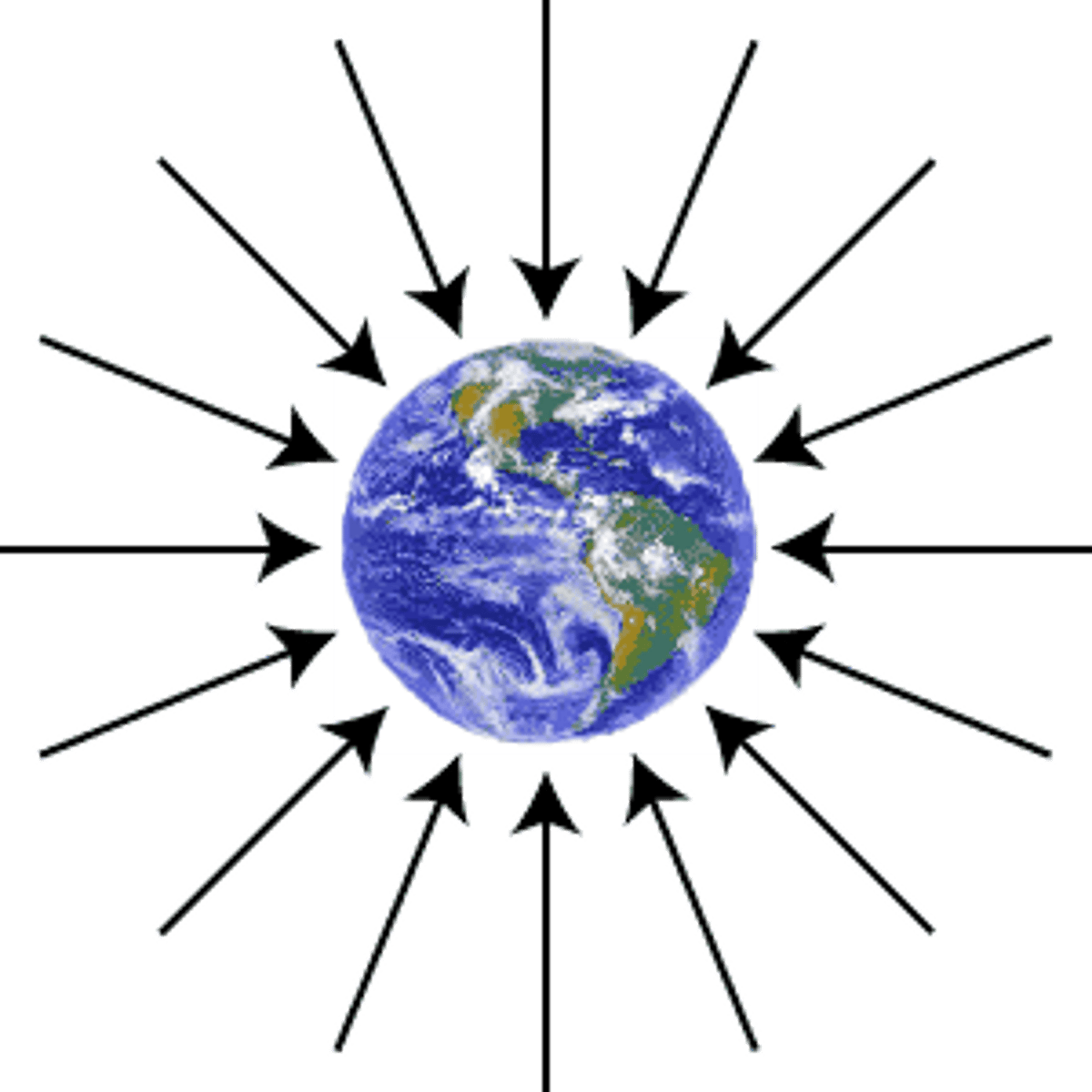
gravitational field
The region of space surrounding a body in which another body experiences a force of gravitational attraction.
electromagnet
A soft metal core made into a magnet by the passage of electric current through a coil surrounding it.
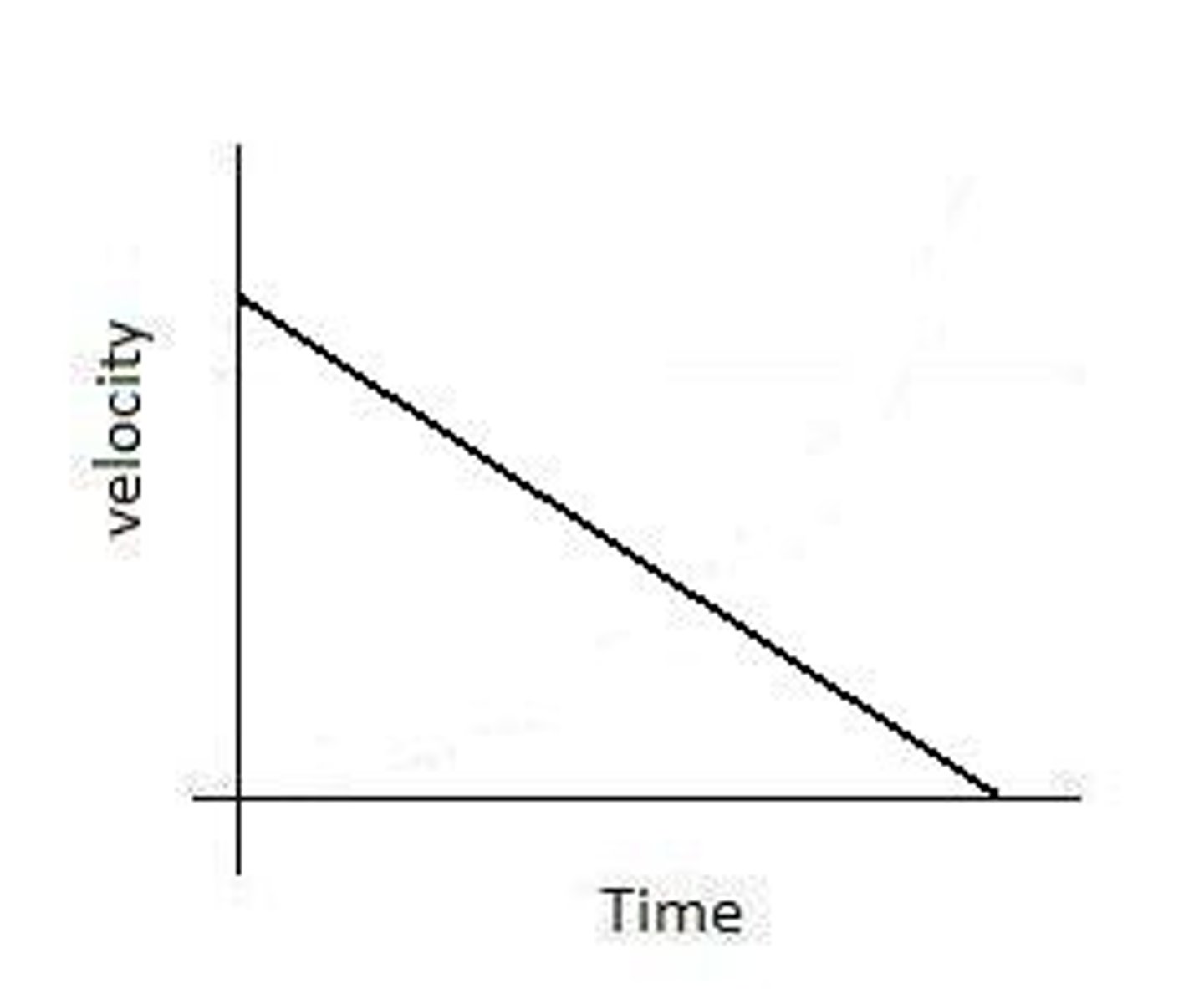
deceleration
Reduction in speed or rate.
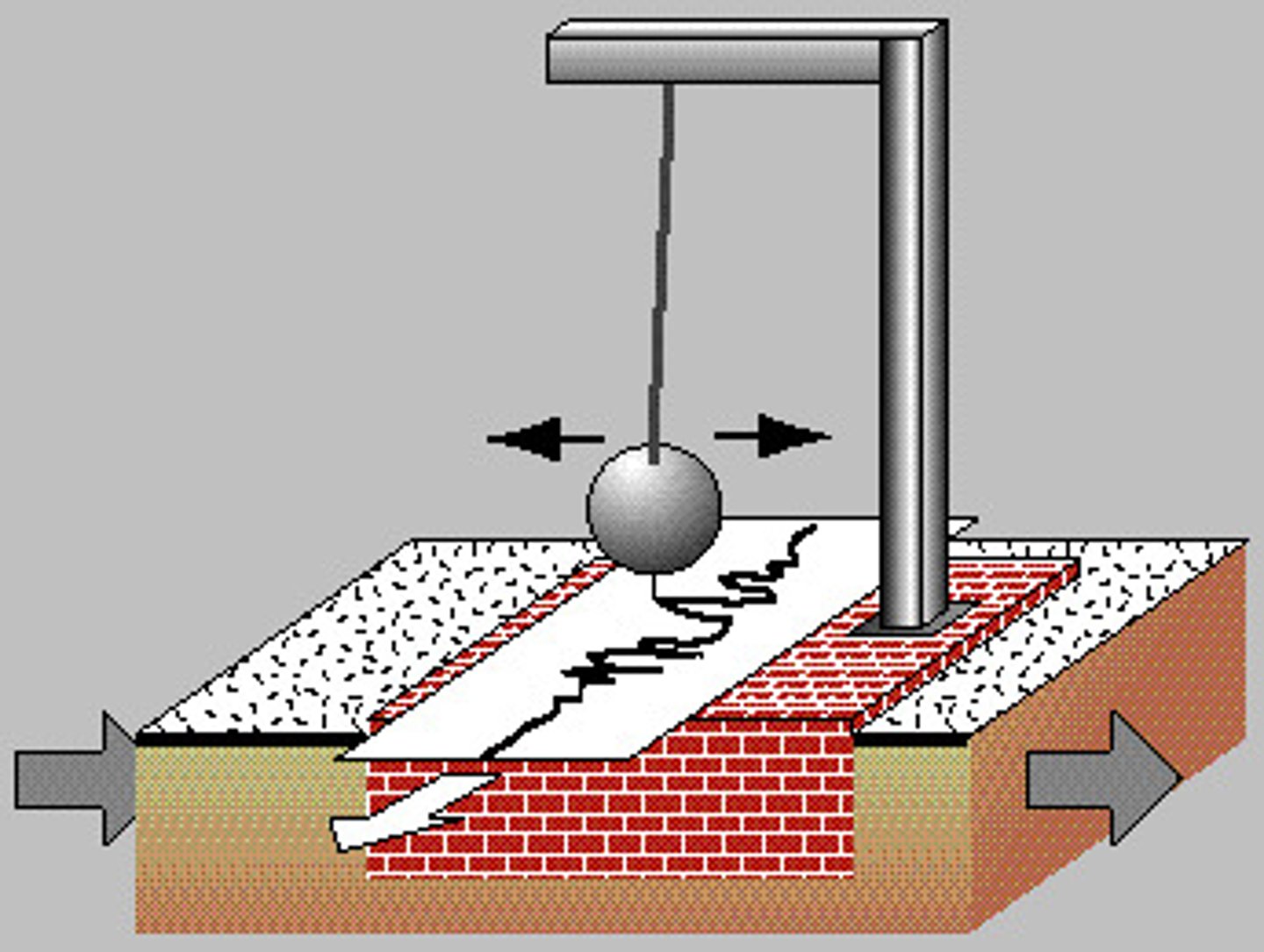
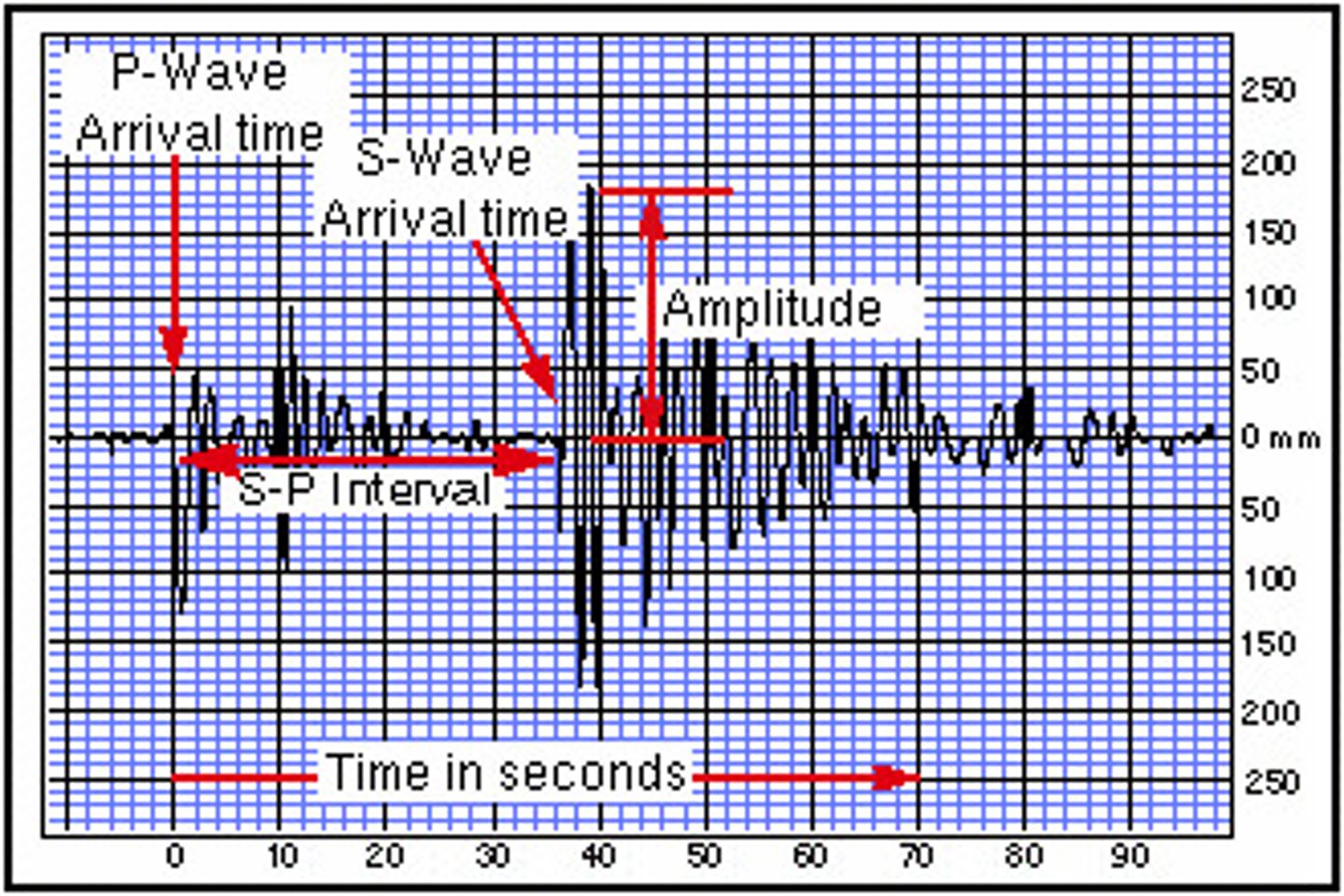
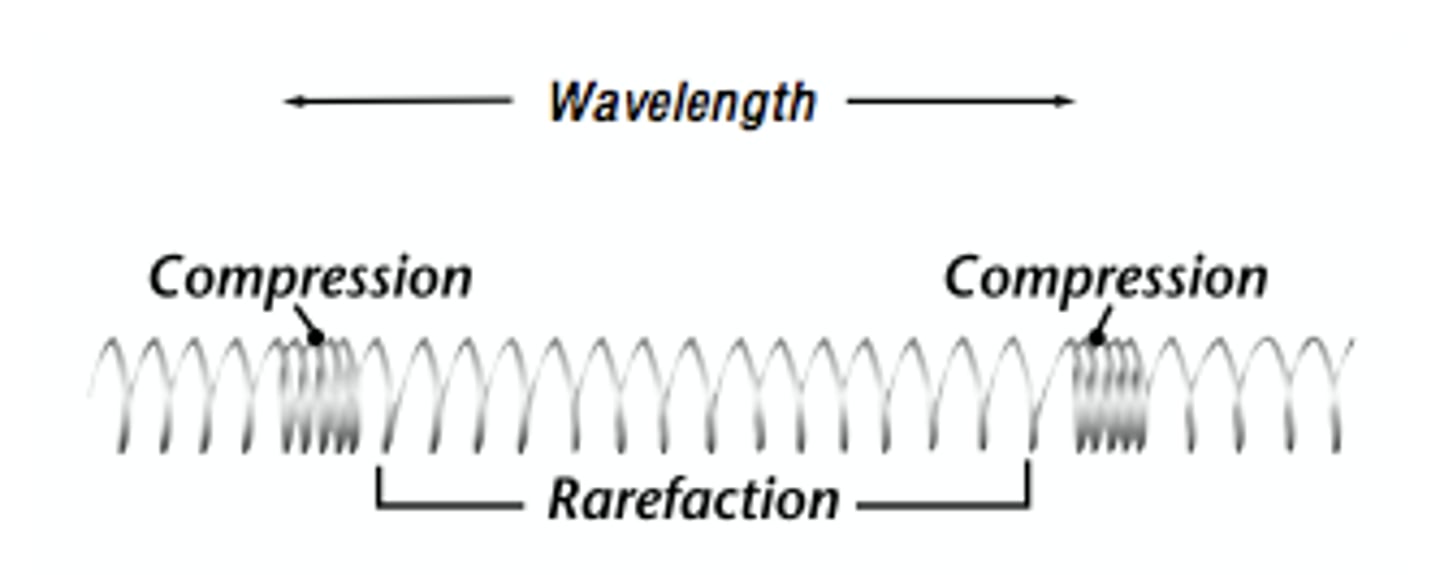
seismograph
A device that records ground movements caused by seismic waves as they move through Earth.
seismogram
A tracing of earthquake motion that is recorded by a sismograph.
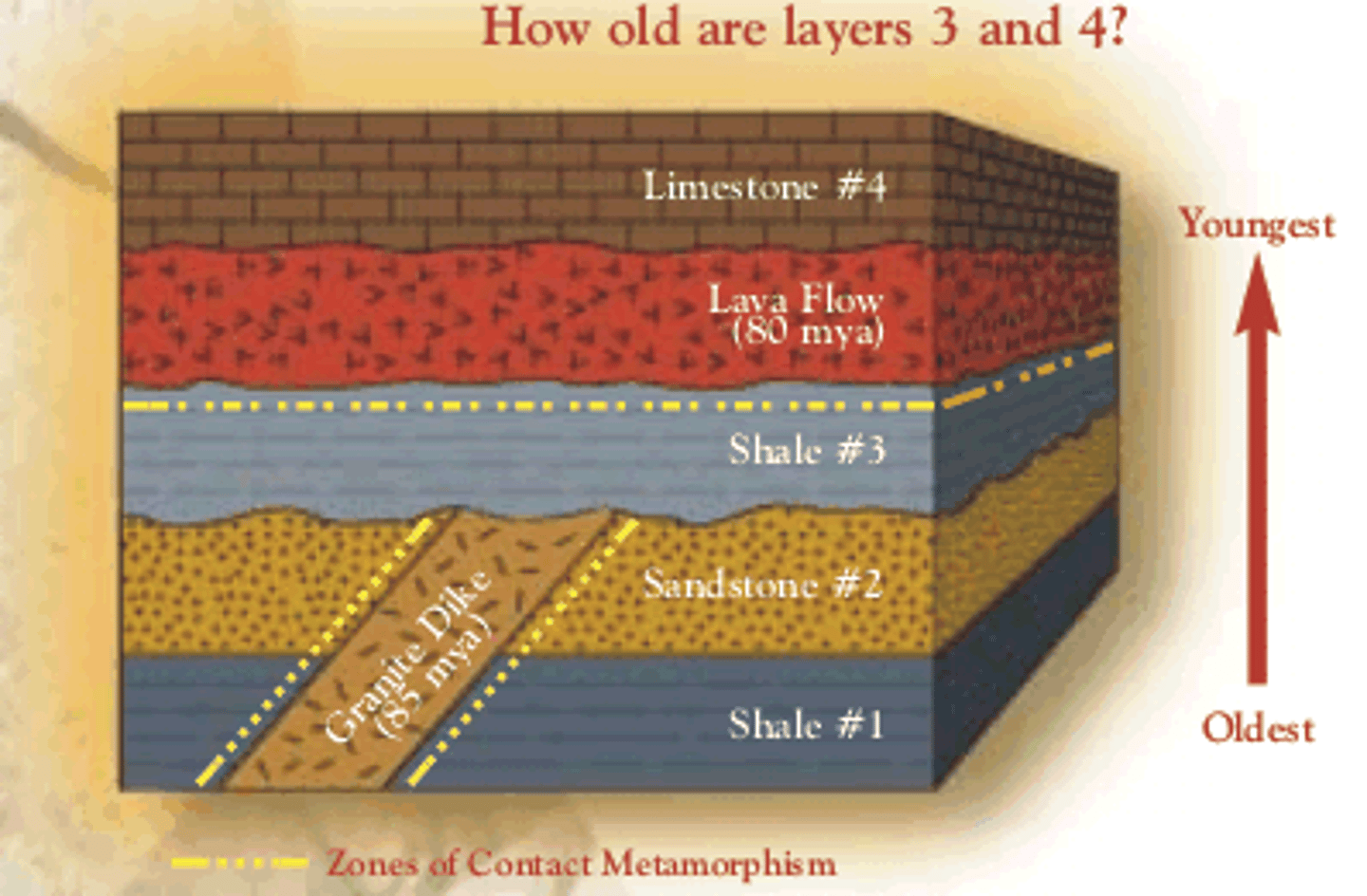
superposition
A principle that states that younger rocks lie above older rocks if the layers have not been disturbed.
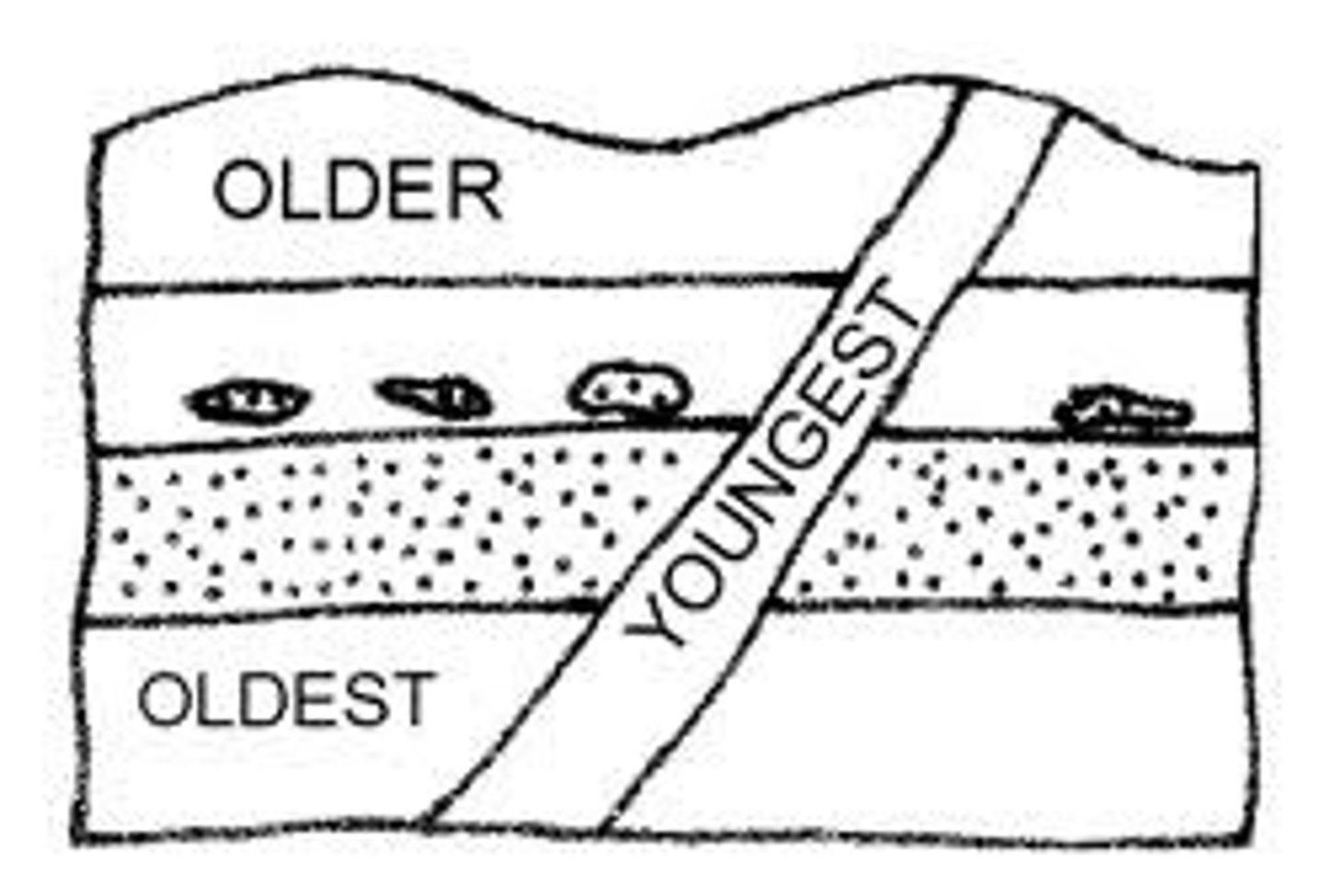
cross cutting
Cut into action that is happening simultaneously. This technique is also called parallel editing. It can create tension or suspense and can form a connection between scenes.
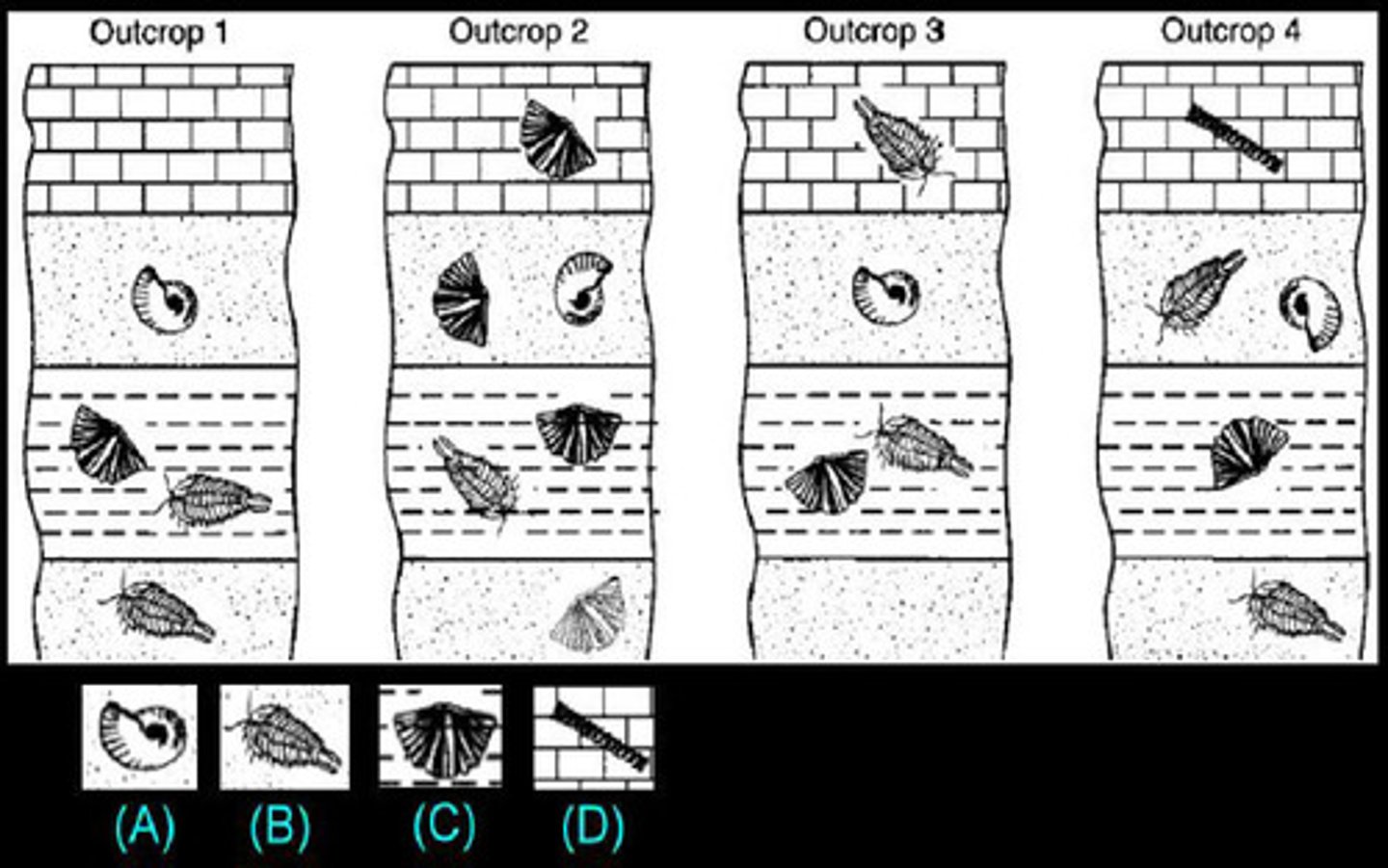
index fossils
Distinctive fossils used to establish and compare the relative ages of rock layers and the fossils they contain.
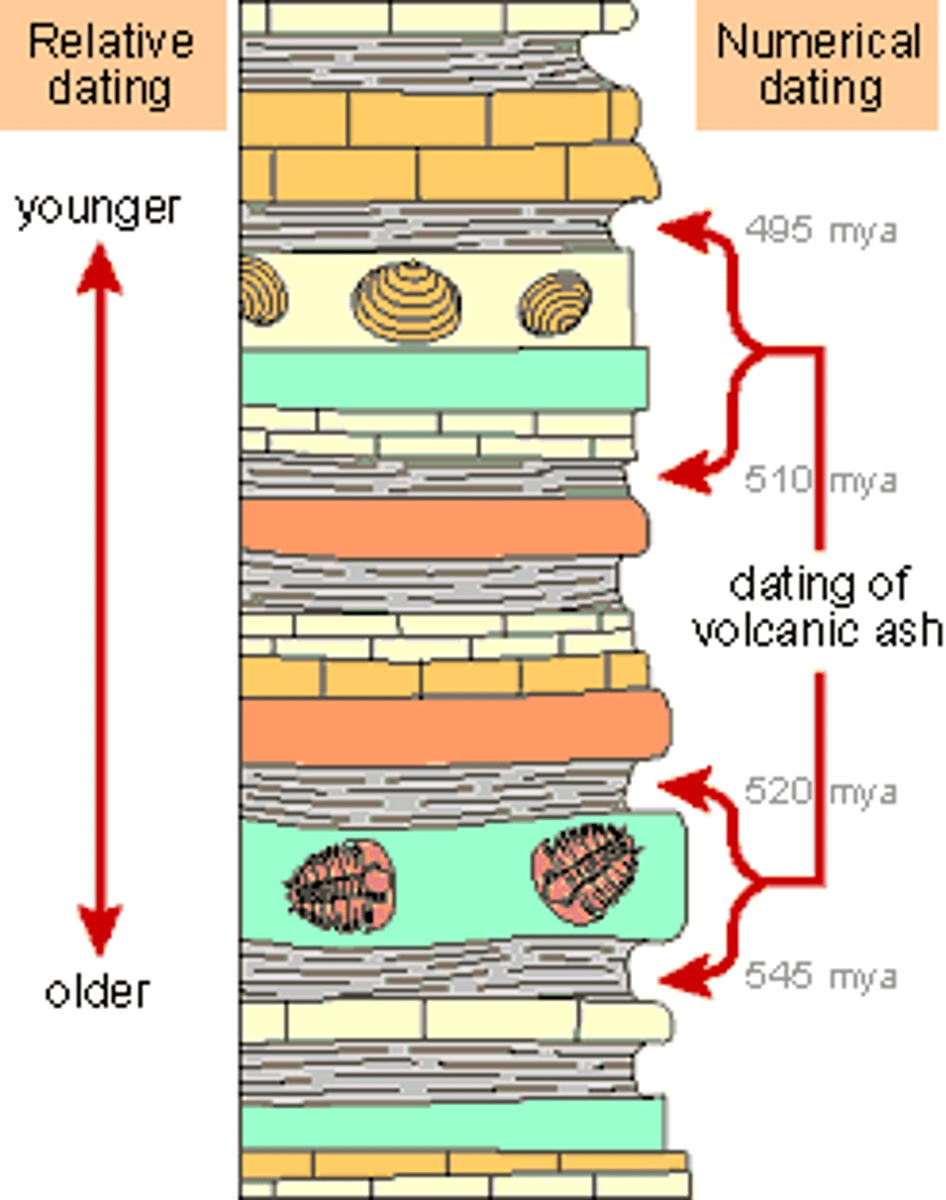
relative dating
RANGE Any method of determining whether an event or object is older or younger than other events or objects.
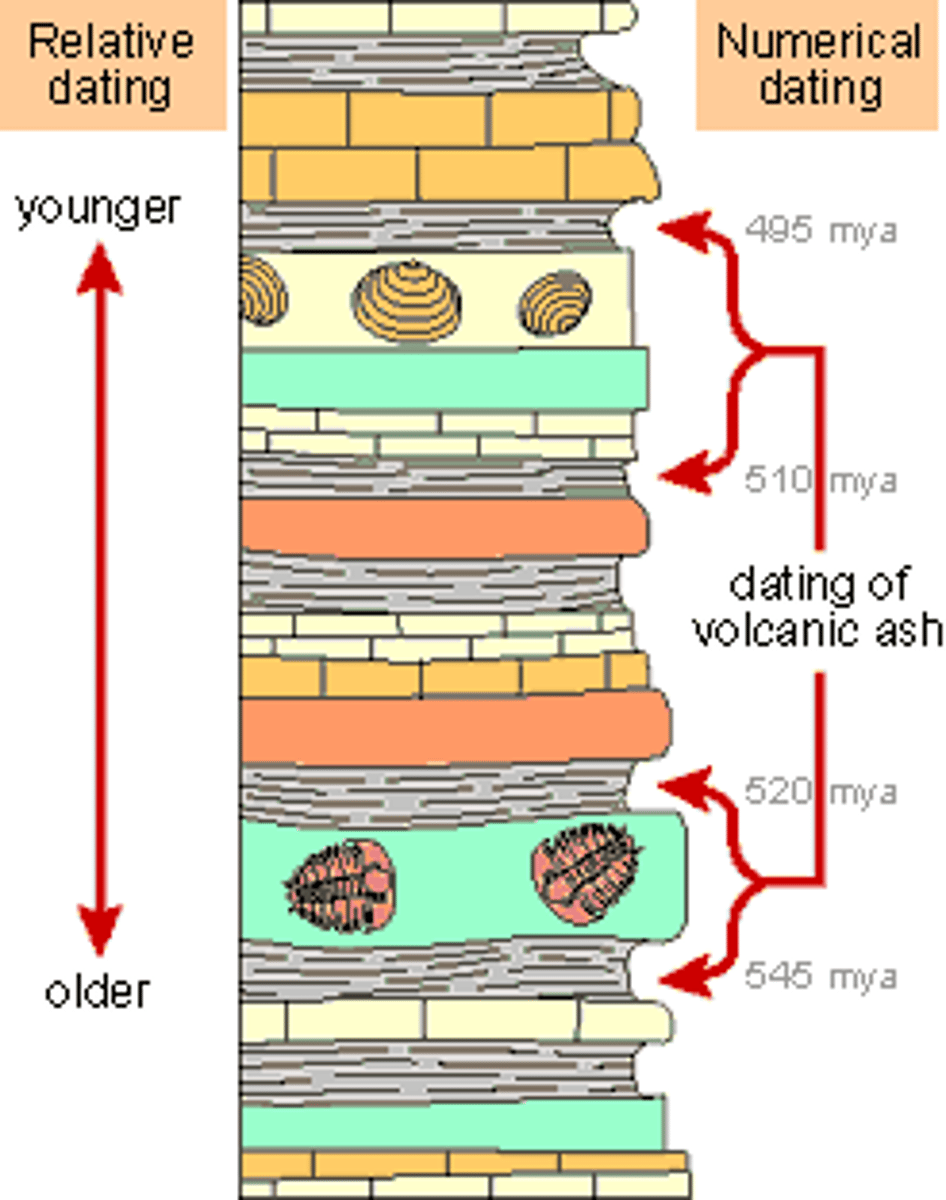
absolute dating
SPECIFIC Any method of measuring the age of an event or object in years.
earthquake
A movement or trembling of the ground that is caused by a sudden release of energy when rocks along a fault move.
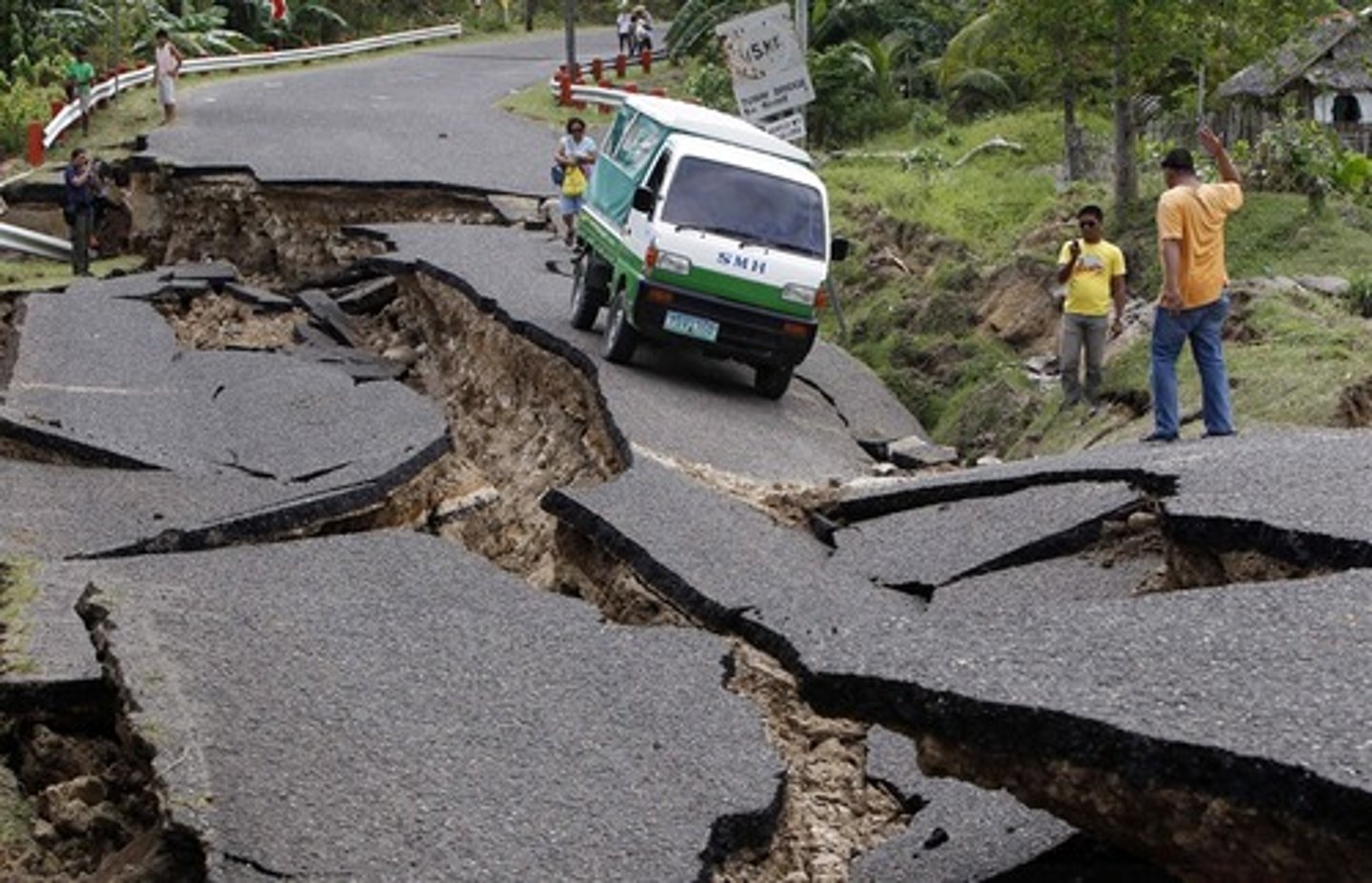

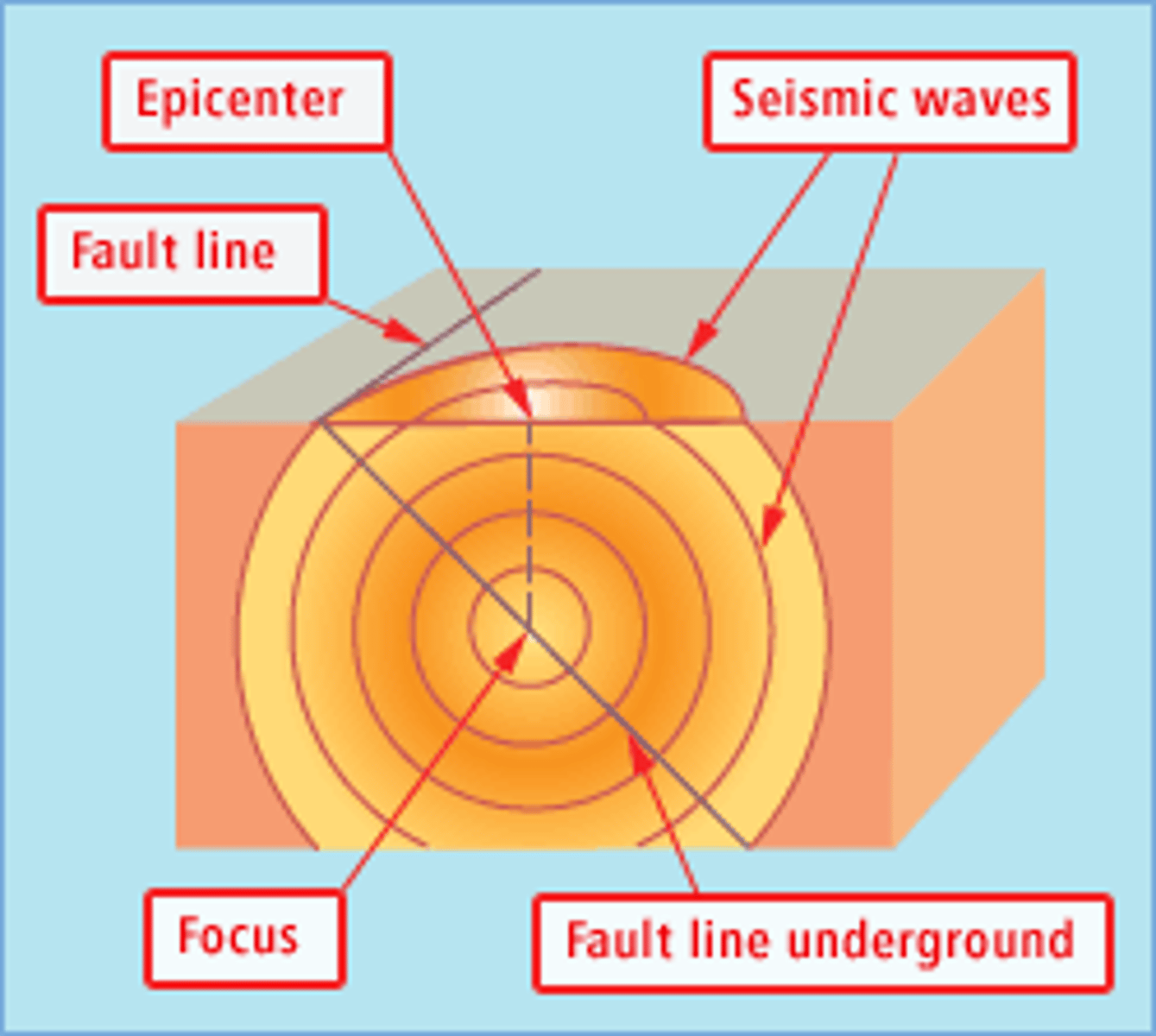
focus
The location within the Earth along a fault at which the first motion of an earthquake.
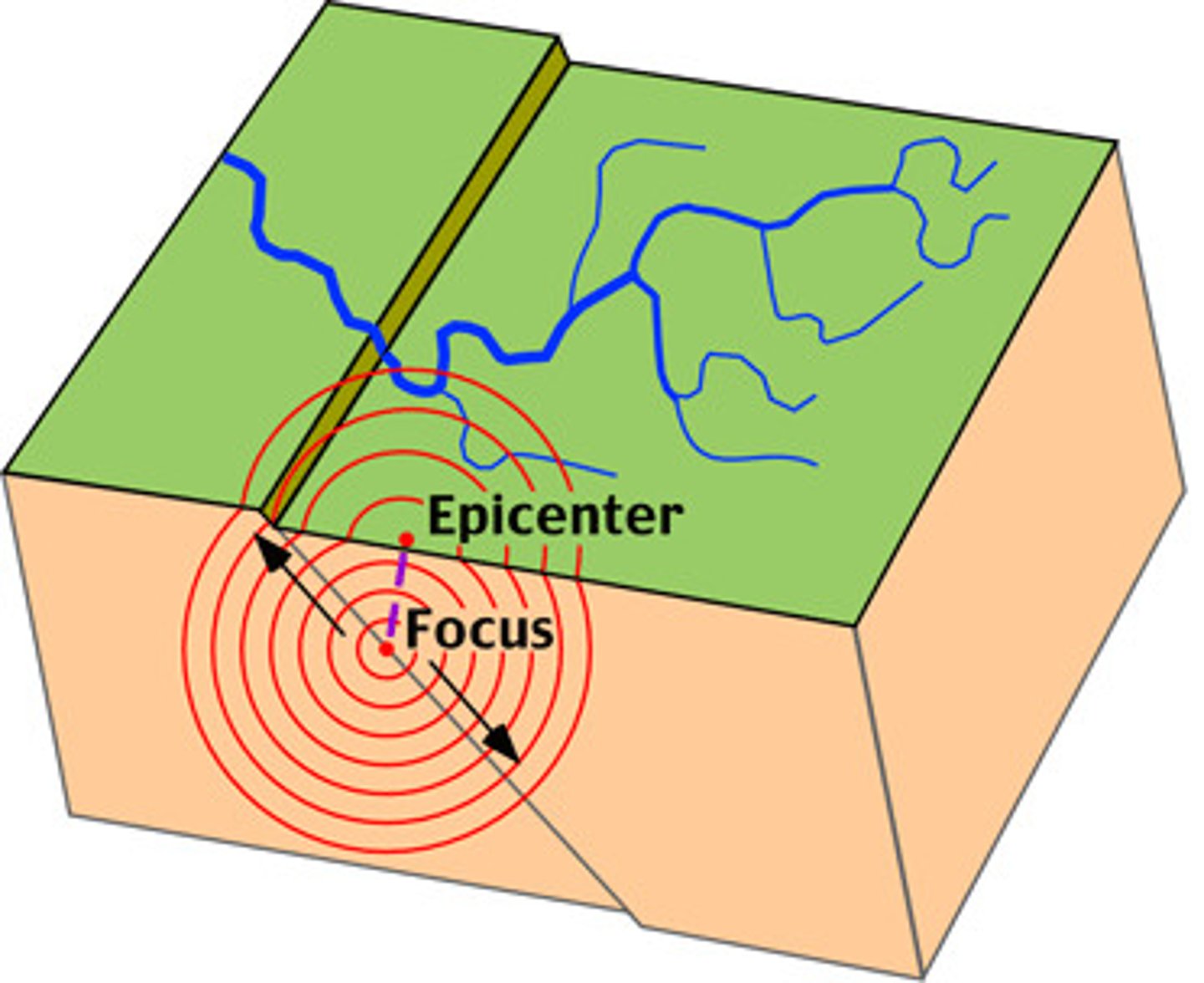
epicenter
The point of an Earth's surface directly above an earthquake's starting point, or focus.
trait
A characteristic that an organism can pass on to its offspring through its genes.
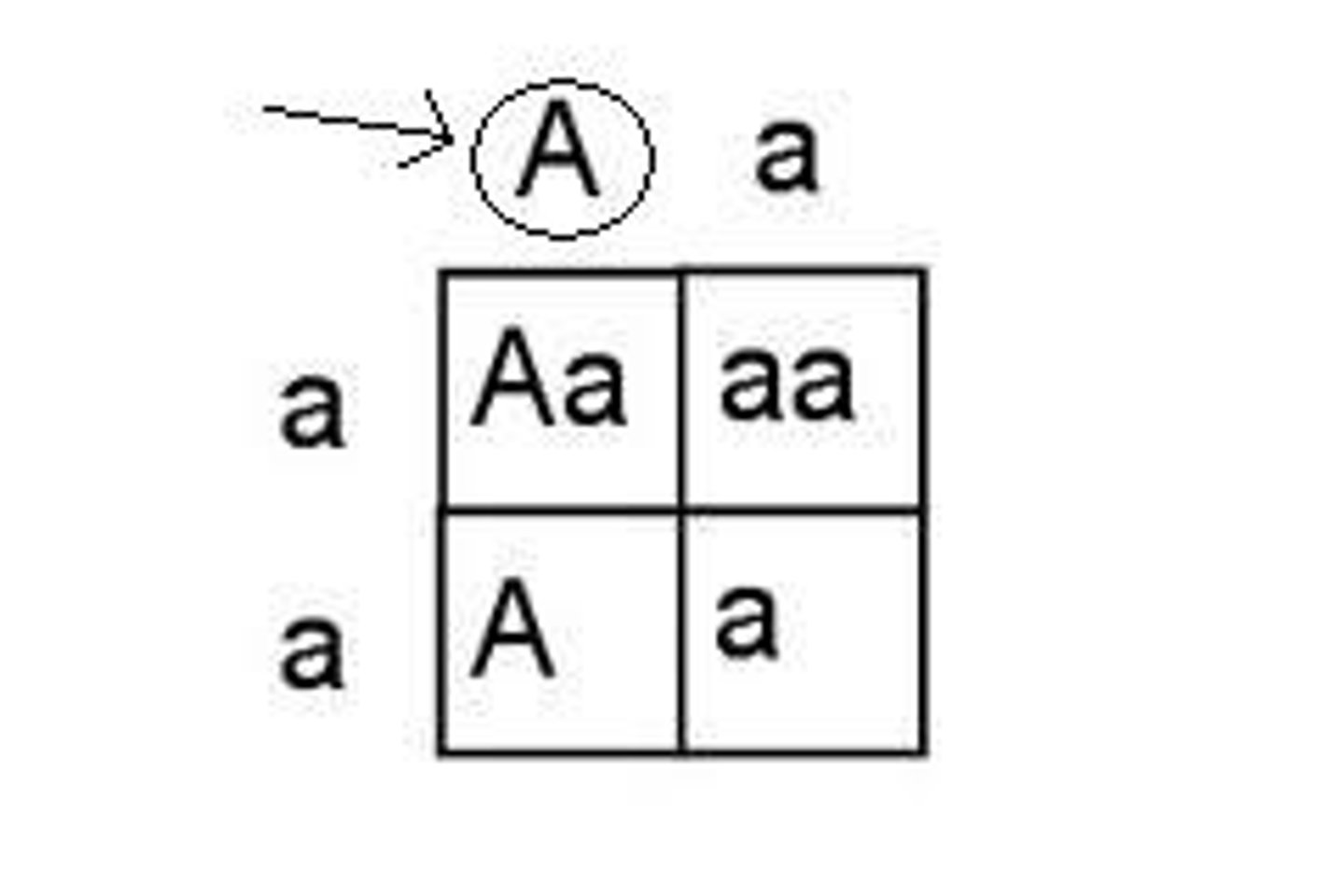
dominant
In genetics, describes an allele that is fully expressed whenever the allele is present in an individual.
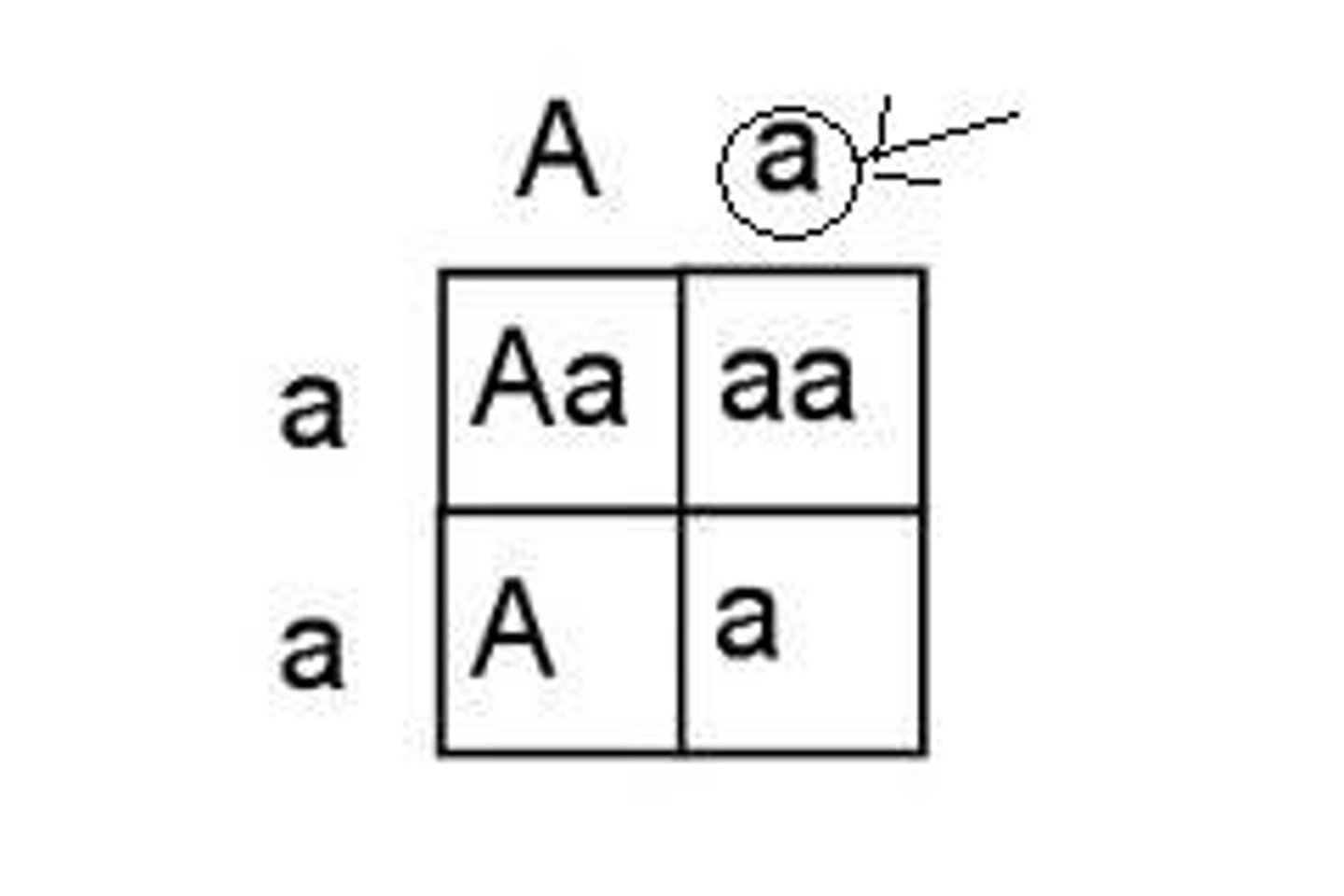
recessive
In genetics, describes an allele that is expressed only when no dominant allele is present in an individual.
allele
One of the alternative forms of a gene that governs a characteristic, such as hair color.
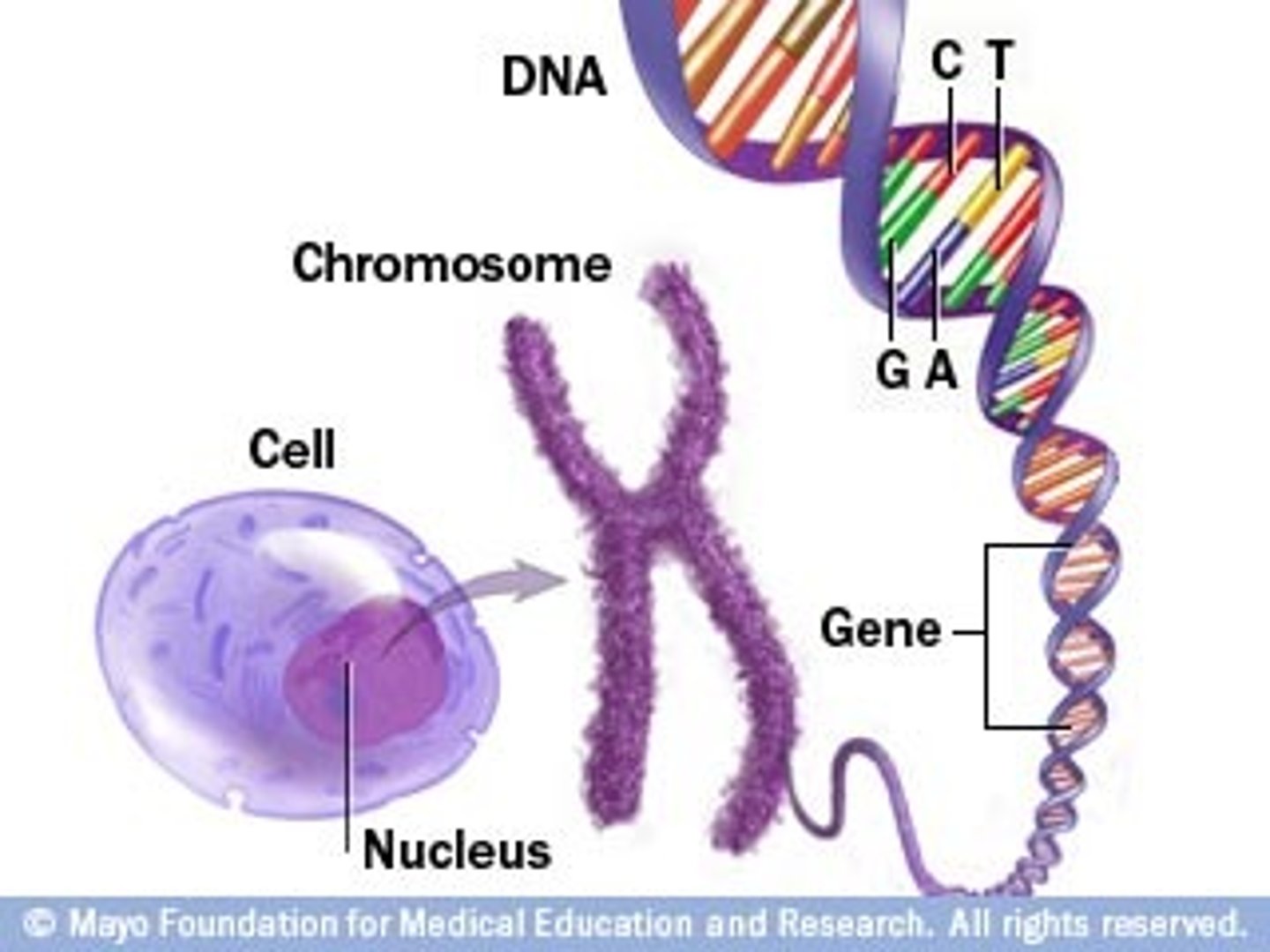
gene
One set of instructions for an inherited trait.
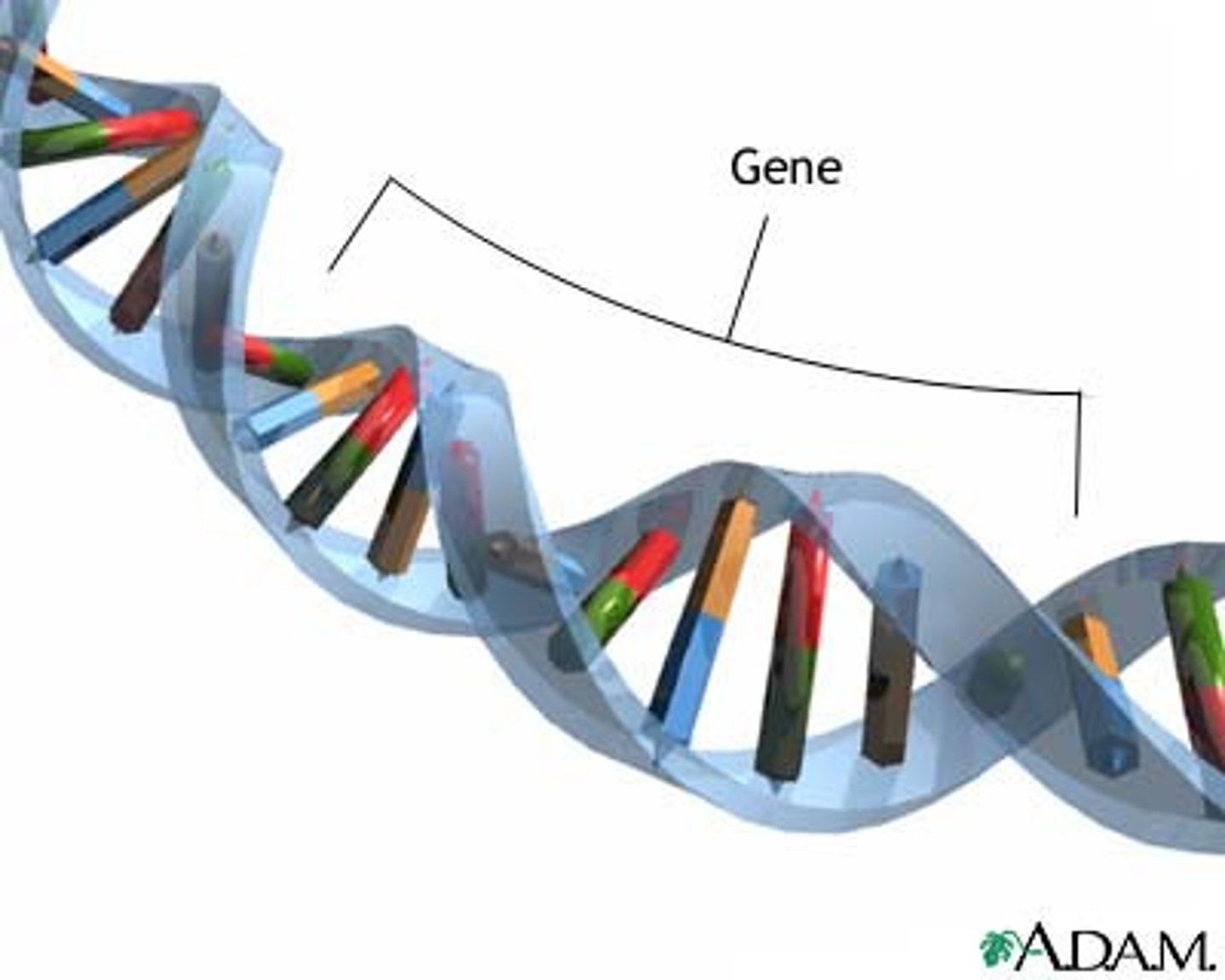
chromosome/DNA
In a eukaryotic cell, one of the structures in the nucleus that are made up of DNA and protein; in a prokaryotic cell, the main ring of DNA.
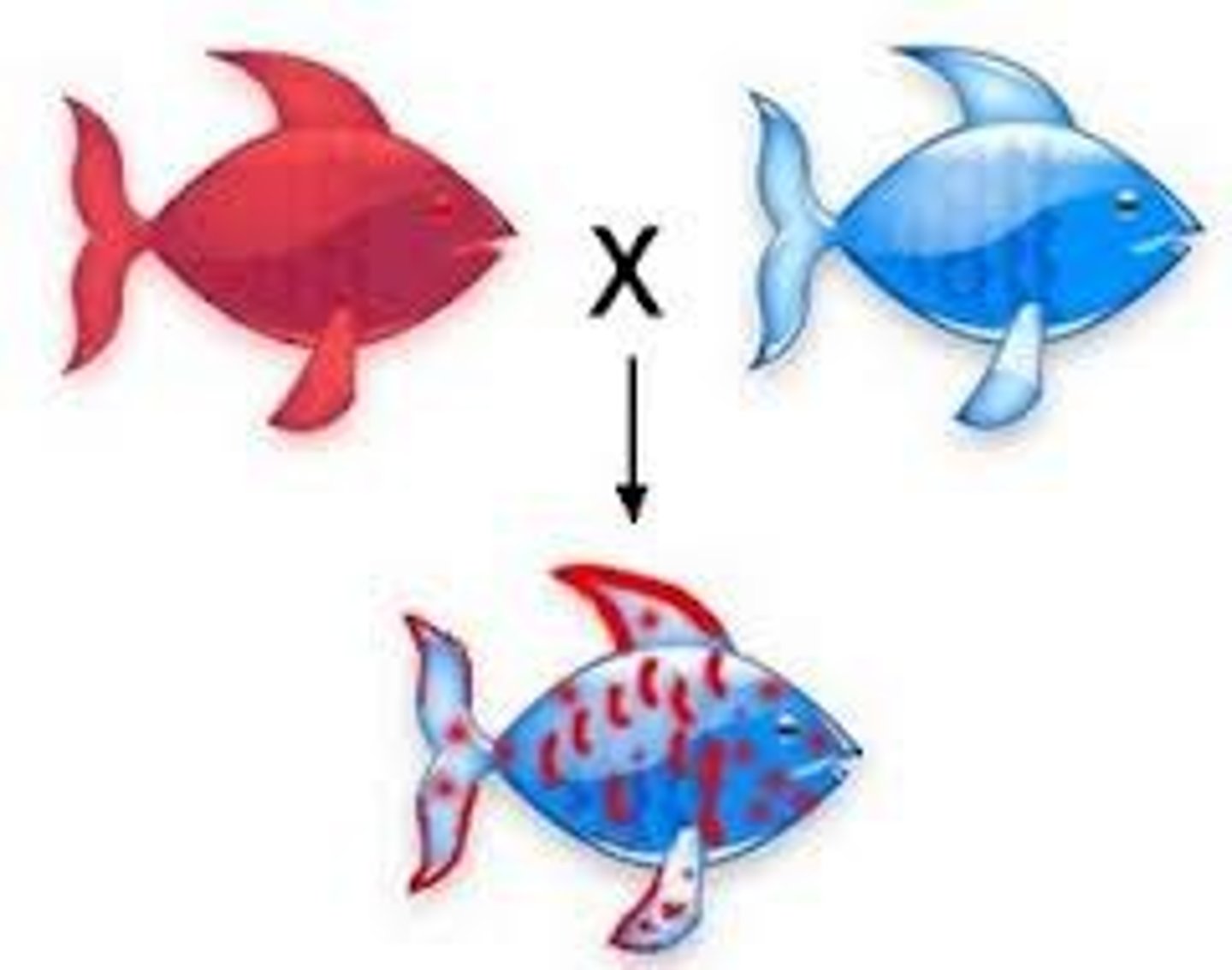
co-dominant trait
Both alleles of a gene contribute independently to the phenotype.
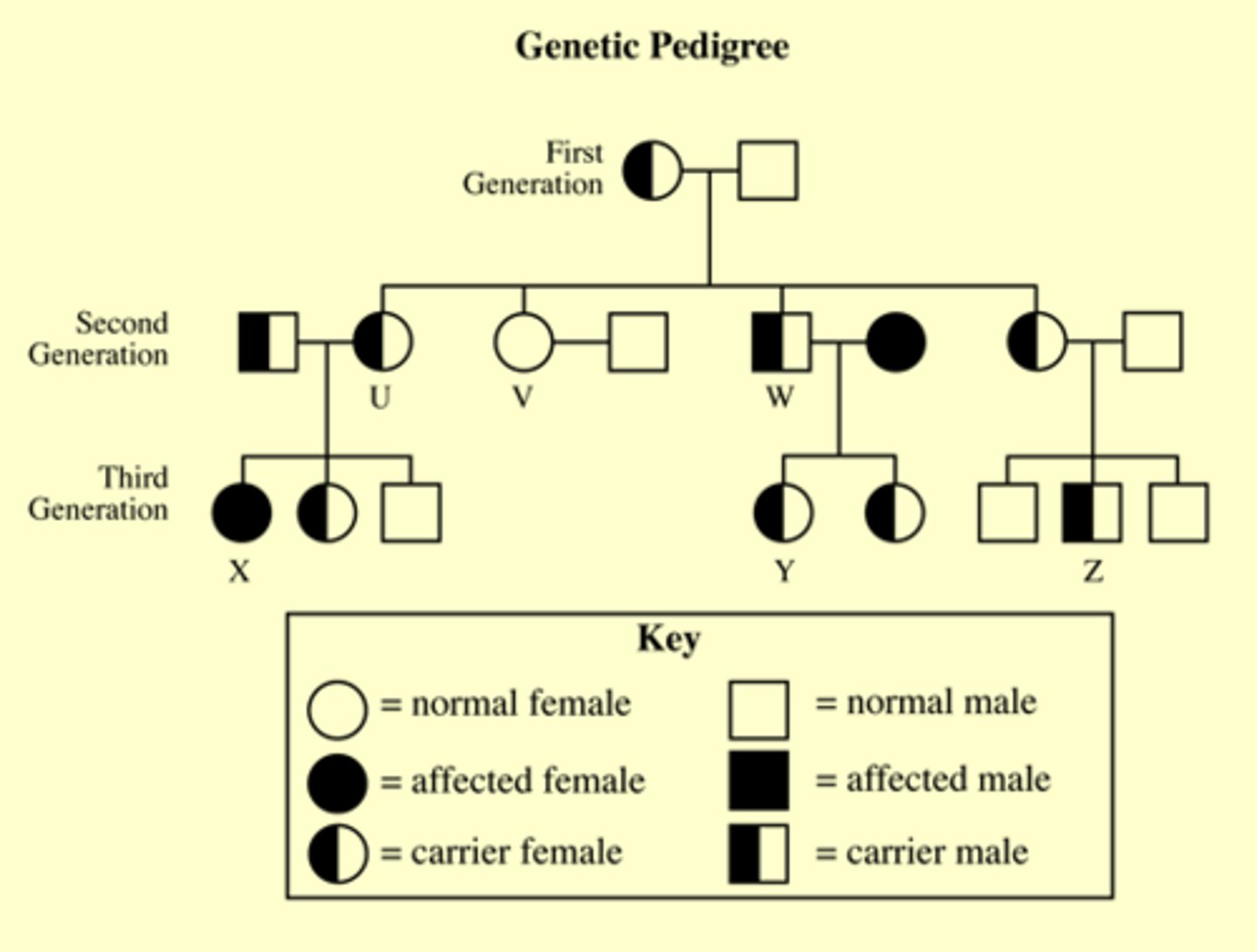
pedigree analysis
Chart showing one trait being carried over many generations.
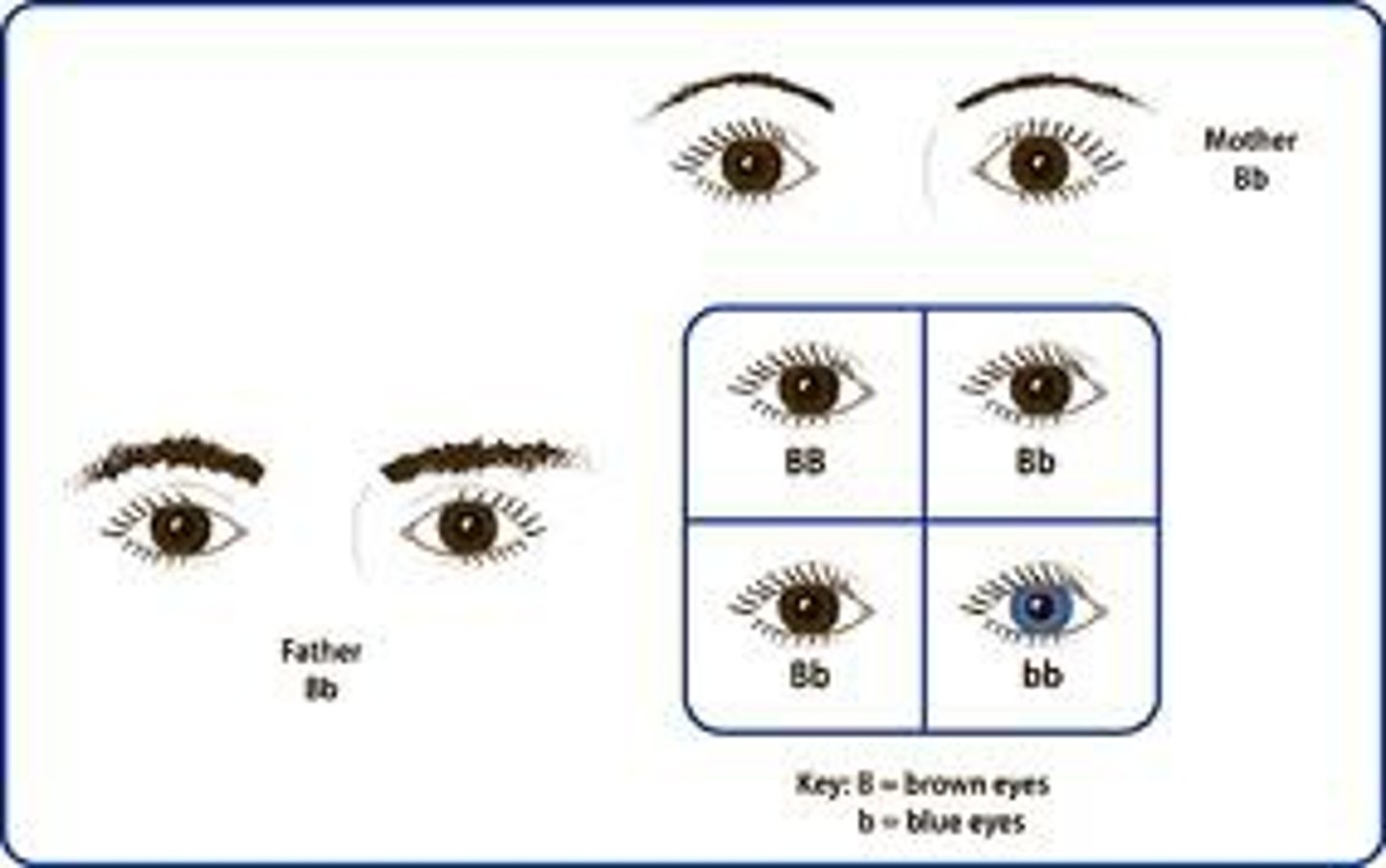
punnett square
A graphic used to predict the results of a genetic cross.
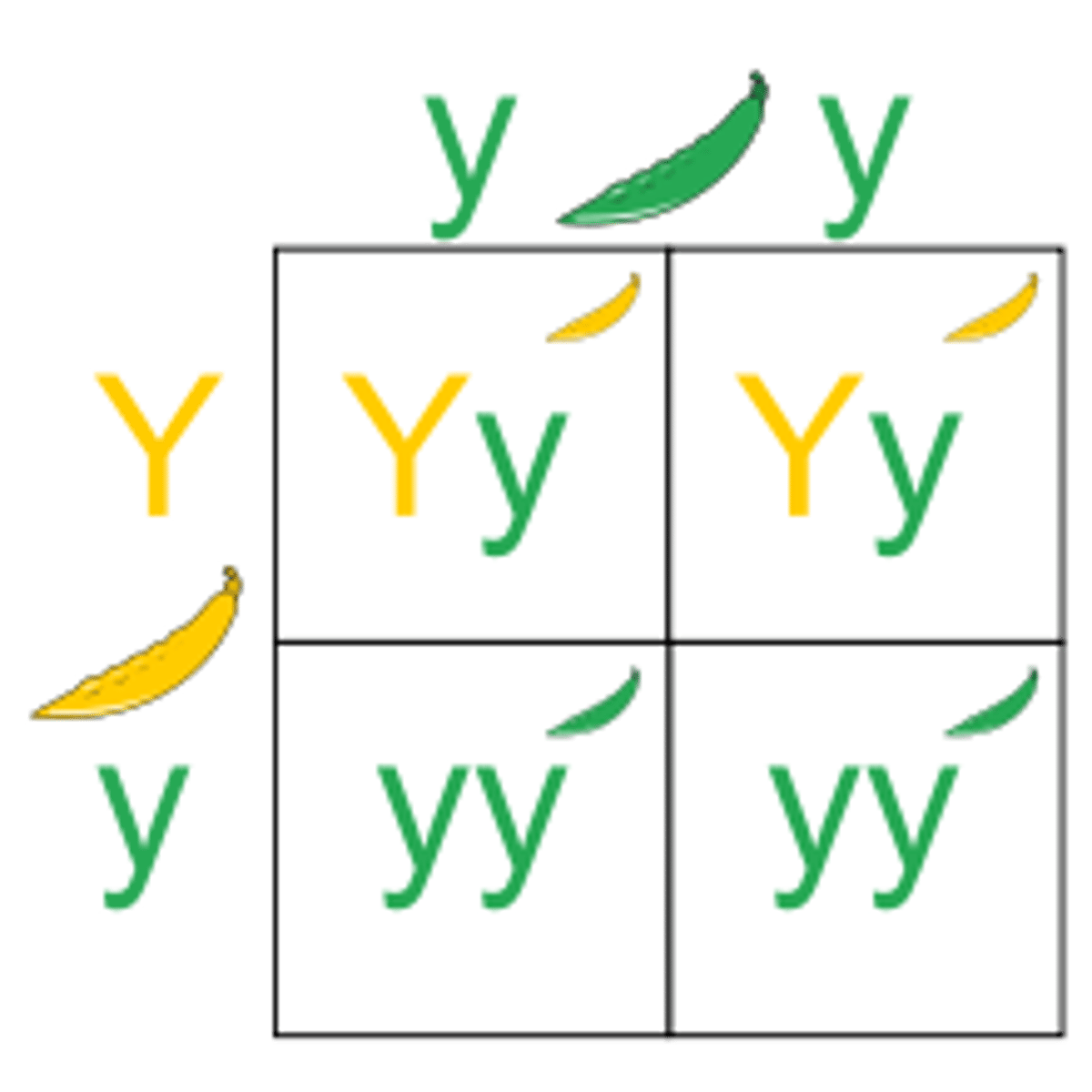
genetic variation
Differences among individuals in the composition of their genes or other DNA segments.

kinetic energy
The energy an object has due to its motion.
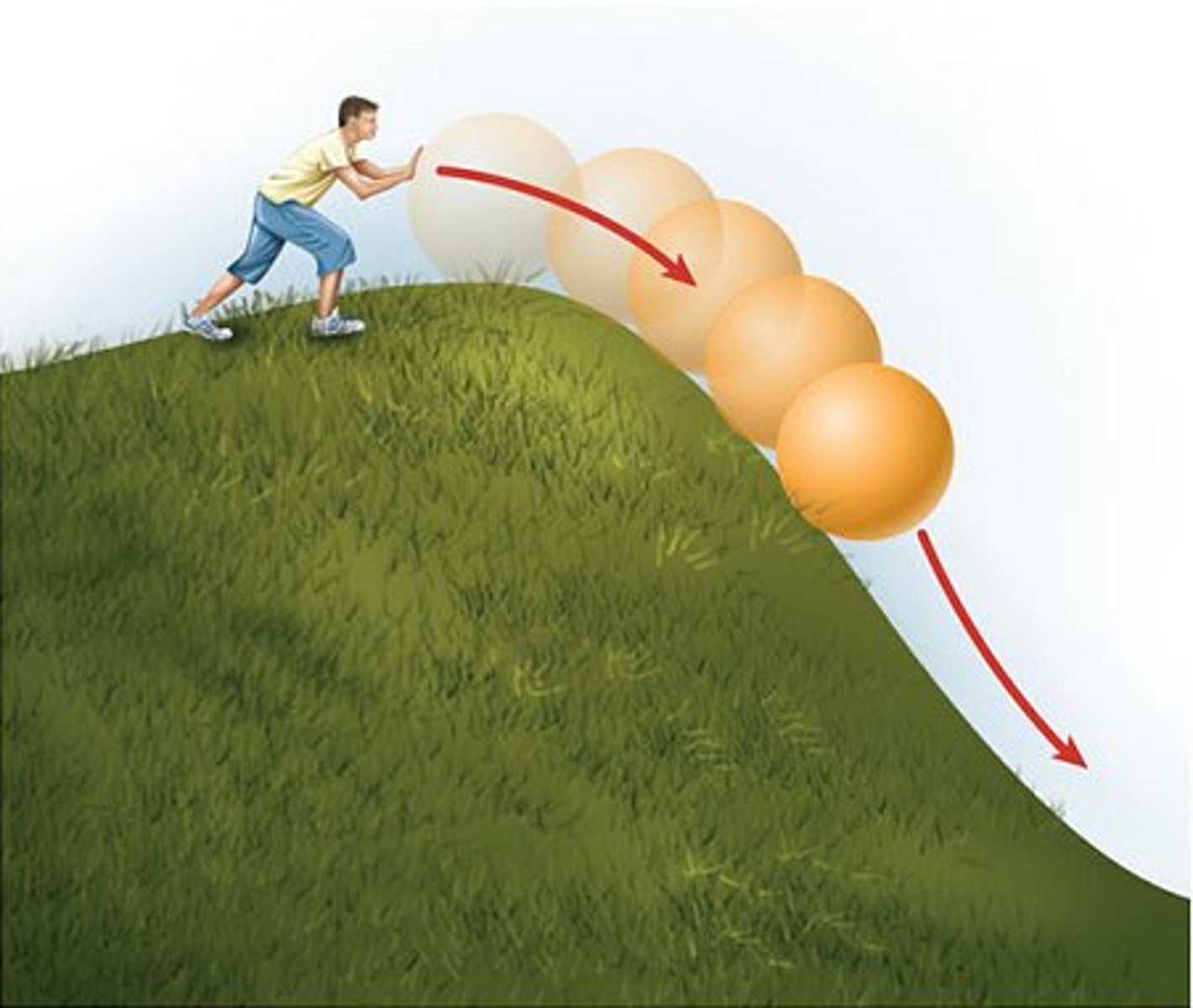

potential energy
Stored energy that results from the position or shape of an object.
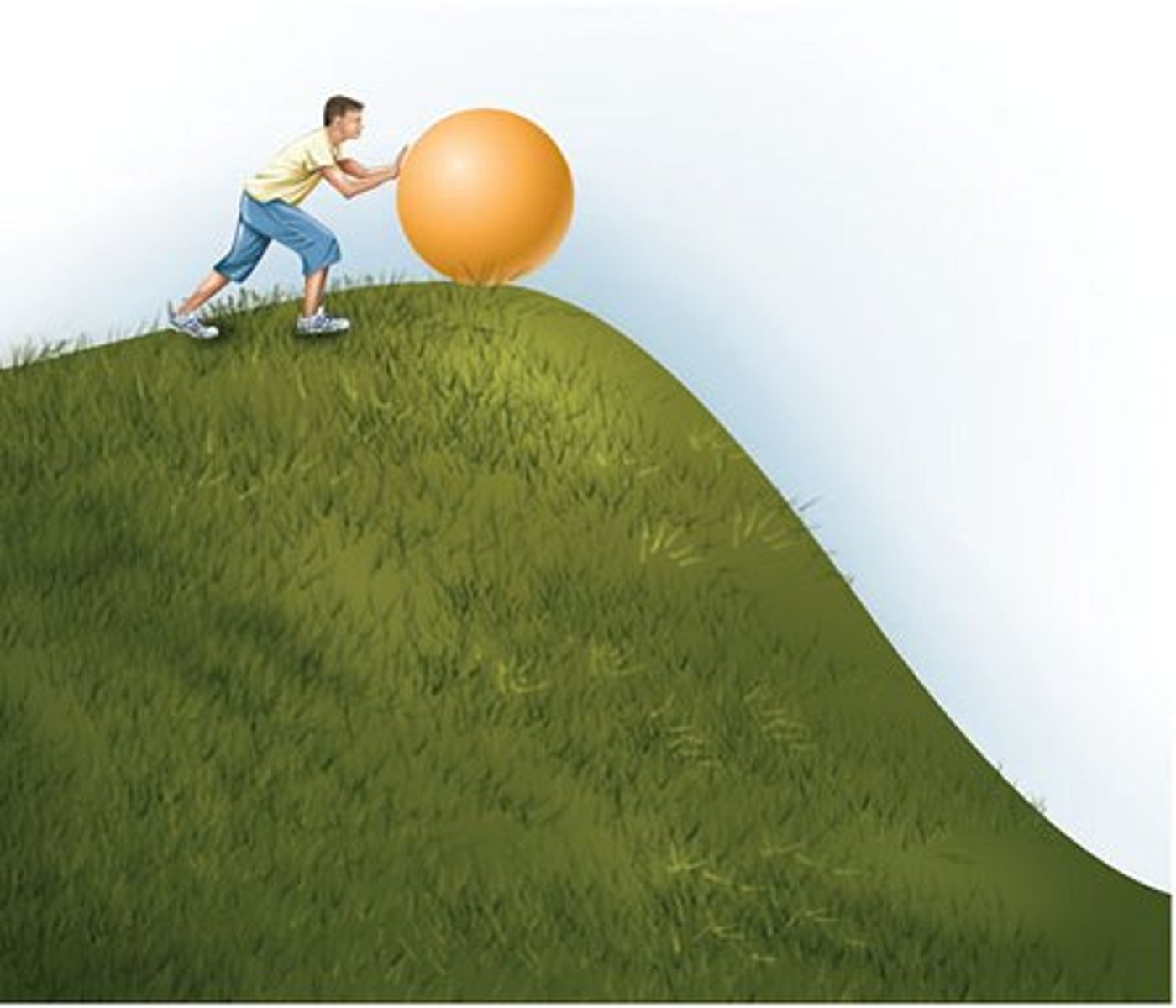

matter
Anything that has mass and takes up space.
reactants
A substance that takes part in and undergoes change during a reaction.
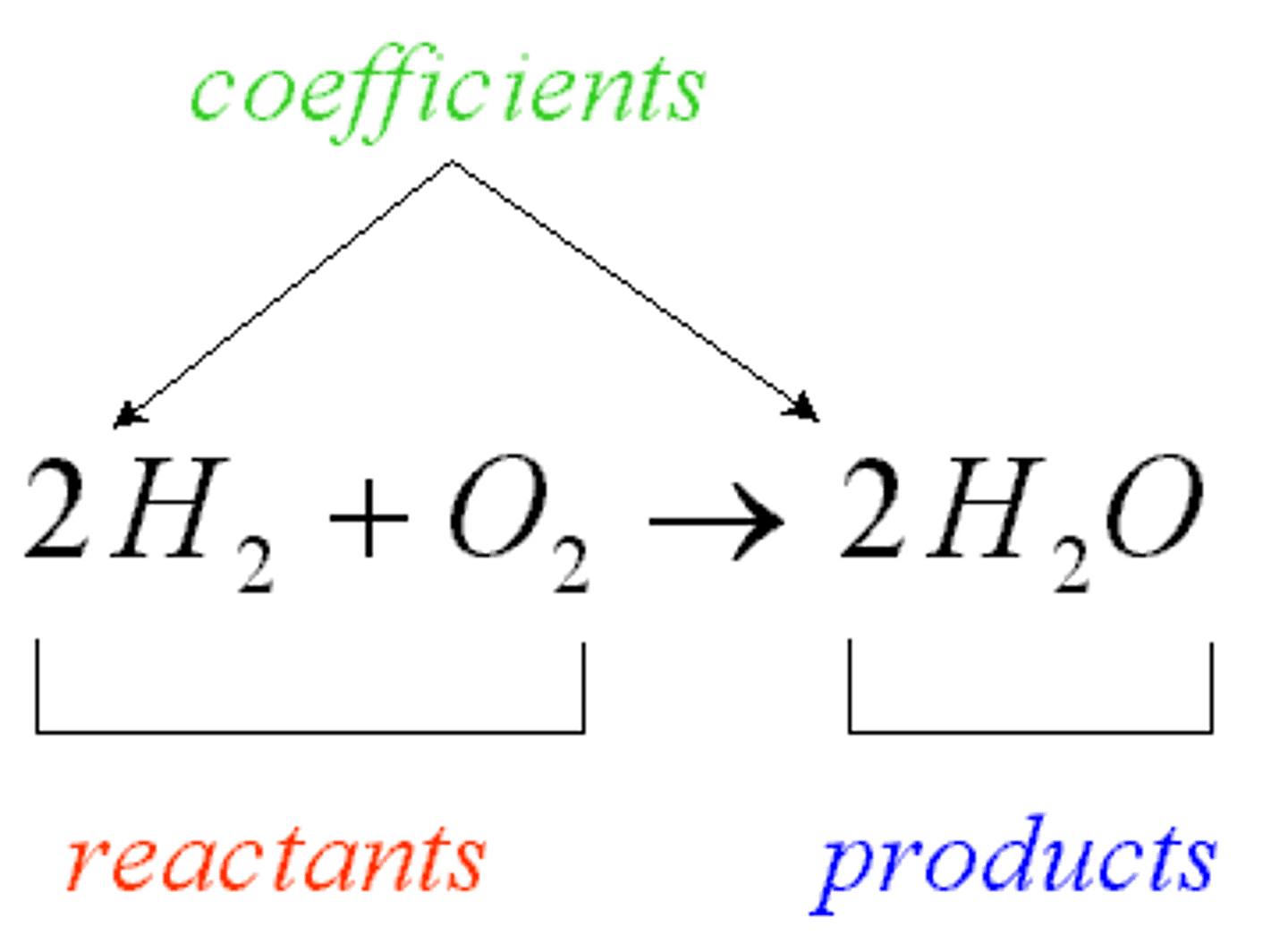
products
The elements or compounds produced by a chemical reaction.
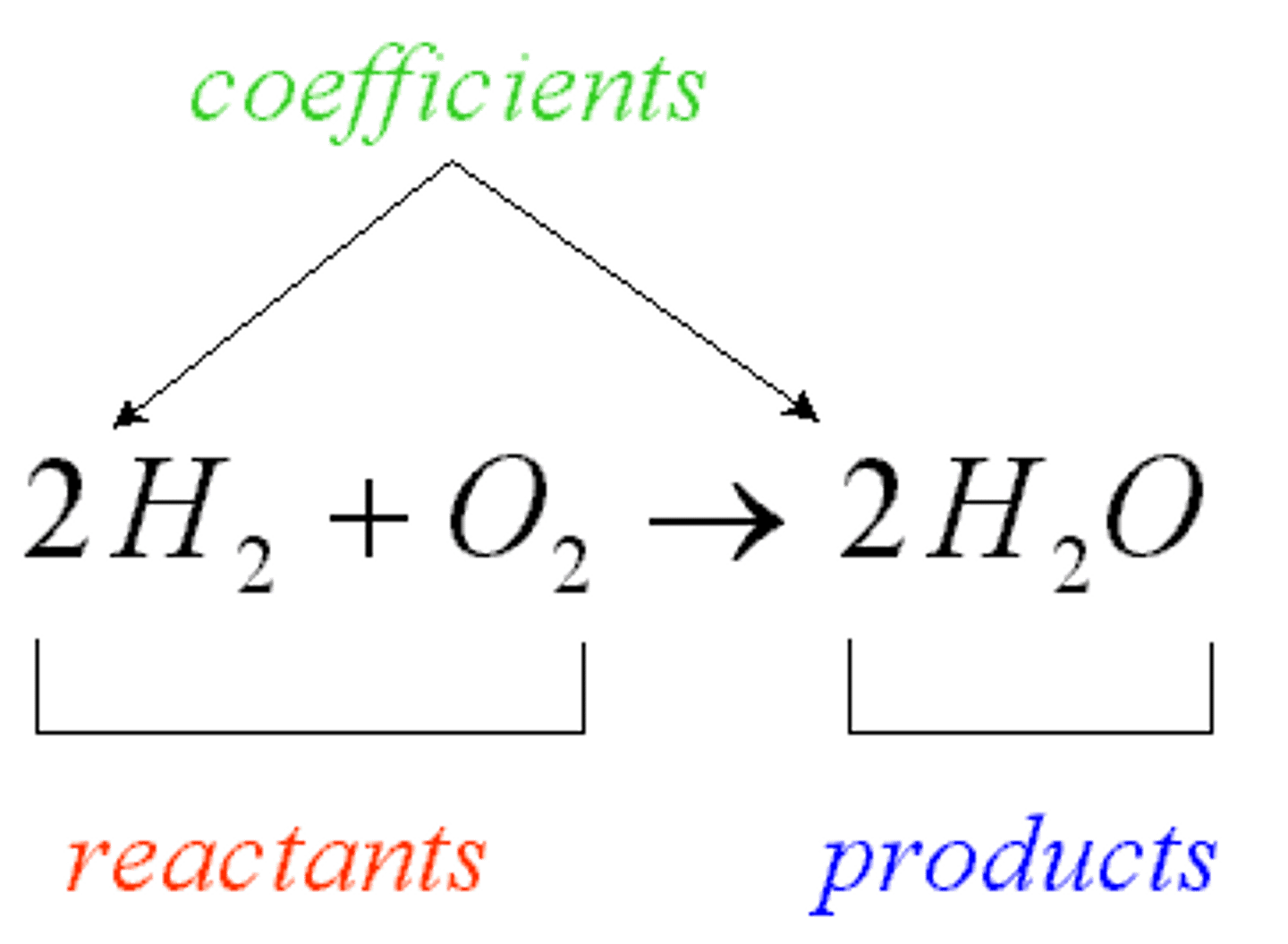
velocity
The speed of an object in a particular direction.
speed
The distance an object travels per unit of time.

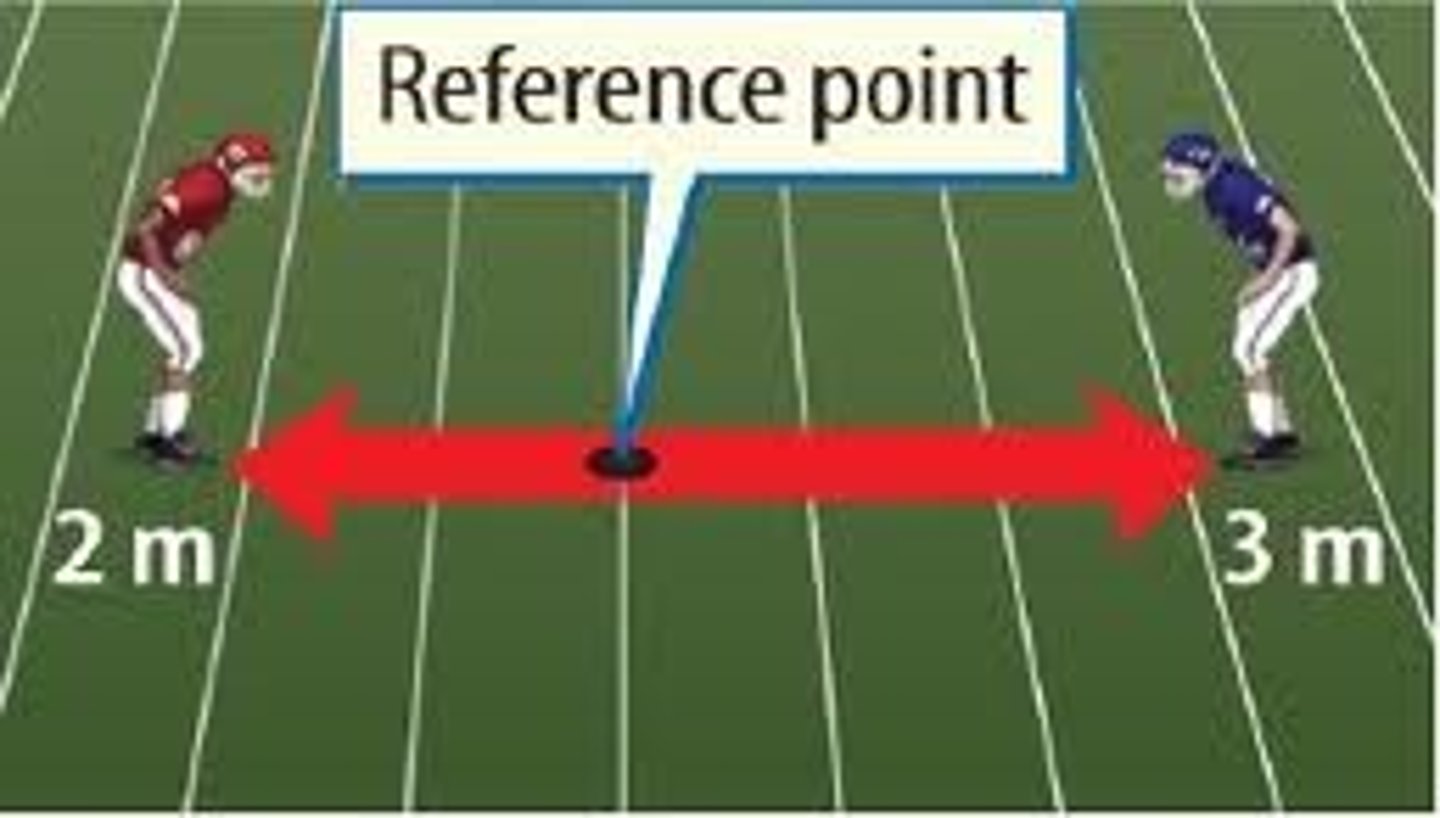
reference point
A place or object used for comparison to determine if an object is in motion.
gravity
A force of attraction between objects that is due to their masses.

mesosphere
The strong, lower part of the mantle between the asthenosphere and the outer core.
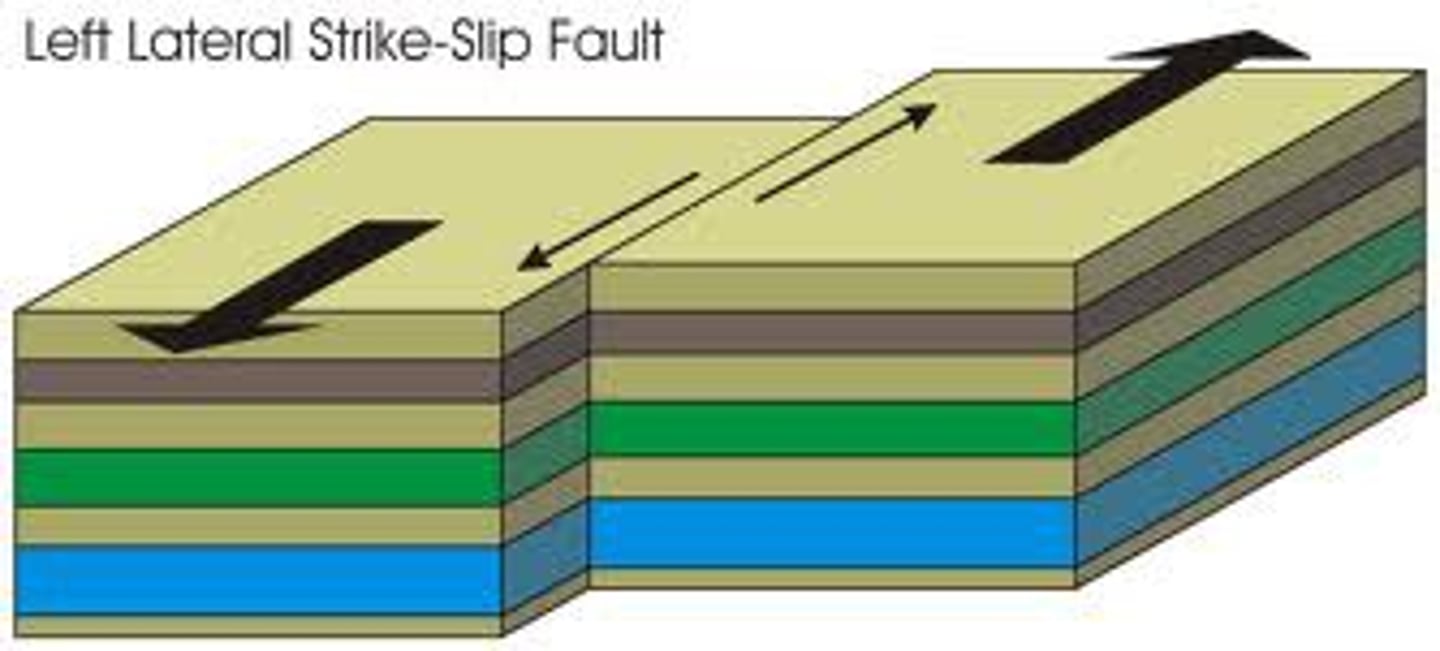
transform boundary
A plate boundary where two plates move past each other in opposite directions.
tension
Stress that stretches rock so that it becomes thinner in the middle.
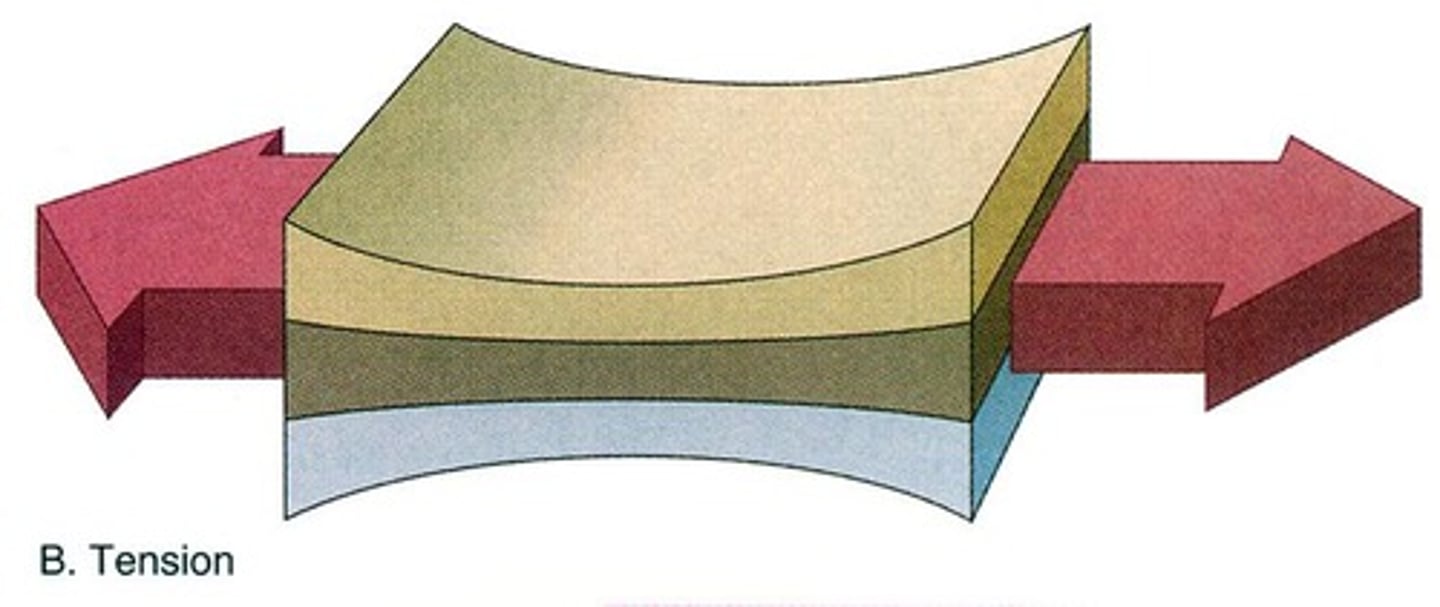
compression
A force that pushes on or squeezes a material.
drift
To be carried away by water or air.
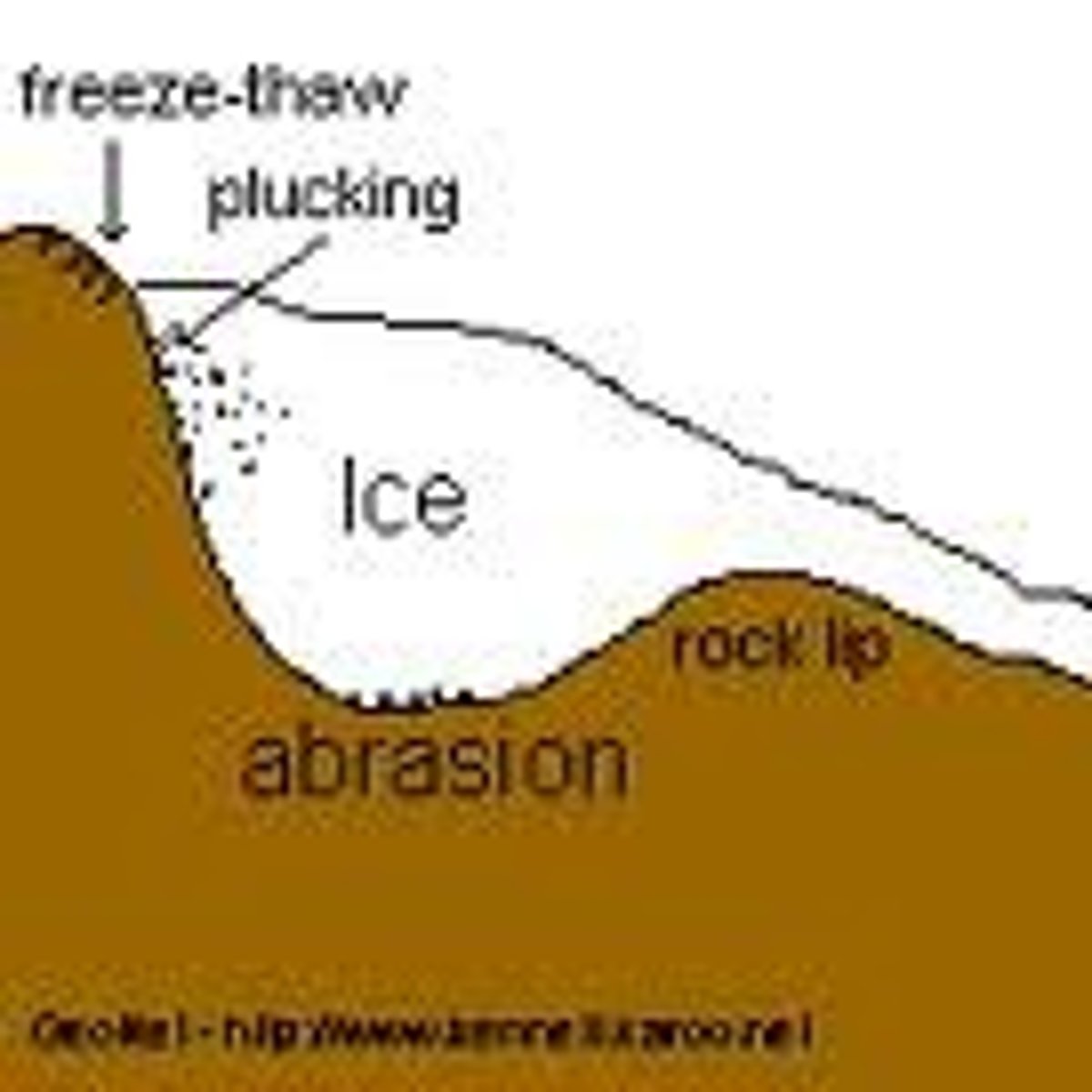
plucking
The process of glacial erosion occurs when water seeps into the crack glacial ice and rock, freezes, causing ice to expand. Then as the ice melts, it causes the rock/ice to become unstable and gravity causes it to move downward.
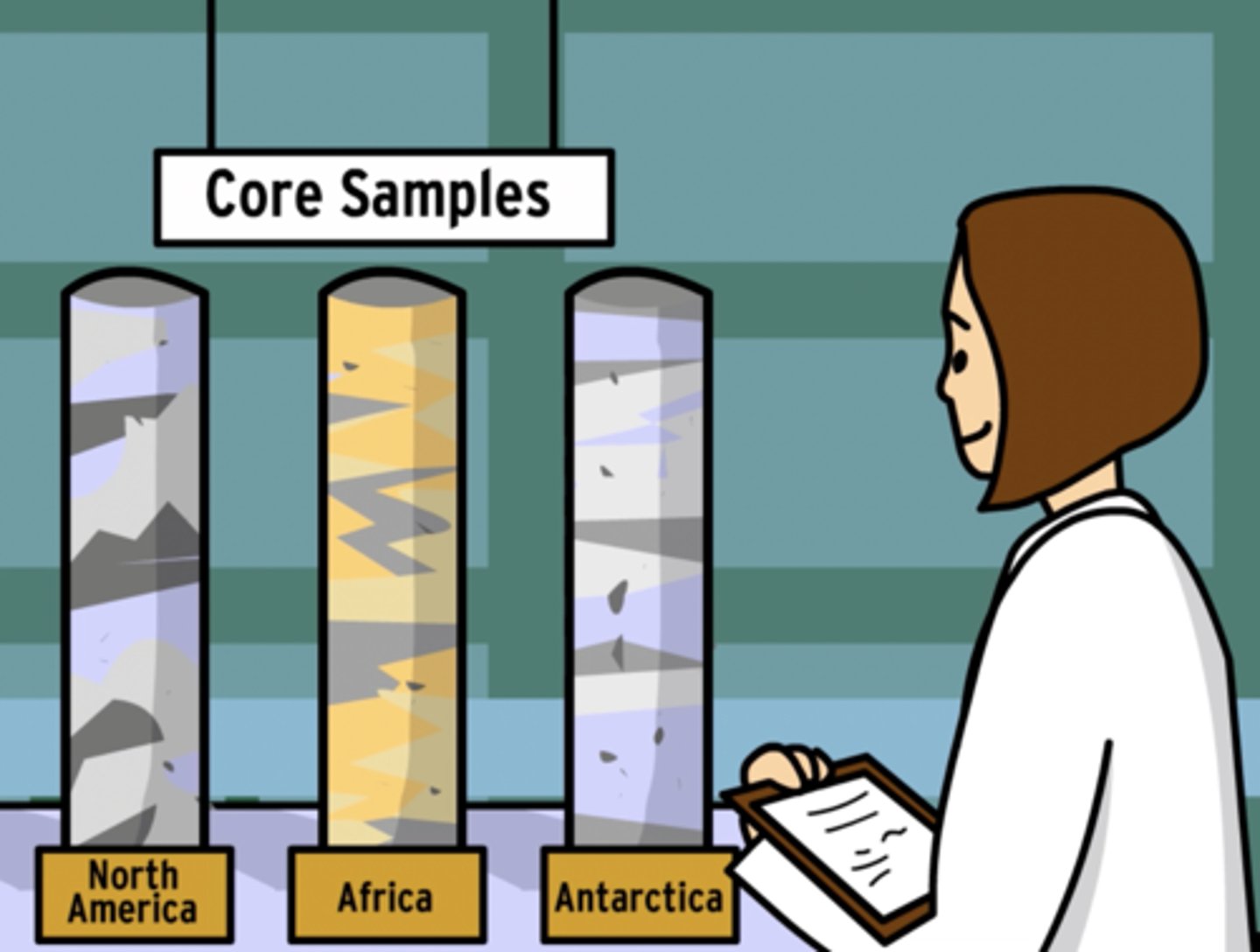
ice core sampling
A method that measures gases trapped within meltwater to study past climates.
glacial striations
Scratches and grooves on bedrock caused by glacial abrasion.
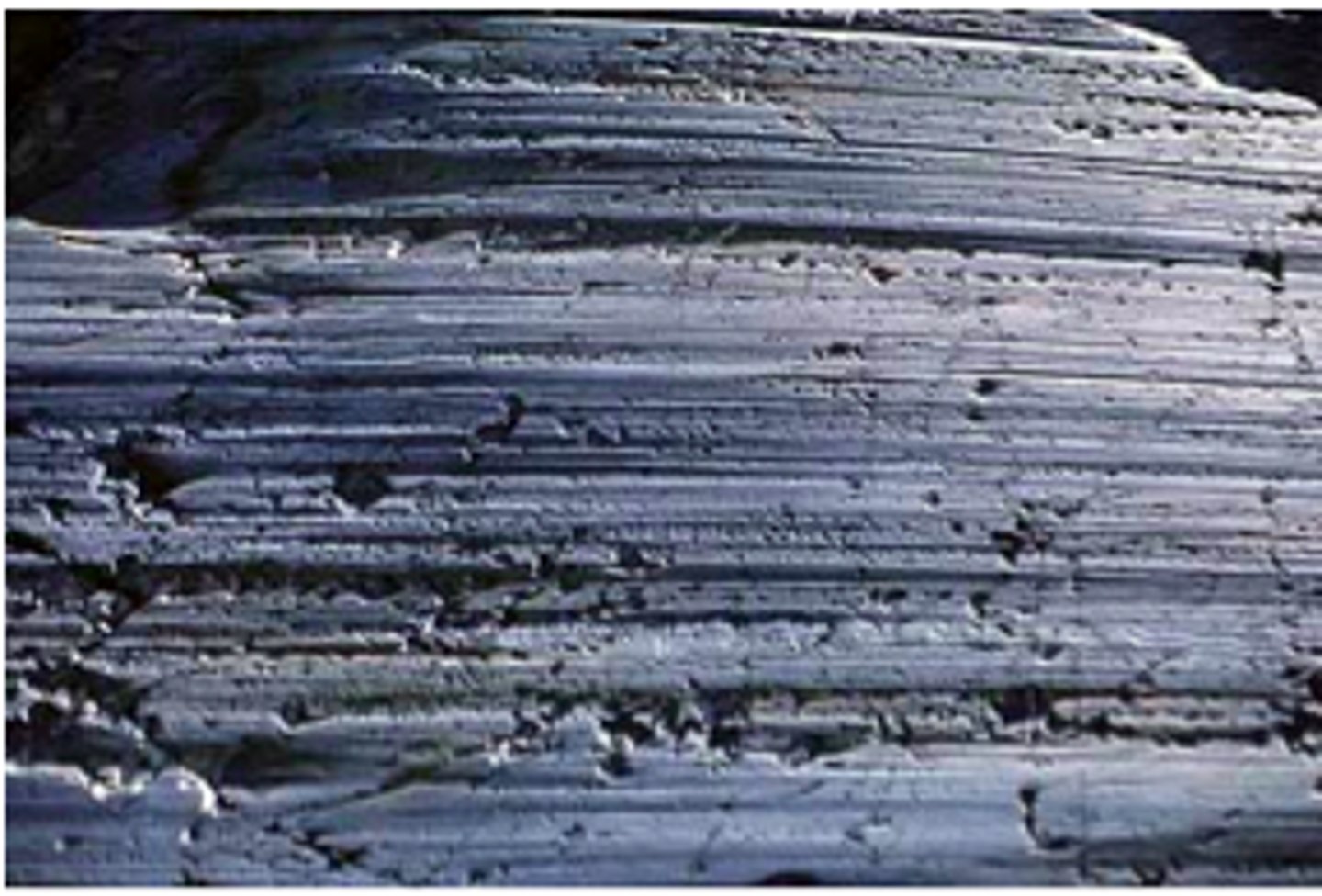

glacial grooves
Grooves in solid rock formations made by rocks that are carried by glaciers.
