Cell bio
1/89
Earn XP
Description and Tags
up to midterm 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
cell is the __
basic unit of biology
Cells are constantly changing; they have the capacity to __, __, and become __
grow
reproduce
specialized
three strands of biological inquiry weave into modern cell bio
Cytology, Biochemistry and Genetics
Cytology
focuses on cellular structure and emphasizes optical techniques
Biochemistry
focuses on cellular structure and function
Genetics
focuses on information flow and heredity and included sequencing of the entire genome (all of the DNA) in numerous organisms
Robert hooke (1665), what did he observe and what did he call it and why
observed cork under microscope- dead plant tissue
first named cells meaning “little room”
what were hookes observation limited by
low magnification power (30X enlargement)
Who produced better lenses that magnified up to 300X in 1673
Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek
what did Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek call the first observed moving single cells
animacules
what were the 2 factors that restricted progress in early cell bio
1- microscopes had limited resolution or resolving power(ability to see fine detail)
2- descriptive nature of cell bio, focus was on observation with little emphasis on explanation
when were compound microscopes used, and describe them
by the 1830s
2 lenses, increased magnification and resolution
using a compound microscope Robert Brown identified the ____ inside a ___ cell
nucleus
plant
using a compound microscope Theodor Schwann identified the ____ inside a ___ cell
nucleus
animal
cell theory and who created what part
1839- Schwann
all organisms consist of one or more cells
the cell in the basic unit of structure of all organisms
1855- Virchow
all cells arise from preexisting cells (he must have observed cell division)
what evidence led scientists to develop the basic principles of cell theory? note how tec played a role in its development
observing a variety of species/organisms under a microscope
had simple microscopes so observations were limited, ad the microscopes developed so did cell theory
difference between simple and compound microscope
simples- 1 lens, 30X magnification
compound- 2 lenses, up to 300X magnification
what problem have microscopes been helpful with
the small size of cells and their components
how small is a micrometer(um) and what is used to see
one millionth of a meter (10^-6 m)
used to view cells and bacterium
how much larger are plant and animal cells than bacterial cells
10-20 times larger
____ are comparable to bacterial cells in size
organelles
how small is a nanometer(nm) and what is used to see
one billionth of a meter (10^-9m)
used to measure molecules and subcellular structures that cant be seen in the light microscope like organelles and ribosomes
how small is an angstrom (Å) and what is used to see
0.1 of a nm (~size of a hydrogen atom)
measures bonds and atoms (within proteins and DNA molecules)
what was the earliest tool of cytologists
light microscope
the light microscope allowed identification of ___, ___ and ___ within cells
nuclei, mitochondria and chloroplasts
in a light microscope, what kind of light passes through a specimen
white light
what is another word for light microscope
brightfield microscopy
what kind of samples are used within the light microscope
samples are dead, alive, fixed and stained
what did the microtome allow
and what began to be used around the same time, what time was this
allowed preparation of very thin slices of samples, 4-10 um thick sections
dyes for cells began to be used around the mid-1800s
what is the limit of resolution
how apart objects must be to appear distinct
sharpness limit
what is resolving power
ability to see fine detail
what did dyes lead to
improved the limit of resolution
the small the microscopes limit of resolution the greater the resolving power
what are paraffin embedded tissues and what ability do they provide
biological tissue that has been preserved, dehydrated, and then embedded in a block of paraffin wax so it can be sliced very thinly for microscope slides
they provide the ability to study subcellular structures
what did the development of coal tar-derived dyes permit
they permitted the differential staining of a host of subcellular structures (parts inside the cell)
initially what were single stains used to facilitate
the study of otherwise transparent cells
what did the dual staining of H____ and E______ staining allow
hematoxylin and eosin
acidic = blue
basic = pink
immunostaining allows labelled __ to reveal the presence of specific molecules
antibodies
explain immunohistochemistry schematic
1- primary antibody= binds to the protein that is of interest (antigen)*
2- secondary antibody already has an enzyme(chemically conjugated) and ONLY binds to the primary antibody (antigen)
3- The substrate of the enzyme will give the colour
4- where the colour is that’s where the protein of interest is
*what the antibody binds to
what quality is based of the quality of the lens of microscopes
optical resolution
what type of microscope is used when dissecting and has low magnification
dissecting light microscope
what light microscope is used to look at cells and bacteria and has a high magnification
compound light microscope
what light microscope is used to look at live cells with high magnification
inverted compound light microscope
what can we used to increase contrast in a basic light microscope
dif types of illumination
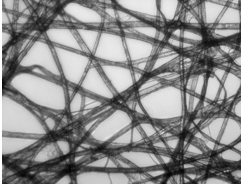
what type of illumination is this
brightfield
little contrast without staining
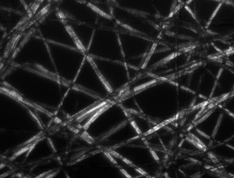
what type of illumination is this
polarized light
cancels out dif wave lengths of light
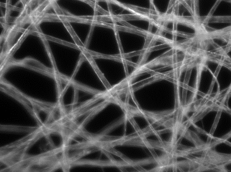
what type of illumination is this
darkfield
only scattered light is viewed
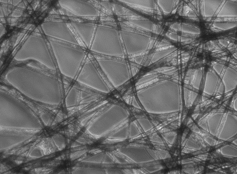
what type of illumination is this
phase contrast
phase rings scatter light to increase contract
live cells
what kind of light do differential interference contract microscopy use
polarized
phase contrast and differential interference contrast microscopes exploit dif in ____ of ___ passing through a structure with a ______ ____ different than the surrounding medium. It makes it possible to see _____ cells clearly
phase
light
refractive index
living
refractive index
how much a material slows down and bends light when it passes through a medium
each part of the cell will have dif refractive intext
fluorescence microscopy detects _______ ___ or labels, to show _____ of substances in the cell
ex- _____, ____
fluorescent dyes
location
immunostaining
DAPI
a fluorescent dye that binds strongly to adenine-thymine-rich region on DNA
fluorophore
molecule that absorbs light at one wavelength (the excitation light) and then emits light at a longer wavelength (the fluorescence you see)
fluorescence microscopy allows detection of ___, ___ _____ or _____ that have been made fluorescent by binding to _____
proteins
DNA sequences
molecule
antibodies
antibody
protein that binds a particular target molecule called an antigen
the antibody can be coupled to a fluorescent ______, which emits _______ whenever the target molecule is bound by the _____
molecule
fluorescence
antibody
_____ ______ protein (GFP) can also be used to study the ____ and ______ distribution of ______ in a ______ cell
Green fluorescent protein
temporal (time) and spatial (space and location)
proteins
living
confocal microscopy
takes photos at dif subsections to remake 2D and 3D images, using a laser beam
digital video microscopy
uses cameras to collect digital images
does confocal microscopy need fluorescence
usually does not its not necessary
what light does fluorescence microscopy absorb and what one does it reflect
absorbs ultraviolet radiation
emits visible light
what are the limits to the resolving power of each class of microscope based on wavelength
human eye
light microcopy
electron microscope
human eye ~0.1mm
light microcopy ~0.0001mm (0.1um)
electron microscope ~0.0000001mm (0.1 nm)
cryo electron microscopy
biological samples are rapidly frozen and then viewed with an electron microscope. The freezing preserves the sample in a near‑natural state without needing chemical fixation or staining
looked under the microscope in cold conditions
limit of resolution
how far apart objects must be to appear as distinct
the small the microscopes limit of resolution the greater its _____ ____
resolving power (ability to see fine details)
low frequency means _____ resolution
high frequency means _____ resolution
poor
good
the good resolution for a light microscopy is related to the _____ ______ of ____
physical nature of light
for visible light the limit of resolution is about ____-_____ ___
200-350 nm
when was the electron microscope developed and what does it use rather than light
1930s
a beam of electrons
how much better is the resolution of the electron microscope compared to the light microscope
100 times better
what is the limit resolution of the electron microscope
0.1-0.2 nm
how much better is the magnification of electron microscopes compared to light microscopes
up to 100 000x
in scanning electron microscopy (SEM) the ____ of a specimen is scanned by detecting ______ _____ from the outer surface
surface
electrons deflected
what are two visualizations of specialized electron microscopy
visualization of specimens in 3 dimensions
visualization of individual atoms
what did Fredrich Wohler do and when
1828
showed that a compound made in a living organism- urea- could be synthesized in the lab
what was though about living organisms prior to Fredich’s work
prior to his work it was thought that living organisms were unique and not governed by the laws of physics and chemistry, that organic molecules could only be made by living organisms
“organic” molecule could be made from inorganic chemicals = vitalism
what does vitalism mean
that organic molecules could NOT be made from inorganic ones because living things supposedly had a special “vital force” that non‑living matter lacked
what did louis paster show and in what year
1860s
showed that yeast could ferment sugar into alcohol
what did Eduard Buchner show and in what year
1897
showed that yeast extracts could ferment sugar into alcohol providing that cells was not a requirement
pasteur but mainly buchner lead to what discovery, and what are they
enzymes = biological catalysts
what did gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, Otto Warberg and Hans Krebs describe the steps of
steps of glycolysis (the embden-Meyerhof pathway) and the Krebs cycle
what did Fritz Libmann show
that adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the principle energy storage compound in most cells
what did Melvin Calvin and his colleagues elucidate
the Calvin cycle
radioactive isotopes
to trace the fate of specific atoms and molecules
what did radioactive isotopes led to the elucidation of
the Calvin cycle
subcellular fractionation
uses centrifugation to separate/isolate dif structures and macromolecules
ultra centrifuges
capable of very high speeds (over 100 000 revs per min)
chromatography
technique to separate molecules from a solution based on size, charge of chemical affinity (chem properties)
electrophoresis
uses an electrical field to move proteins, DNA, or RNA through a medium based on size and chrage
mass spectrometry
used to determine the size and composition of individual proteins