Explanations of attachment: learning theory
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Who studied the learning theory of attachment
Dollard and Miller 1950
Why is it called 'cupboard love' explanation
It emphasises the importance of food in attachment formation
Children learn to love who feeds them
Role of classical conditioning
UCS - food
UCR - pleasure
This response is not learned so it's an unconditioned response
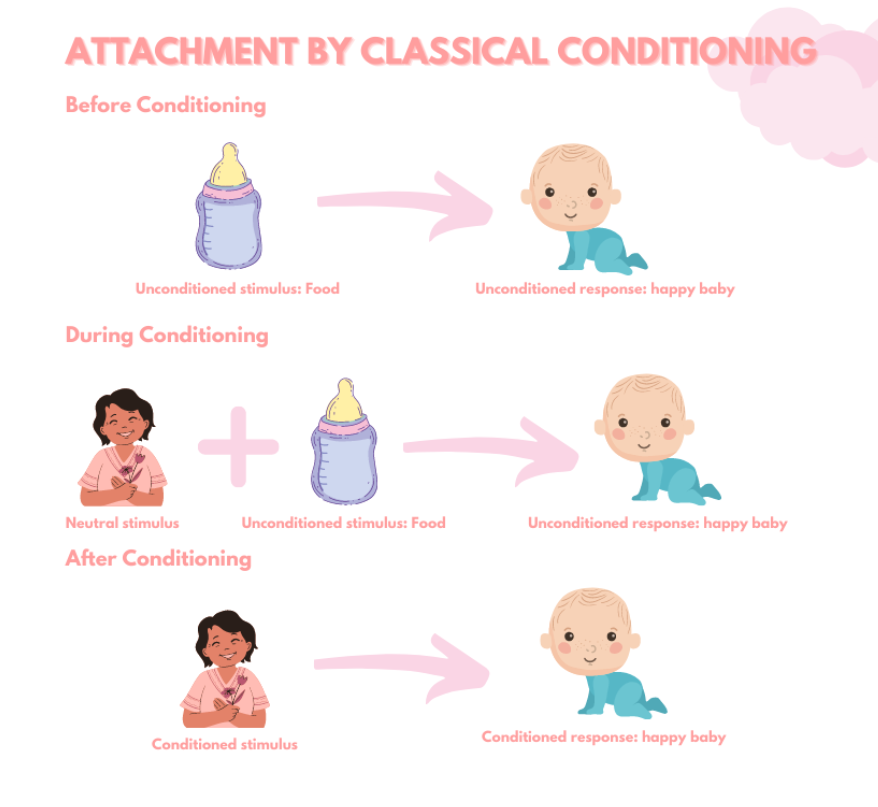
The caregiver becomes an attachment figure
Role of operant conditioning
explains why babies cry for comfort
Cying is reinforced by caregivers
Negative reinforcement for crying
Baby cries
Baby is reinforced for crying, caregiver receives negative reinforcement because crying stops
Positive/negative reinforcement strengthens and attachment
Hunger is a primary drive
An innate biological motivator
We are motivated to eat to reduce hunger drive
Attachment is a secondary drive
Learned by association between caregiver and satisfaction of primary drive
One limitation is counter evidence from animal studies
Lorenz's geese imprinted on the first moving object they saw
Harlow's monkeys attached to cloth mother in preference to the milk dispensing one
In both attachment did not develop through feeding
Shows factors other than feeding are important
Another limitation is counter evidence from human studies
Schaffer and Emerson showed that many babies were not attached to the person who fed them
Isabella et al. Found interactional synchrony related to attachment quality
Suggests other factors are more important than feeding
One strength is some elements of conditioning could still be involved
It seems unlikely that association with food is attachment
However conditioning plays a role e.g. babies choice of caregiver may be determined by the fact that a caregiver becomes associated with comfort
Conditioning could still be important in choice of attachment figures though not the process of attachment formation