Appendicular skeleton
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
How many bones? what does it include?
126, shoulder girdle, upper/lower arm, wrist, hand, pelvic girdle, thigh, leg, ankle, foot
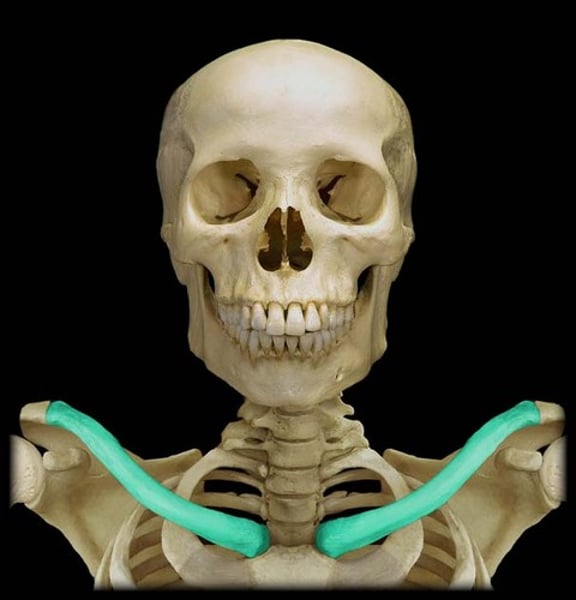
Articulation and location: Clavicle
sternoclavicular joint(with sternum, medial)
acromioclavicular joint(with acrommion in scapula, lateral)
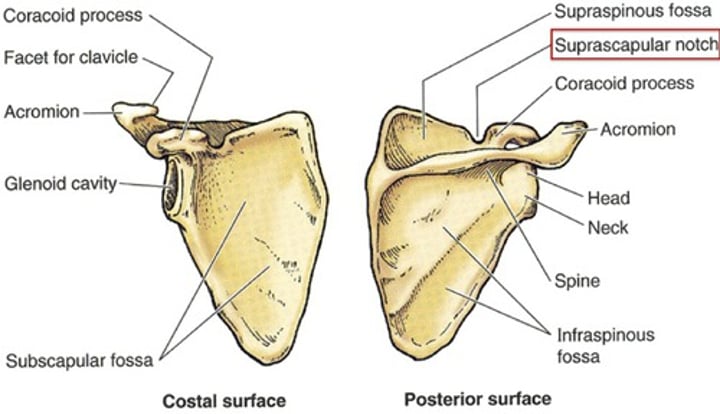
Articulation and location: Scapula(shoulder blade)
Landmarks: acrommion, scapular spine, glenoid cavit
- acromioclavicular joint(clavicle)
- glenohumeral joint(humerus)
Shoulder joint characteristics
- glenohumeral joint
very mobile cause glenoid cavity is shallow, more flexibility and less stability
- glenoid labrum, fibrocartilage layer that provides depth to glenoid vavity
- many ligaments, muscles, tendons, and bursa to strengthen
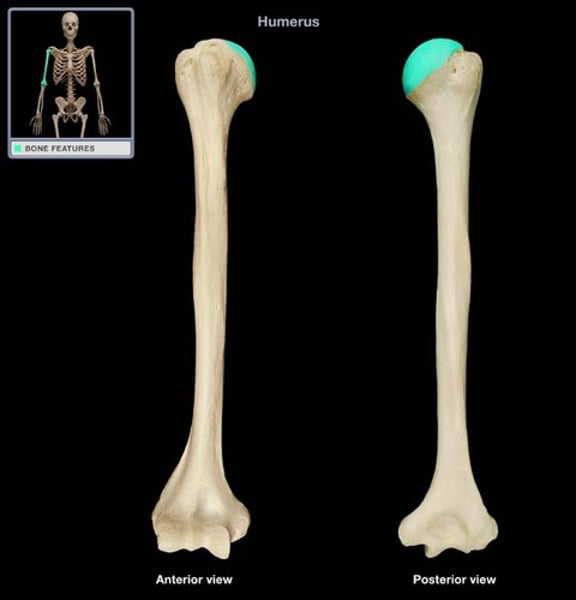
Articulation and location: Humerus
Landmarks: head, capitulum, tochlea
- glenohumeral joint(proximal, glenoid cavity)
- humeroradial joint and humeroulnar joint (distal, radius and ulna
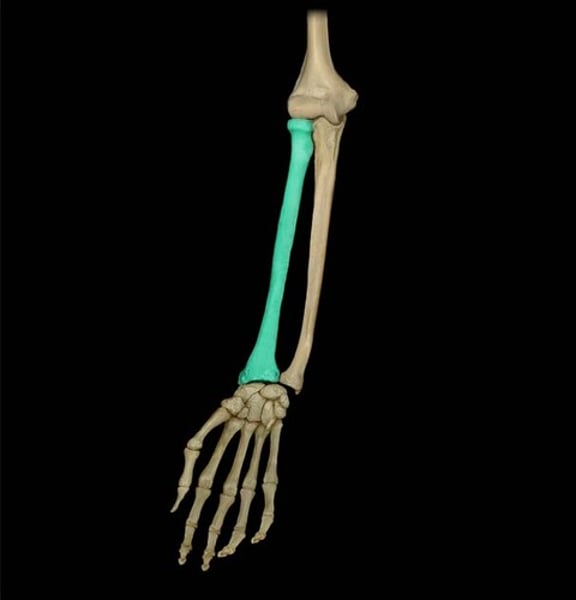
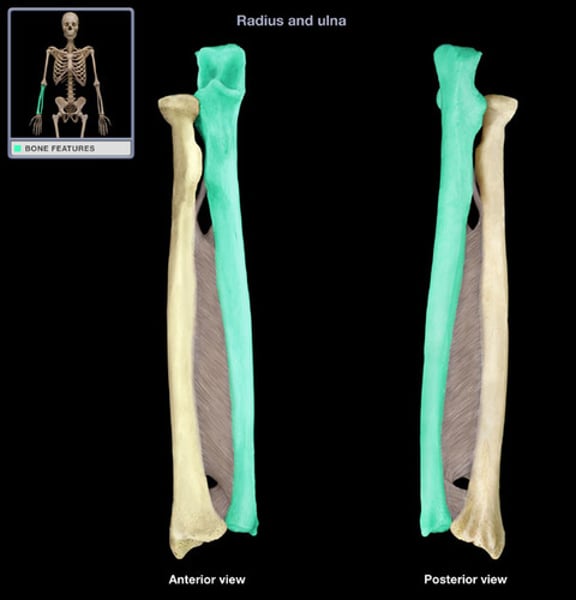
Articulation and location: Radius
thumb side of forearm, head and styloid process
- humeroradial joint(humerus, proximal)
- proximal radioulnar joint
- radiocarpal joint(distal, wrist bones)
- distal radioulnar joint
Ulna
pinky side of forearm, olecranon(elbow bone) and styloid process
- humeroulnar joint and proximal radioulnar joint
- distal radioulnar joint and fibrocartilaginous disk(not with carpal bones)
Radioulnar Joint(proximal)
allows for forearm rotation(supination and pronation)
Radioulnar joint(distal)
stabilizes forearm during rotation
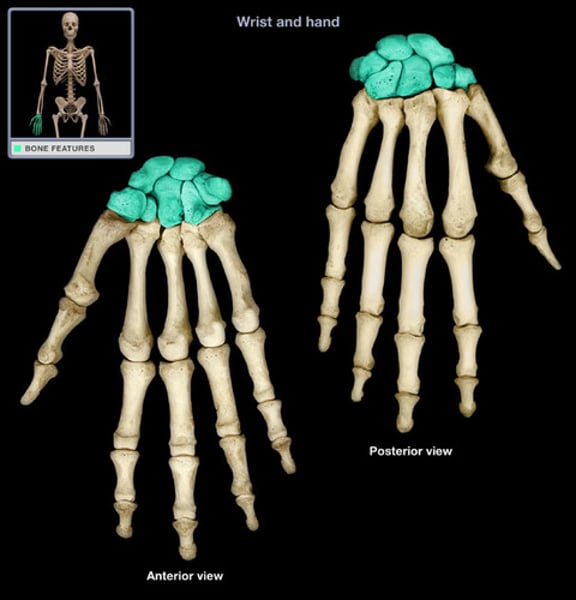
Carpals (wrist)
8 small bones bound by ligaments
- radiocarpal joint for wrist and hand movements
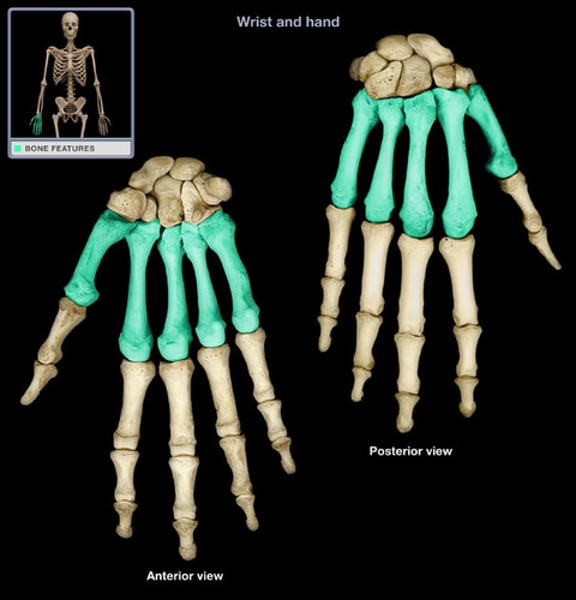
Metacarpals
- heads of metacarpals(knuckls) articulate with phalanges
- thum is most movable joint(opposition)
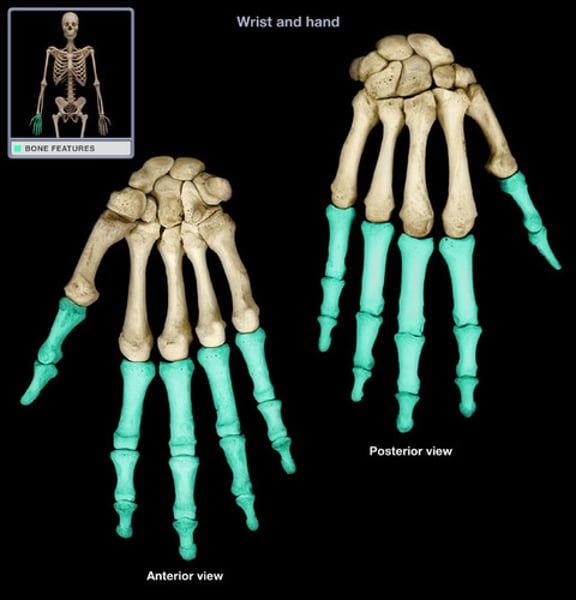
Phalanges
-manipulation of objects
- 3 per finger, thumb has 2
- interphalangeal joints
Pelvic Girdle functions and bones
- sacrum, 2 coxal bones
- stable base, attaches lower limbs to axial skeleton, strongest ligaments
- transmits weight and supports
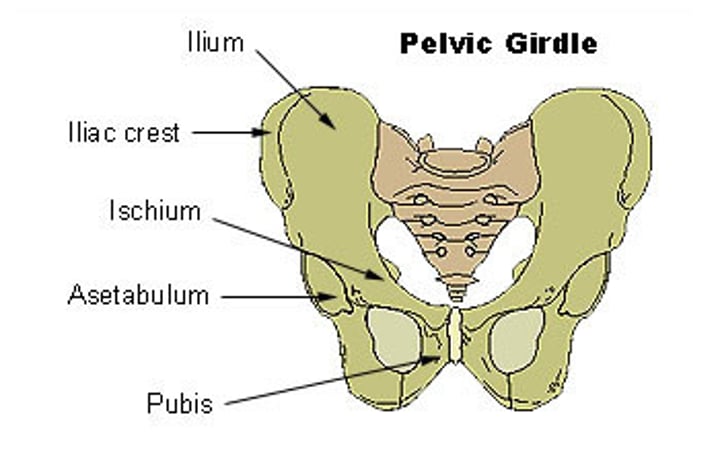
what is the acetabulum?
Hip socket, where femur articulates with pelvis
what makes up the coxal bones?
- 3 bones fused together
- ilium, ishium, and pubis
- includes sacruiliac joint(SI joint)
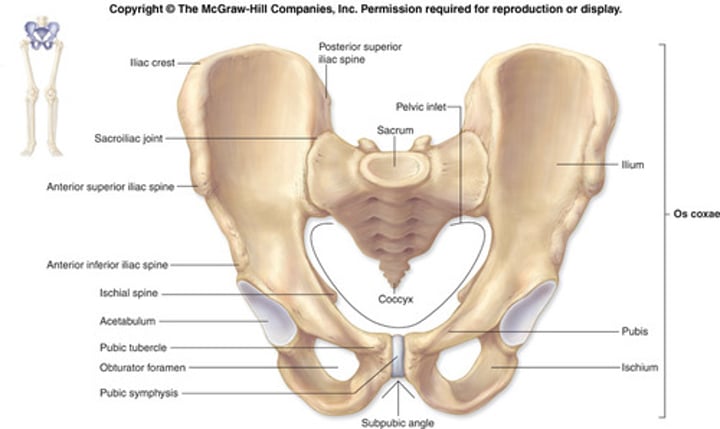
Ilium
largest, uppermost bone
Ishium
- strongest, lowermost
- includes ishial tuberosity which you sit on
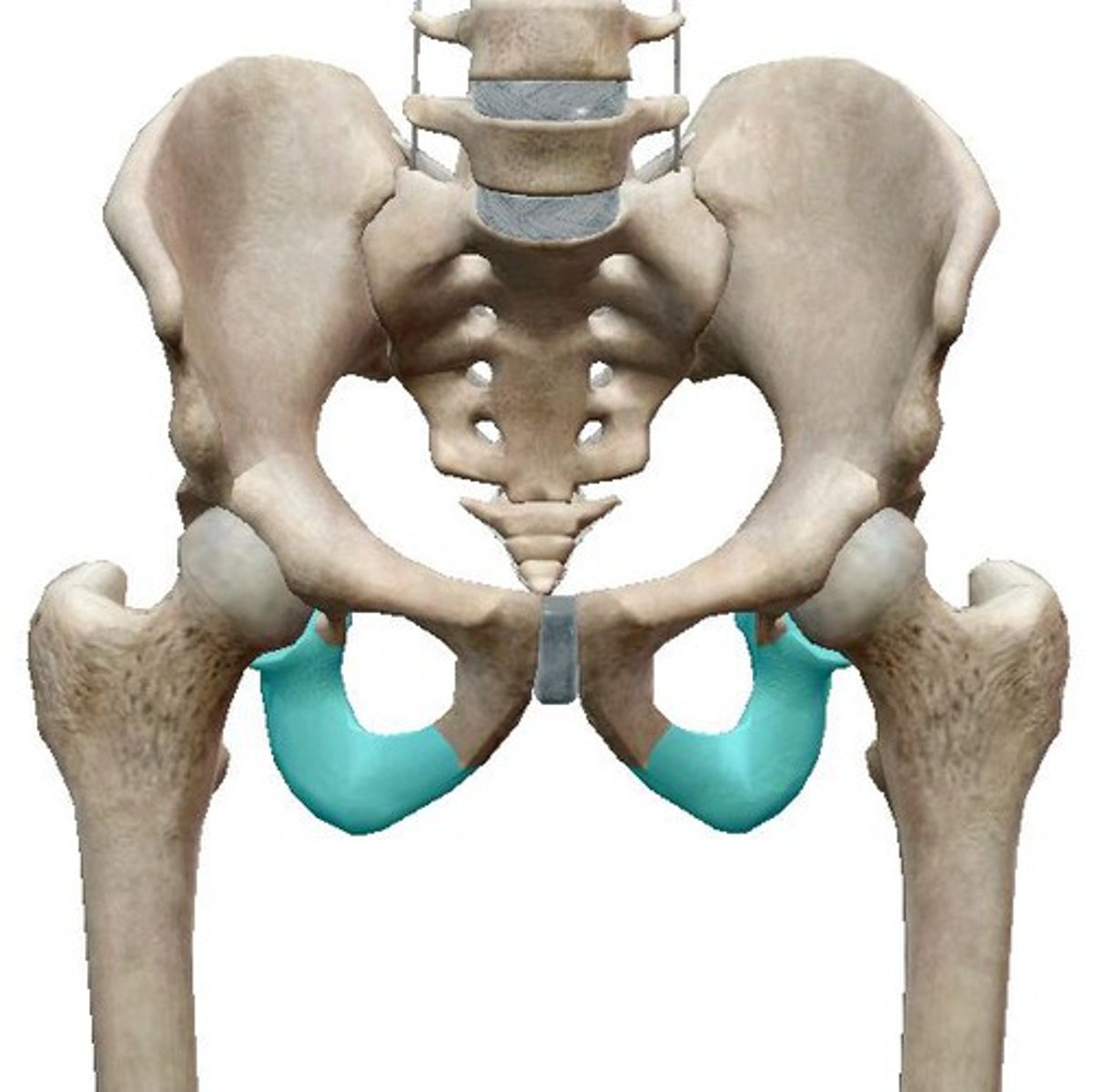
Pubis + SI joint
anterior most, SI joint joins sacrum
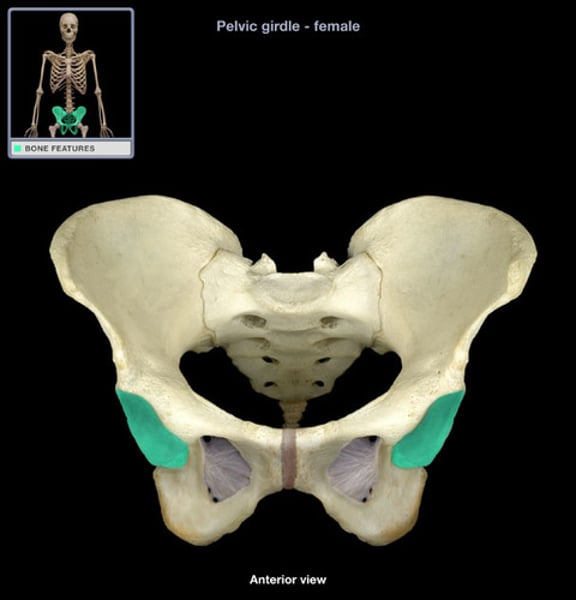
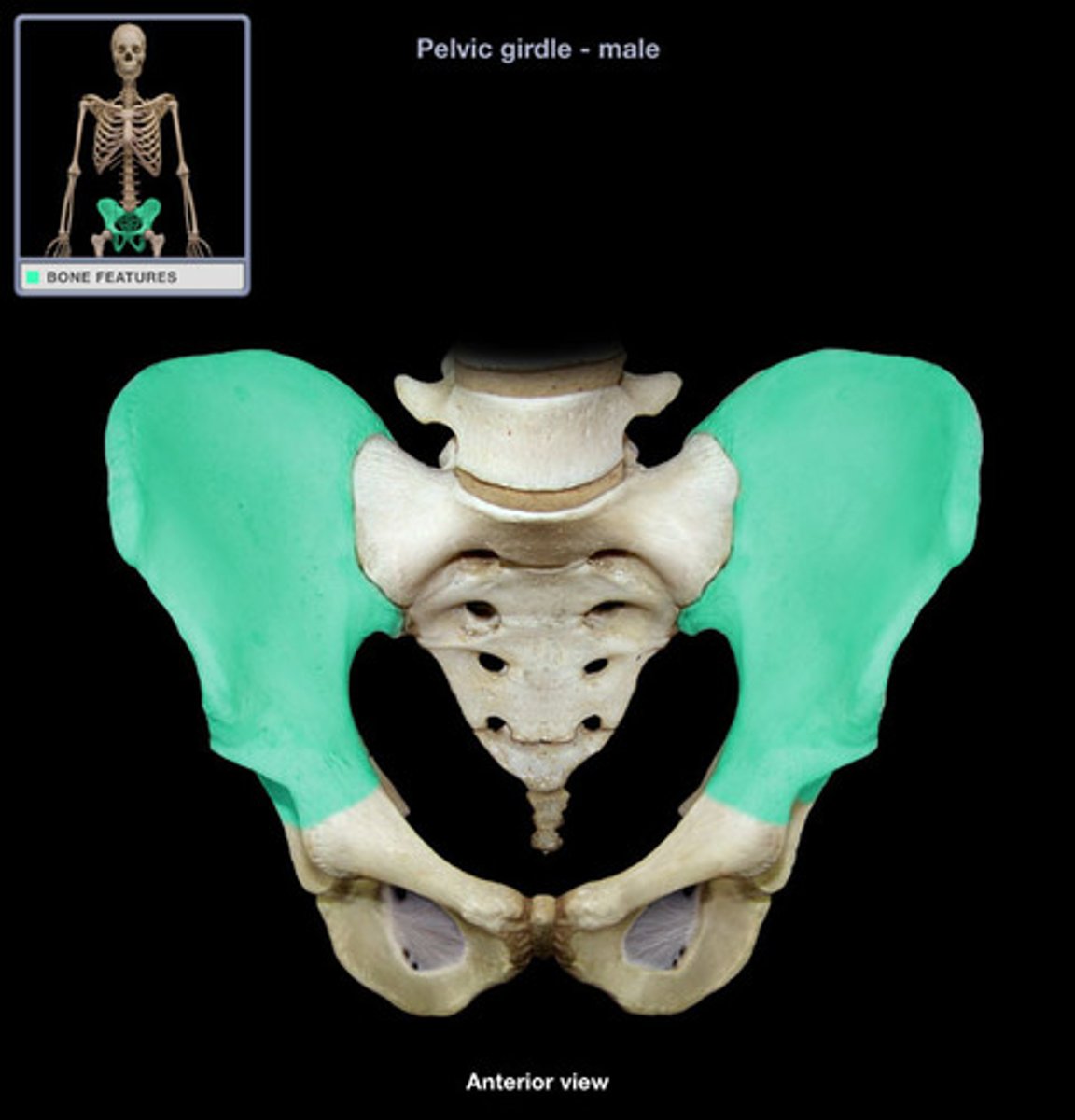
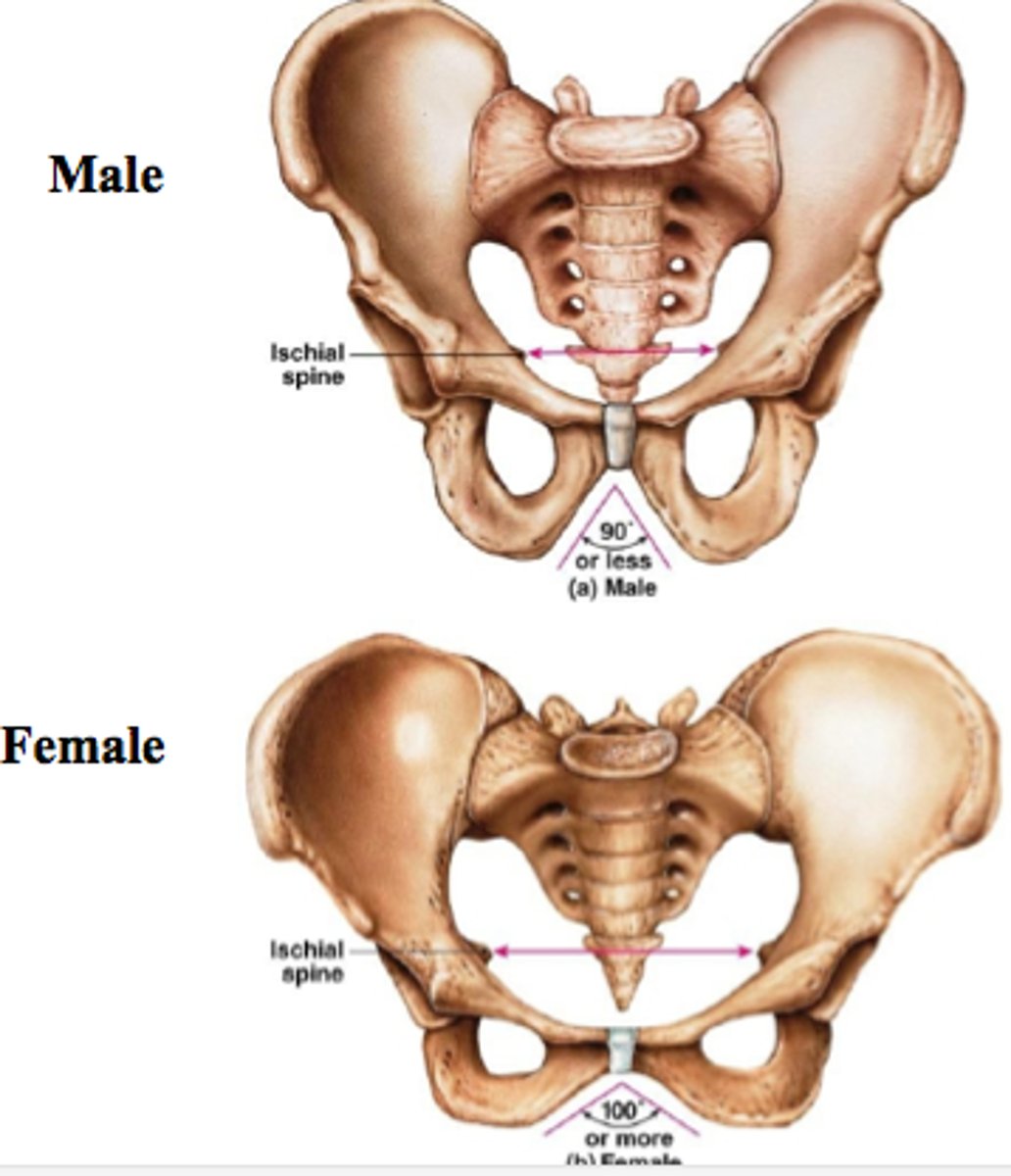
Differences between male and female pelvic girdles
Female: shallow, more broad with flaring, wider pubic arch
male: larger and heavier, deep, funnelshaped, narrow pubic arch
Hip Joint characteristics
- the femoral head fits into acetabulum
- femoracetabular joint
- more stable due to. shape of head, has joint capsule and ligaments
- acetabular labrum: fibrocartilage lining of cavity
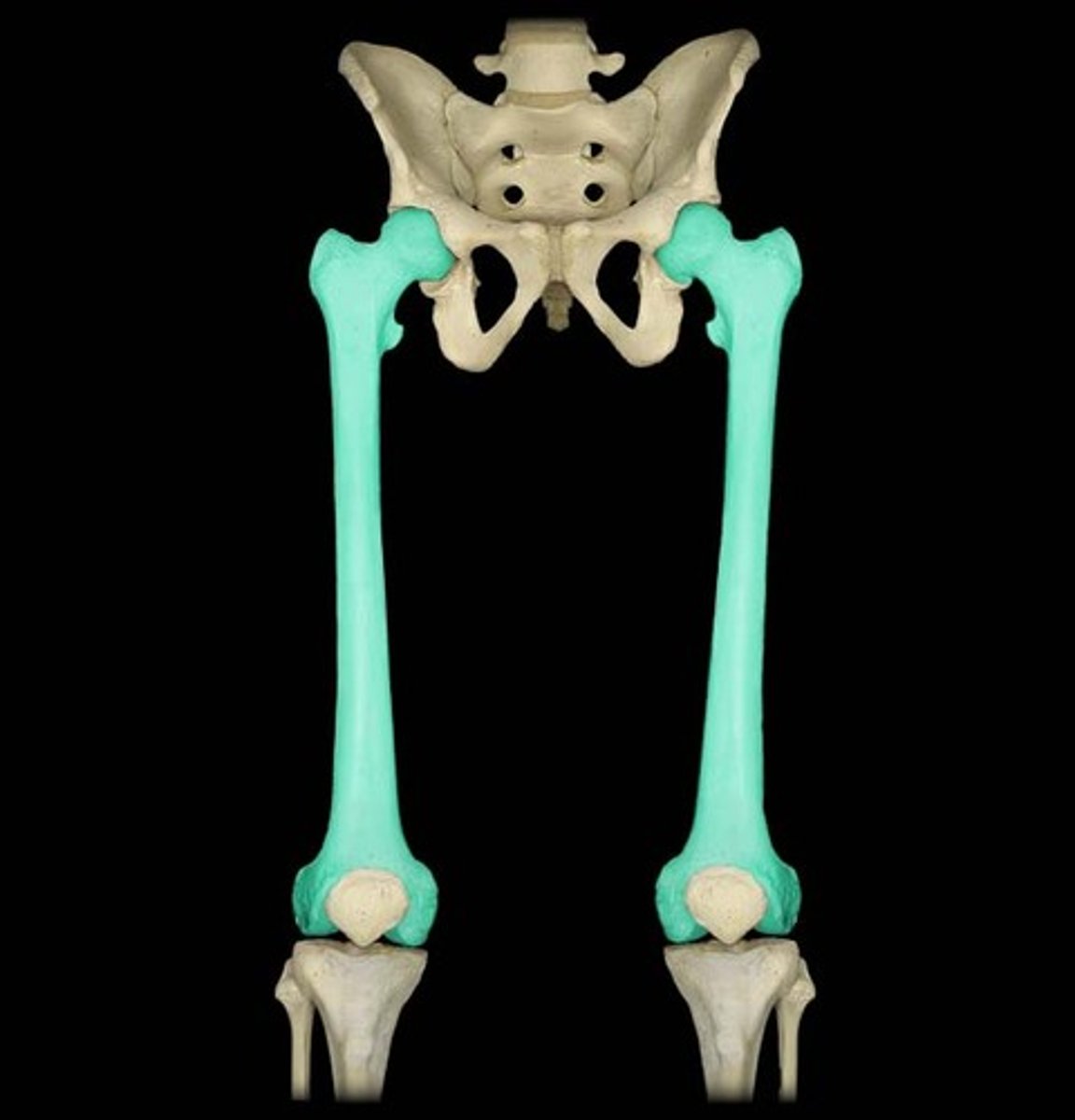
Articulation and location: Femur
Landmarks: femoral head and neck
- Femoracetabular joint(hip joint, proximal)
- tibiofemoral and patella femoral joint(distal)
Articulation and location: Patella
- sesamoid bone, acts as pulley for quad
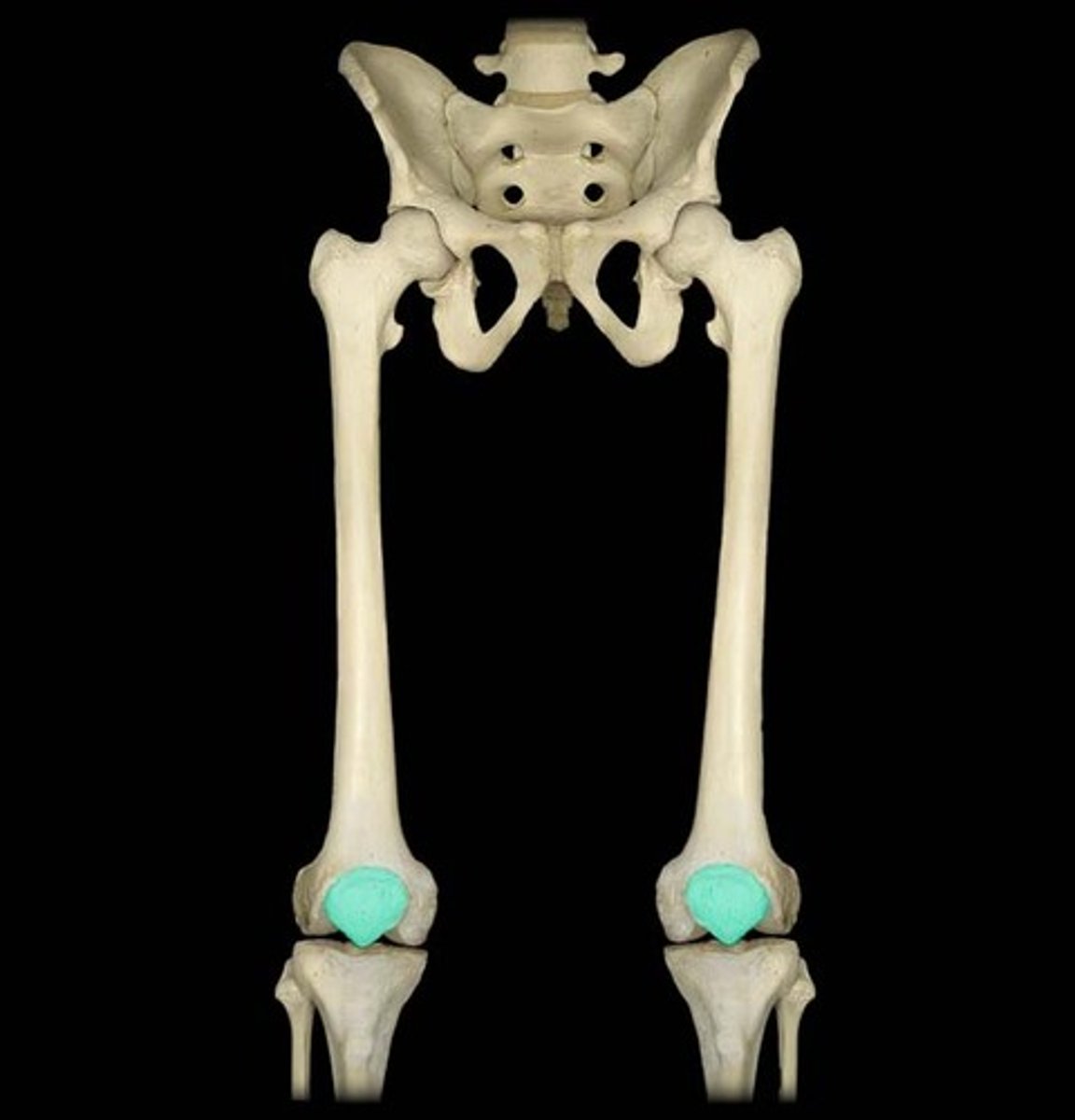
Tibiofemoral joint characteristics
- largest and one of most complex
- joint capsule, cartilage, ligaments, tendons
- allows for flexion and extension, internal and external rotation, main weight bearer
Articulation and location: TIbia
- more medial, larger and stronger
- tibiofemoral joint and proximal tibiofibular joint(similar to ulna nad radius)
- distal tibiofibular joint and tibiotalar joint(with talas bone in foot)
- medial malleolus(bump on ankle)
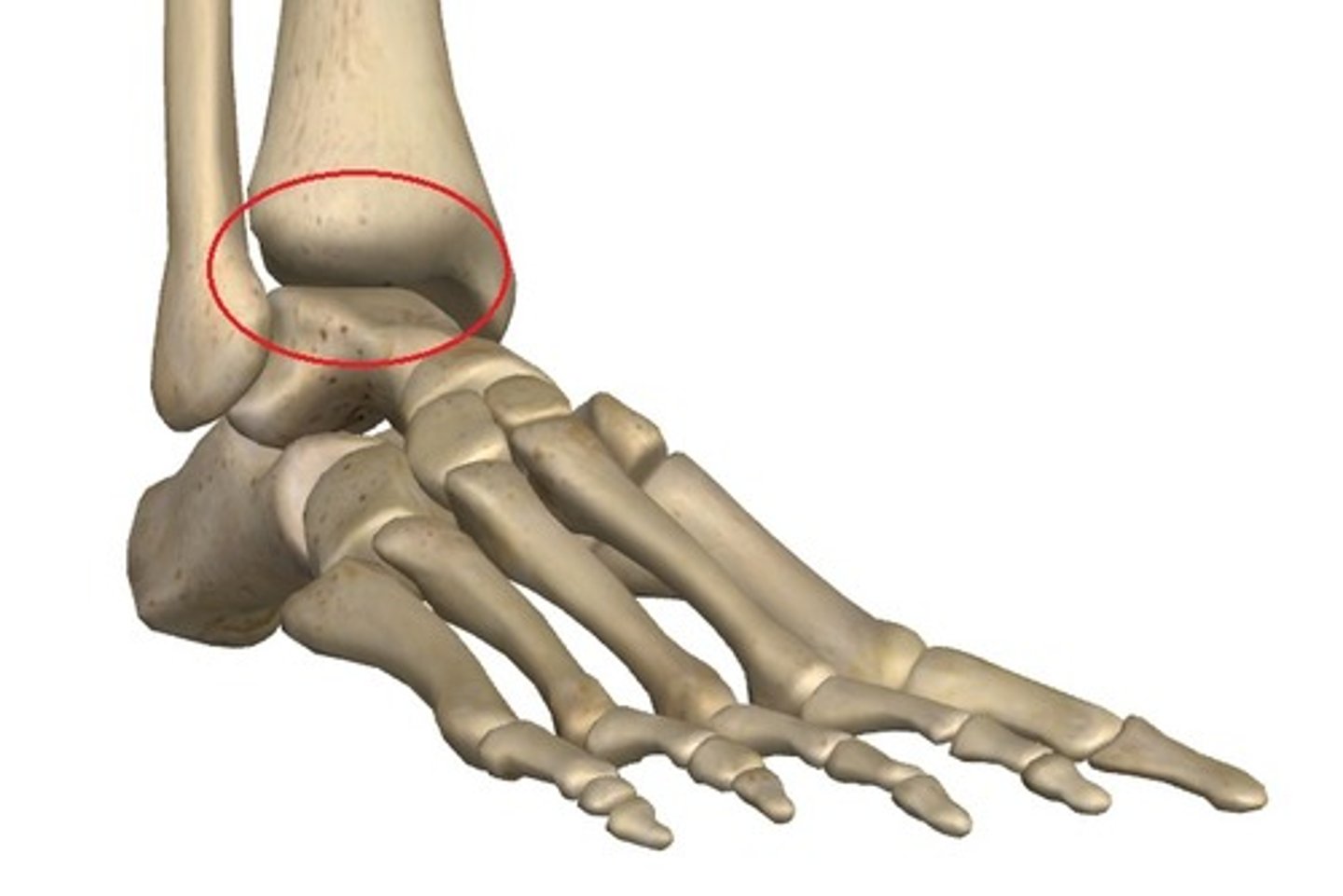
Ankle joint name
tibiotalar joint
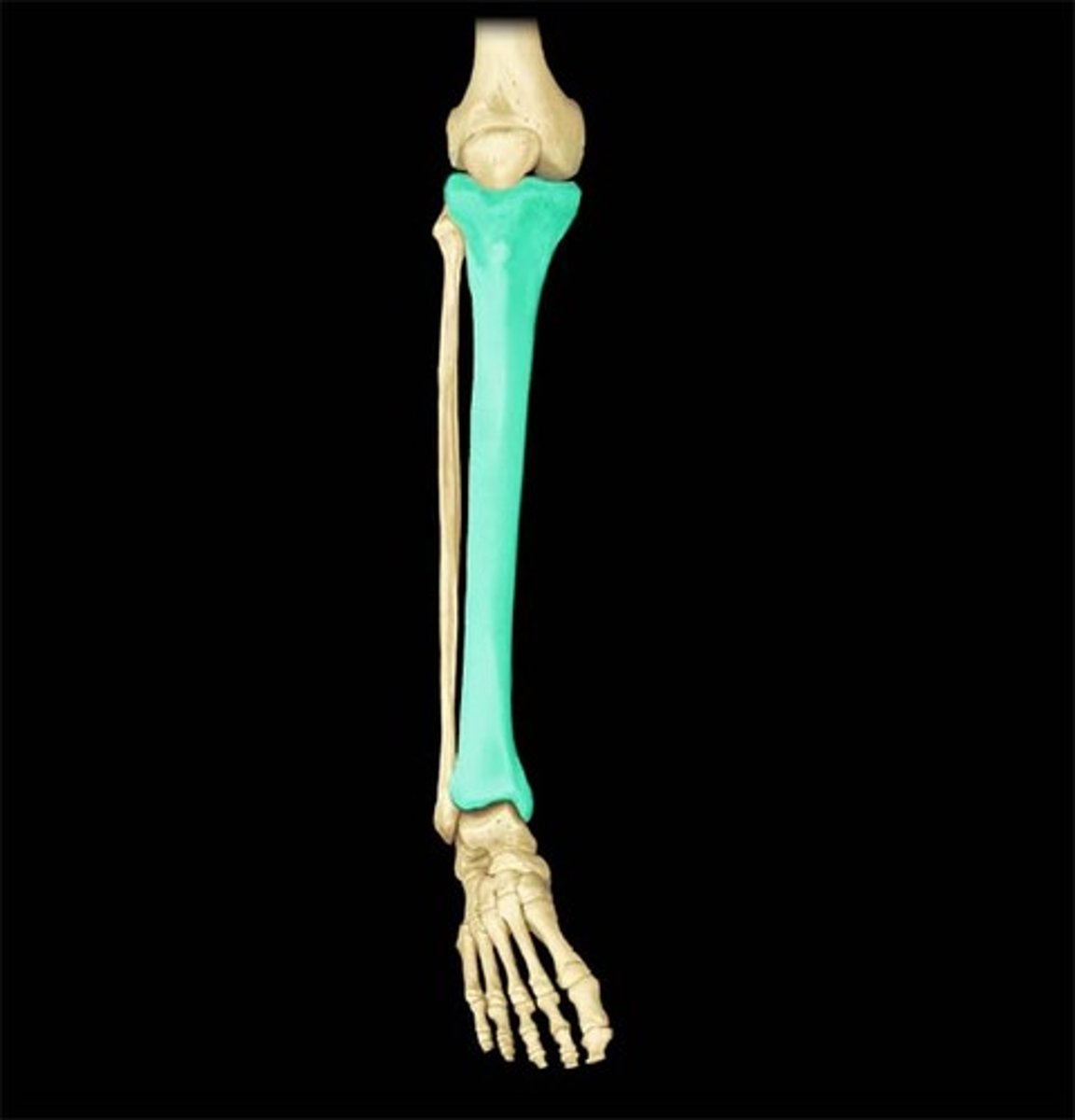
Articulation and location: Fibula
- smaller, lateral, deep, stabilizes ankle joint
- tibiofular distal and proximal
- fibulotalar joint
- Lateral malleolus(bump on ankle)
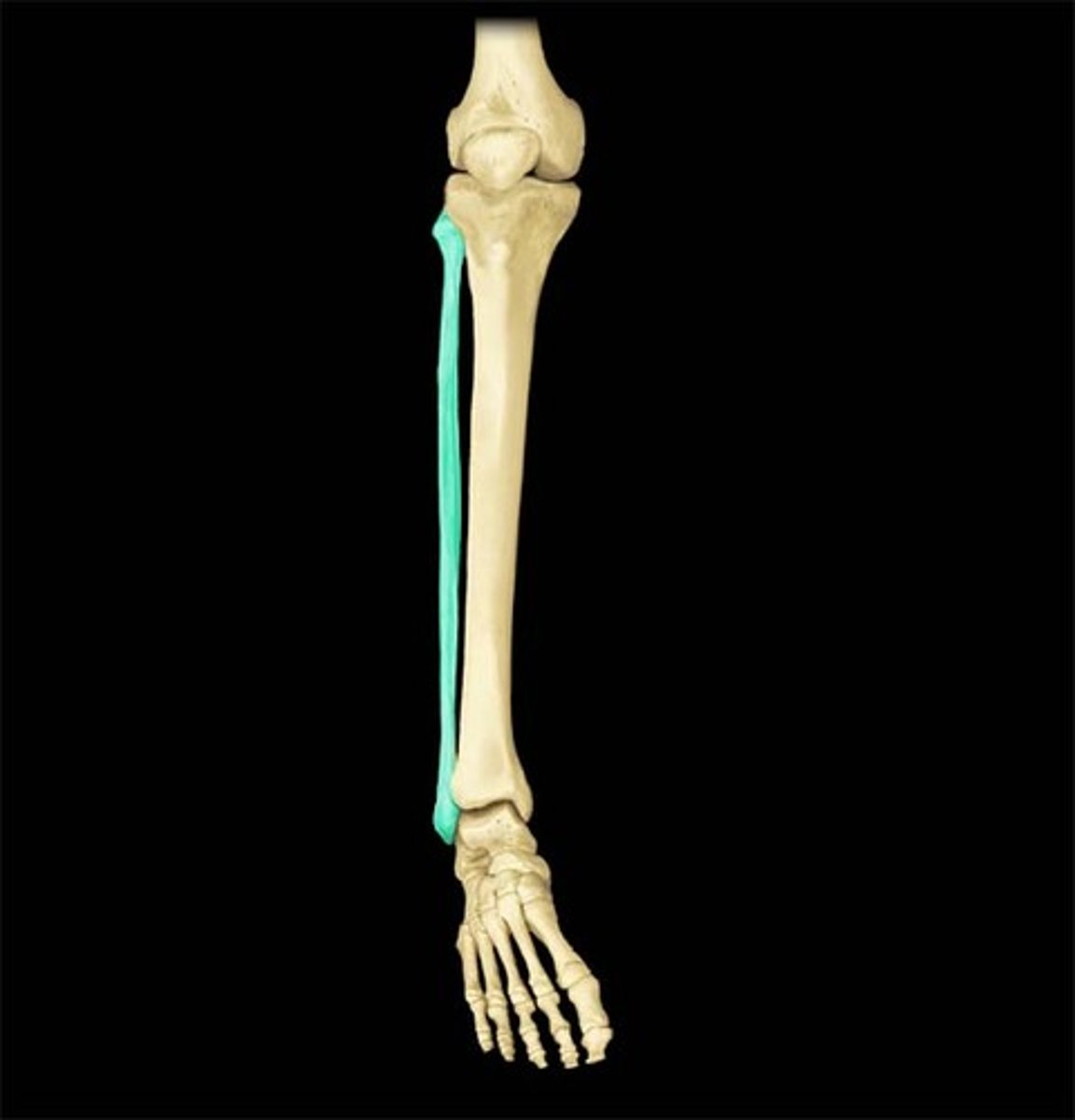
Tarsals (ankle)
- 7 bones bound by ligaments
- 2 main ones
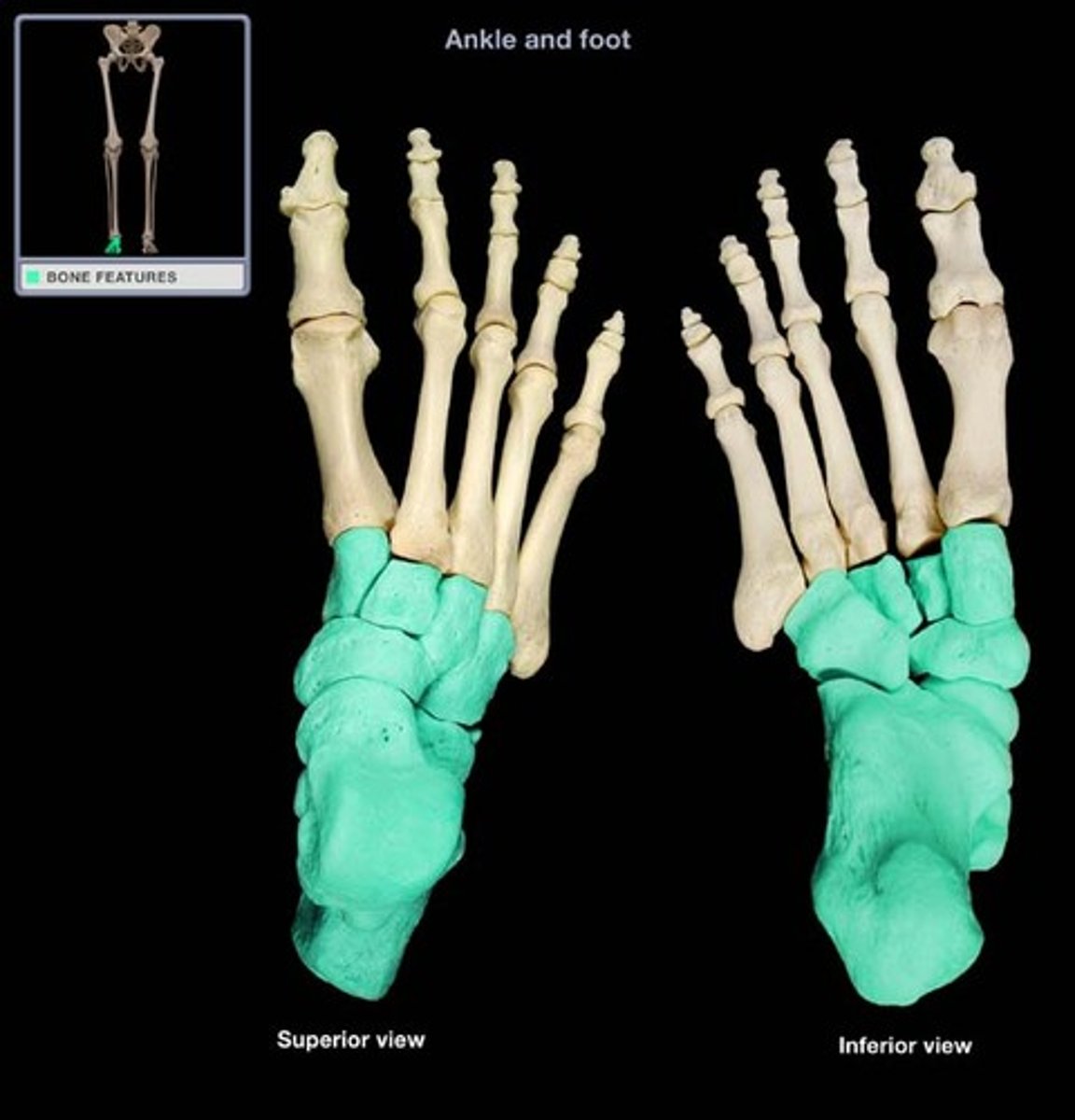
talus
articulates with tibia and fibula to form ankle joint
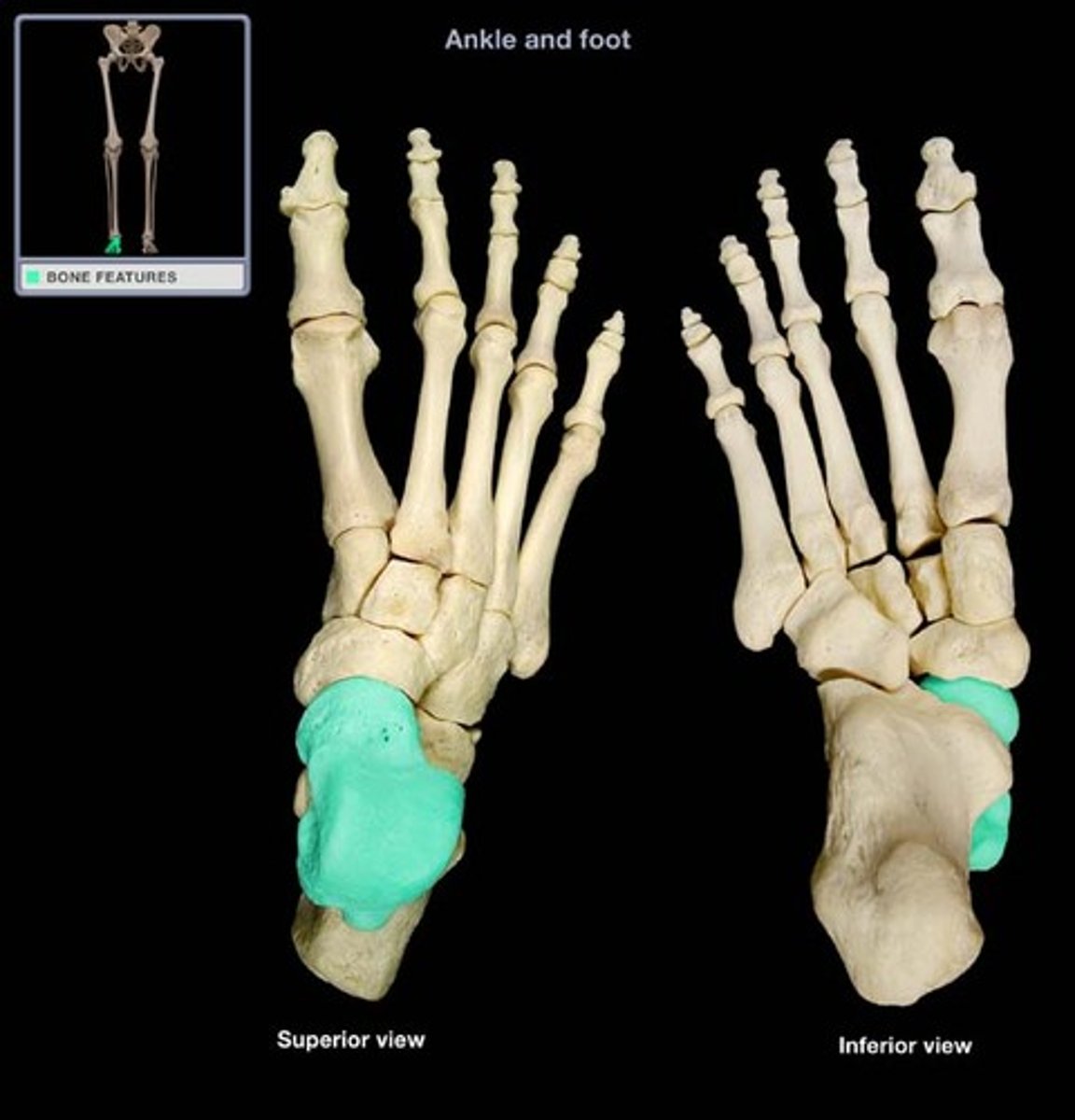
calcaneus
heel bone, largest and strongest tarsal
metatarsals
first one is thicker due to more weight, similar to metacarpals
phalanges(toes)
flexion and extension, 2 per toe