Introduction to Signal Transduction in Cell Communication and Developmental Biology
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What is signal transduction?
The process by which a cell converts an external signal into a functional response.
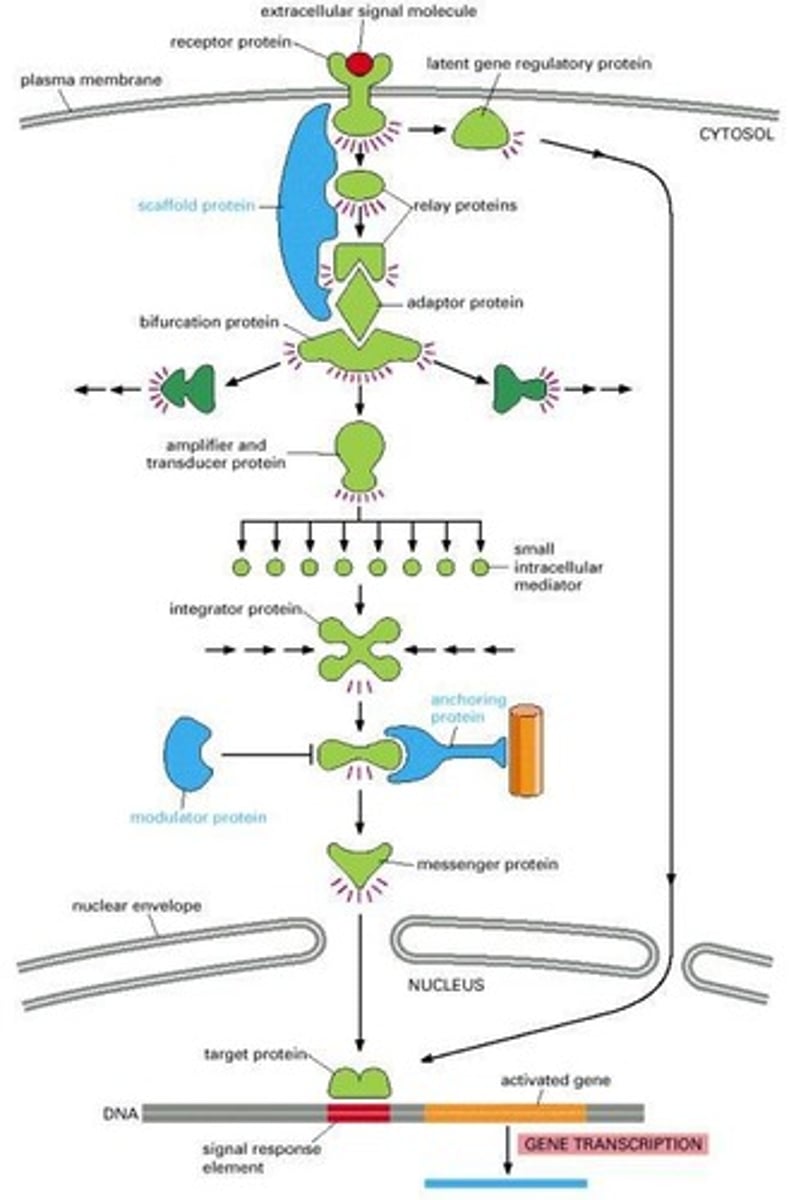
What are the key components of signal transduction?
Receptors, ligands, and second messengers.
What role do receptors play in signal transduction?
They bind to signaling molecules (ligands) and trigger a conformational change that initiates the signaling pathway.
What are ligands in the context of signal transduction?
Signaling molecules such as hormones or neurotransmitters that bind to receptors.
What are second messengers?
Small molecules that propagate the signal inside the cell, like cyclic AMP (cAMP) and calcium ions (Ca²⁺).
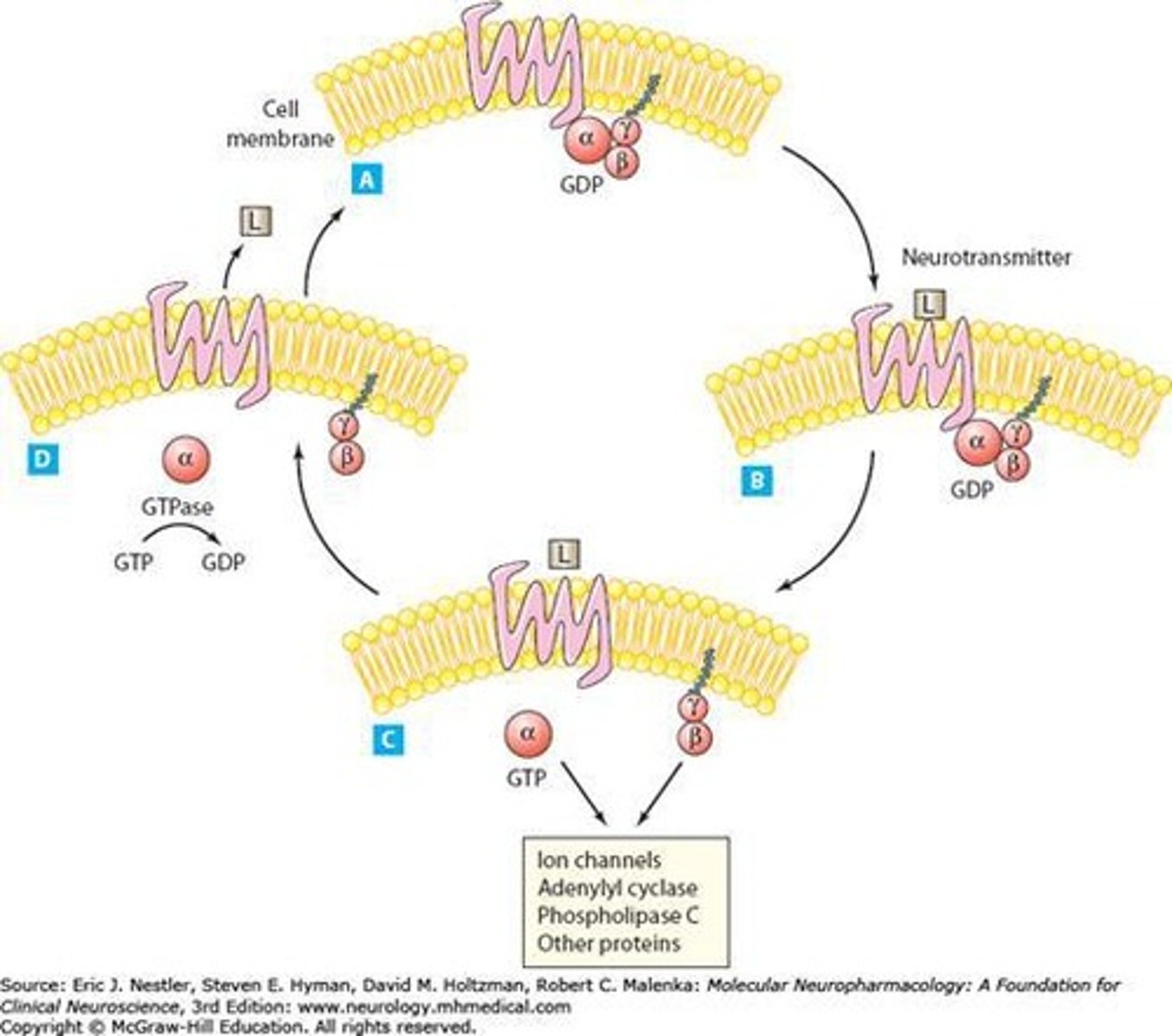
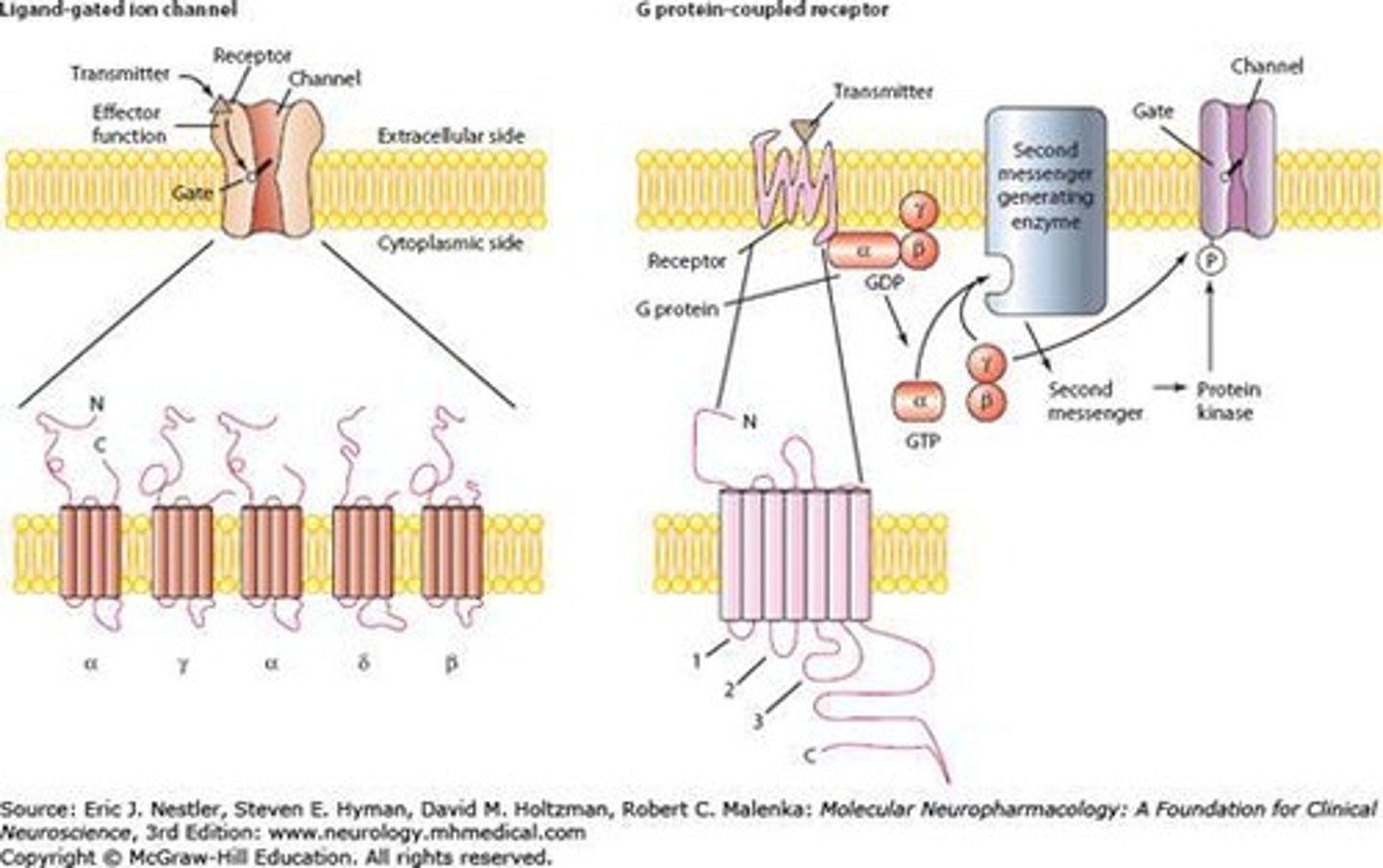
What are G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCRs)?
Receptors that activate G-proteins, leading to cellular responses.
What is the function of Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs)?
They phosphorylate tyrosine residues on themselves and other proteins, triggering downstream signaling events.
What do ion channel receptors do?
They open or close ion channels in response to ligand binding, altering the cell's membrane potential.
What are the three main steps in signal transduction?
Reception, transduction, and response.
What occurs during the reception step of signal transduction?
The ligand binds to the receptor.
What happens during the transduction step?
The receptor undergoes a conformational change, activating intracellular signaling molecules.
What is the outcome of the response step in signal transduction?
The signal is relayed to cellular machinery, resulting in specific responses like gene expression or metabolism changes.
What are the characteristics of signal transduction?
Specificity, locality, selectivity, amplification, and outcomes.
What types of molecules can signal in signal transduction?
Ions, metabolites, peptides, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, organelles, and vesicles.
What is the role of G-proteins in signal transduction?
They diversify signals and responses in the nervous system.
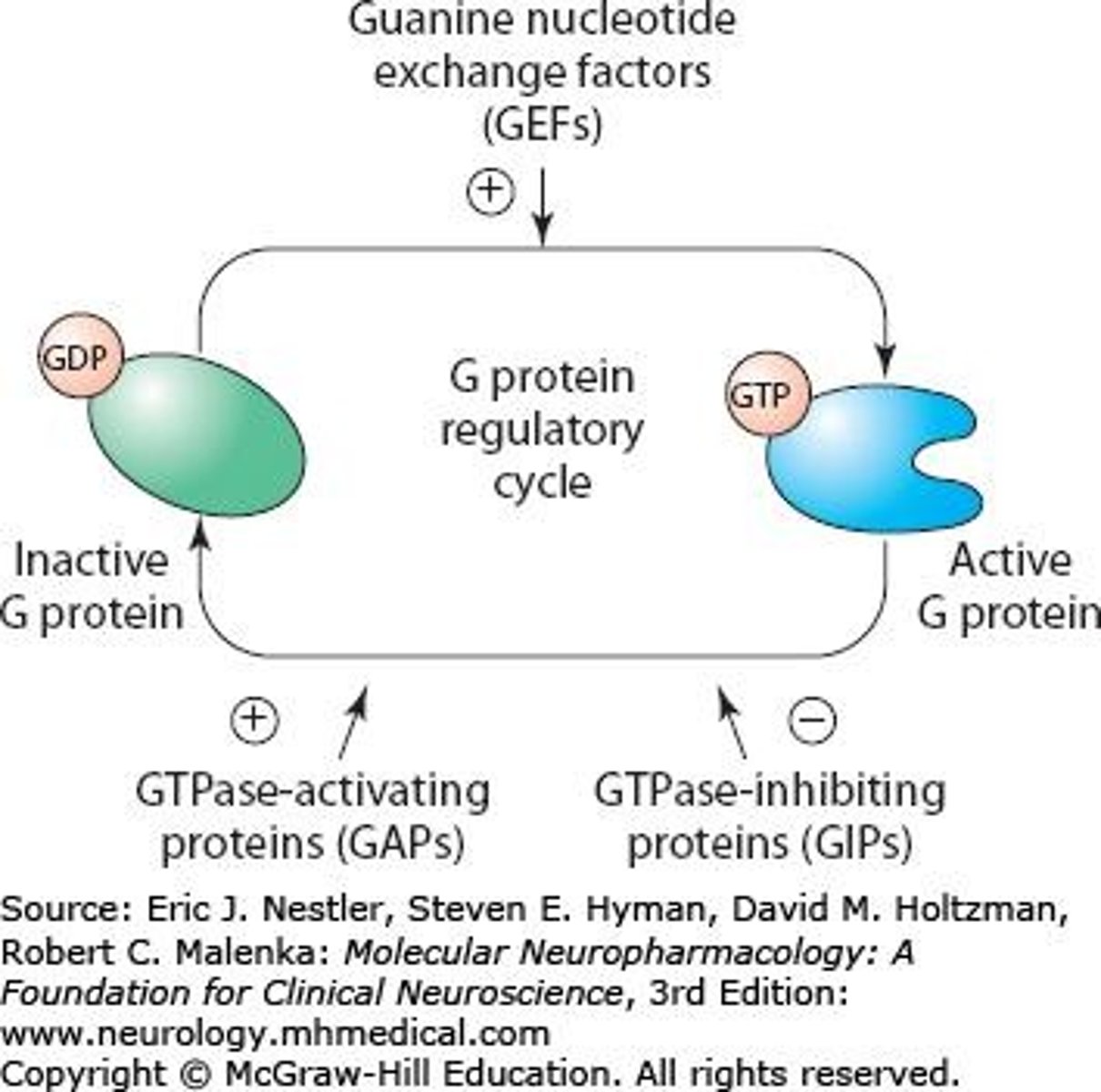
How do structural changes in receptors affect signal transduction?
They influence the outcomes of signal transduction.
What determines the signaling magnitude and duration?
The concentration of active proteins available to signal.
What is the significance of protein-protein interactions in signal transduction?
They are critical to achieving specific biological outcomes.
What is the importance of the turnover rate in signal transduction?
It determines the promptness of the response to extracellular signals.
What is the role of lipids in signal transduction?
They act as crucial modulators of the signaling process.
What is the difference between canonical and non-canonical Wnt signaling?
Canonical Wnt signaling involves β-catenin, while non-canonical pathways do not rely on β-catenin and can activate different cellular responses.