NPB: Brain Stem Control of Motor Movements
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Where does the input come from?
Sesnory receptors
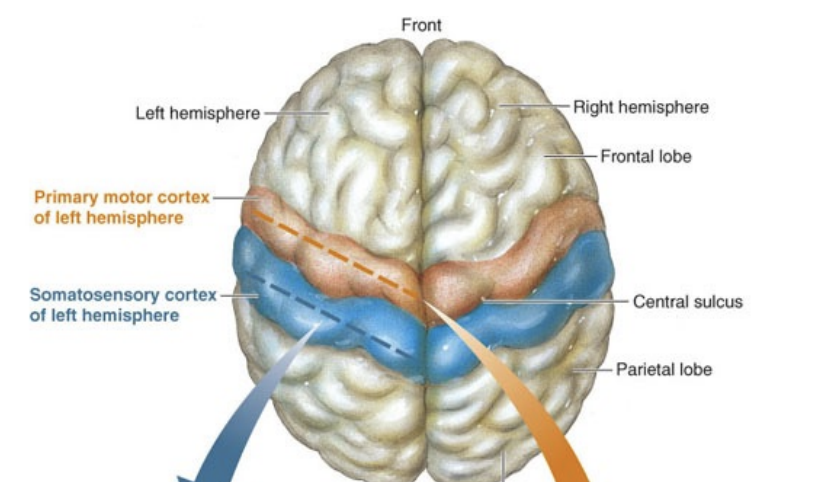
What is the primary function of the primary motor cortex?
Initiating voluntary motor movements
What body map is found in the primary motor cortex?
motor homunculus
What is the primary function of the somatosensory cortex?
Processing touch, pressure, pain, and proprioception
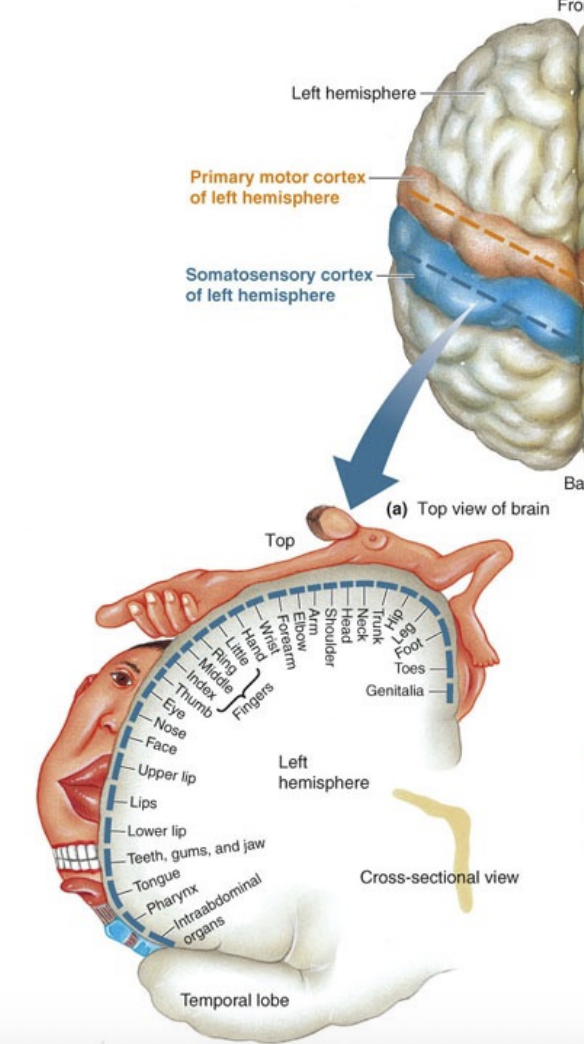
What happens when a highly sensitive area like the lips is stimulated?
It activates a large area in the somatosensory cortex
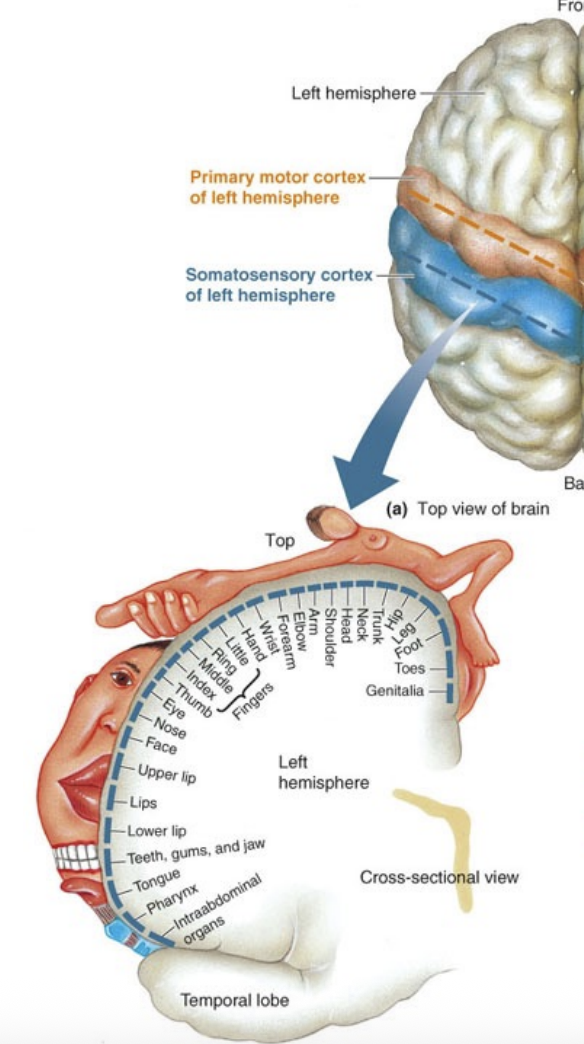
The somatosensory cortex allows you to know where you are being _______.
touched
What is the main function of the prefrontal cortex?
Decision-making
impulse control
planning
personality
What can happen if the prefrontal cortex is damaged (e.g., by a head injury)?
Poor judgment
Risky behavior
Personality changes
Loss of impulse control
Brain Stem is important for ___
posture
The brainstem can receive input from ___ system
vestibular
The brainstem sends projection to the ___ which influence ___(lower/higher) motor neuron
spinal cord, lower
T/F: Eye movements can be controlled by signals coming from the vestibular system.
True, the vestibular system sends info about head position/motion to coordinate eye muscle movements, helping maintain stable gaze
T/F: Fixation movements of the eyes are made possible by input from the vestibular system.
True, vestibular system detects head movement
Which two types of input does the brainstem integrate to help control movement and gaze?
A) Visual and auditory
B) Visual and vestibular
C) Vestibular and olfactory
D) Motor and tactile
B) Visual and vestibular
What is the primary role of the cerebrum in motor control?
A) Maintaining posture and balance
B) Sending reflex signals to the spinal cord
C) Planning and initiating voluntary movements
D) Coordinating eye movements during head turns
C) Planning and initiating voluntary movements
What does “cortical input” refer to in the context of motor control?
A) Sensory signals from the spinal cord
B) Reflexive responses from the brainstem
C) Motor planning signals from the cerebral cortex
D) Muscle tension feedback from the Golgi tendon organ
C) Motor planning signals from the cerebral cortex
The basal ganglia process information from the cerebral cortex, thalamus, and brainstem, then send information back to the __________ via the __________.
cerebral cortex, thalamus
T/F: The basal ganglia send information directly to the spinal cord to control movement.
False, basal ganglia sends the information indirectly to the spinal cord from the cerebral cortex via the thalamus
What is one of the key roles of the basal ganglia in motor control?
A) Generating reflex responses
B) Directly stimulating all motor pathways
C) Suppressing unnecessary motor contractions
D) Controlling heart rate and blood pressure
C) Suppressing unnecessary motor contractions
The basal ganglia help movement by suppressing __________ motor contractions and allowing __________ motor activities.
unwanted, desired
Which brain structure is primarily involved in storing motor learning and fine-tuning movements?
A) Cerebrum
B) Brainstem
C) Basal ganglia
D) Cerebellum
D) Cerebellum
Which of the following is NOT a role of the cerebellum?
A) Motor learning
B) Integrating vestibular input
C) Suppressing unwanted movements
D) Correcting unanticipated movements
C) Suppressing unwanted movements; because this is the basal ganglia’s role
The cerebellum receives sensory input from the cortex, brain stem, and __________.
spinal cord
T/F: The cerebellum helps fine-tune movements by adjusting activity in response to unanticipated changes.
True, It actively modifies motor output during motion to keep movements accurate.
What is a likely effect of cerebellum damage?
A) Increased reflexes
B) Enhanced memory formation
C) Loss of fine motor coordination
D) Faster reaction time
C) Loss of fine motor coordination
T/F: Damage to the cerebellum can lead to poor balance and uncoordinated movements.
True, it can lead to shaky unwanted/uncoordianted movement
Which area is highly represented in the primary motor cortex due to the need for fine movement control?
A) Knee
B) Thumb
C) Hip
D) Elbow
B) Thumb
T/F: The tongue has a large representation in the somatosensory cortex because of its sensitivity.
True, because we use our tongue for speech, moving and feeling things in our mouth, and for taste.
The __________ is a body part with fine touch discrimination, requiring a large area in the somatosensory cortex.
Thumb
Which two body parts are strongly represented in both the primary motor cortex and the somatosensory cortex due to their roles in fine motor control and detailed sensory input?
A. Elbow and Knee
B. Tongue and Thumb
C. Toes and Back
D. Jaw and Shoulde
B. Tongue and Thumb
Which of the following areas are classified as motor association (associative) cortices that plan movement before it is executed?
A) Primary motor cortex and somatosensory cortex
B) Cerebellum and thalamus
C) Premotor cortex and supplementary motor area
D) Occipital lobe and basal ganglia
C) Premotor cortex and supplementary motor area
T/F: The supplementary motor area and premotor cortex send planning input to the primary motor cortex.
True
After repeated head injuries in contact sports like soccer, a person begins making poor decisions and showing impulsive behavior. Which brain region was most likely affected?
A) Primary motor cortex
B) Cerebellum
C) Prefrontal cortex
D) Somatosensory cortex
C) Prefrontal cortex
What neuron type directly controls voluntary muscle contraction?
alpha motor neuron
Does the cerebellum directly control the alpha motor neuron?
No, because the alpha motor neuron is the one telling your muscles to contract and the cerebellum coordinate movement, but does not directly tell muscles what to do → cerebellum sends info → brainstem/motor cortex → alpha motor neuron
What type of neuron originates in the primary motor cortex and connects to lower motor neurons?
A. Sensory neurons
B. Interneurons
C. Upper motor neurons (UMNs)
D. Autonomic neurons
C. Upper motor neurons (UMNs)
Where do upper motor neurons synapse?
A. In the thalamus
B. In skeletal muscles directly
C. On lower motor neurons in the spinal cord
D. In the cerebellum
C. On lower motor neurons in the spinal cord
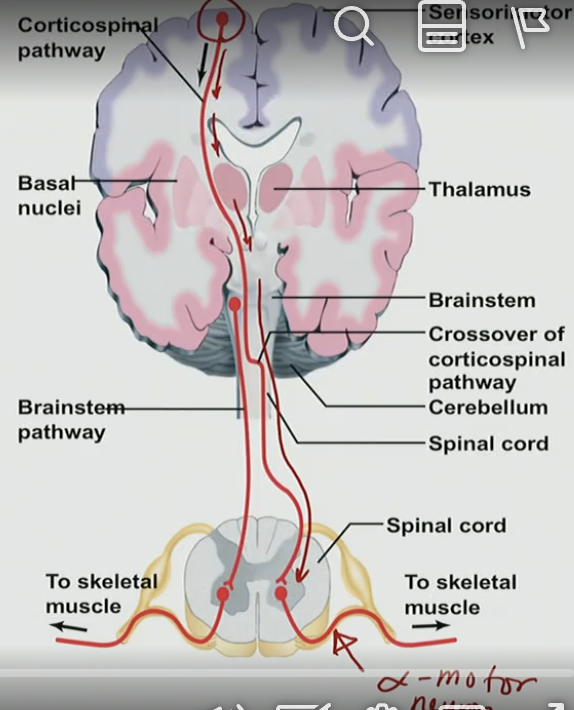
What is the main function of the corticospinal tract?
A. Transmit motor commands from the cortex to the spinal cord
B. Send sensory information to the brain
C. Regulate breathing
D. Control vision
A. Transmit motor commands from the cortex to the spinal cord
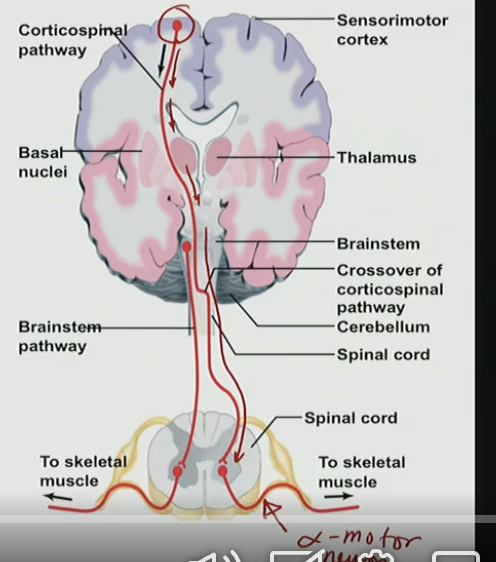
90% of corticospinal tracts cross over at which location?
A. Thalamus
B. Spinal cord
C. Cerebellum
D. Medulla
D. Medulla
Which muscles are controlled by the lateral corticospinal tract?
A. Trunk muscles
B. Limb muscles
C. Abdominal muscles
D. Eye muscles
B. Limb muscles
What percent of corticospinal tracts cross over at the spinal cord instead of the medulla?
A. 10%
B. 50%
C. 90%
D. 0%
A. 10%
Which tract controls trunk muscles?
A. Corticobulbar tract
B. Anterior corticospinal tract
C. Spinocerebellar tract
D. Lateral corticospinal tract
B. Anterior corticospinal tract