4. pulpal and periapical pathology and inflammatory lesions of the jaw part 2
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
what is inflammation of bone, specifically extension of inflammation from/beyond periapical region to the marrow space, cortex, cancellus portion of bone and periosteum?
osteomyelitis
pyogenic organisms can reach bone marrow through what four mechanisms?
abscessed teeth
post-surgical infection
trauma ie untreated tooth fracture
hematogenous spread
what are some predisposing conditions of osteomyelitis?
malnutrition
diabetes
leukemia
anemia
alcoholism
HIV
diabetes w reduced bone vascularity
Pagets
florid osseous dysplasia
fluorosis
what are some relevant terms and synonyms of osteomyelitis?
acute osteomyelitis
acute suppurative osteomyelitis
acute pyogenic osteomyelitis
proliferative periostitis
periostitis ossificans
is osteomyelitis synonymous with Garre’s osteomyelitis?
NO
which osteomyelitis?
mandible, PM area
acute osteomyelitis
which osteomyelitis?
characteristic clinical features:
pain, swelling, redness, fever, purulent discharge, mobility in involved teeth
acute osteomyelitis
Dental sequelae
long-term or secondary dental problems that result from a previous dental disease or trauma
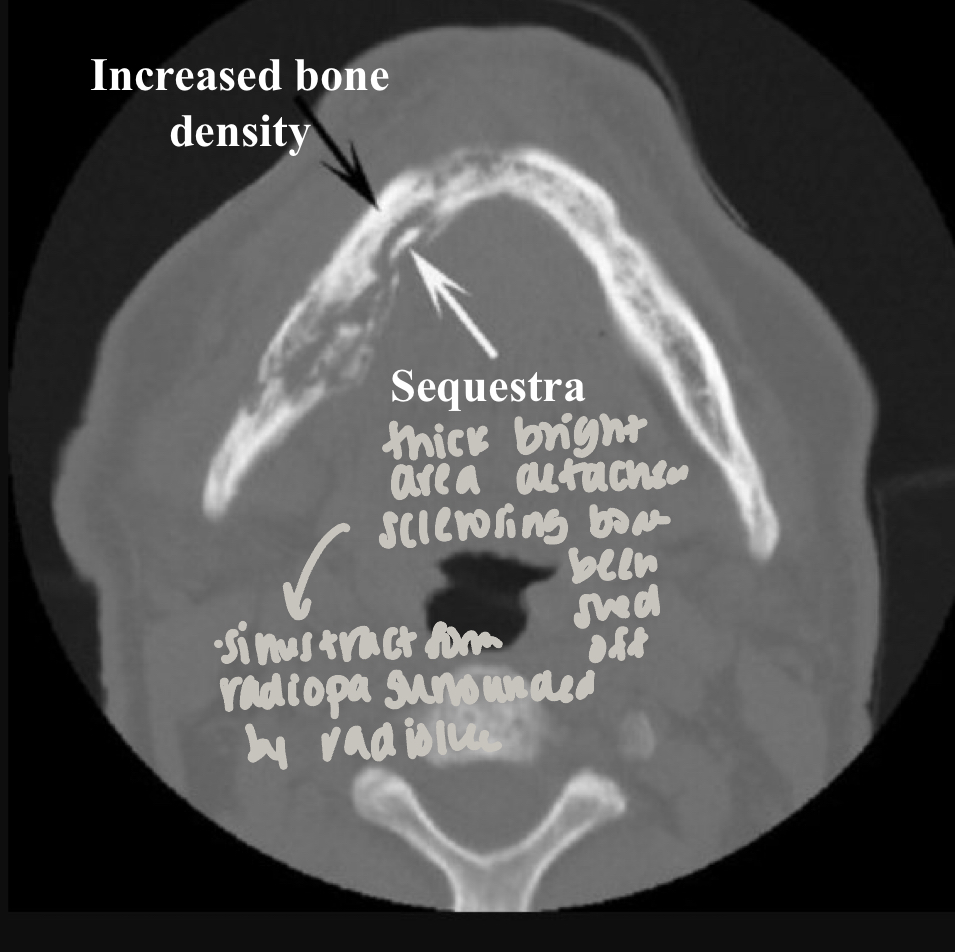
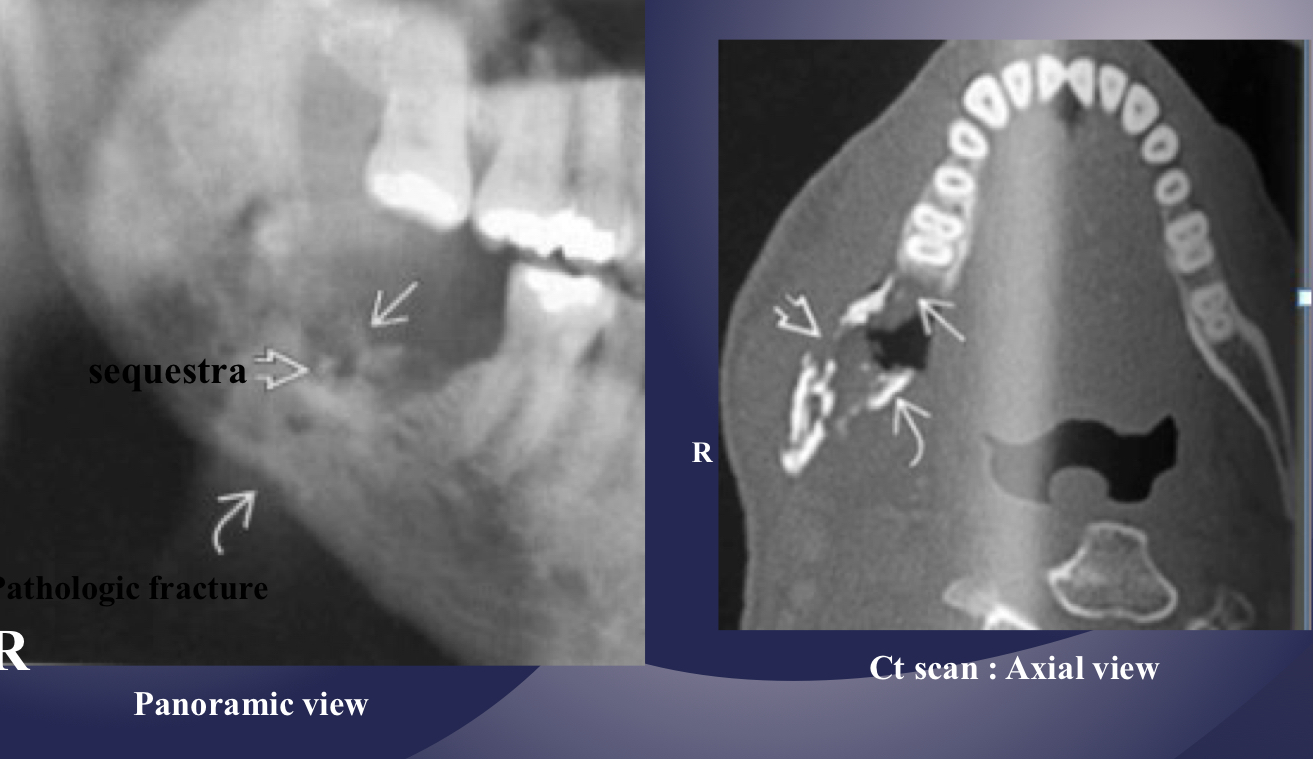
islands of necrotic bone, may vary in size
which osteomyelitis?
sequela of inadequately treated acute phase
may arise de novo
CRMO
SAPHO syndrome
clinical features: intermittent recurrent pain and swelling
chronic osteomyelitis
CRMO of chronic osteomyelitis
Chronic Recurrent Multifocal Osteomyelitis
also occurs in long bones of children, pain, swelling
SAPHO syndrome of chronic osteomyelitis
Synovitis (inflammatory arthritis), Acne (pustulosa), Pustulosis (psoriasis), Hyperostosis (acquired), Osteitis (osteomyelitis)
which osteomyelitis?
no radiographic features bc no manifestation in early stages; may vary in stage
acute osteomyelitis
which osteomyelitis phase?
periphery:
poorly defined
non-corticated
gradual transition to normal trabeculae
acute
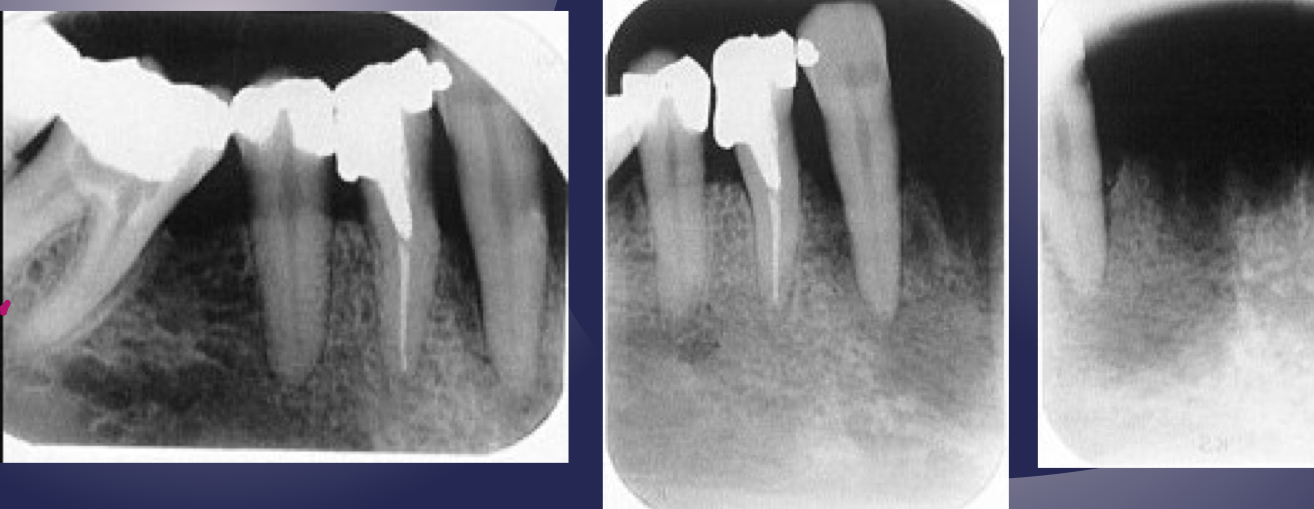
which osteomyelitis phase?
internal structure:
decrease in bone density, loss of sharpness of trabeculae
localized or scattered regions of radiolucency, ill defined periphery
mixed radiolucent-radiopaque areas
“moth-eaten”
irregular outline
help: mandibular trabeculae looks like lasagna but here more granular and indistinct
acute
moth bitten acute osteomyelitis
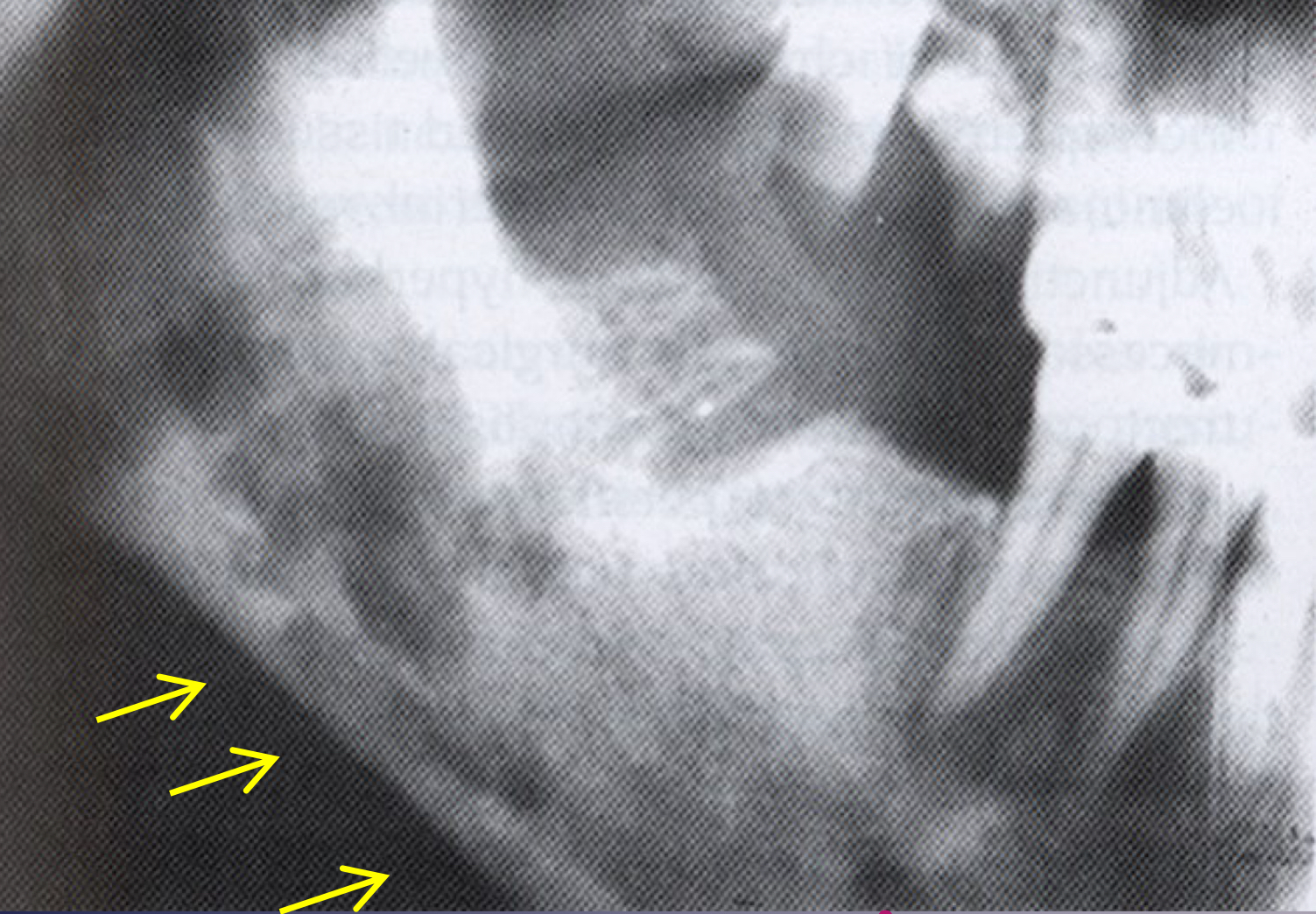
which osteomyelitis phase?
internal structure:
sequestration, sinus tract or fracture
acute
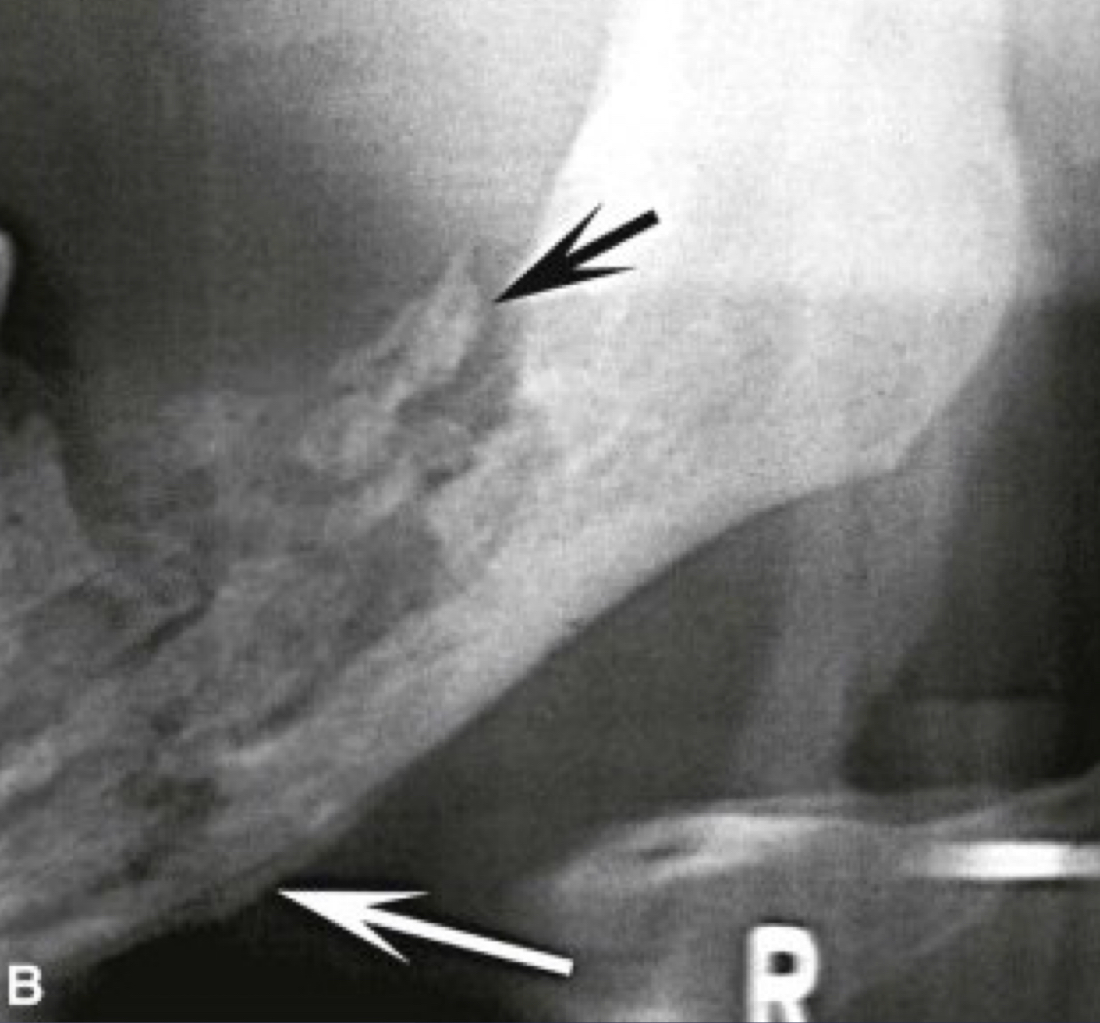
white and black arrow
which imaging is method of choice for seeing internal structure (sequestrea) of acute osteomyelitis?
CT/CBCT
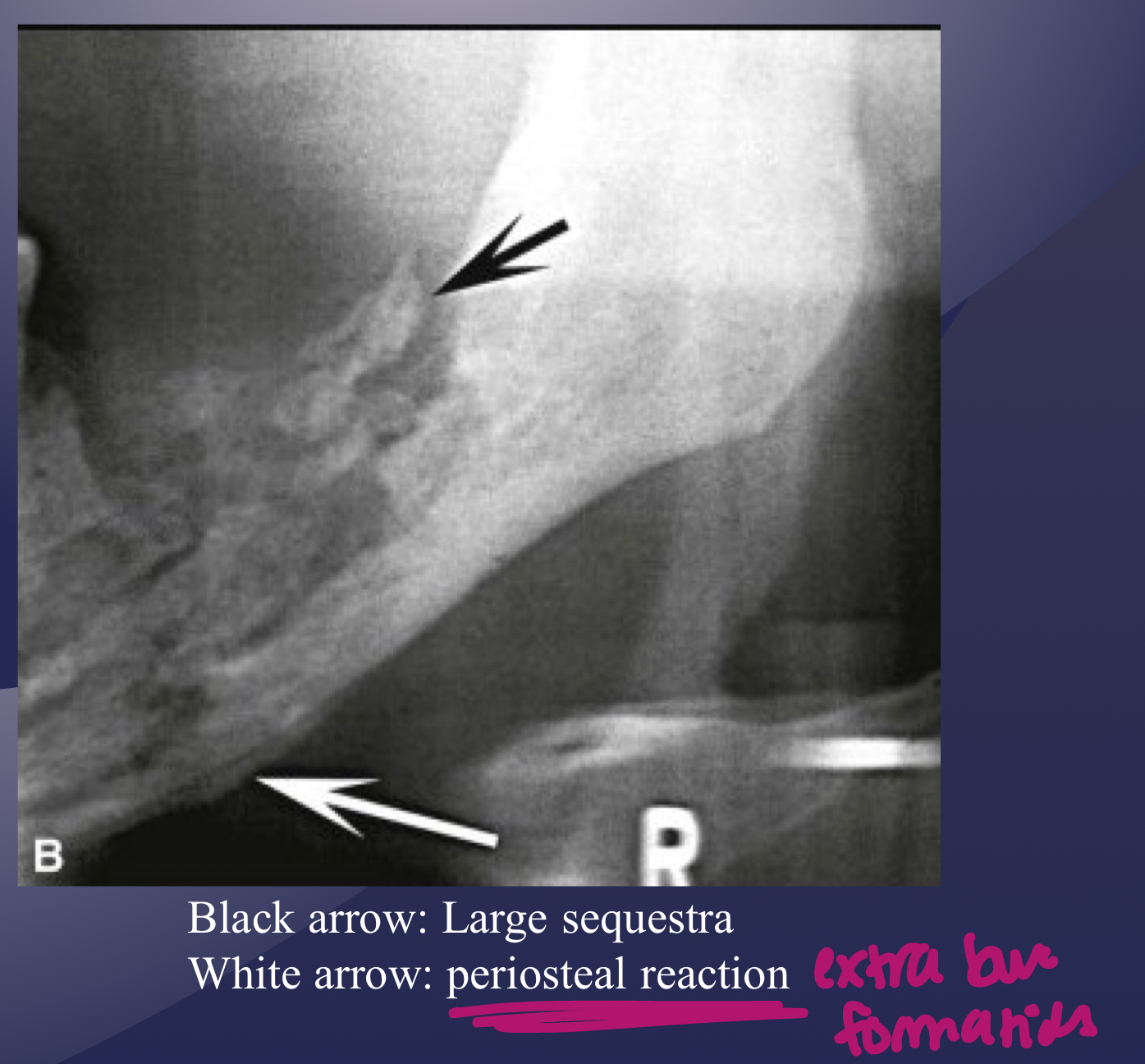
which osteomyelitis phase?
some effects on surrounding structures:
bone formation, periosteal stimulation = onion skin
bone resorption
acute
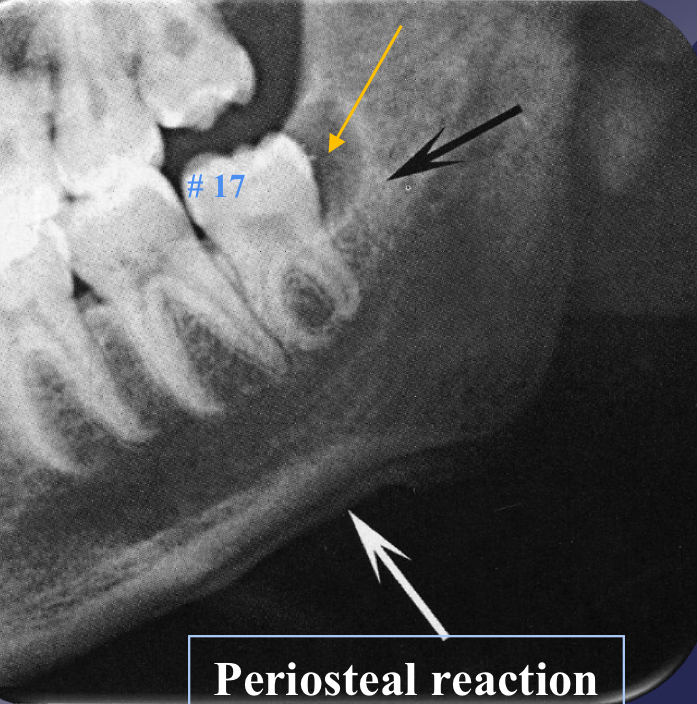
periosteal reaction
new bone formation parallel to the cortex (almost looks like periosteum lifted and bone under)
proliferative periostitis and the onion skin periosteal reaction have the same radiographic appearance
true

which osteomyelitis phase?
some effects on surrounding structures:
fistulous/sinus tract
acute
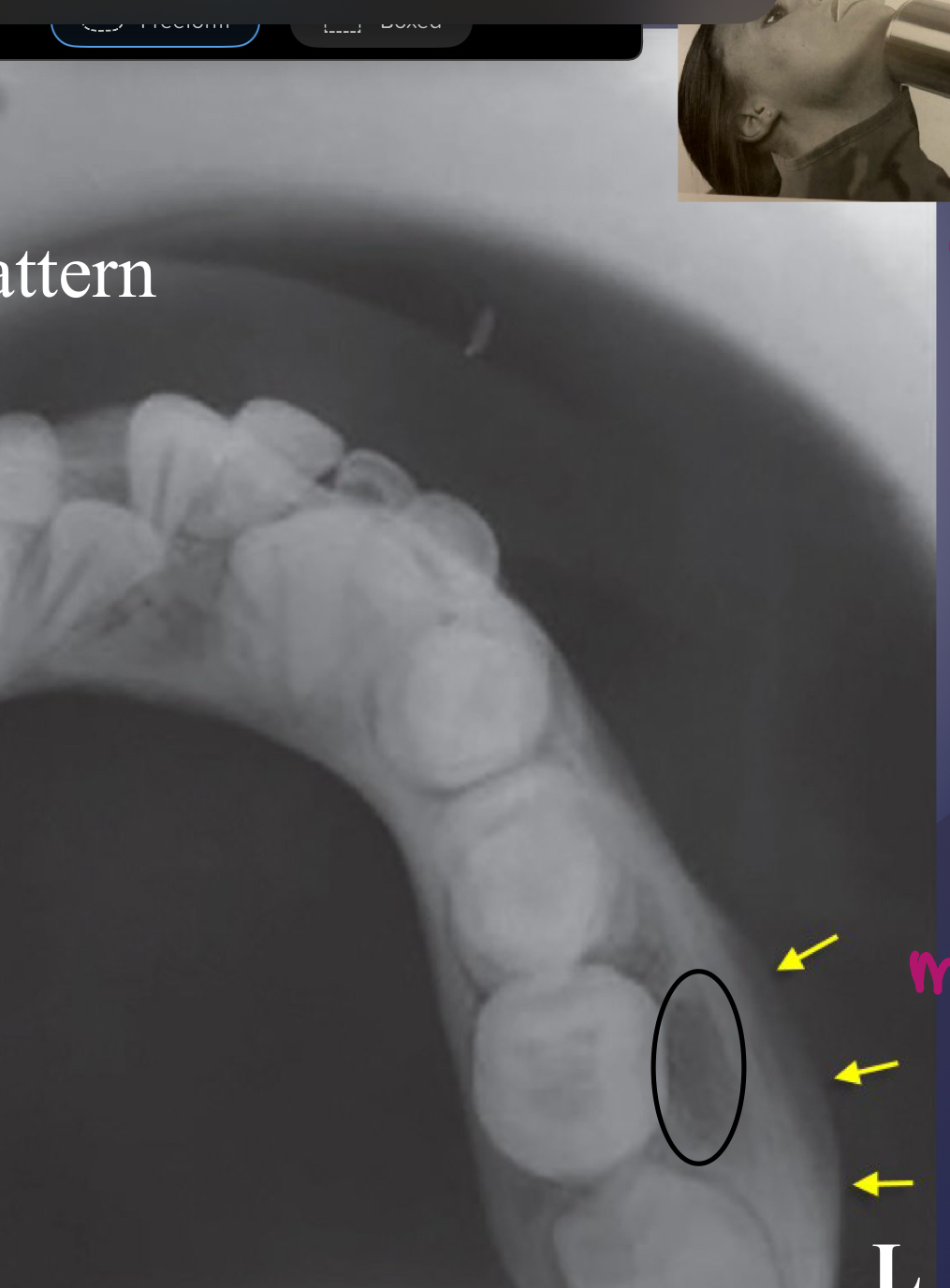
what’s going on here?

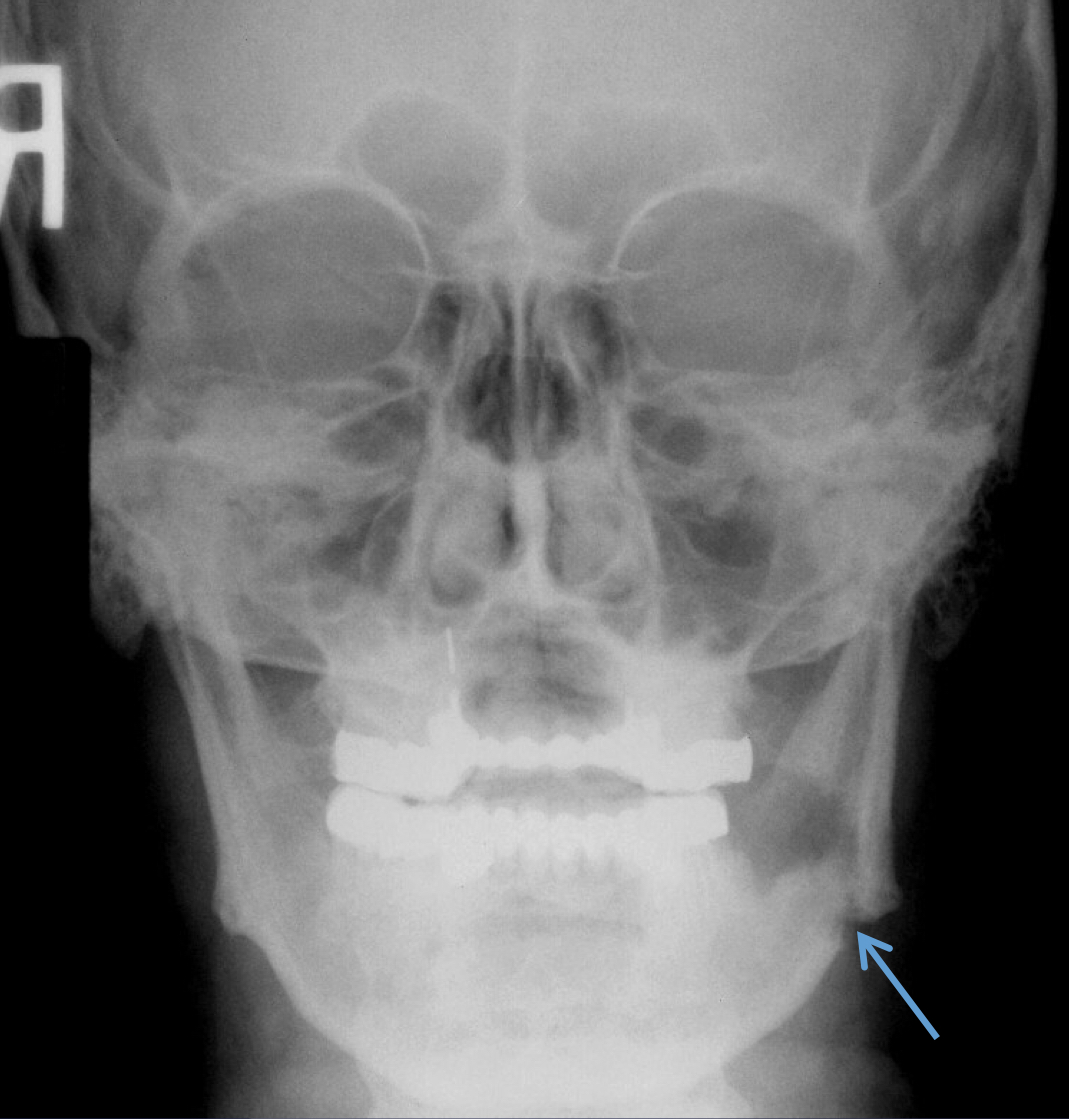
what is going on here?
pathological fracture, facture on a compromised boone
which type of chronic osteomyelitis?
primary response: proliferation reaction
sclerotic appearance of involved bone
subperiosteal bone deposition
slight jaw enlargement
involves large segment of jaw
diffuse sclerosing osteomyelitis
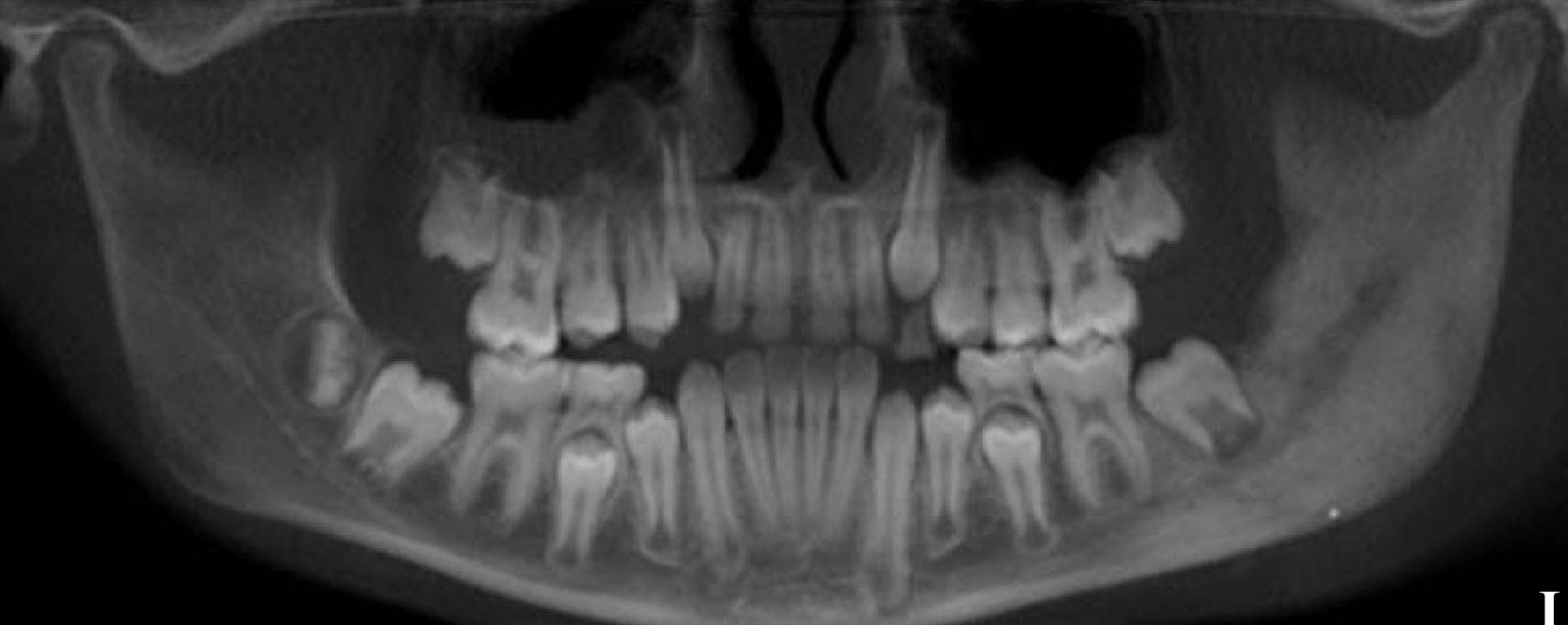
diffuse sclerosing osteomyelitis, young pt
diffuse sclerosing of left angle-ramus of mandible = L more radiopaque than R

which chronic osteomyelitis?
diffuse sclerotic bone
case of SAPHO syndrome bc wrist and mandible involved
what is ORN?
osteoradionecrosis: radiation induced damage to bone resulting from exposure to therapeutic doses of radiation, clinically exposed necrotic bone and radiologic changes similar to osetomyelitis
what minimum dose for hypocellularity and hypovascularity in head and neck region of ORN?
50 Gy
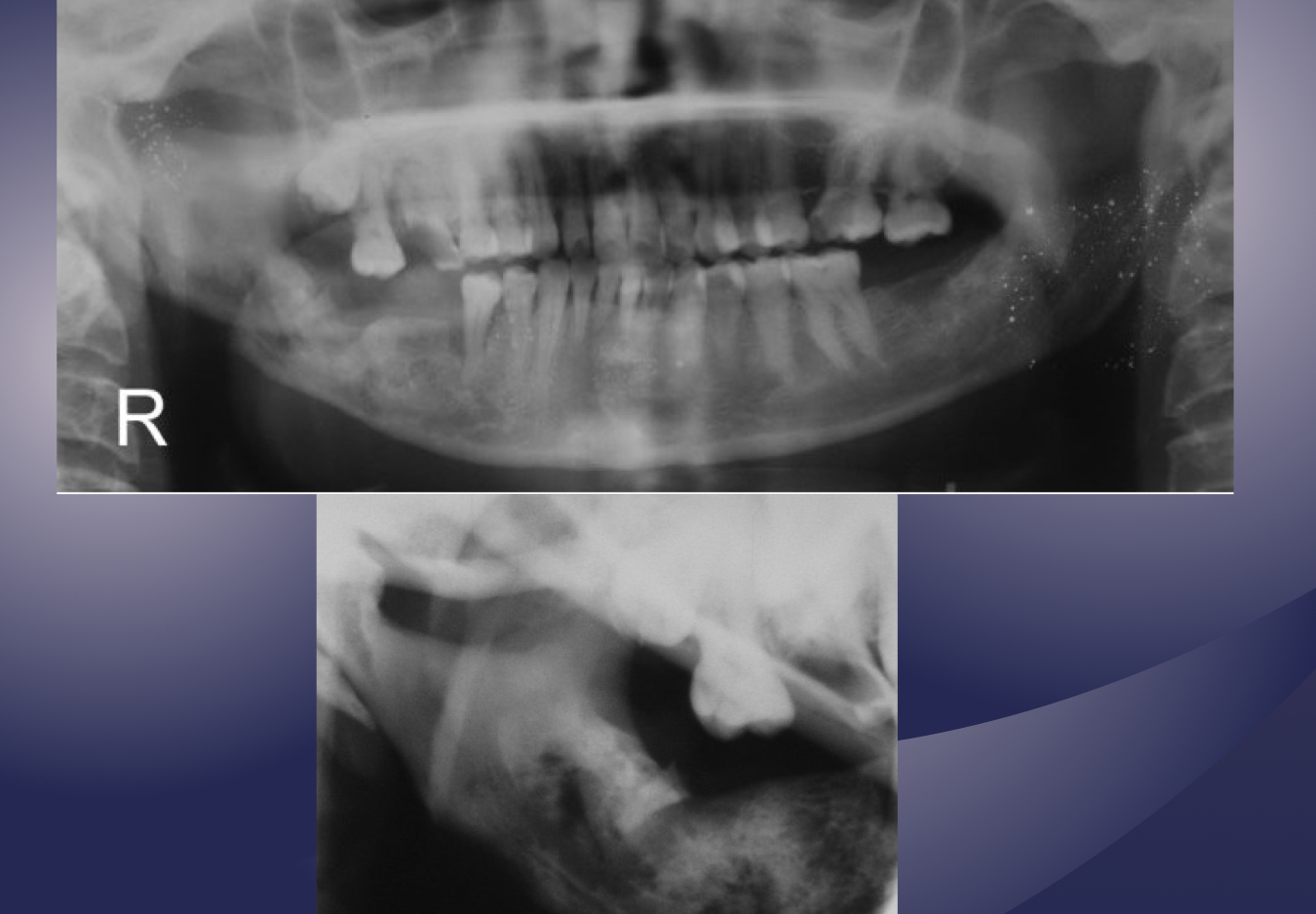
ORN
ORN at third molar extraction site
BRONJ stands for
bisphosphonate related osteonecrosis of the jaws (chemotherapy and osteoporosis drugs)
bone exposure in pts w history of iv/oral bisphosphonates
following invasive dental surgical procedure
radiographic features indistinguishable from osteoradionecrosis and osteomyelitis
BRONJ
BRONJ and ORN are the same radiographically but different pathologically
true
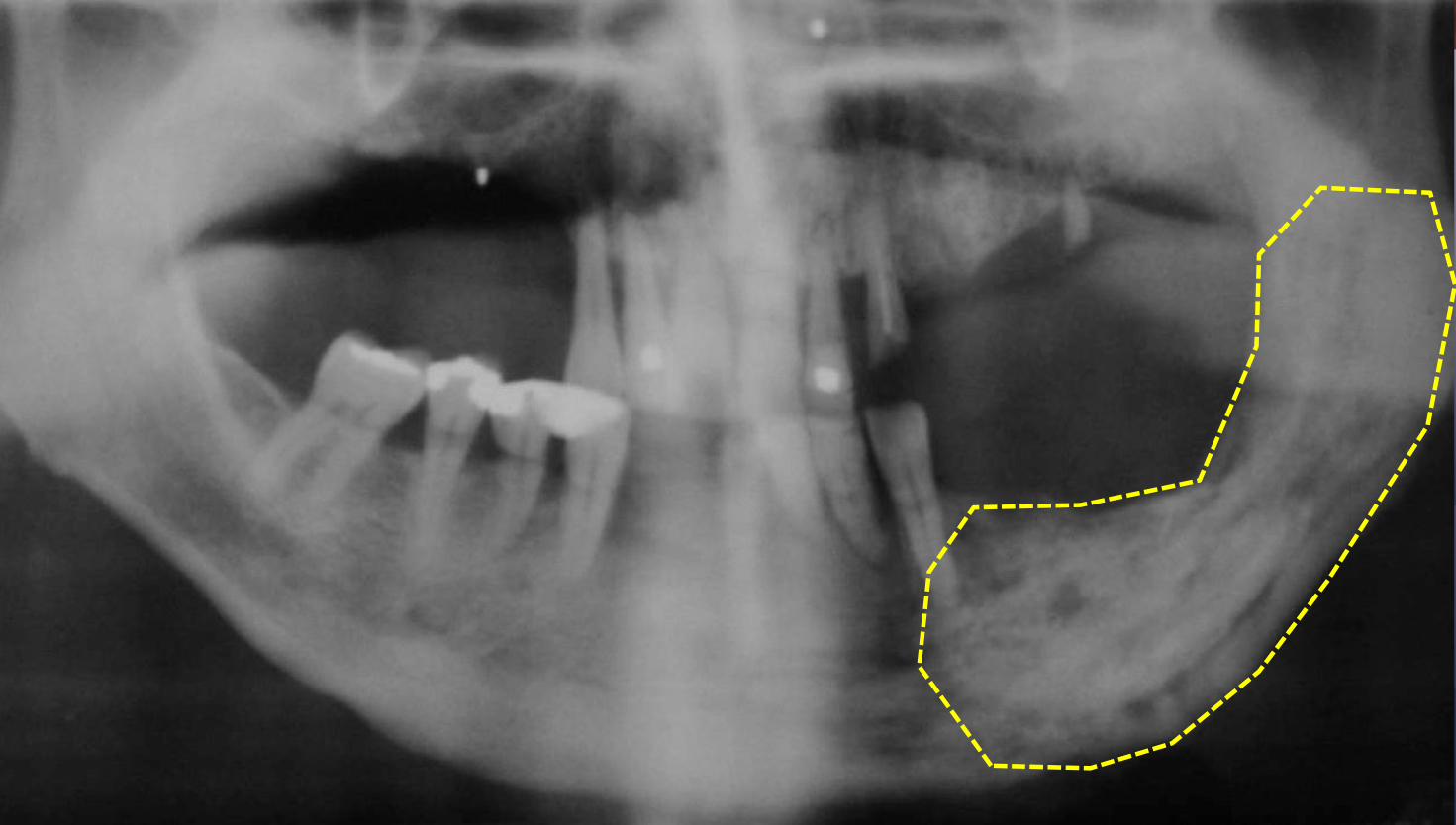
BRONJ
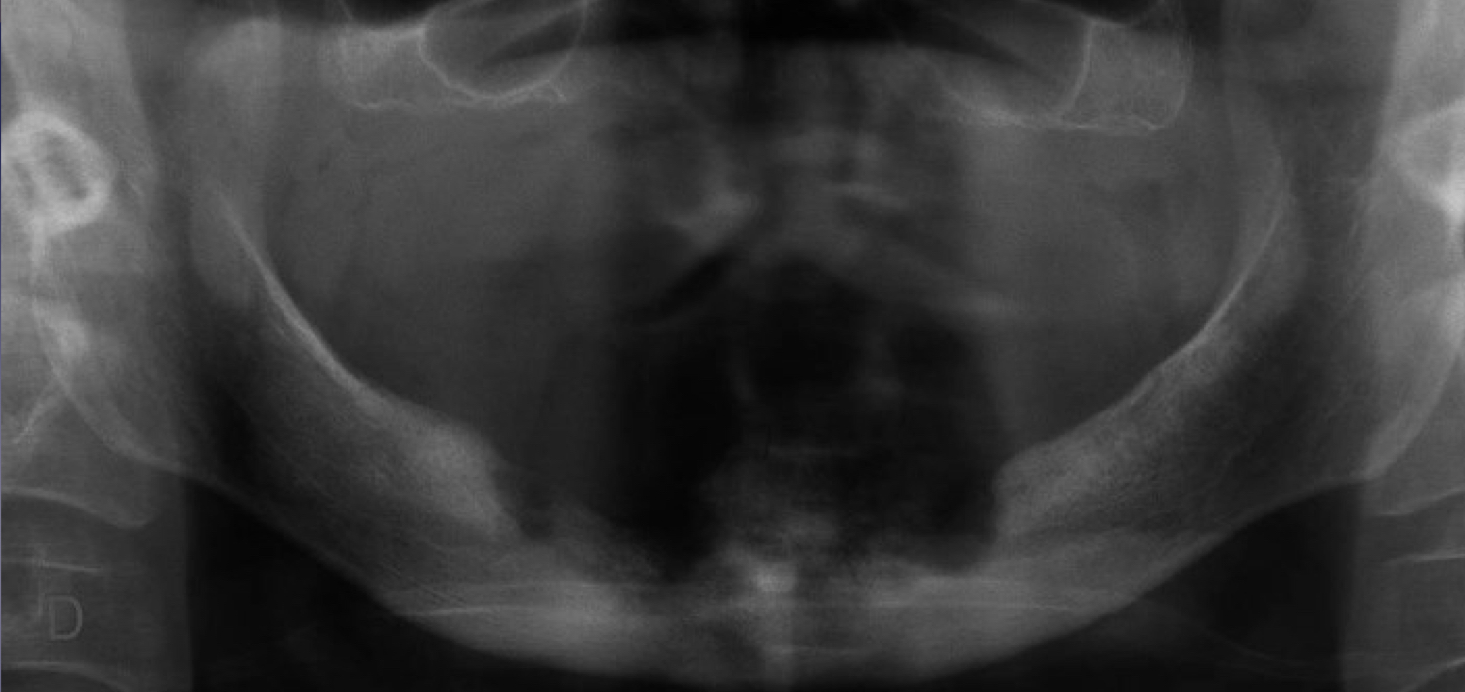
BRONJ
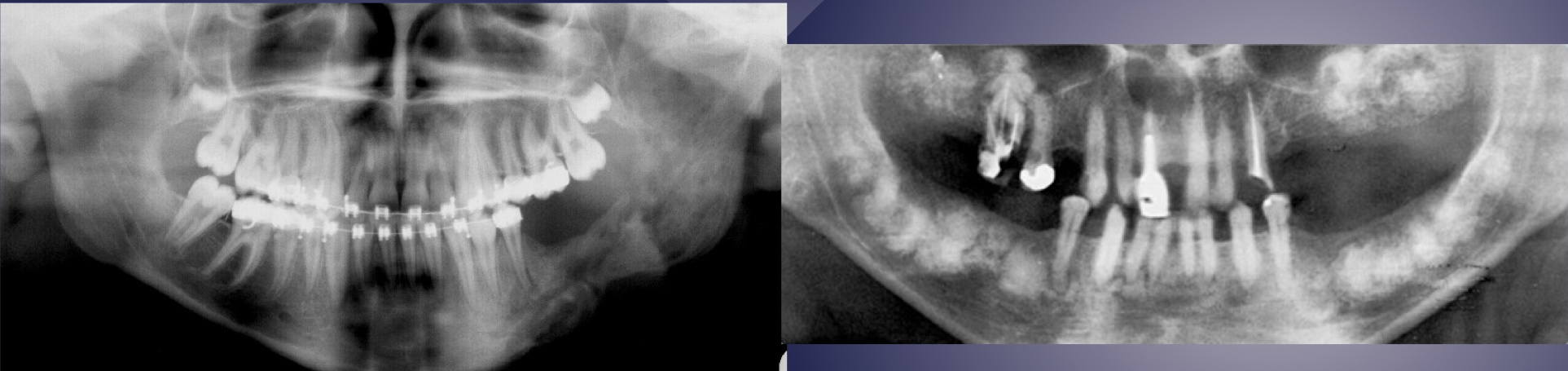
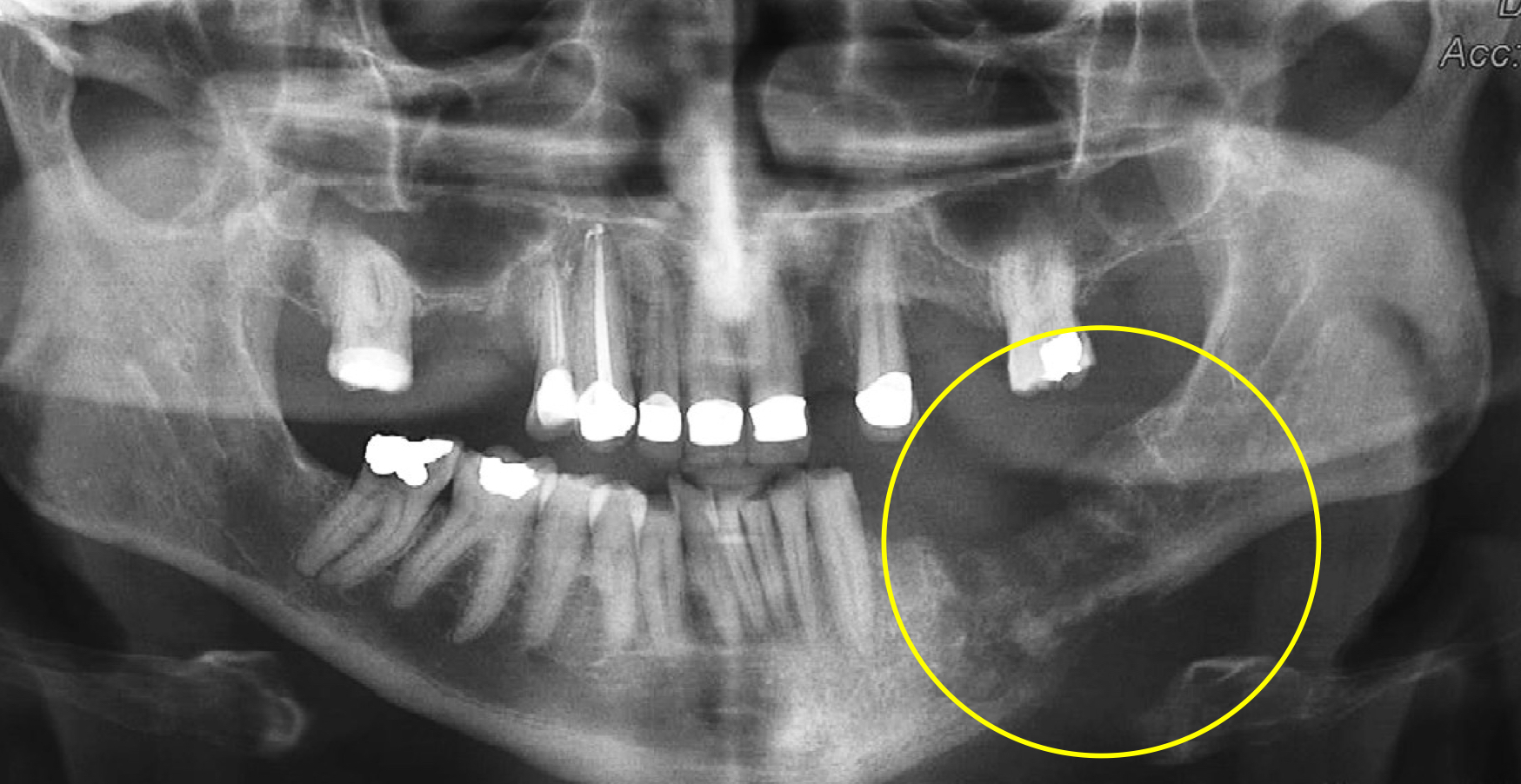
which is osteomyelitis?
L picture: osteomyelitis: ill-defined, mixed density lesions above and below IAN canal, moth eaten VS R: not osteomyelitis, well defined radiopaque lesions in maxilla and mandible above IAN canal
pericoronitis
soft tissue inflammation surrounding the crown of partially erupted tooth
pericoronitis, sometimes does not have radiographic features since it’s soft tissue
late: localized rarefaction and sclerosing
osteomyelitis: periosteal reaction
enlarged follicle is a sign of pericoronitis
false
what is mucositis?
localized thickening of mucosa
sinusitis
generalized thickening of mucosa
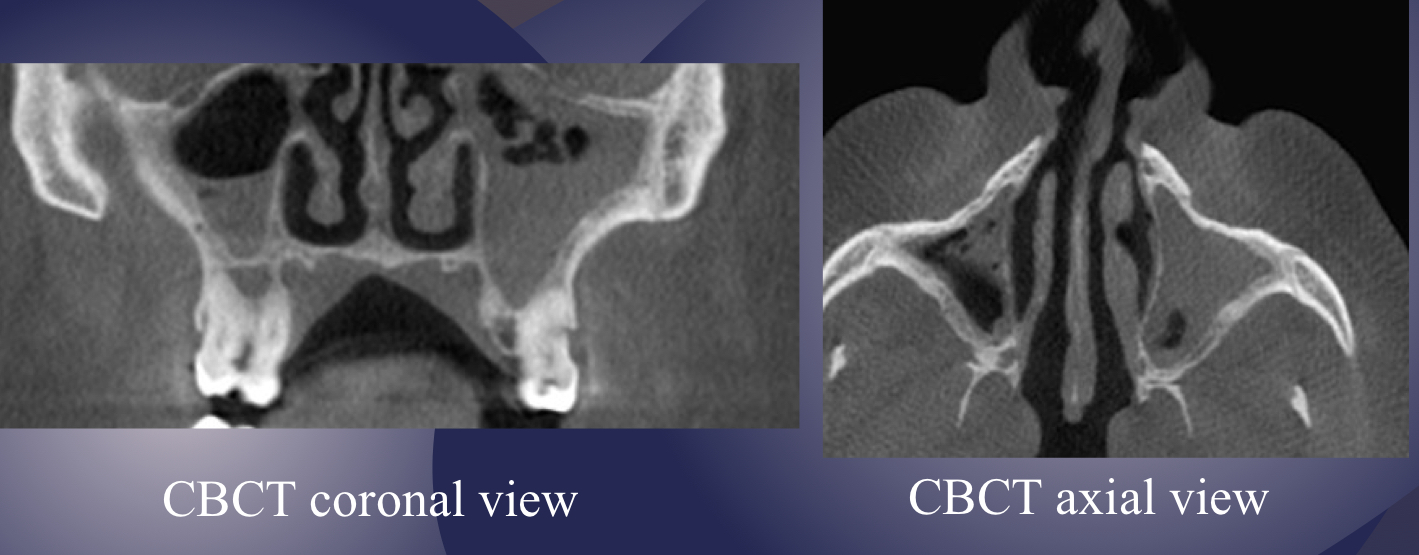
what is going on here?
severe sinusitis and sclerotic changes in bony walls (osteogenic reaction)
not a true cyst
obstruction or dilatation of the duct of seromucous glands in sinus resulting in submucosal accumulation of secretions
non-corticated margins, soft tissue dome shaped radiopacity in maxillary sinus
mucous retention pseudocyst
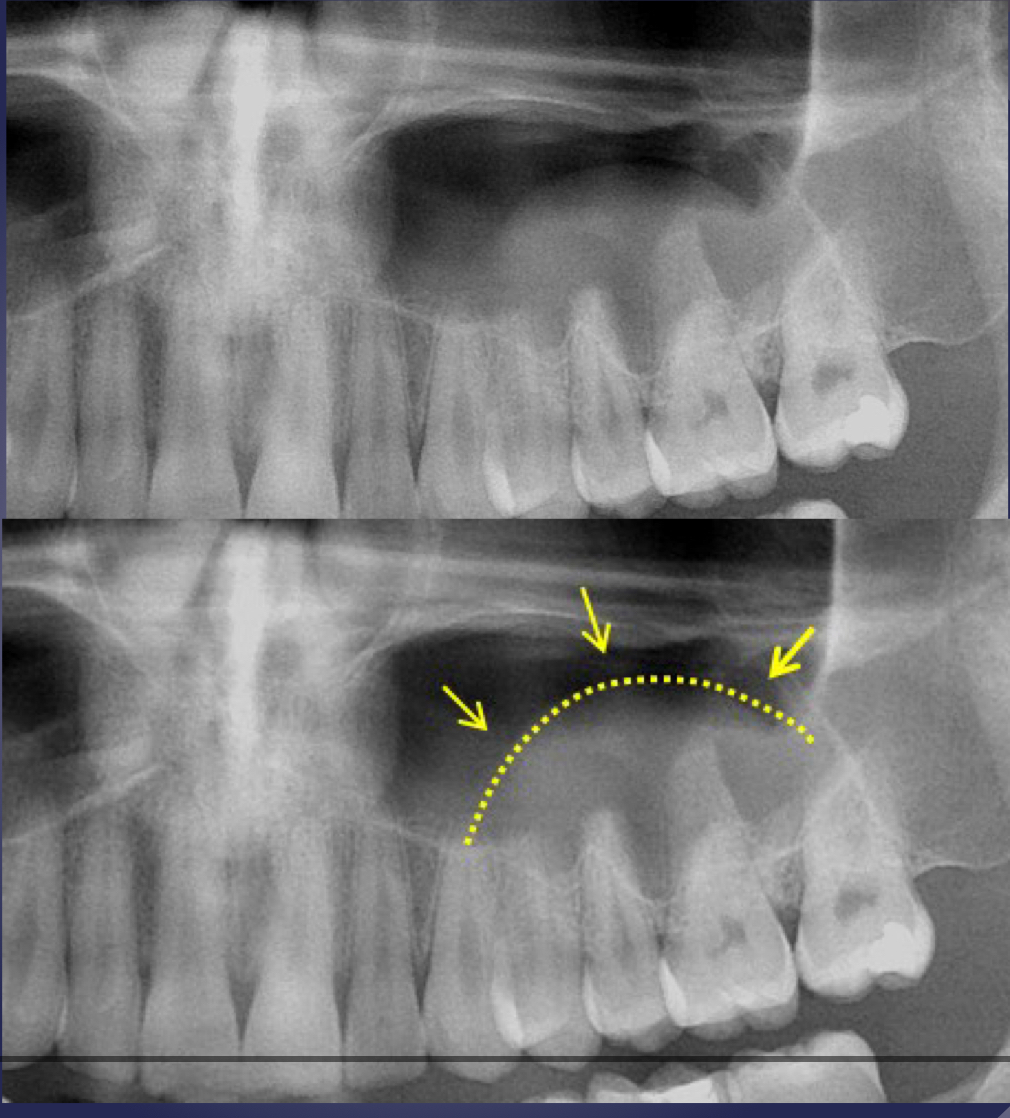
mucous retention pseudocyst
radiographic features:
relative radiopacity on the floor of sinus
well-defined, not corticated
dome-shaped
mucous retention pseudocyst