Ultimate Midterm Chemistry Study Guide - 50/50% chance to pass
1/209
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
210 Terms
Liquid → Gas
Vaporzation
What is vaporization?
Endothermal, speeds up
Gas → Liquid
Condensation
What is condensation?
Exothermic, slowing down
Gas → Solid
Deposition
What is deposition?
Exothermic, slowing down
Solid → Gas
Sublimation
What is sublimation?
Speeds up, Endothermic
Solid → Liquid
Melting
What is melting?
Speeding up, endothermic
Liquid → solid
freezing
What is freezing?
slowing down, exothermic
What is a vapor? (Explain)
When you have to apply heat, different temperature in room
What is a gas? (Explain)
Same as temperature in the room, you can’t see it
What is evaporization? (Explain)
happens naturally, doesn’t have heat applied
what is vaporization? (Explain)
happens controlled, has heat applied
what happens with water boiling?
tries to become gas, gravity pushes it down, particles are moving and colliding, atmosphere pressure pushes it down, vapor pressure becomes stronger causes particles to go up (Once vapor pressure=atmosphere pressure=boiling point)
What is the Kinetic Molecular Theory?
The movement of particles explination
3 examples in the molecular theory
particle motion, size, energy
What is Particle Motion?
Moving in constant random motion in straight lines
What is Particle Size?
Compare small particle with the empty space in between a particle
Particle energy
Deals with mass and velocity
No matter solid liquid or gas they all have the same
Temperature
Strong metromolecular force leads to
Solid
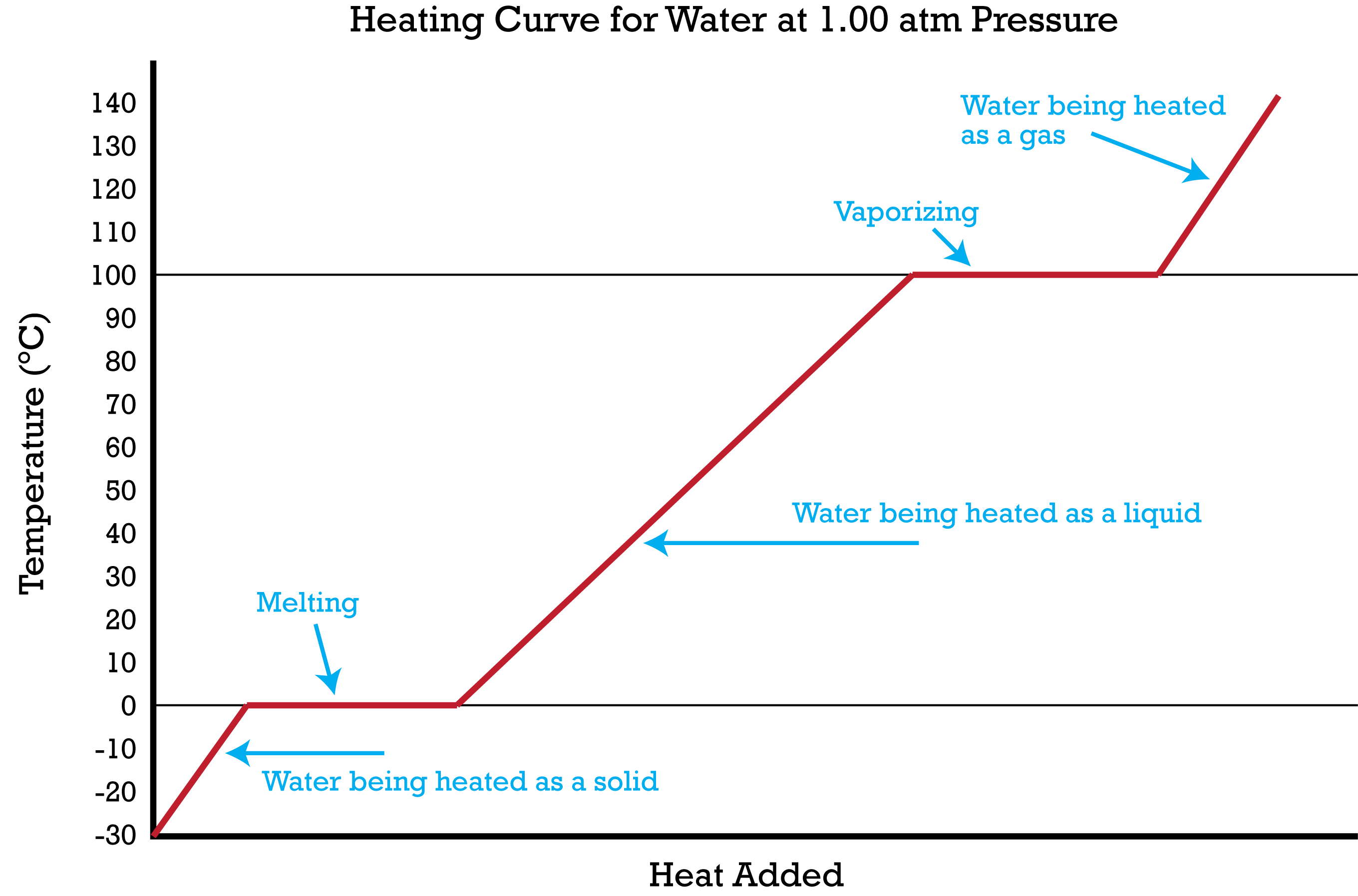
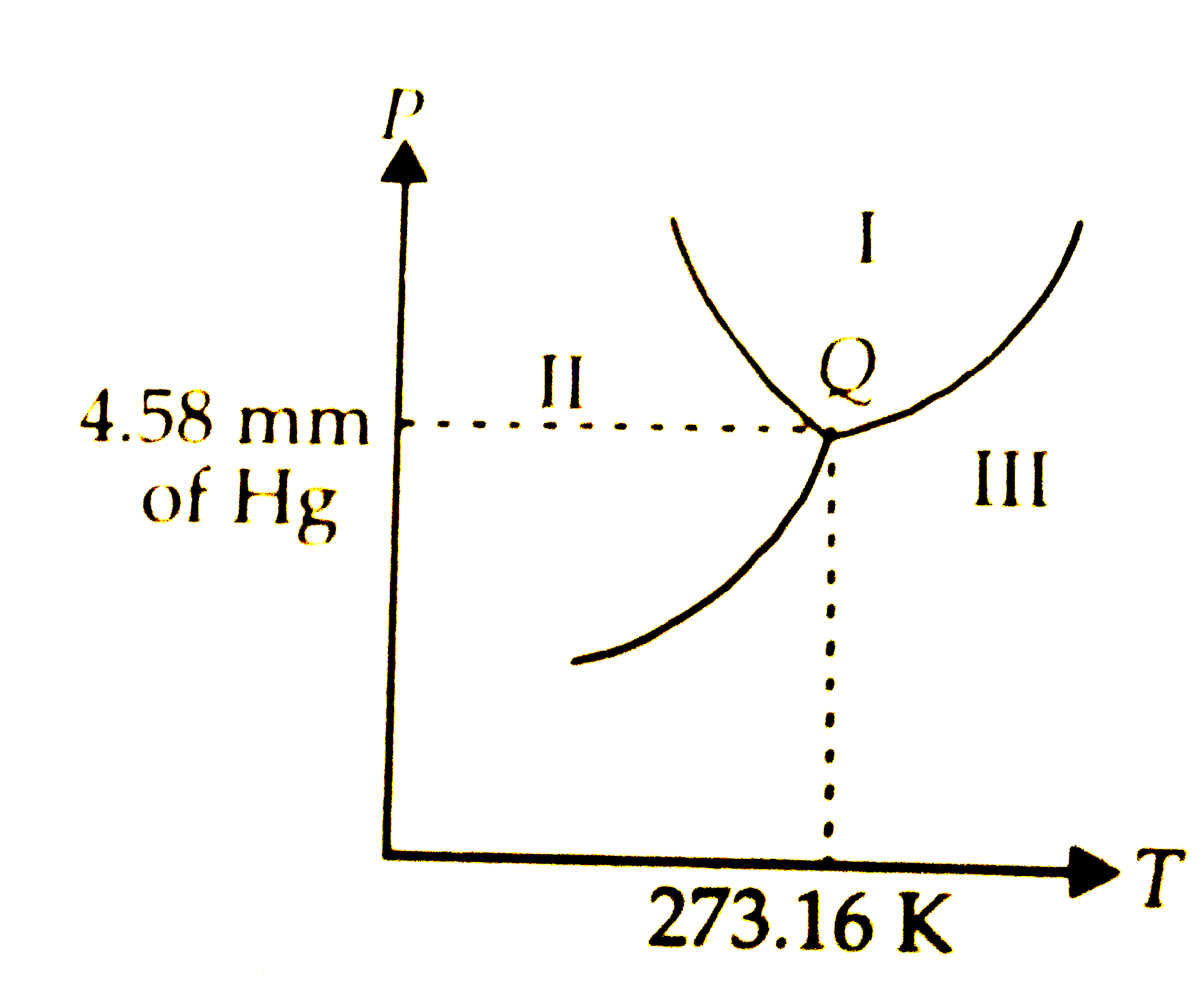
name of diagram?
Heating and cooling diagram
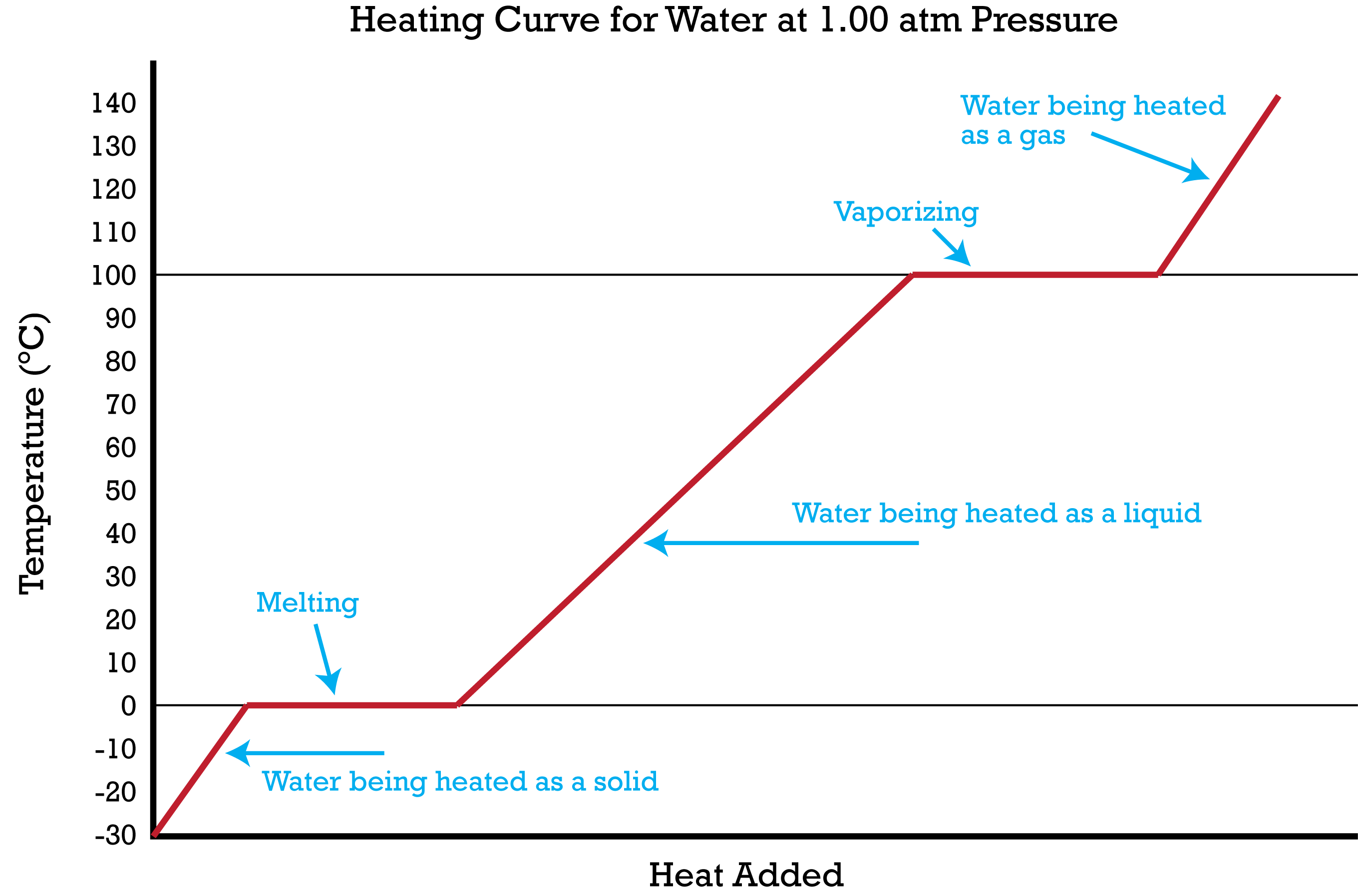
Where is the boiling point?
100c
Where is the melting point?
0c
STP should be what
ST 0c
SP 1atm
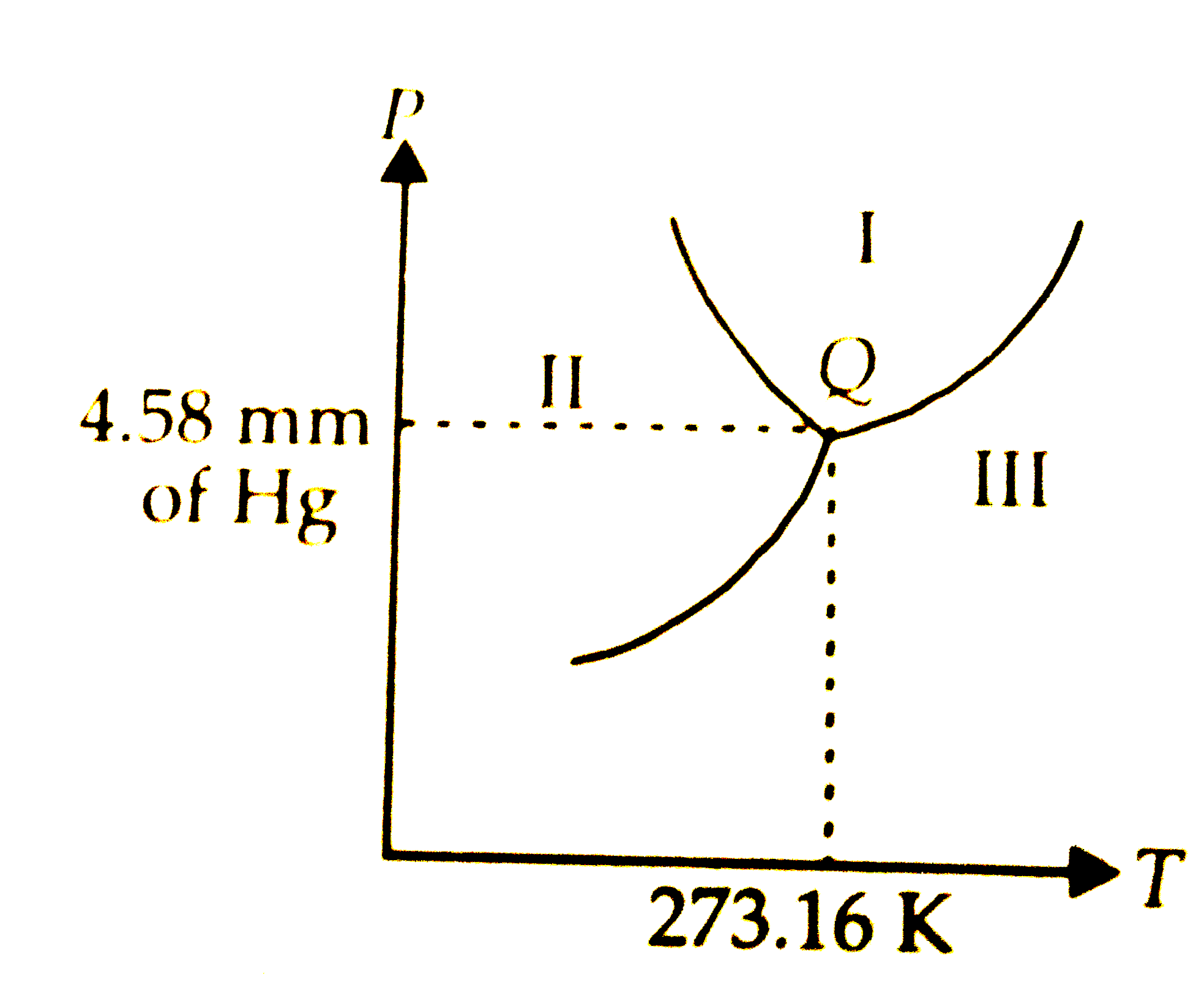
Tripple point
where all 3 points meet
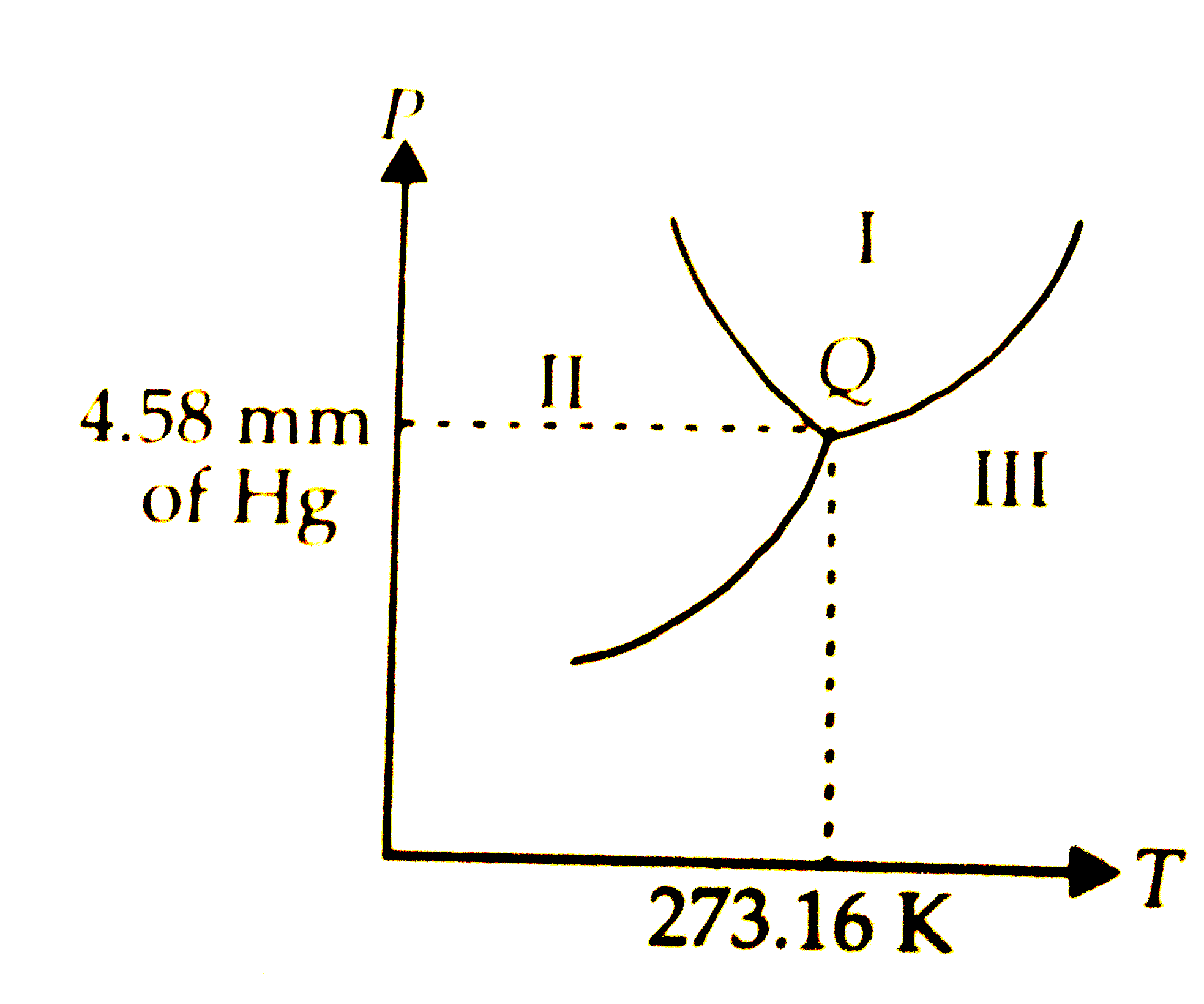
Where is gas?
iii
Where is liquid?
i
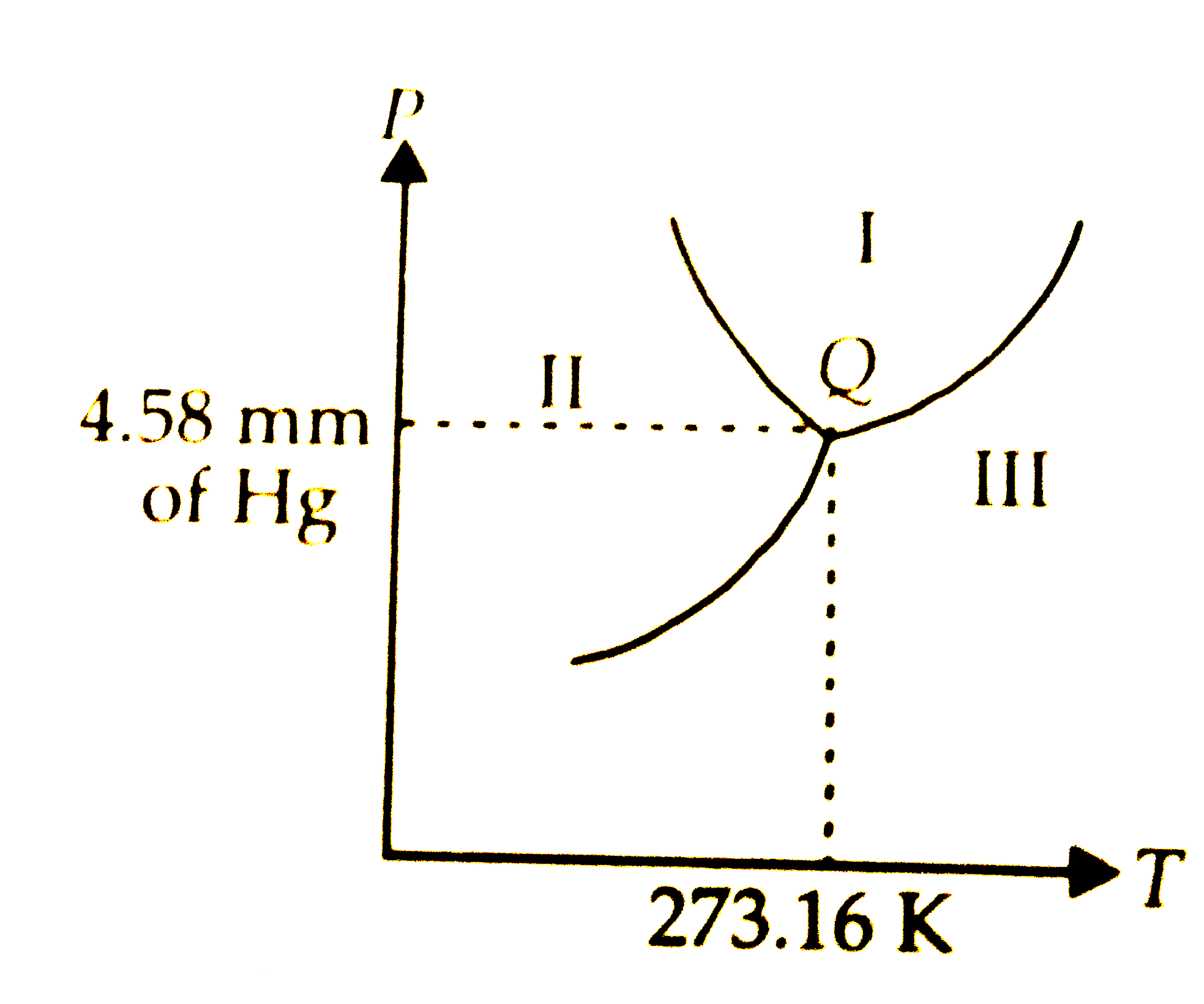
Where is solid?
ii
How to find boiling/freezing temperatures?
must hit the designated line
Critical point
critical temp and pressure is where water cannot coexist as a liquid (superficial state)
what is a superficial state?
substance behaving with properties both a liquid and a gas.
temp stays what during phase change?
the same
How does gas compression occur?
due to having a weak force they have no attraction to each other, being far apart and compressed.
How does a gas expand?
due to going in a straight constant random line until they collide with something, expanding everywhere.
Solid (What is this?)
defined volume and size, particles are still absolute, strong attraction
gas (what is this?)
undefined volume and size, separated by space, no attraction
liquid (what is this?)
indefined shape and volume, weaker attraction, higher energy
Air pressure
Particles in the air move in all directions pressure is exerted in all directions
When is pressure strong?
At surface
Do gas, liquid, and solid have the same kinetic energy?
Yes they have the same energy because of the temperature, but they have different masses and inter molecular force.
Physical change
The change of its appearance, but still has the same chemical compound
Chemical change
Change in its chemical compound; a new substance; a new chemical property
Indicators of chemical change
Color change, temperature, odor, formation, gas production, heat released, or light released
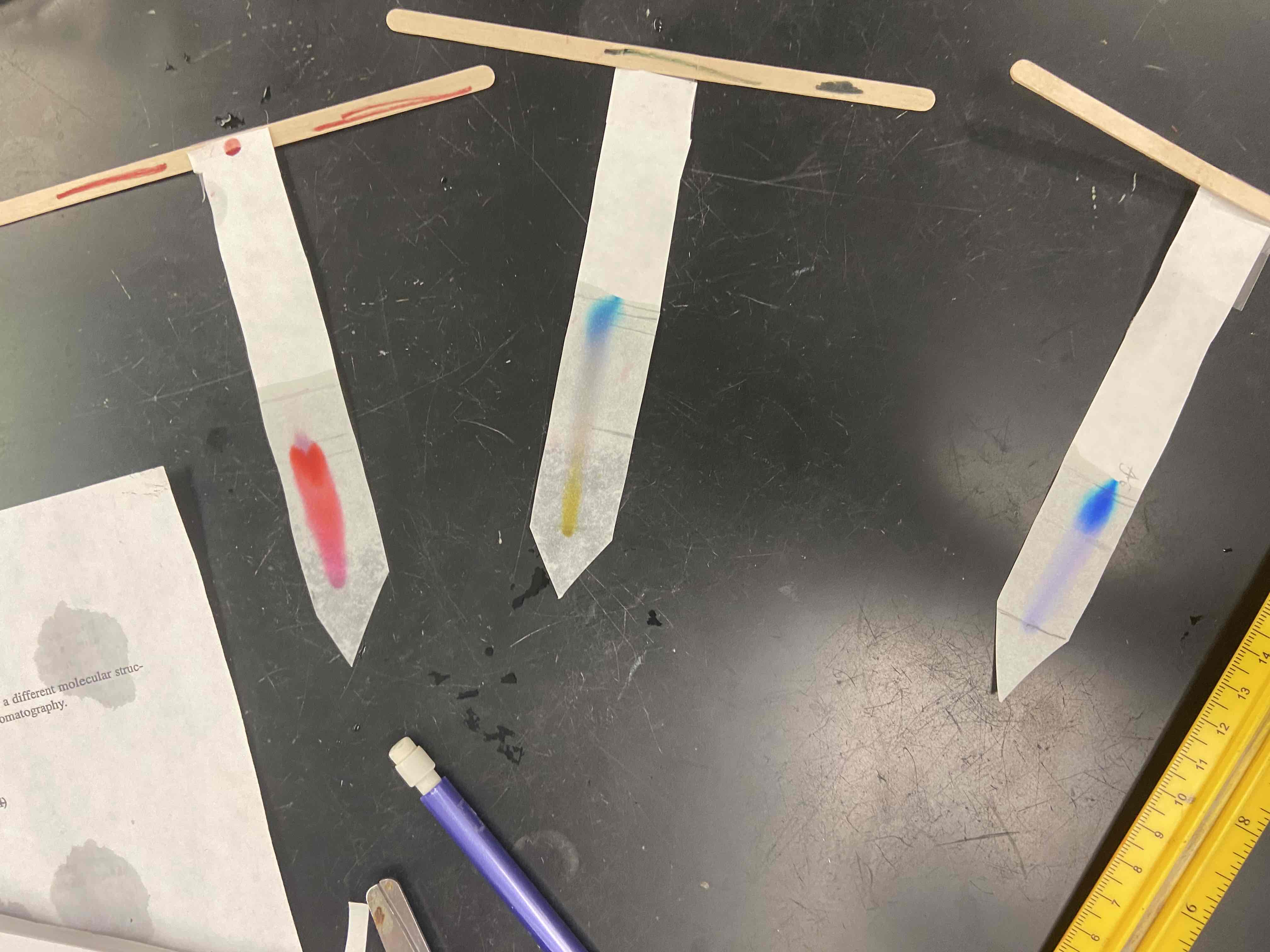
Chromatography (two or more dissolved liquid)
Most soluble substance moves castes, trying to figure out which is more pure (for example blue is more pure due to having no other color change.)

Decanting (solid → liquid)
Pour liquid off at the top carefully
Filtration (solid→liquids)
Uses a porous barrier
Filtration (solids → solids)
using a porous barrier
Magnetic properties
If it’s iron, nickle, colbat, etc you use magnets
Sublimation (solid→solid)
Can be used when once solid sublimates but others don’t
Ex; the solid would turn into a gas at its boiling point, which causes only 1 to go up. That’s how you seperate.
Fraction Distilation (liquid→ liquid)
Liquids together with boiling points that are closest together. If the boiling points are way off, start with the lowest boiling point and seperate them all.
Ex; the liquid would turn into a gas at its boiling point, which causes only 1 to go up. It then hits the cold part and it comdences, back to a liquid on the other part of the bottle.
Oversaturated (solid→liquid)
For example rock candy. You’d put a stick and remove all the certain particles as it attaches to a stick.
Distillation simple (solid → liquid)
Used on water with different (major) boiling points
Crystallization (solid→liquid)
Used on sugar (collecting all the sugar in the pot)
2 types of matter
Substance and mixture
What is substance
Pure, one element
What is mixture
Something with two or more substances mixed together (physically bonded)
Elements
It’s basic element (O, Fe)
Compound
Chemically bonded
(H2O)
Miscible
Gives a slut ion, one or more substances dissolve in the liquid; you won’t be able to tell if it’s a mixture
Immicible
You can tell it’s a mixture
When particles bounce off the wall…
They have the same elastic energy, not Lossing energy when bouncing off and staying the same
Why does air pressure increase as you move towards the center of the earth?
Activity on the surface
gravity pushing everything down
particles collide into each other down there, and as they collide they create higher pressure.
Extensive
Mass, volume, length
Intensive
density, color, odor, melting boiling point, which are internal properties
what controls the phase of a substance
temperature and pressure
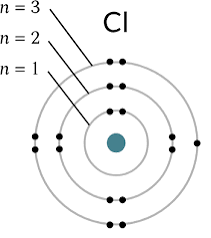
what is Bohrs Model?
Atomic mass?
A set of # due to total of isotope
Atomic number?
# of protons
Isotope?
Protons with different number as neutrons
Abundant isotope?
They appear the most (for example highway in the graph.)
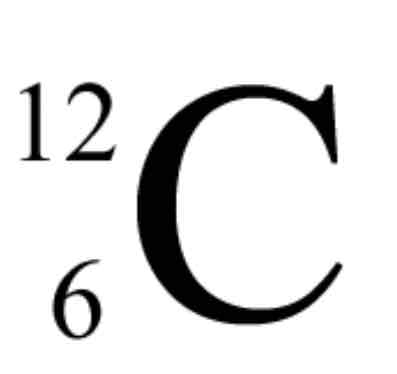
What is the top?
Mass #
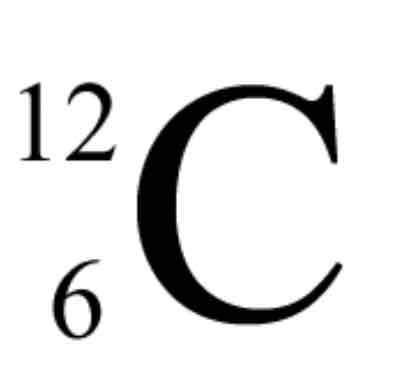
What is the bottom?
Atomic #
Why is protons and electrons the same #?
For they can stay neutral
What is the equation to find atomic mass?
Atomic # x % = atomic mass (amu)
How do you find a mass number? (Out of a lot of isotopes)
Do ur normal thing but set it up like an equation with the total mass out (seen in the periodic table)
Who created Bohrs Model?
Bohr
Who created Plum Pudding model?
Thompson
What did Rutherford find?
A nucleus in the center, where the proton is found. Did this by Gold foil.
What did Aristole do?
That atoms moved through a empty space, everything is made up of earth air Fire and Water
What did democritus do?
Made up of tiny particles, but could not prove it
What are the scientists discoveries in order?
Dulton
Thompson
Rutherford
Bohr
What did Dulton do?
Came up with the Dulton Atomic Theory
What is the Dulton Atomic Theory
All mater is made of atoms
Same items are identical
Atoms are indestructible
How do you find Mass Number?
Protons + neutrons
Radioactivity =
Nuclear Energy
Radioactivity does NOT =
Chemical reaction
Each orbital has a what?
Fixed amount of energy
What did Aufbau say?
Electrons should be placed at its lowest orbital
What did Paulixclusion say?
must have 2 electrons in the opposite side (like facing opposite direction)
What does Hunz Say?
Electrons in each orbital before paring
What is Electron configuration (definition)?
Arrangement of Electrons
What is electron configuration (write it down)
Ex: 1s²2s²
What is the electron dot structure?
( With X’s in Cambridge )

How do you release energy?
Jumping electrons release energy due to being excited, but then going to grown level. They release this in forms of waves.
What do protons determine?
type of Element
Atomic # =
Protons