Physical Science Test 1 Study Guide - Ch. 1 and 2
1/119
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This is just a Gen. Ed. class test from UCA.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
Measurement
Number + Unit
Meter/Length
Originated as the distance from the north pole to the equator as 10,000,000 meters, then changed to how far light travels in a vacuum in 1/299,792,458s.
Kilo/Mass
Originally the kilogram was the mass of (0.10m)^3 of 1 liter of water, now the standard kilo is a platinum iridium cylinder kept at the French Bureau of Weights & Measures. (Water density - 1Kg/1L)
Second/Time
Original measurement was 1/86,400 part of a mean solar day (86,400s = 24 hours/day, 3600s/hour), now it is a certain number of oscillations of cesium 137 atoms.
Data
Measurement information used to describe objects, conditions, events, and changes.
Ratio
Analysis through quotations of 2 numbers.
Generalizations
A concept obtained by inference from specific cases.
Symbols
Represents quantities, measured properties.
Equations
Mathematical relationships between properties, define concepts, specify relations.
Laws
A statement describing what always happens under certain conditions.
Principals
A rule or mechanism by which specific scientific phenomena work.
Hypothesis
Tentative explanation for observation.
Experiment
Recreation of an event or occurrence to test hypothesis.
Controlled experiment
Control & experimental groups involved.
Scientific Communication
Ensures ideas are confirmed.
Pseudoscience
Misleading & often absurd claims of scientific results.
Theory
Based on hypothesis, experimental support, forms the framework.
Model
Collection of a theory to represent it.
Speed
Change in position with respect to time; 10 mi/hr, 10m/s, etc.
Vector
When both direction and magnitude are specified.
Scalar
When only magnitude is specified
Distance
10mi, 10km, 10m, etc.
Displacement
(Distance + Direction) 10mi east, 10km north, 10m south, etc.
Velocity
Describes speed and direction (where & how fast), graphical representation in vectors, length = magnitude; arrow = direction; (Speed + Direction) 10 mi/hr east, 10m/s south, etc.
Acceleration
Rate in which motion changes over time, speed or direction or both can change, can be negative.
Uniform Acceleration
Constant, straight-line acceleration; average velocity simply related to the initial and final velocity.
Force
A push or pull capable of changing an object's state of motion.
Gravitational force
Mass interactions
Electromagnetic force
Charge interactions
Weak force
Certain nuclear reactions
Strong force
Holds nuclei together
Inertia
Measure of an object's tendency to resist changes in motion (including rest).
Free Fall
An object thrown downward or upwards, a falling object is considered to be free falling if one disregards the effect of air-resistance.
Mass
Quantitative measure of inertia; the amount of matter.
Weight
Force of gravity acting on the mass of an object.
Impulse
A force acting on an object for some time; produces a change in momentum.
Conservation of Momentum
When outside forces are not present, the combined total of all objects does not change; can be exchanged.
Air Resistance
Prevents a falling object from reaching the speed it would have otherwise due to the acceleration due to gravity; it increases with speed.
Terminal Speed
When falling objects eventually reach a state when weight is balanced by the opposing force of air resistance; it depends on an object's shape, size, and mass.
Circular Motion
The movement of an object on a circular path; resulting accelerated motion (direction changing/centripetal acceleration).
Centripetal Force
A force that makes a body follow a curved path; acts on circular motion.
Centrifugal Force
Apparent outward tug as direction changes.
Significant figures
Zeros are not significant after decimal (leading zeros) before non-zero numbers
All non-zero numbers are significant
Zeros after non-zero numbers in a decimal are significant
Percent error
The difference between estimated value and the actual value in comparison to the actual value and is expressed as a percentage.
Smallest division on a meter stick
Millimeter
Triple beam balance
An instrument used to measure mass very precisely.
Different instruments used in making measurements
Protractor, meter stick, triple beam balance, thermometer, ruler, scale, etc.
Weightlessness
Constant free fall, zero apparent weight, but weight is always present just not measurable.
Impulse Momentum Theorem
The the impulse applied to an object is equal to the change in its momentum.
𝒔 = 𝒅/𝒕
speed
𝒂 = Δ𝒗/Δ𝒕
acceleration
𝒗 = Δ𝒙/Δ𝒕
velocity
𝛒 = 𝒎/𝑽
density
𝑭 = 𝒎𝒂
force
𝒑 = 𝒎𝒗
momentum
𝑭 = 𝒎𝒂 = 𝒎Δ𝒗/Δ𝒕 = Δ𝒑/Δ𝒕
𝑭𝒕 = 𝒎 * Δ𝒗
impulse
2𝛑r = c
circumfrence
𝒗 = 𝒈𝒕 and 𝒅 = (.5)𝒈𝒕2
free fall
𝑭C = 𝒎𝒂C
𝒂C = 𝒗2/𝒓
centripetal force & acceleration
𝑭 = -𝑮 (𝑴𝒎/𝒓2)
Law of Gravitation
𝒈 v.s 𝑮
𝒈 = 9.80 m/s²
𝑮 = the universal gravitational constant
𝒗f = 𝒗i + (𝒂𝒕)
final velocity
𝑭net = 𝒎𝒂
net force
speed formula in words
distance/time
acceleration formula in words
change in time/time interval
velocity formula in words
displacement/change in time
density formula in words
mass/volume
force formula in words
mass * acceleration
momentum formula in words
mass * velocity
impulse formula in words
change in momentum
force • time = mass • Δ velocity
free fall formula in words
gravity * time
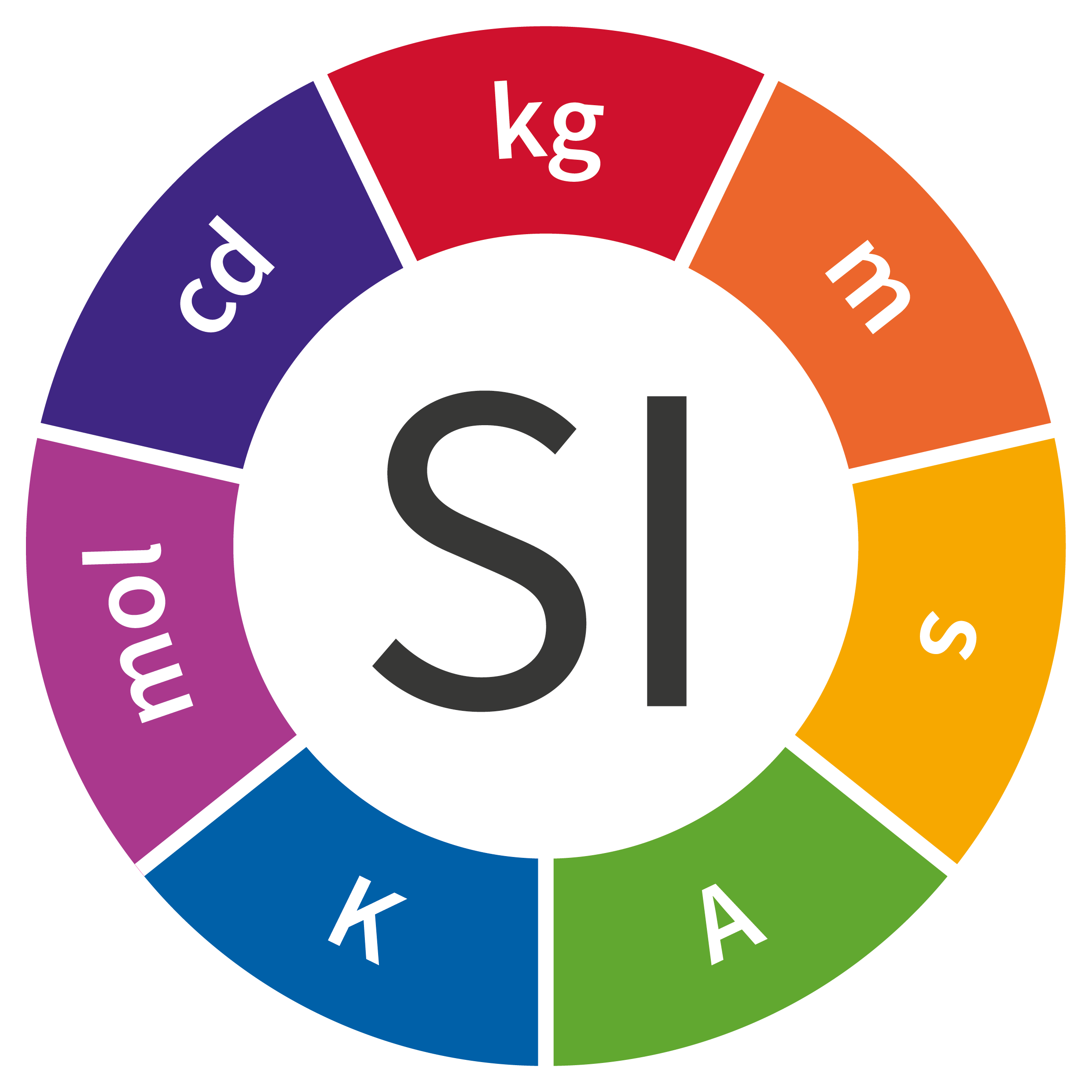
Length
Meter
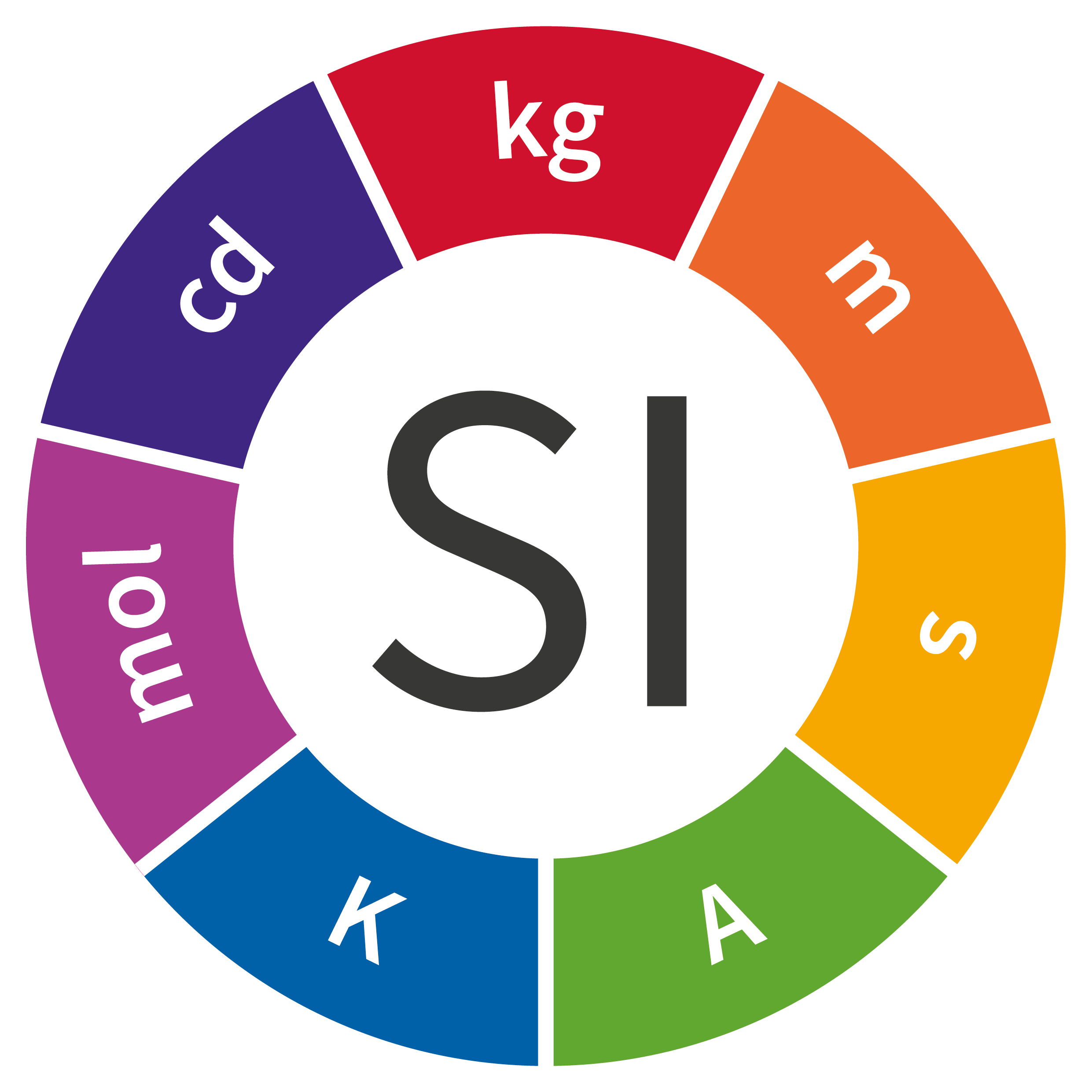
Mass
Kilogram
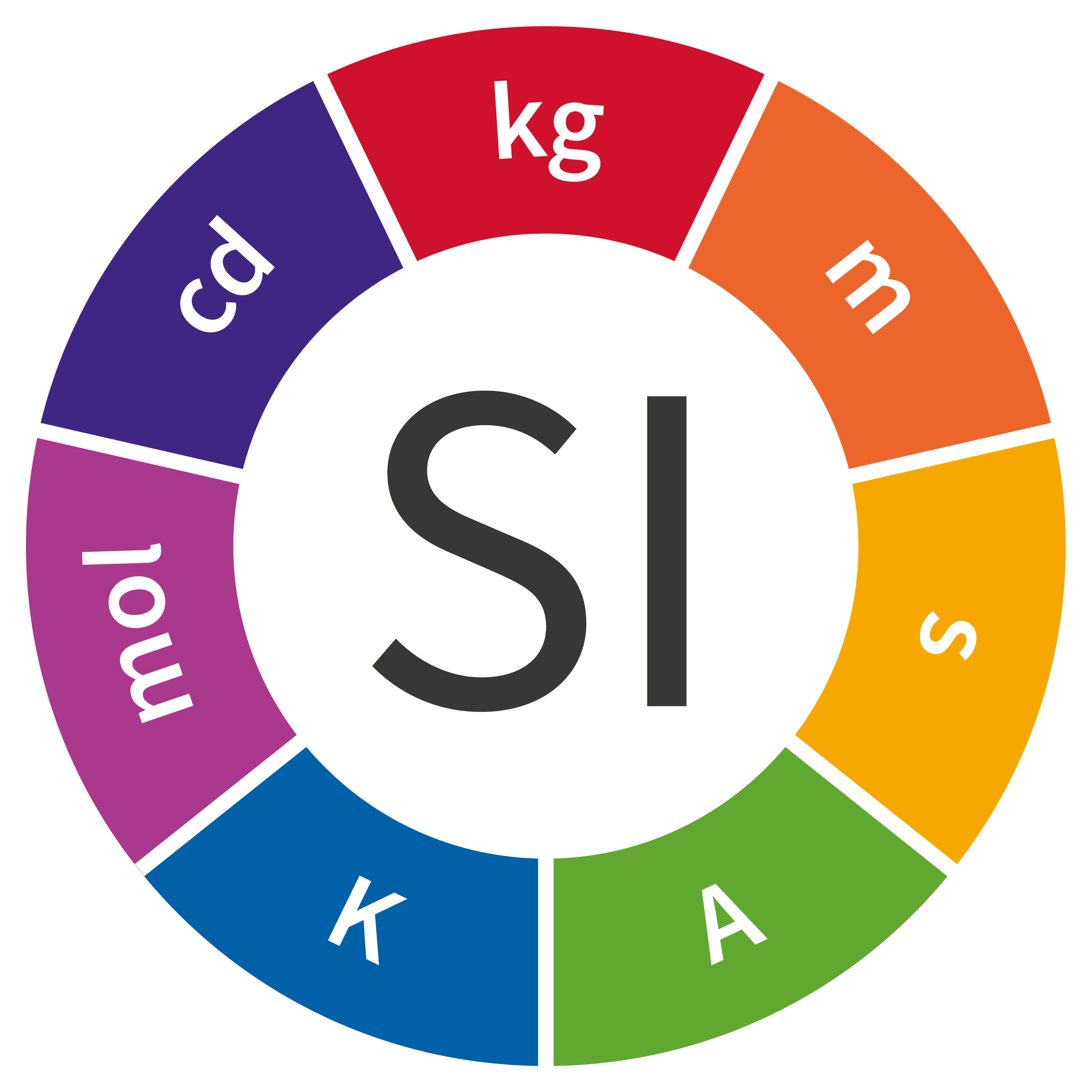
Time
Second
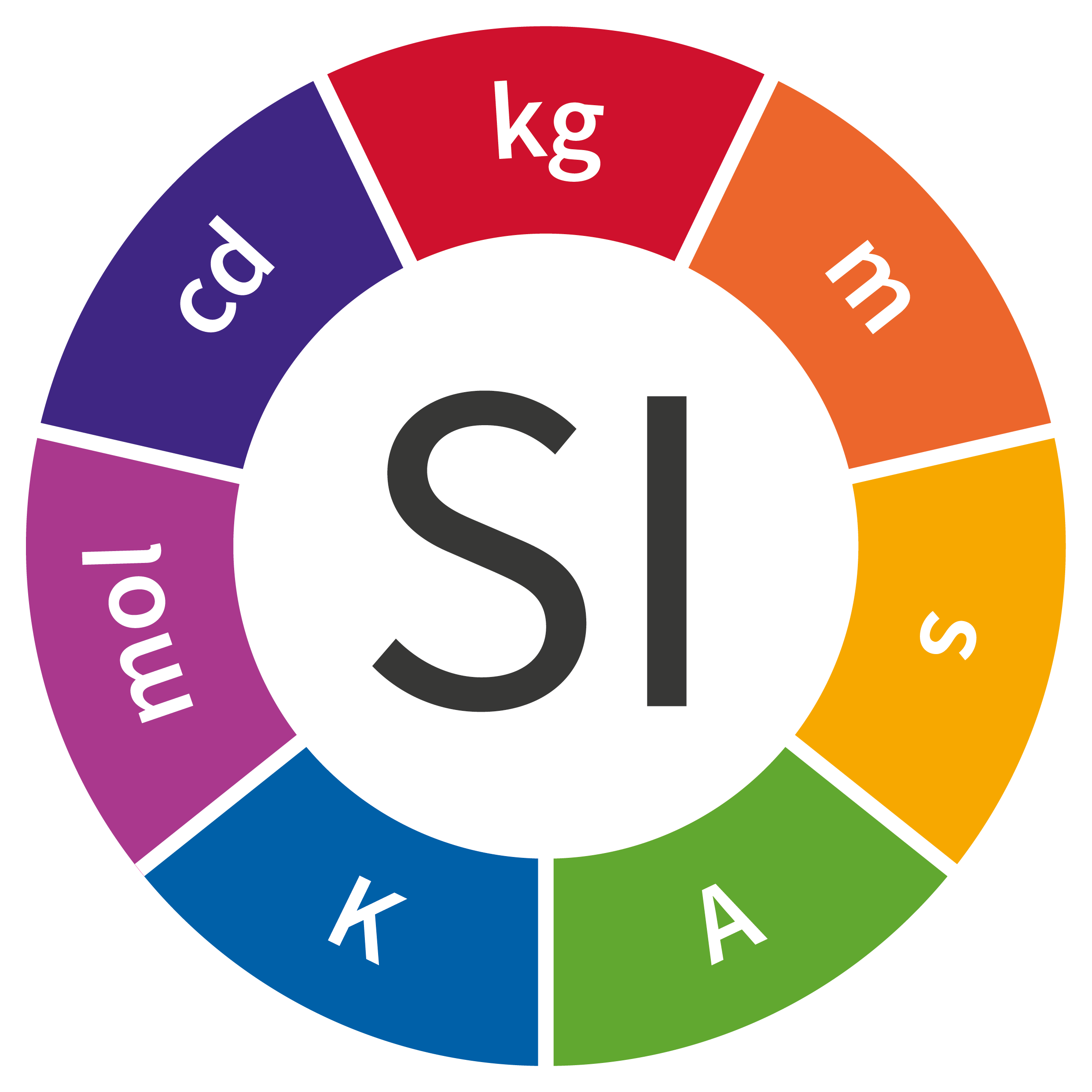
Electric Current
Ampere
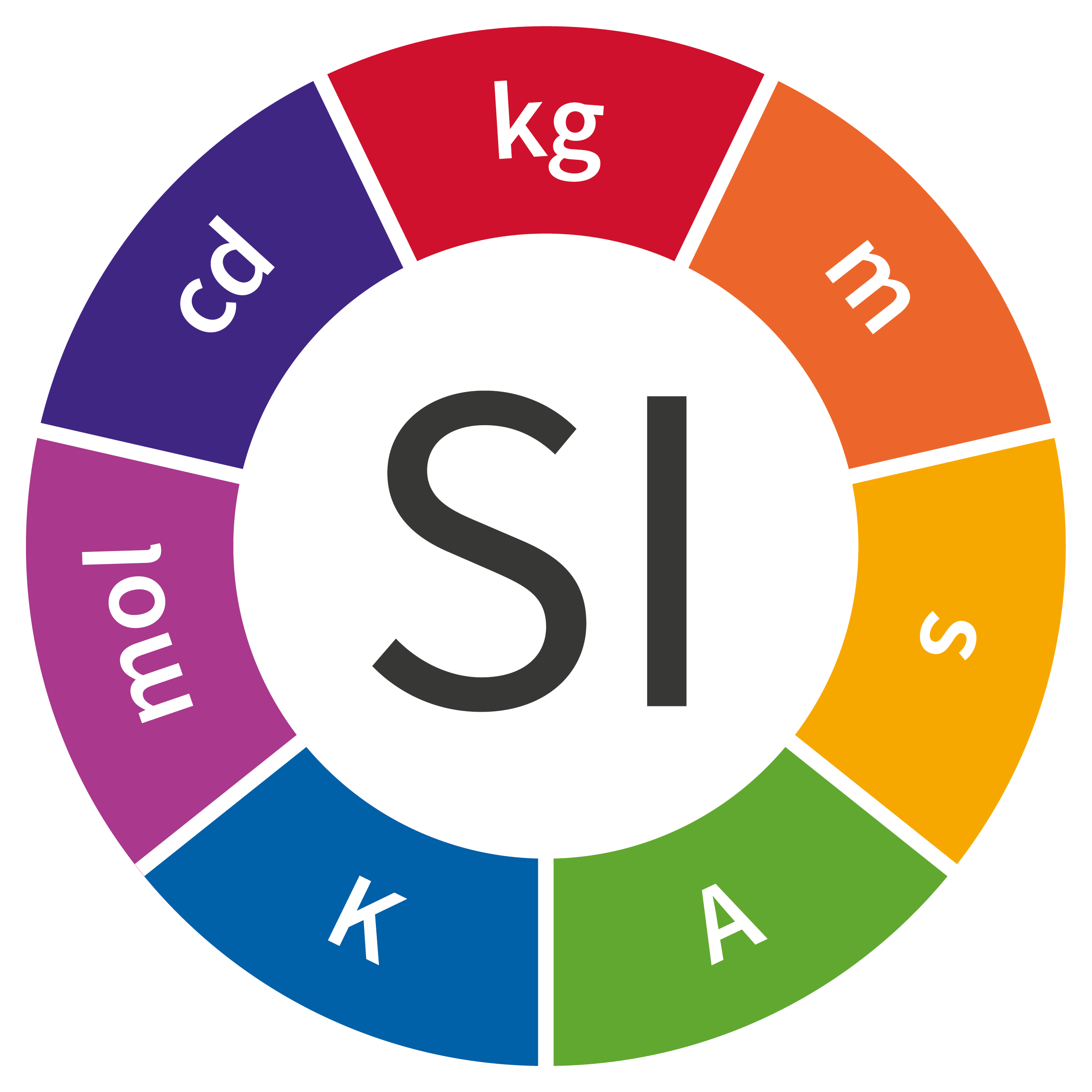
Thermodynamic Temperature
Kelvin
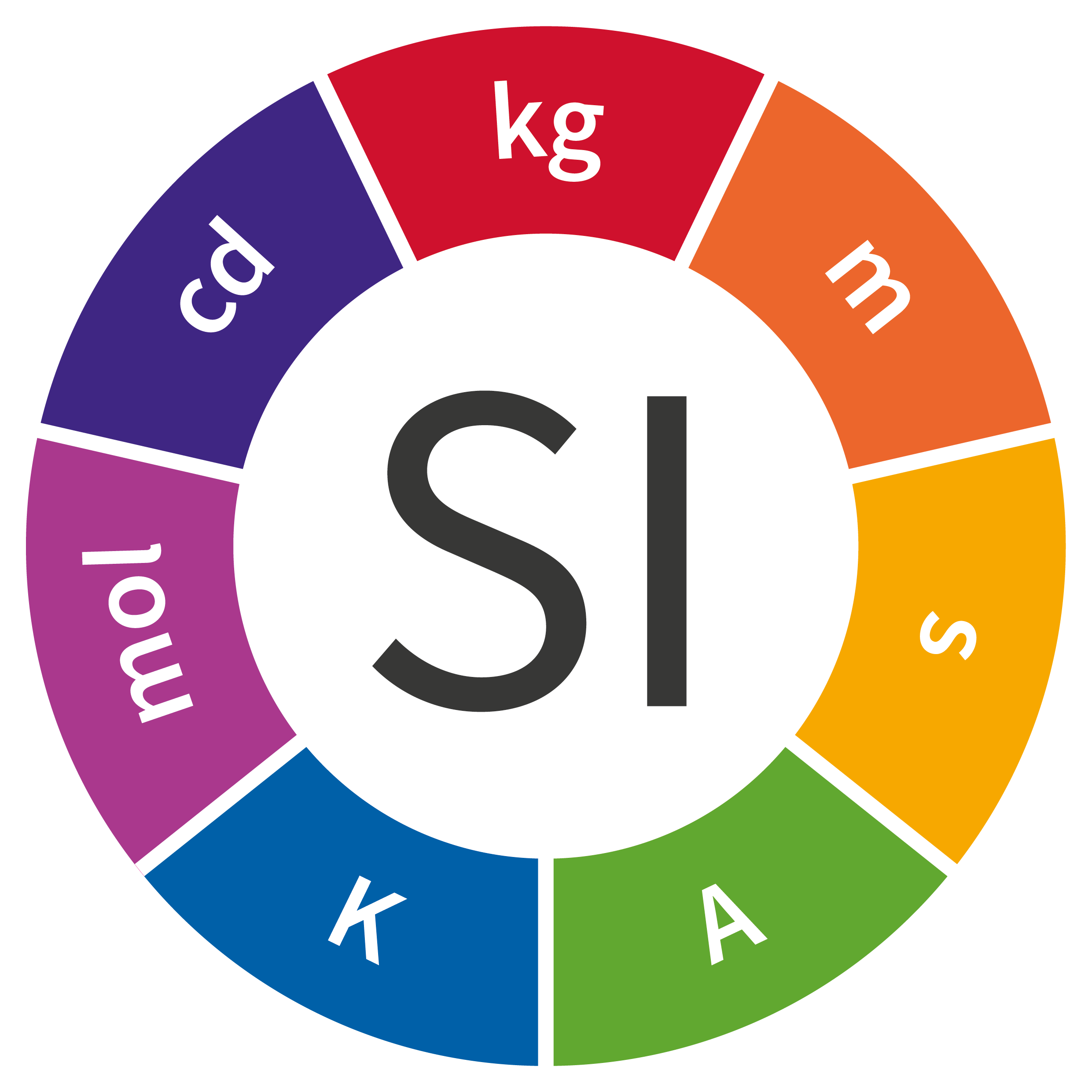
Amount of Substance
Mole
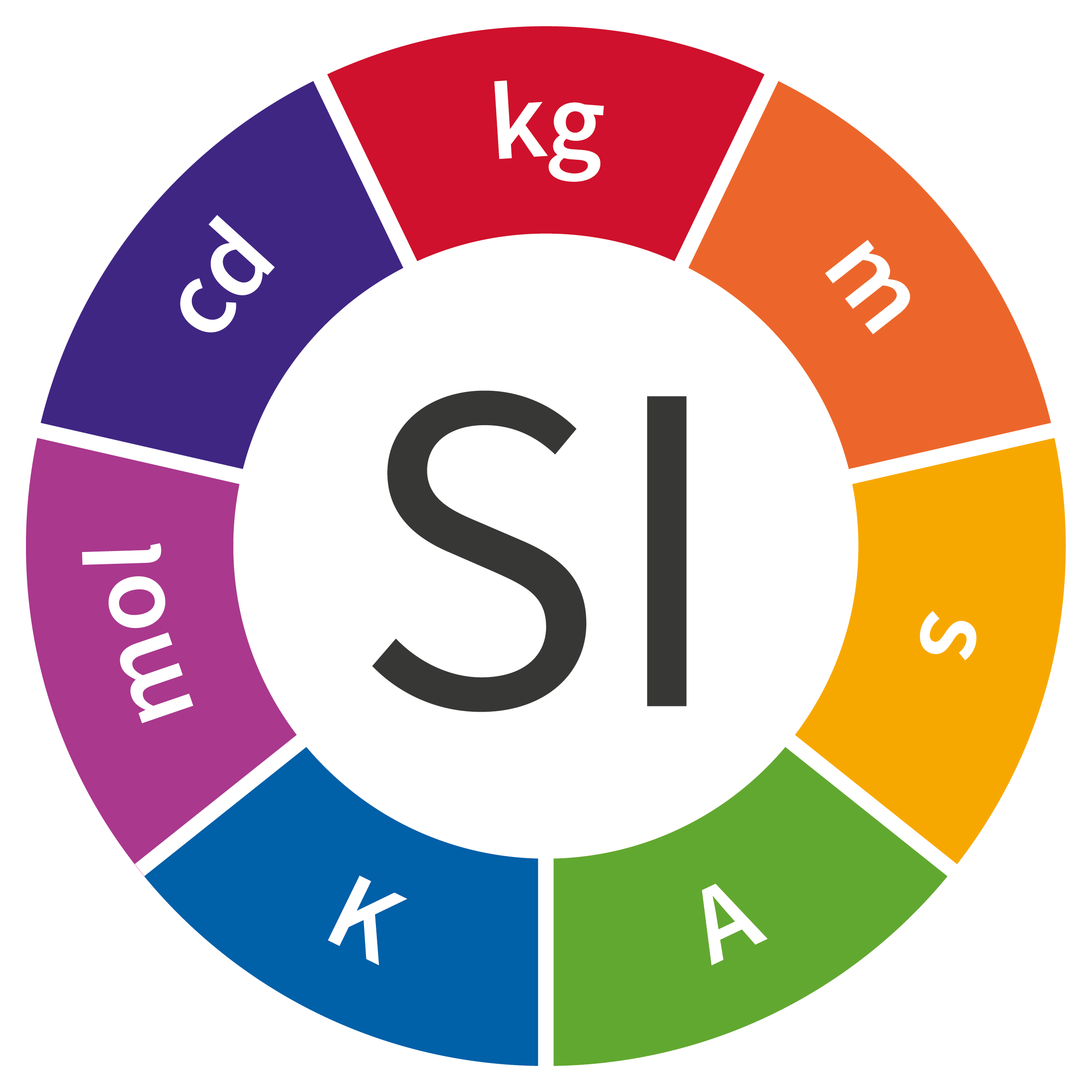
Luminous Intensity
Candela
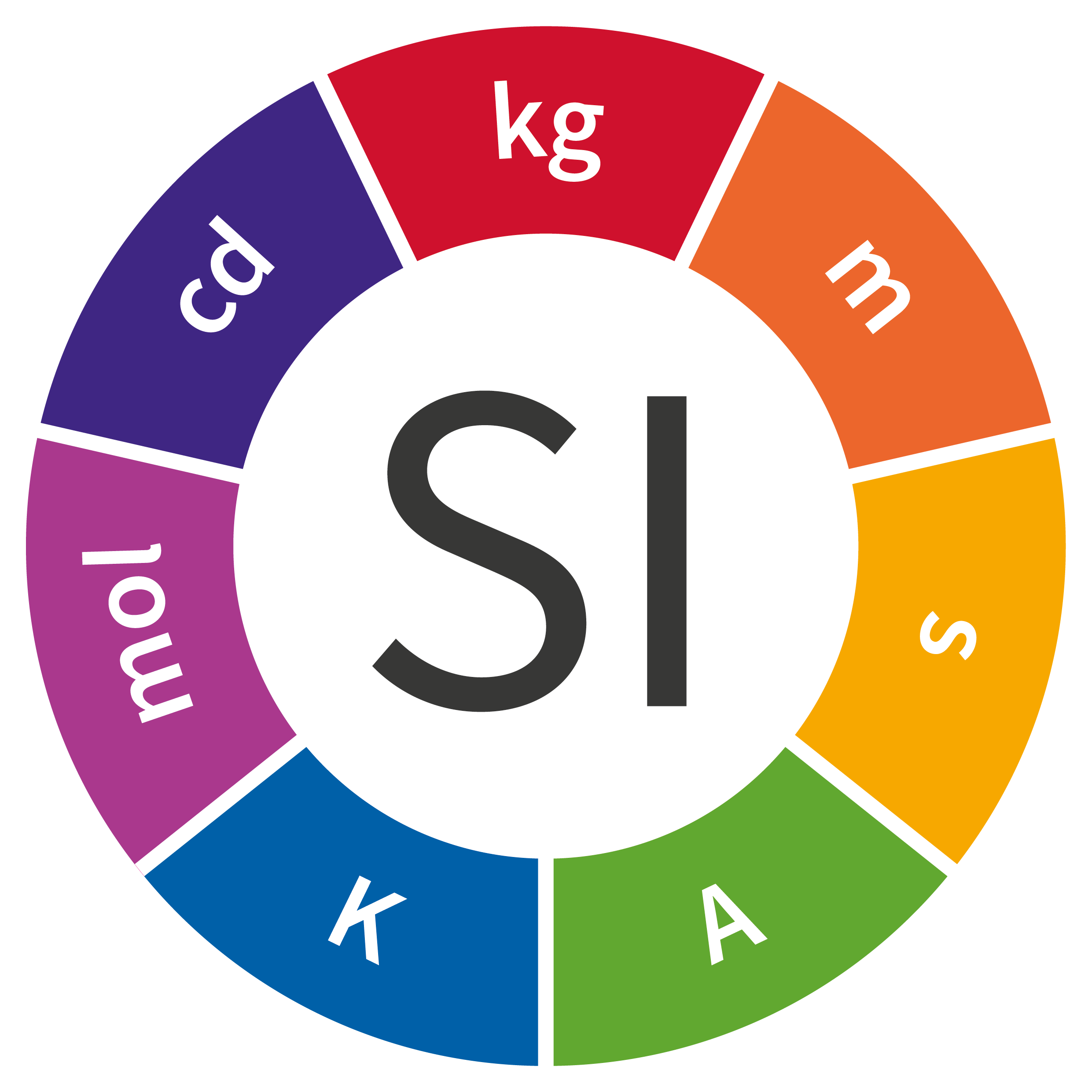
Meter
m
Kilogram
kg
Second
s
Ampere
A
Kelvin
K
Mole
mol
Candela
cd
Force
Neuton
Electric Charge
Coulomb
Celsius Temp.
Degree Celsius
Fahrenheit Temp
Degree Fahrenheit
Neuton
N
Coulomb
C
Degree Celsius
℃
Degree Fahrenheit
℉
10^12
Tera
10^9
Giga
10^6
Mega
10³
Kilo
10²
Hecto
10^1
Deka
10^-1
Deci