Chemical Bonding: Ionic, Covalent, and Metallic Bonds with Lewis Structures
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
What are the electrostatic forces that hold groups of atoms or ions together called?
Chemical bonds
What type of bond involves transferred electron(s)?
Ionic bond
What type of bond involves a shared electron pair?
Covalent bond
What is the term for a 'sea' of shared electrons in metallic bonding?
Metallic bond
Who proposed the Lewis Theory of bonding?
Gilbert Lewis in 1916
What does the octet rule state?
Atoms tend to lose, gain, or share electrons to achieve a noble gas electron configuration (filled shell).
What is the maximum number of electrons hydrogen can hold?
2 electrons (duet) in the 1s orbital
What do Lewis symbols represent?
Elemental symbols with dots indicating valence electrons.
What do unpaired dots in Lewis symbols indicate?
Bonding capacity
What is an anion?
A negatively charged particle that gains electron(s).
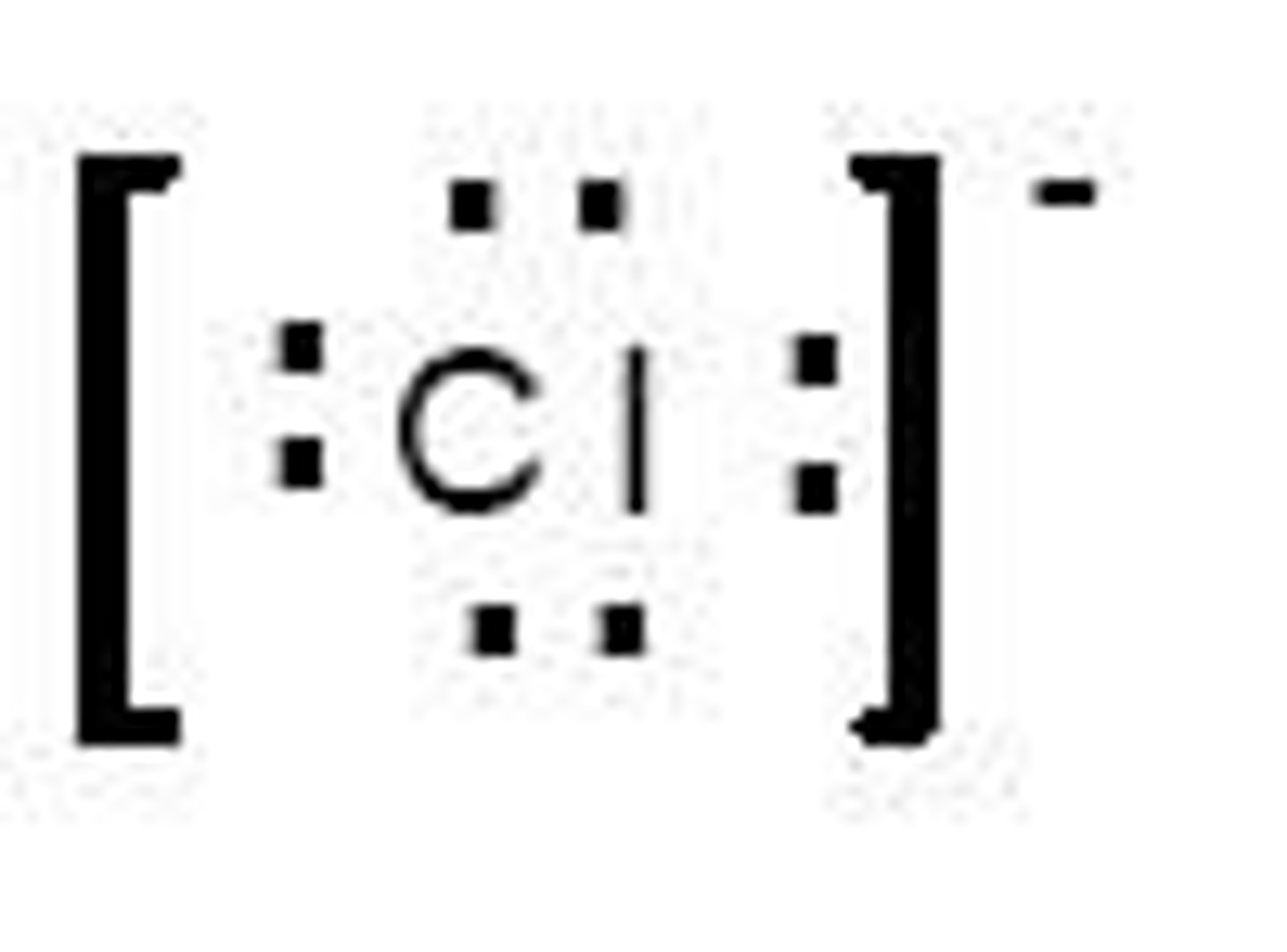
What is a cation?
A positively charged particle that loses electron(s).
What is lattice energy?
The energy required to completely separate one mole of a solid ionic compound into gaseous ions.
How does lattice energy change with ion size?
Larger ions result in weaker attraction and smaller lattice energy.
How does lattice energy change with ion charge?
Larger charges result in stronger attraction and larger lattice energy.
What is the trend in melting points of ionic compounds?
Ionic compounds generally have high melting points due to strong attractions between ions.
What is the octet rule in relation to covalent bonds?
Atoms share electrons to achieve eight electrons in their outer shell.
What is a Lewis electron-dot formula?
A formula using dots to represent valence electrons.
What do bonding pairs of electrons represent in Lewis structures?
Pairs of electrons shared between two atoms in a covalent bond.
What is a lone pair of electrons?
An unshared pair of electrons associated with one atom.
What happens to the energy of two hydrogen atoms as they approach each other?
The energy decreases until a minimum is reached, then increases dramatically.
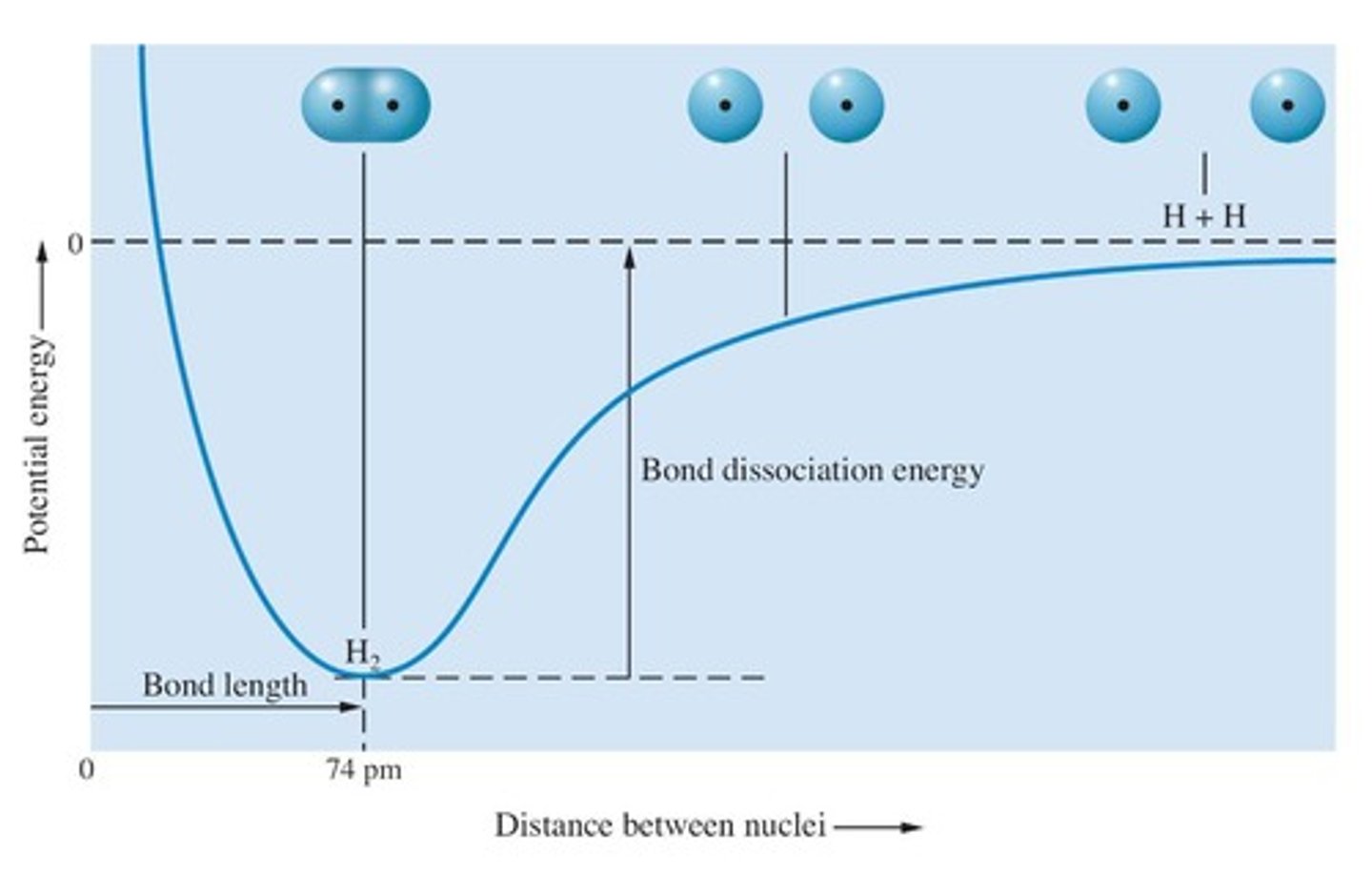
What is the bond length?
The distance between atoms when energy is at a minimum.
What is the significance of the electron affinity in ionic bonding?
It is the energy change when an electron is added to an atom.
What is ionization energy?
The energy required to remove an electron from an atom.
What is the relationship between ionic compounds and electrical conductivity?
Ionic compounds conduct electricity when dissolved in water or in liquid state.
What is the general behavior of ionic solids when struck?
They are brittle and shatter.
What is the role of the electron in forming covalent bonds?
Electrons are shared between nonmetals to achieve noble gas configurations.
What is the energy change when ionic compounds form?
Energy is released, making the overall process exothermic.
What does the term 'isoelectronic' refer to?
Atoms or ions that have the same electron configuration as a noble gas.
What is a single bond?
Two atoms sharing one pair of electrons.
What is a double bond?
Two atoms sharing two pairs of electrons.
What is a triple bond?
Two atoms sharing three pairs of electrons.
What do Lewis structures represent?
The positions of electrons in a molecule, indicating bonding and lone pairs.
What is a coordinate covalent bond?
A bond formed when both electrons of the bond are donated by one atom.
How does a polar covalent bond differ from a nonpolar covalent bond?
In a polar covalent bond, bonding electrons spend more time near one atom, while in a nonpolar bond, they are shared equally.
What is electronegativity?
A measure of an atom's ability to draw bonding electrons to itself.
How does electronegativity change across the periodic table?
Electronegativity increases from the lower-left corner to the upper-right corner.
What is the significance of the difference in electronegativity (ΔEN)?
It helps determine the polarity of a bond; larger differences indicate more polar bonds.
What is the electronegativity range for a polar covalent bond?
0.5 to 1.9.
What is the electronegativity range for an ionic bond?
Greater than or equal to 2.0.
What is the first step in writing Lewis dot formulas?
Total all valence electrons in the molecular formula.
What is the second step in writing Lewis dot formulas?
Arrange the atoms radially, placing the least electronegative atom in the center.
What is the third step in writing Lewis dot formulas?
Count the number of electrons required to give every atom an octet.
What happens if you have more available electrons than needed in Lewis structures?
Distribute the excess electrons to satisfy the octet rule.
What is delocalized bonding?
A type of bonding where a bonding pair of electrons is spread over multiple atoms.
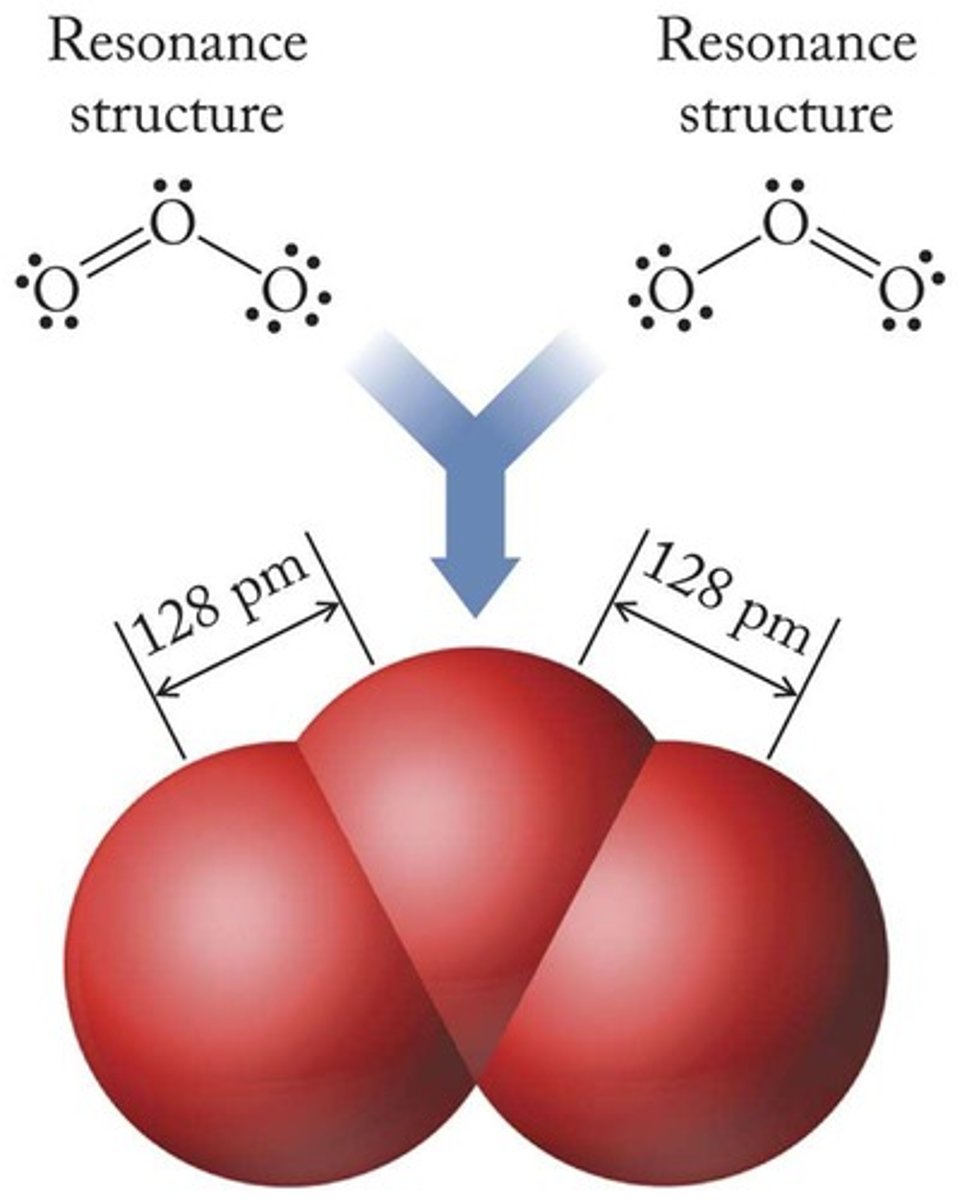
What are resonance structures?
Different Lewis structures that represent the same molecule with delocalized electrons.
How are bond lengths in ozone (O3) related to resonance?
Both bond lengths in ozone are identical due to delocalized bonding.
What is the significance of shared electrons in Lewis structures?
Shared electrons count toward the stability of each nucleus, contributing to the octet rule.
What is the octet rule?
Atoms tend to bond in such a way that they have eight electrons in their valence shell.
What is the role of lone pairs in Lewis structures?
Lone pairs represent non-bonding electrons that can affect molecular shape and reactivity.
What is the difference between bonding pairs and lone pairs in Lewis structures?
Bonding pairs are shared between atoms, while lone pairs are not involved in bonding.
What is the formula for calculating the total number of electrons in PCl3?
Total valence electrons = 5 (P) + 3 × 7 (Cl) = 26 electrons.
What is the electron configuration of hydrogen in a covalent bond?
Hydrogen achieves a stable configuration with two valence electrons.
What is the electron configuration of chlorine in a covalent bond?
Chlorine achieves a stable configuration with eight valence electrons.
What is the bond length in relation to bond order?
As bond order increases, the bond length decreases.
What is a resonance structure?
A resonance structure represents a molecule where electron distribution can be depicted in multiple ways.
What is the formula for calculating formal charge (FC)?
FC = (# valence electrons) - [# nonbonding e- + ½(# bonding e-)]
What are the criteria for choosing the most stable resonance structure?
1. Formal charges equal or close to zero. 2. Negative formal charges on the more electronegative element.
What is an example of an electron-deficient molecule?
BF3 is an example of a molecule with fewer than eight electrons.
What is a free radical?
A molecule with an odd number of electrons, making it highly reactive.
What is meant by an expanded valence shell?
Atoms with more than eight electrons in their valence shell, such as in SF6.
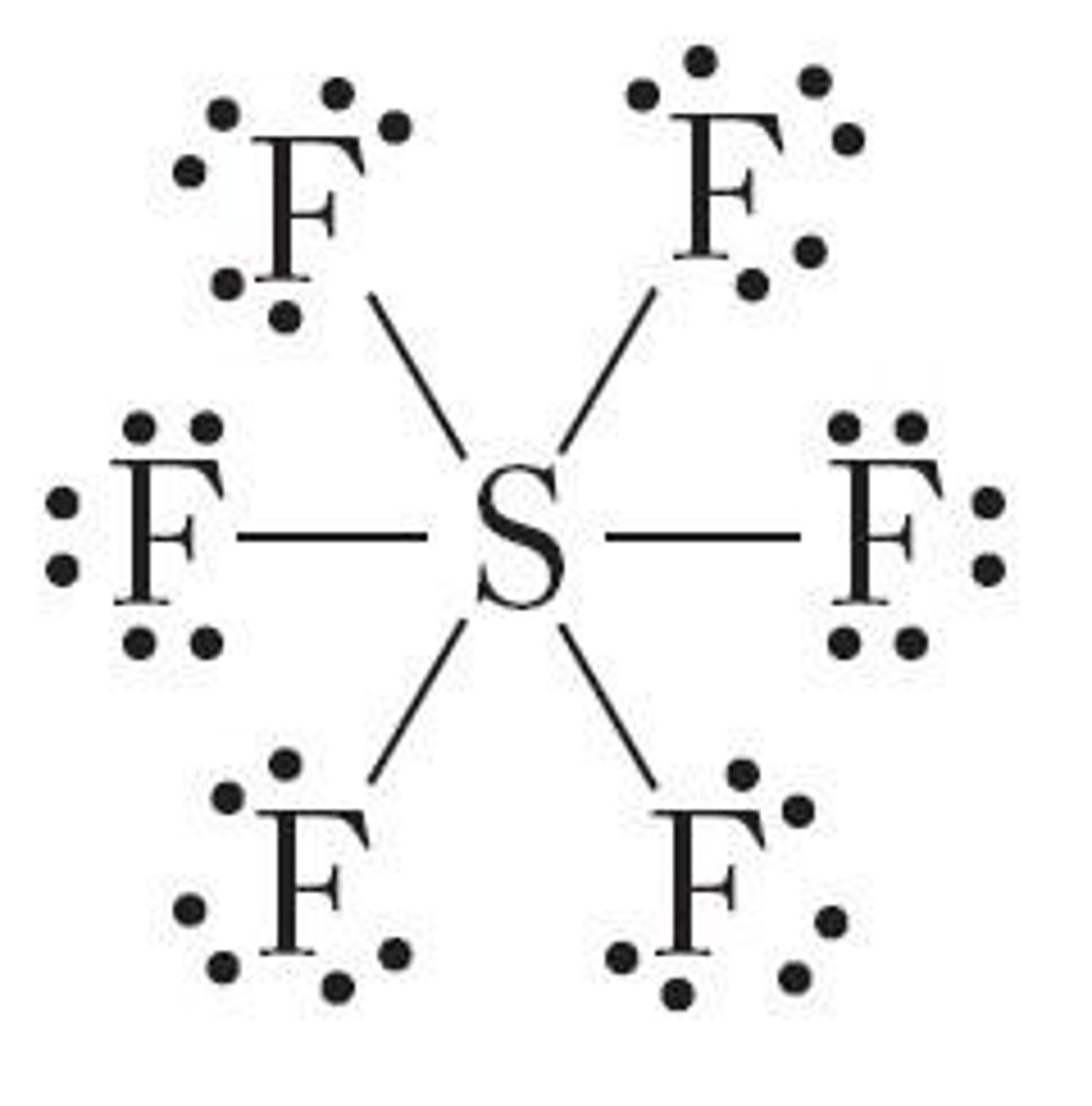
What is the bond energy?
The energy needed to break one mole of covalent bonds in the gas phase.
What happens to bond energy when bonds are formed?
Forming bonds releases energy.
What is the bond order for a single bond?
The bond order for a single bond is 1.
What is the bond order for a double bond?
The bond order for a double bond is 2.
What is the bond order for a triple bond?
The bond order for a triple bond is 3.
What does the bond length depend on?
Bond length depends on the identity of the atoms and the number of bonds between them.
What is the significance of formal charges in Lewis structures?
Formal charges help determine the most likely electron-dot formula for a molecule.
What does a higher bond order indicate about bond strength?
A higher bond order indicates a stronger bond.
What is the relationship between bond length and bond energy?
As bond length decreases, bond energy increases.
What is the bond length of a C=C bond?
The bond length of a C=C bond is approximately 134 pm.
What is the bond length of a C-C bond?
The bond length of a C-C bond is approximately 154 pm.
What is the bond length of a C≡C bond?
The bond length of a C≡C bond is approximately 120 pm.
How does the presence of electronegative elements affect expanded valence shells?
Expanded valence shells occur when bonded to strongly electronegative elements.
What is the bond energy of a C-H bond?
The bond energy of a C-H bond is approximately 413 kJ/mol.
What is the bond energy of a C=O bond in CO2?
The bond energy of a C=O bond in CO2 is approximately 804 kJ/mol.
What is the bond energy of a N≡N bond?
The bond energy of a N≡N bond is approximately 945 kJ/mol.
What is the significance of using bond energies to estimate ΔHrxn?
Using bond energies allows for estimating the enthalpy change of a reaction.
What is the bond energy of an O=O bond?
The bond energy of an O=O bond is approximately 498 kJ/mol.
What is the bond energy of a Cl-Cl bond?
The bond energy of a Cl-Cl bond is approximately 242 kJ/mol.
What is the relationship between metallic bonding and conductivity?
Metallic solids conduct electricity well due to the delocalized electrons.
What happens to the electrical conductivity of metals as temperature increases?
The electrical conductivity of metals decreases as temperature increases.