UF BACE Practice missed Qs
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Which of the following should be used to calculate the amount of compound required to make a solution?
Molecular weight
Carbohydrates
Example: cellulose. Functions: energy storage, receptors, structure of plant cell wall.
Lipids
Example: cholesterol. Functions: membrane structure, energy storage.
The enzyme maltase catalyzes the break down of maltose into glucose. A technician added maltase to a solution of maltose to be incubated at 37°C. Samples were taken from the reaction tube every five minutes over the course of one hour, to measure the glucose concentration. After an hour, the technician noticed the water bath failed to reach 37°C (it only warmed to 25°C).
Which of the following is the most likely outcome of the reaction?
The enzyme activity would decrease, yielding the same level of glucose over a longer time period.
Circular, long DNA containing several thousand genes
Prokaryotic DNA
Cytoplasmic, circular DNA containing only a few genes
Plasmid DNA
Select the option that represents the correct order of assembly in the cell:
Amino acid, polypeptide, protein
How does DNA differ from one species to another?
The number of genes and non-coding regions
When transforming a DNA code to an mRNA code how would the ATGC change?
A becomes U , T becomes A, GC stays the same
The three-dimensional structure of a protein is largely determined by the amino acid sequence.
True
A single base pair change in a gene's DNA sequence can affect the shape and function of the protein it encodes.
True
Which of the following features of bacterial plasmids can be used as a marker when growing bacterial cultures?
Antibiotic resistance gene
The observable traits of an organism are referred to as the:
Phenotype
collection of genes responsible for the various genetic traits of a given organism. It refers specifically to the genes, not the traits; that is, the raw information in an organism's DNA. An allele can be made up of two dominant genes, a dominant and a recessive gene, or two recessive genes.
Genotype
Which type of ELISA is the most appropriate to determine the concentration of a specific antigen in a sample?
Quantitative ELISA
Which of the following is typically measured using a spectrophometer set at a wavelength of 600 nm?
The concentration of bacteria in a suspension
hypothesis
testable explanation for a scientific problem or question.
"Bioethics" is best described as:
The study of decision making as it applies to moral decisions that must be made due to advances in biology and technology.
Sumpter and Jobling concluded that the expression of vitellogenin in male fish was dependent on the concentration of industrial chemicals in the environment.
Which of the following assays would most likely be used to measure how much vitellogenin is in a blood sample?
ELISA
Bradford assay
colorometric assay used to measure protein concentration.
BSA
Bovine Serum Albumin
What is Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA)?
protein used to generate a standard curve when performing a Bradford assay, to determine the protein concentration of samples
A technician is asked to streak plates with E. coli using the quadrant method. To start, the technician dips the sterile loop into the inoculant stock and performs the first streak in quadrant 1 of the labeled agar plate.
Organize the following steps from 1 to 4 to continue the process into quadrant 2:
1. Flame the loop and let it cool/aseptically open a new disposable loop
2. Open the lid of the Petri plate just enough to insert the loop
3. Streak across quadrant 1 and into quadrant 2
4.Streak back and forth to cover quadrant 2
What is the purpose of using the quadrant method when streaking bacteria on agar plates?
To dilute out individual bacterial cells leading to isolated colonies
Qualitative
Data in the form of recorded descriptions rather than numerical measurements.
Quantitative
Data that is in numbers
Okazaki fragment
A short segment of DNA synthesized away from the replication fork on a template strand during DNA replication. Many such segments are joined together to make up the lagging strand of newly synthesized DNA.

Poly(A) tail
Modified end of the 3' end of an mRNA molecule consisting of the addition of some 50 to 250 adenine nucleotides.
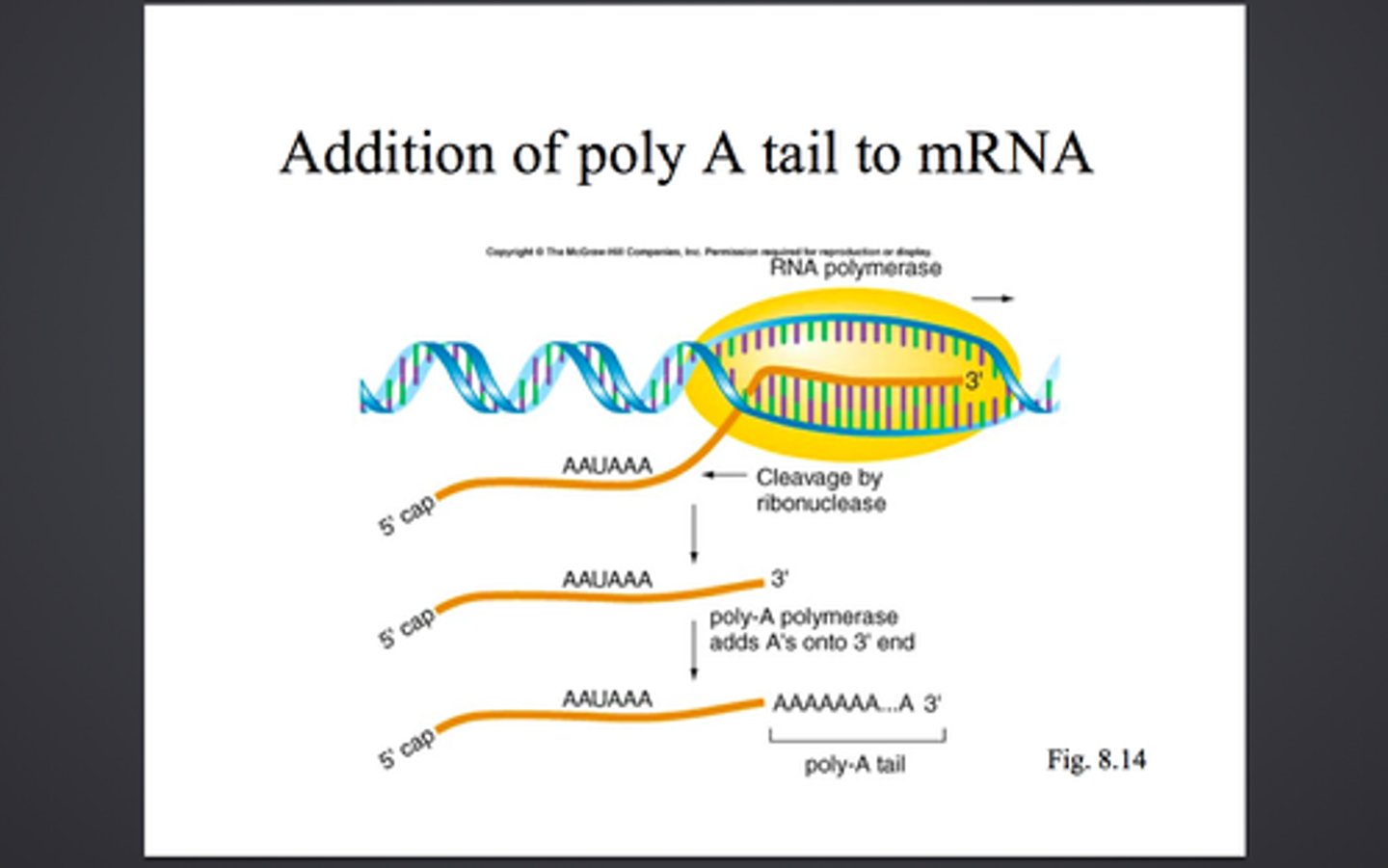
5' cap
The 5' end of a pre-mRNA molecule modified by the addition of a cap of guanine nucleotide.

Promoter
specific region of a gene where RNA polymerase can bind and begin transcription
Complimentary base pairing between two DNA strands is due to the formation of:
Hydrogen bonds
Cellulose is an important raw material for textiles and a variety of other industries. Which of the following is a function of polysaccharides in the cell?
Providing structure and energy storage within cells
Lipids are composed mainly of which of the following atoms?
Carbon and hydrogen
Carbohydrates are composed mainly of which of the following atoms?
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
Process which uses oxygen as a raw material
Aerobic Respiration
Process which releases carbon dioxide and ethyl alcohol
Anaerobic Respiration
Process by which glucose is utilized by a cell
Both Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
Process which uses carbon dioxide as a raw material
Neither Aerobic or Anaerobic Respiration
Why are enzymes necessary in living organisms?
Enzymes increase the rate of chemical reactions which would otherwise occur too slowly to sustain life.
Which of the following affects the rate of a chemical reaction?
concentration, prescence of a catalyst, heat
Made of four nitrogenous bases
all DNA
Contained in a nucleus
Eukaryotic DNA
Long, circular DNA with several thousand genes
Prokaryotic DNA
Small, circular DNA floating in the cytoplasm
Plasmid
Double helix structure of repeating nucleotides
all DNA
Linear, very long pieces of DNA with many thousands of genes
Eukaryotic DNA
When DNA replicates, each original strand of DNA serves as a template for a new strand. What type of replication is this?
Semi-conservative replication
Many enzymes used in biotechnology applications occur naturally within the cell. Which of the following enzymes are involved in DNA replication?
DNA Polymerase
epitope
The part of an antigen that is recognized by the immune system
Which of the following should NOT be used to disinfect an area that is potentially contaminated by DNA?
Alcohol
Objectives are located beneath the stage
Bright Field Microscope
Light source is located above the specimen
Inverted Microscope
Uses a laser light to scan samples that have been dyed
Confocal Microscope
Uses electrons to scan samples in near-vacuum conditions
Electron Microscope
Enzymes best retain their function__________
within a narrow pH range.
buffered solvent is made with a _______
a combination of a weak acid and its conjugate base
anion exchange column chromatography
process that separates substances based on their charges using an ion-exchange resin containing positively charged groups, such as diethyl-aminoethyl groups (DEAE). In solution, the resin is coated with positively charged counter-ions (cations).
What type of gel is typically used for protein electrophoresis?
Polyacrylamide
Which of the following can be used as vehicles for delivering new DNA to a cell?
Lipid, Plasmid, Virus
common technique used to transform bacteria
Electroporation
Why is a blocking step typically included in a western blot?
To prevent non specific binding of the antibody used for detection
Measuring protein or DNA concentration (Determining the amount of a protein present)
spectrophotometer
Determining the presence of a specific protein
ELISA
Determining the size and purity of a specific protein
SDS PAGE
Determining the time period protein remains active
Stability
Shaking is necessary to _____
oxygenate an aerobic liquid culture for optimal growth
Which of the following methods is used to obtain single, isolated bacterial colonies?
Streak plate method
Measures the hydrogen ion activity in water-based solutions
pH meter
A device for regulating the temperature of anything subjected to heat
Water bath
Measures and delivers volumes under 1.0 mL
Micropipet
Used to quantify biological or chemical events within a microtiter plate
Plate reader
Used to measure the absorption of light by a substance in order to quantify it
Spectrophotometer
Connects to an electrophoresis tank to create an electric field between the electrodes
Power supply
Which of the following is the correct method to make 1 L of 10% sodium chloride?
Dissolve the appropriate amount of sodium chloride in a small volume of dH2O, then adjust the volume to 1 L
Monoclonal antibodies
a collection of identical antibodies that interact with a single antigen site (clones of a unique parent cell)
BamH I
a type II restriction endonuclease, having the capacity for recognizing short sequences of DNA and specifically cleaving them at a target site.

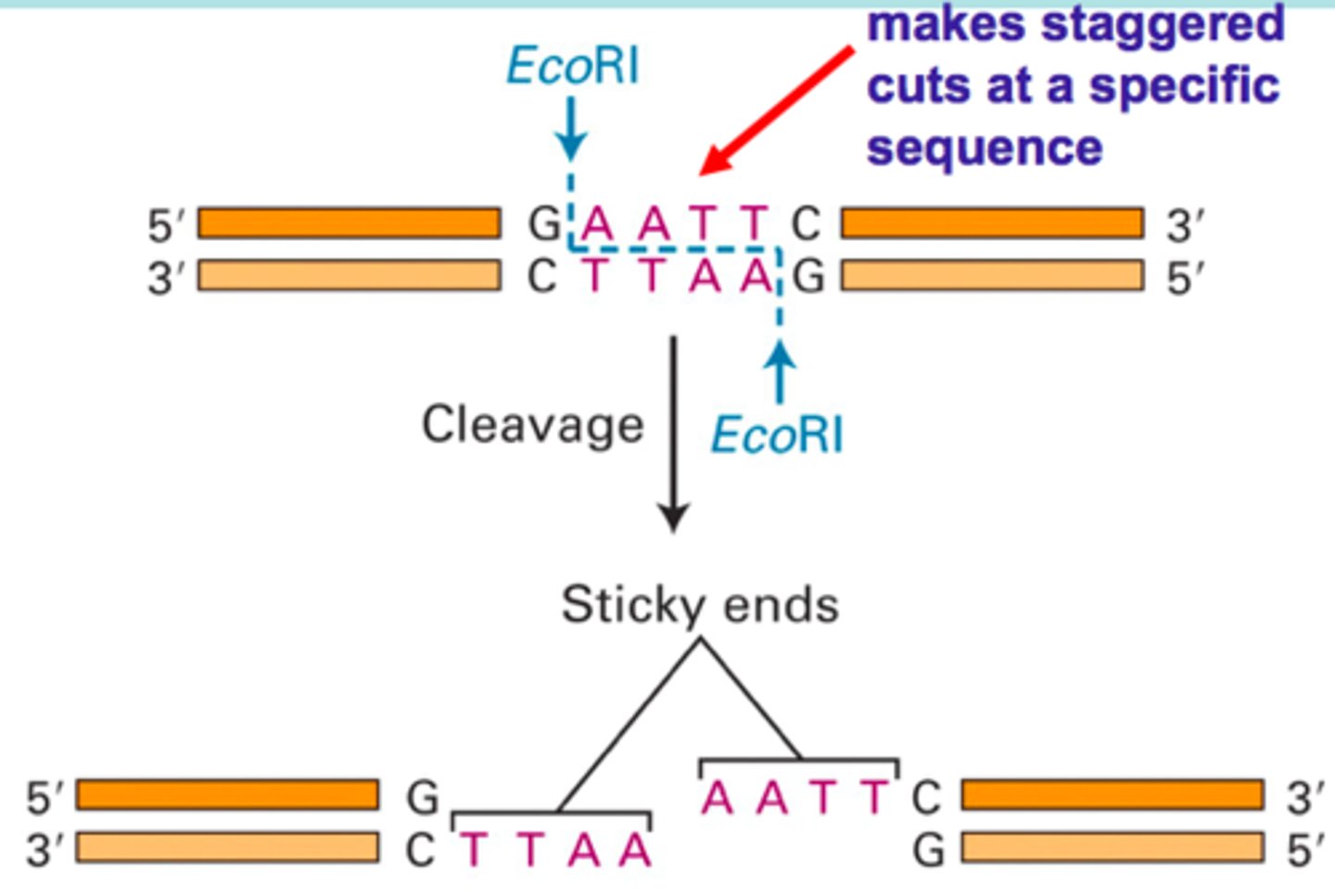
EcoRI
a restriction enzyme that specifically cuts DNA with sequence GAATTC and creates sticky ends
HindIII
type II site-specific deoxyribonuclease restriction enzyme (used to digest DNA)
Which type of ELISA is the most appropriate to determine the concentration of a specific antigen in a sample?
Quantitative