electrode potential
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
half cells = ?
half equation which contains non metals
what is the most common half cells
Hydrogen gas with H+ or uses platinum
what are the standard conditions ?
100 KPa , 298 K and 1.00 mol dm-3 soulatioms
some solutions will have variable oxidation states
Fe 2+ or Fe3+
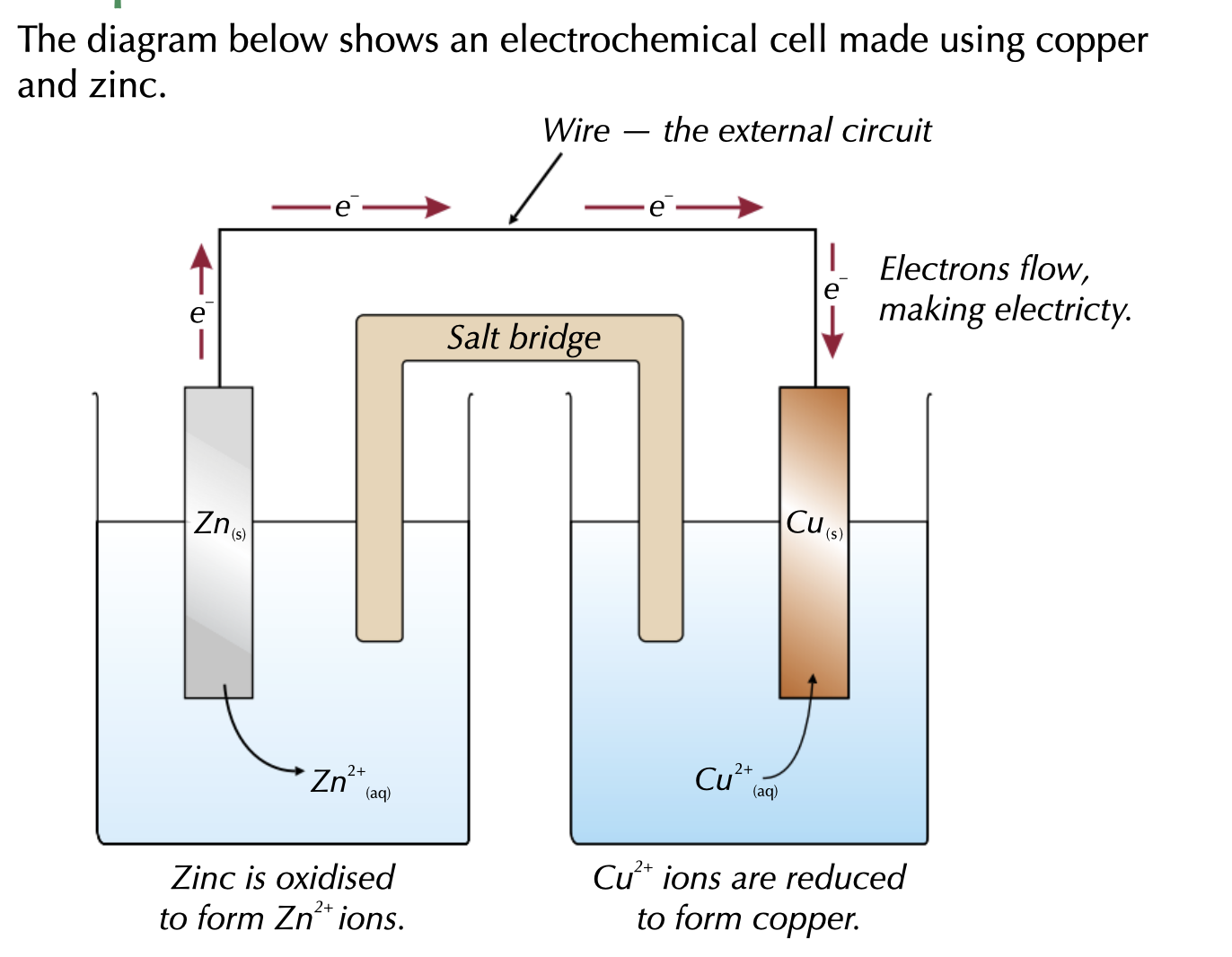
direction of the electrons will depend on ?
on other half cells in the circuit.
before the potential of any half cell could be measured, a potential assigned to one particular half cell
electrode chosen was standard hydrogen electrode ( SHE ) and this electrode is assigned the potential of 0 volts
SHE
is a primary standard as it’s the potential to which all others are compared.
standard hydrogen electrode
H2(g) 298K / 100 kPa / 1.00 mole dm-3 → Pt electrode allow equilibrium between H2 and H+
assigned an electrode potential E0 of 0.00 V
2H+ (aq) + e- ↔ H2(g) reduction
Pt electrode provide a sink / source of electrons , which go through a conductor “ metal”
connect SHE to another electrode to records the potential difference ( voltage )
standard electrode potential def
The SEP or E° of a system is defined as the measured potential difference between the two electrodes of a cell in which the potential of the electrode of interest is measured relative to the standard hydrogen electrode and in which all the chemical species have a concentration of 1M.
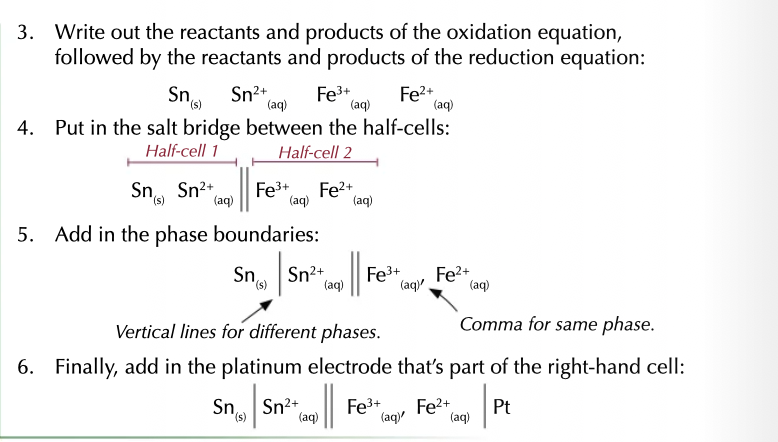
representing cells
most positive on right
Reduced | oxidised || oxidised | reduced
ROOR
vertical line separate phases double line for salt bridge insert metals on the outside.
calculating electrode potential
E0 cell = E0 RHS - E0 LHS
results should be positive for the reaction to be feasible or spontaneous.
Combining half cells together
Before the potential of any half-cells could be measured, a potential had to be assigned to one particular half-cell (then the potential of all the other electrodes could be measured against it).
When two half cells are combined together the resulting electrochemical cell has:
a positive terminal;
a negative terminal.
The half cell with the more positive electrode potential becomes the positive terminal and electrons flow towards it.

factors that affect the electrode potential
temp, con.c and pressure

standard electrode potential
more negative = stronger reducing agent, easier to lose electrons
go most easily from right to left
Most negative electrode in a cell will always produced the electrons.
add pic
add exam QUESTIONS