Body Tissues and Histology Anatomy and Physiology Honors Unit 2
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What is Epithelial tissue?
Epithelial tissue is the lining tissue that
forms the boundary between our body and
the external environment.
Epithelial tissue functions include: Protection, Absorption, Filtration, Secretion
What is the top surface of an epithelial tissue called?
Free surface/Apical surface
What is the bottom surface of an epithelial tissue called?
The Basal Surface
What is the membrane underneath the basal surface called?
The Basement membrane
All of the tissues within the Epithelial tissue are?
Avascular (No blood vessels)
How are Epithelial tissues classified?
By the number of layers and the shape of the cells
What is the difference between Simple Epithelial Tissue and Stratified Epithelial tissue?
Simple Epithelial Tissue: One layer of cells
Stratified Epithelial tissue: More than one layer of cells
Describe what a Simple Squamous epithelium tissue is:
Simple Squamous epithelium tissue: A single, flat layer of cells that is thin
and permeable.
• Function: rapid diffusion of materials
• Found in blood vessels & lung tissues
Describe what a Simple Cuboidal epithelium tissue is:
Simple Cuboidal epithelium tissue: A single layer of cube-shaped cells.
• Function: Secretion & absorption of
substances
• Found in the tissues of the kidney
Describe what a Simple Columnar epithelium tissue is:
Simple Columnar epithelium tissue: A single layer of tall, closely packed cells. May have cilia and goblet cells, which secrete
mucus
• Function: Secretion of mucus for protection &
absorption of substances
• Found in the lining of the digestive tract Cilia (hair-like extensions)
Describe what a Stratified Squamous Epithelium is:
These thick layers which provide protection for the
underlying layers. Squamous above, cube layer below.
Found in the epidermal layer of the skin
Describe what a Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium is:
More than one layer of cuboidal cells and is rare in the body
Found in salivary & mammary glands
Describe what a Stratified Columnar Epithelium is:
Free surface is lined with columnar cells and is also rare in the body
Found in your larynx and the male urethra
Describe what a Pseudo-Stratified Epithelium is:
Pseudo-stratified epithelium: cell nuclei
are found at different levels, so it appears
stratified, though it is not.
Function: Secretion & Absorption
Found in most of the upper respiratory
tract
Describe what a Transitional Epithelium is:
The free surface cells of transitional epithelium vary in appearance based on the stretching of the tissue. “Transition” meaning change shape with elasticity
Found in the lining of
the urinary bladder
What is glandular epithelium?
A gland is made of a
group of cells that
secrete a fluid
substance.
Glands are classified in
two ways:
Complexity and How substances are
secreted (Exocrine and Endocrine)
What is the difference between Endocrine and Exocrine glands?
Exocrine Gland: Secretes Substances outwards through a duct (Sweat glands for example)
Endocrine Gland: Ductless glands that secrete hormones through bloodstream (Thyroid gland for example)
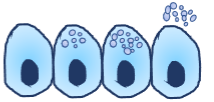
What is the Merocrine Gland? (A type of exocrine gland)
Cells excrete the products (substances) via exocytosis. Mero meaning “part”.
Examples: Sweat Glands
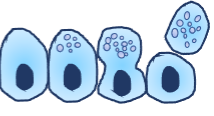
What is the Apocrine Gland? (A type of exocrine gland)
A portion of the cell pinches off with the secreted products. Apo = “tip”.
Example: Mammary Glands
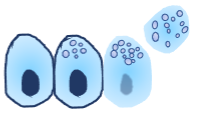
What is the Holocrine Gland? (A type of exocrine gland)
Cells rupture and spill products into the duct. “Hol” = whole.
Example: Sebaceous (oil) glands in skins
What is the overall summary of the Endocrine glands?
Endocrine glands secrete hormones into the blood
so they can be delivered over longer distances. Endocrine cells are packed tightly together with
capillaries running through the glandular tissue. Cells excrete products through exocytosis into the
blood.
Glandular tissue is a specialized type of
epithelial tissue. Endocrine glands secrete hormones into the blood, while exocrine glands use tube-like ducts to secrete their products. Exocrine glands differ in the portion of the cell that is secreted with the product.
Describe the Hyaline
Describe Elastic Cartilage
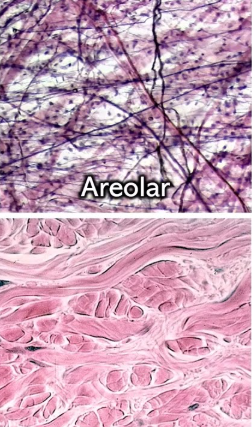
Which connective tissue is this?
Areolar
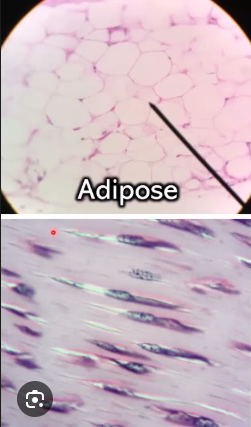
Which connective tissue is this?
Adipose
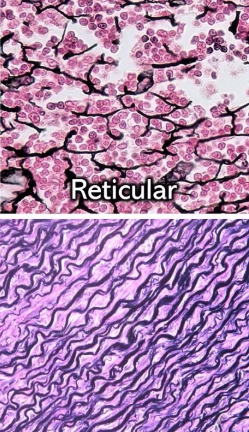
Which connective tissue is this?
Reticular
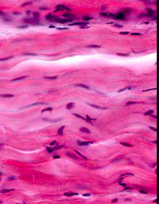
Which connective tissue is this?
Regular
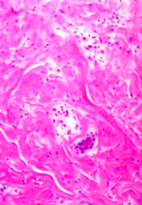
Which connective tissue is this?
Irregular
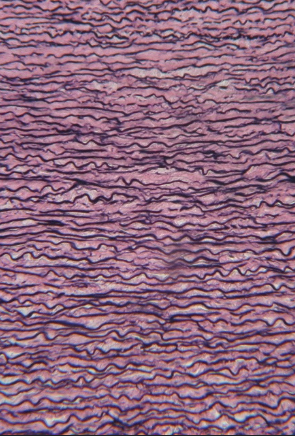
Which connective tissue is this?
Elastic
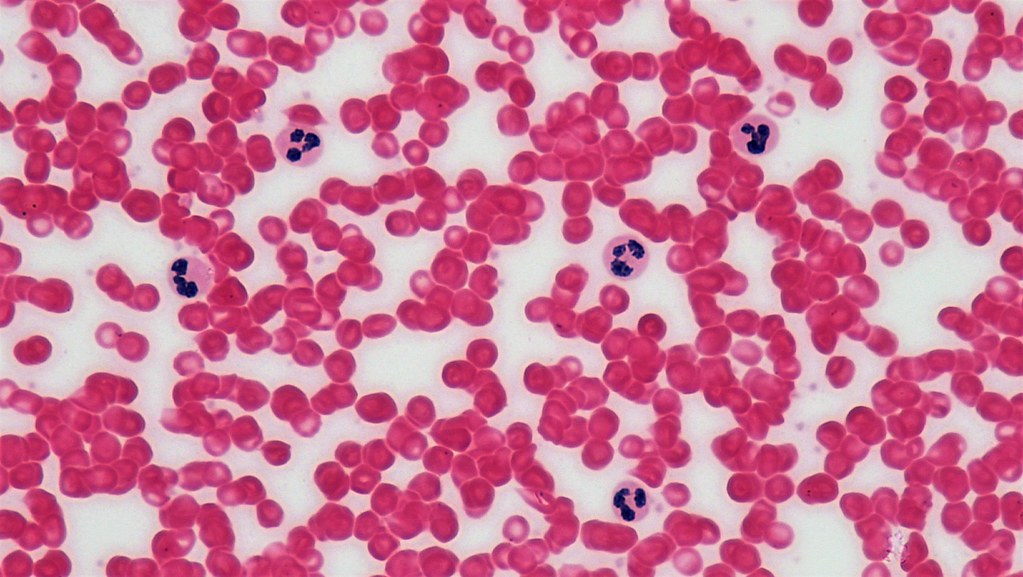
Which connective tissue is this?
Blood
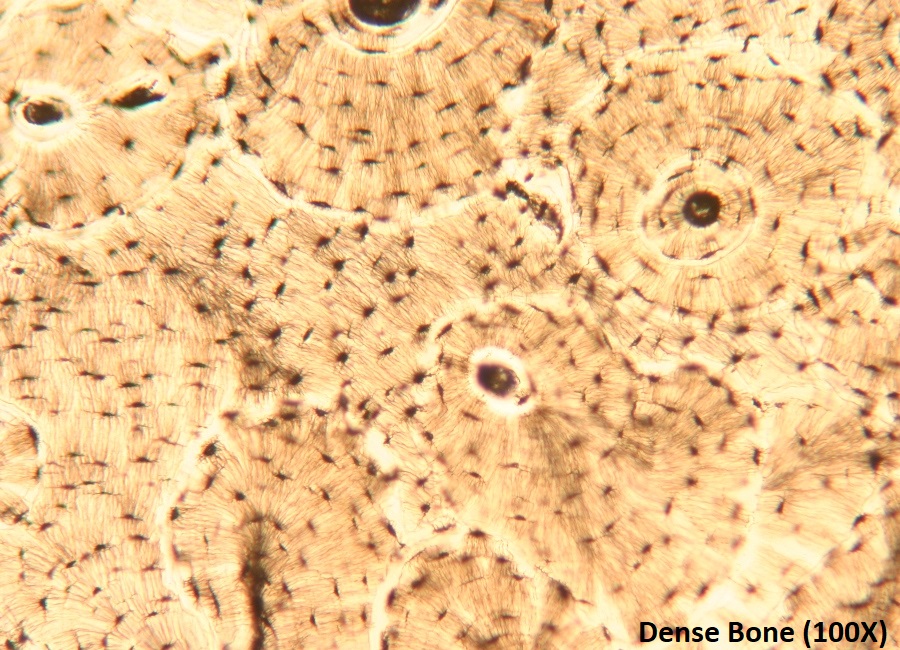
Which connective tissue is this?
Bone
What is the smooth muscle?
Description: The smooth muscle is non-striated and controls involuntary movement throughout the body. They tend to have one nucleus per cell and have slower contractions due to sustaining longer periods.
Function: Smooth muscle is responsible for moving substances through different tracts and regulating internal flow/pressure.
Found Where: Smooth Muscle is found in the digestive tract (walls of stomach/intestines), blood vessels (veins/arteries), respiratory tract, eyes, bladder and uterus.
Cardiac Muscle
Description: The Cardiac Muscle is striated/branched fibers and controlled involuntary movement, it usually contains one cell and does not fatigue under normal conditions.
Function: The Cardiac Muscle is responsible for pumping blood through the body and maintaining a consistent heartbeat to keep the body in rhythm.
Found Where: Found only in the heart muscles.
Skeletal Muscle
Description: The skeletal muscle is striated/striped appearance and controls voluntary movement; it has multiple nuclei and has quicker contractions which fatigues easily.
Function: Responsible for voluntarily movements of skeleton, controls posture and provides heat protection.
Found where: in bones, tendons, biceps, triceps, quads, etc…
Nueroglia
Description: Known as Glial Cells, supports and protects cells in the nervous system, responsible for 90% of all nerve cells and unable to transmit impulses.
Function: Regulate the environment around the neurons, supports and protects the neuron’s structure and functions, can regenerate after injury but cannot generate nerve impulses, and aid in repair.
Nuerons
Description: Neurons are responsible for 10% of nerve cells, they are unable to regenerate, longest life span cells, and includes Soma (Nucleus)/Dendrites (Receives signals)/Axon (Sends signals away) in the structure.
Function: Converts stimuli into nerve impulses, transmits information, passes impulses to other neurons/muscle fibers/or glands.