NURS3804 Chapter 12: Fluid Volume and Electrolytes
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
- 0.9% NaCl
- lactated ringers
What are examples of isotonic IV fluids?
- expands blood volume
- dilutes medications
- keeps vein open
What are functions of 0.9% NaCl?
fluid resuscitation
What is the main function of lactated ringers?
- D5W is isotonic until it metabolizes glucose
- it then becomes hypotonic
Explain the tonicity of dextrose 5% in water (D5W).
- infants
- head injury
What are contraindications for D5W?
- decreased pH
- increased CO2
- decreased HCO3
How does acidosis affect pH, CO2, and HCO3?
- increased pH
- decreased CO2
- increased HCO3
How does alkalosis affect pH, CO2, and HCO3?
hypoventilation which can be caused by:
- sedation
- airway obstruction
- mechanical ventilation
- neuromuscular disease
- pulmonary edema
- increased ICP
What causes respiratory acidosis?
- diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)
- shock
- severe diarrhea
- renal failure
- salicylate overdose
- dehydration
- liver failure
What causes metabolic acidosis?
hyperventilation which can be caused by:
- anxiety
- high altitudes
- mechanical ventilation
- acute pulmonary problems
What causes respiratory alkalosis?
- loss of gastric juices
- diuretics
- overuse of bicarbonate
- Cushing's syndrome: excess cortisol results in excretion of K+
What causes metabolic alkalosis?
- confusion
- dysrhythmias
- hypoventilation
- dizziness
- increased irritability
- nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
- anxiety
- seizures
- tremors
- muscle cramps
- tingling of fingers and toes
What are signs and symptoms of metabolic alkalosis?
- headache
- hypotension
- hyperkalemia
- muscle twitching
- warm, flushed skin
- nausea, vomiting
- decreased muscle tone and reflexes
- Kussmaul respirations: hyperventilation
What are signs and symptoms of metabolic acidosis?
- rapid, shallow respirations
- hypotension
- pale or cyanotic skin and mucosa
- headache
- hyperkalemia
- dysrhythmias
- drowsiness
- dizziness
- muscle weakness
- hyperreflexia
What are signs and symptoms of respiratory acidosis?
- hyperventilation
- tachycardia
- decreased or normal BP
- hypokalemia
- numbness and tingling of extremities
- hyper reflexes and muscle cramping
- seizures
- increased anxiety and irritability
What are signs and symptoms of respiratory alkalosis?
intracellular
Is the majority of the fluid in the body intracellular or extracellular?
275-290 mOsm/kg
What is the osmolality for isotonic solutions?
they do not affect the cells, but they do increase the ECF
How do isotonic solutions effect the cells?
< 250 mOsm/kg
What is the osmolality for hypotonic solutions?
cause them to swell
How do hypotonic solutions effect the cells?
> 375 mOsm/kg
What is the osmolality for hypertonic solutions?
cause them to shrink
How do hypertonic solutions effect the cells?
- fluid volume overload can cause edema
- prolonged infusions may lead to alkalosis or acidosis
- rapid infusion may lead to hypernatremia and electrolyte depletion
What are complications of isotonic IV fluids?
- monitor I/O's and electrolytes
- monitor for s/s of fluid volume excess
- monitor liver function of patients receiving LR since the liver metabolizes lactate
What are nursing considerations for isotonic IV fluids?
- 0.45% NaCl
- 0.33% NaCl
- 0.25% NaCl
What are examples of hypotonic IV fluids?
- hypernatremia
- hyperglycemia
- used as a maintenance fluid
What are indications for hypotonic IV fluids?
- fluid overload
- decreased electrolyte concentrations
- over hydration
- pulmonary edema
- rapid infusion may lead to hemolysis of RBCs
What are complications of hypotonic IV fluids?
- monitor I/O's and electrolytes
- monitor for s/s of fluid volume deficit
- use caution in patients with liver disease, shock, or trauma
- do not administer to patient with increased ICP
What are nursing considerations for hypotonic IV fluids?
- 3% NaCl
- 5% NaCl
- D5%LR
- D5%1/2NS
What are examples of hypertonic IV fluids?
- treats severe hyponatremia
- decreases ICP with cerebral edema
What are indications for hypertonic IV fluids?
- renal failure
- heart failure
- cellular hydration
What are contraindications for hypertonic IV fluids?
- administer slowly and use an infusion control pump
- monitor for hypervolemia, hypernatremia, and respiratory distress
- in dextrose solutions, assess glucose in diabetic patients before administration
What are nursing considerations for hypertonic IV fluids?
- dextran solutions
- albumin
- hetastarch
What are examples of colloids?
plasma volume expansion
What are colloids used for?
- monitor I/O's
- monitor for anaphylaxis reaction or renal failure (dextran)
What are nursing considerations for colloids?
- administer within 30 minutes of receiving from blood bank
- blood should not be hanging for longer than 4 hours
- never add meds to blood products
- 18 or 20 gauge IV
- check vitals per policy
- change tubing after 4 hours
What are general guidelines for blood administration?
- extreme (greater than 25%) loss of blood volume
- contains plasma to help draw fluid back into blood vessels
What are indications for whole blood?
- anemia: increases O2 carrying capacity
- increases substantial hemoglobin deficits in those who have lost up to 25% of total blood volume
What are indications for packed red blood cells (PRBCs)?
increases clotting factor levels in patients with demonstrated deficiency
What are indications for fresh-frozen plasma (FFP)?
management of acute bleeding
What are indications for cryoprecipitate and plasma protein factors?
- incompatibility with immune system
- transfusion reaction
- anaphylaxis
- transmission of pathogens to recipient
What are adverse effects of blood products?
potassium
Which electrolyte is the major intracellular cation?
sodium
Which electrolyte is the major extracellular cation?
3.5-5.0 mEq/L
What is the normal serum range for potassium?
- PO
- IV infusion (must be diluted)
What routes are used for potassium?
- bananas
- strawberries
- oranges
- avocados
- tomatoes
- cucumbers
- tuna
- spinach
What are examples of foods that are high in potassium?
- potassium wasting diuretics
- laxatives
- corticosteroids
Which drugs promote potassium loss?
hypokalemia
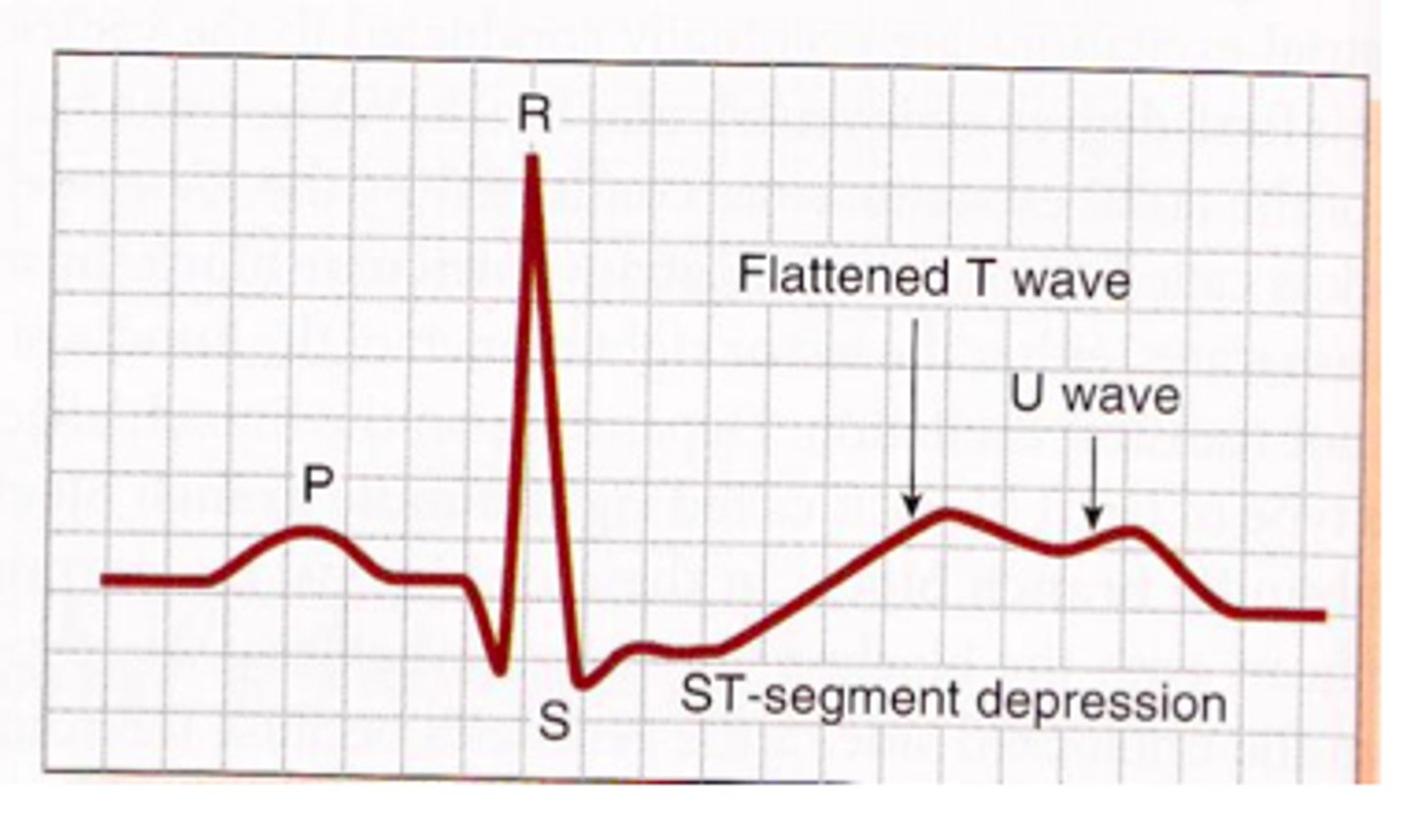
hyperkalemia
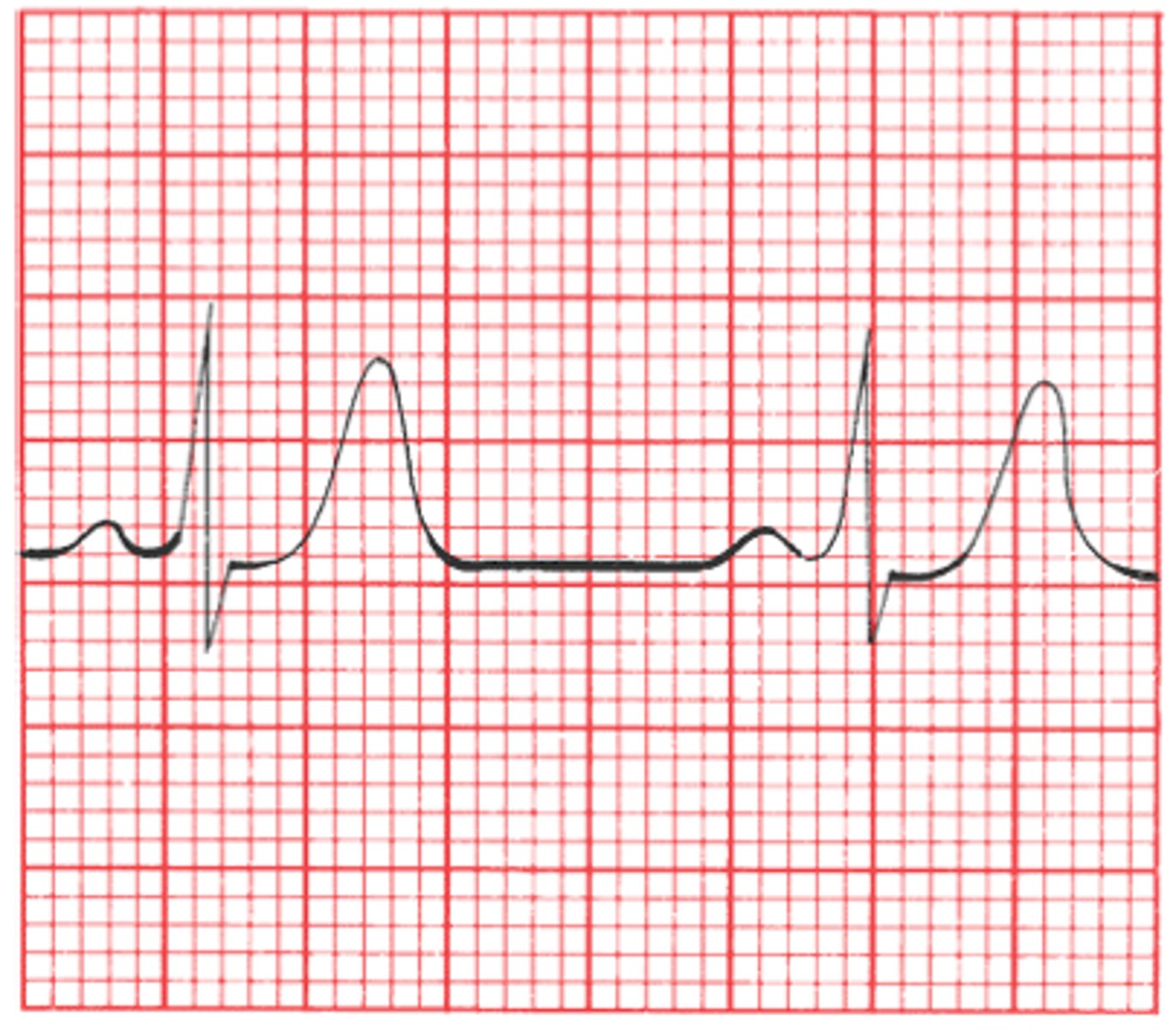
- oral K
- IV K diluted with NS on an IV pump (not IV push)
How is hypokalemia treated?
- reduce potassium rich foods
- administer sodium bicarbonate and calcium gluconate
- polystyrene sulfonate (Kayexalate) enema
- administration of insulin and glucose
How is hyperkalemia treated?
135-145 mEq/L
What is the normal serum range for sodium?
- maintains fluid volume balance
- plasma osmolality
- maintains neuromuscular irritability
- conduction of nerve impulses
What are functions of sodium?
- fast food
- processed food
- bacon
- decaffeinated coffee
What are examples of foods high in sodium?
- administer PO sodium
- administer isotonic NS
- administer hypertonic saline
How is hyponatremia treated?
- restrict sodium
- administer hypertonic solutions
How is hypernatremia treated?
8.6-10.2 mg/dL
What is the normal serum range for calcium?
4.64-5.28 mg/dL
What is the normal serum range for ionized calcium?
- PO calcium
- calcium gluconate
How is hypocalcemia treated?
- bisphosphonates
- NS
- calcitonin
- loop diuretics
How is hypercalcemia treated?
1.5-2.5 mEq/L
What is the normal serum range for magnesium?
- PO magnesium
- IV magnesium
How is hypomagnesemia treated?
- laxatives
- antacids
- chronic kidney disease
What causes hypermagnesemia?
can cause cardiac dysrhythmias
Why is an imbalance of magnesium dangerous?