BIOL101: Ch.3 - The Molecules of Life
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
Carbon and hydrogen
If a molecule is organic it will have _____ and ______
Native State
Is the specific, functional three-dimensional structure a protein or nucleic acid naturally folds into, allowing it to perform its biological role inside a cell
Both
Which can return to its native state: organic or inorganic?
Organic
If a molecule has the chemical formula CH4 is it organic or inorganic?
Inorganic
If a molecule has the chemical formula NH3 is it organic or inorganic?
Inorganic
Is CO2 organic or inorganic?
Carbon tends to share electrons rather than donate or receive which is why we can make a lot of different structures
What makes carbon molecules versatile as molecular ingredients?
One stick symbolizes one single bond; one pair of electrons (2)
When you see one stick connecting two chemical elements like this C-C what does that mean? How many electrons are being shared?
Double bond; 2 pairs of electrons (4)
When you see two sticks connecting two chemical elements like this C=C what does that mean? How many electrons are being shared?
Hydrocarbon
If a molecule is made of just carbon and hydrogen, what is it called?
Functional Group
A combination of atoms attached to the carbon backbone which always reacts in the same way
Hydroxyl Group
Which functional group is this: OH?
Alcohol
What property does OH confer to the molecule?
Carboxyl Group
Which functional group is this: COOH?
Acid
What property does COOH confer to the molecule?
Donates H+ which decreases the pH in solution
What makes COOH an acid?
Amino Group
Which functional group is this: NH2?
Amine
What property does NH2 confer to the molecule?
Phosphate Group
Which functional group is this: PO4?
Strong negative charge
What property does PO4 confer to the molecule?
Amino and carboxyl group
Which two functional groups are found on an amino acid?
Isomer
Two molecules with the same chemical formula but different structures
No, they don’t have the same chemical formula
Are these two chemicals isomers?
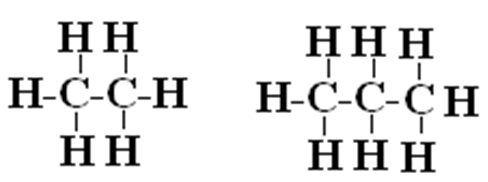
Two subunits
How many monomers in a dimer?
Dehydration synthesis
Which reaction builds polymers?
Hydrolysis
Which reaction breaks down polymers?
H2O
What is removed during dehydration synthesis?
H2O
What is added during hydrolysis?
Hydrolysis
Which reaction releases energy?
Dehydration synthesis
Which reaction requires the addition of energy?
The enzymes bring the two monomers close together
Why do enzymes speed up hydrolysis or dehydration synthesis reactions?
Carbohydrate
Which organic molecule has CHO in a ratio 1:2:1?
Lipid
Which organic molecule has CHO but many more C than O?
Proteins
Which organic molecule will contain CHON?
Nucleic Acids
Which organic molecule will contain CHONP?
Lipid
A molecule has the formula C10H20O2, what is it?
Carbohydrate
A molecule has the formula C6H12O6, what is it?
C6H12O6
Glucose, fructose and galactose all have the same chemical formula, what is it?
Glucose, Fructose, Galactose, Ribose, Dexoyribose
What are the 5 monomers of carbohydrates?
Is for energy
What is the function of glucose?
Is for energy
What is the function of fructose?
Is for energy
What is the function of galactose?
C6H12O6
What is the chemical formula for Glucose, Fructose, Galactose?
Blood and cells
Where is glucose found?
Fruit
Where is fructose found?
Milk
Where is galactose found?
Heredity
What is the function for ribose?
C5H10O5
What is the chemical formula for ribose?
Heredity
What is the function for deoxyribose?
RNA
Where is ribose found?
DNA
Where is deoxyribose found?
C5H10O4
What is the chemical formula for deoxyribose?
Glucose and fructose
Sucrose is made of _____ and _____
Glucose and galactose
Lactose is made of ____ and _____
Glucose and glucose
Maltose is made of _____ and _____
Sucrose, lactose, maltose
What are the disaccharides?
Plants
Where is sucrose found?
Milk
Where is lactose found?
Degradation of starch
Where is maltose found?
Starch, glycogen, cellulose, chitin
What are the 4 polysaccharides?
Dehydration reaction
What process is used to join two monosaccharides to make a disaccharide?
plants
Starch is the energy storage molecule of _____
animals
Glycogen is the short term energy storage molecule of _____
plant cell walls
Cellulose is a structural molecule in ______
different cell types (exoskeleton, shell, cell walls)
Chitin is a structural molecule in __________
Fat
What is the long term energy storage molecule in animals?
Hydrophobic
Are lipids hydrophilic or hydrophobic?
1 glycerol, 3 fatty acids
What are the building blocks of a triglyceride?
Have double bonds, bend at every bond, liquid, don’t “stack” well, are healthier
What are the characteristics of an unsaturated fatty acid?
Have single bonds, straight chains, solid, “stack” well, unhealthy
What are the characteristics of a saturated fatty acid?
Solid
Are saturated fats solid or liquid at room temperature?
Saturated
Which are more unhealthy? Saturated or unsaturated?
Unsaturated
Saturated or unsaturated fatty acid?
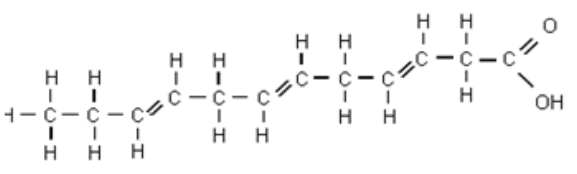
Saturated
Saturated or unsaturated fatty acid?
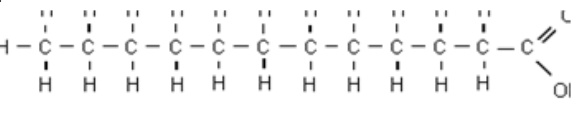
Cholesterol
What is the precursor for all steroids?
In phospholipids, there is a glycerol with 2 fatty acids and in triglycerides, there is a glycerol with 3 fatty acids
How does a phospholipid differ from a triglyceride?
The head
Which part of a phosphor lipid is hydrophilic?
The tail
Which part of a phosphor lipid is hydrophobic?
C
What is the correct organization of phospholipids in a plasma membrane?
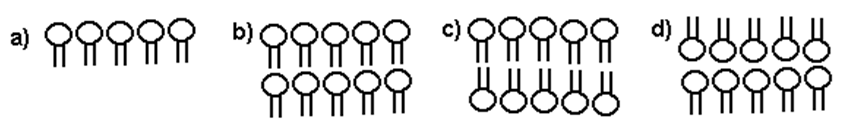
Sensing light, defending cells against viruses, breaking food polymers into smaller molecules, changing the shape of a cell
List some functions of proteins.
Amino acids
What are the monomers of proteins?
Polar, nonpolar, and charged
What are the bonds proteins (or amino acids) form with each other
Carboxyl and amino
What are the 2 functional groups found in amino acids?
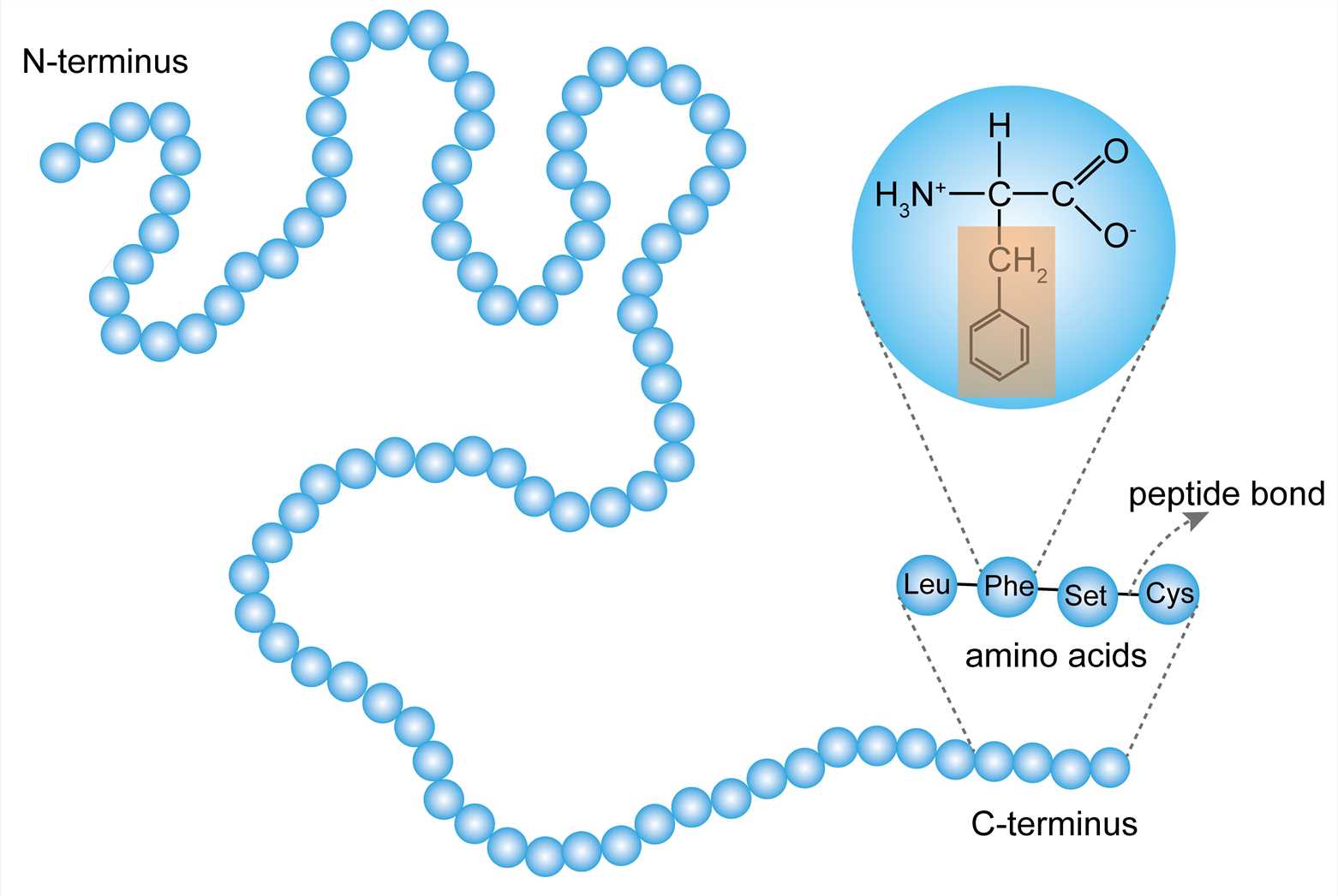
Primary Structure
Which level has a straight chain of AA?
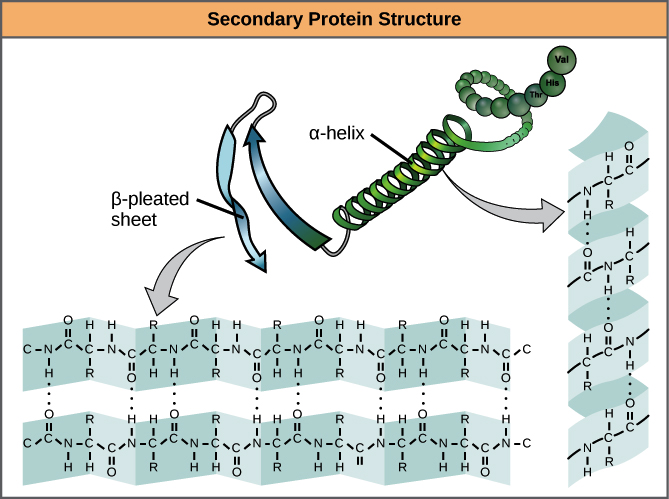
Secondary Structure
Which level do alpha helix and beta sheet form?
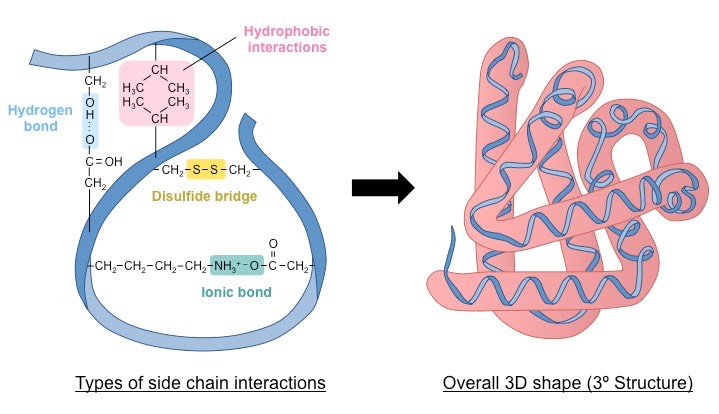
Tertiary Structure
Which level does the 3D structure emerge?
Quaternary
Which level do several polypeptides come together to make a protein?
Condensation
What term describes the reaction that occurs when 2 amino acid monomers are covalently linked together, forming a peptide bond?
Peptide bonds
What type of bonds join amino acids together to form the primary structure of a protein?
Hydrogen bonds
What type(s) of interaction mediate protein secondary structure?
Molecular chaperone
What is the name of the protein that monitors folding?
Prions
What are misfolded proteins called?
The substitution of one amino acid for another at a particular position in hemoglobin, the blood protein that carries oxygen, causes this disease
Describe sickle cell anemia.
One
How many amino acids are “wrong” in sickle cell anemia?
Causes protein to fold into different shape
How is the hemoglobin protein affected by this tiny change?
Applying heat and changing the pH
What are 2 ways to denature a protein?
No
Does a denatured protein work correctly?
Nucleotides
The monomers of nucleic acids are called:
Five carbon sugar, deoxyribose (DNA), ribose (RNA)
What are the 3 parts of a nucleotide?
Deoxyribose
What sugar is present in DNA?