Homeostasis and Feedback Mechanisms in Human Biology
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What is homeostasis?
The maintenance of a stable internal environment within an organism.
Which body systems are involved in regulating body temperature?
The nervous, circulatory, and muscular systems.
What happens to blood vessels in the skin when body temperature decreases?
Blood vessels constrict, reducing heat loss.
What physiological response occurs when body temperature increases?
Muscles begin shivering, generating heat.
What is the claim regarding the human body's ability to regulate temperature?
The human body can regulate internal body temperature.
What evidence supports the claim about temperature regulation?
When temperature decreases, blood vessels constrict and muscles shiver to generate heat.
What is a feedback mechanism?
A process that helps maintain homeostasis by responding to changes in the internal environment.
What hormone is released to lower blood glucose levels?
Insulin.
What indicates a disruption of homeostasis?
A rapid rise in the number of red blood cells.
What is the role of the pancreas in blood sugar regulation?
The pancreas secretes insulin to lower blood sugar levels.
What does the diagram of blood temperature regulation illustrate?
Feedback mechanisms help to maintain homeostasis.
Which statement does NOT describe a feedback mechanism?
White blood cells increase the production of antigens during an allergic reaction.
What do the 'chemicals' in the feedback mechanism diagram represent?
Hormone molecules.
What biological process is represented in the feedback mechanism diagram?
A feedback mechanism maintaining homeostasis.
What is active transport?
The movement of substances across a cell membrane against their concentration gradient, requiring ATP.
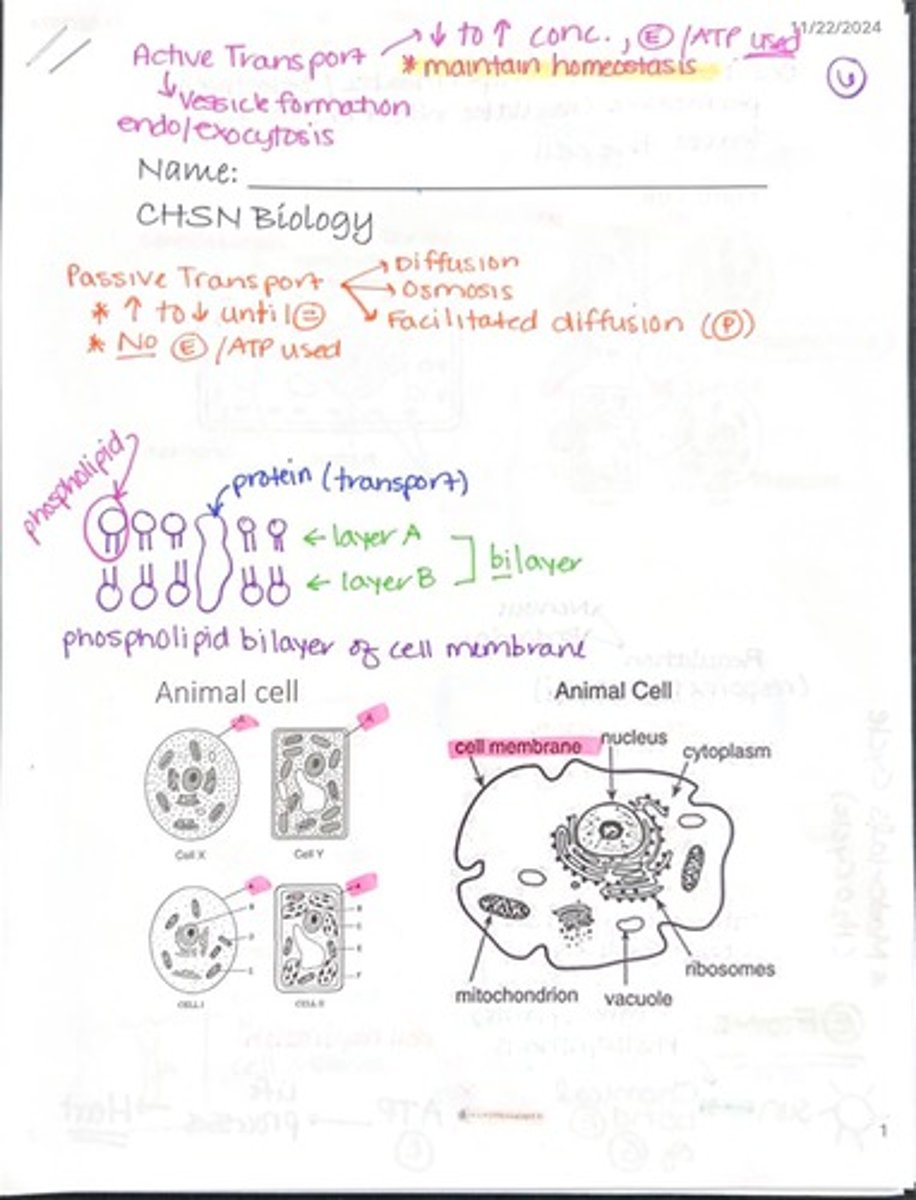
What is passive transport?
The movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy, following the concentration gradient.
What happens to cells in a hypertonic solution?
Cells shrink due to water moving out.
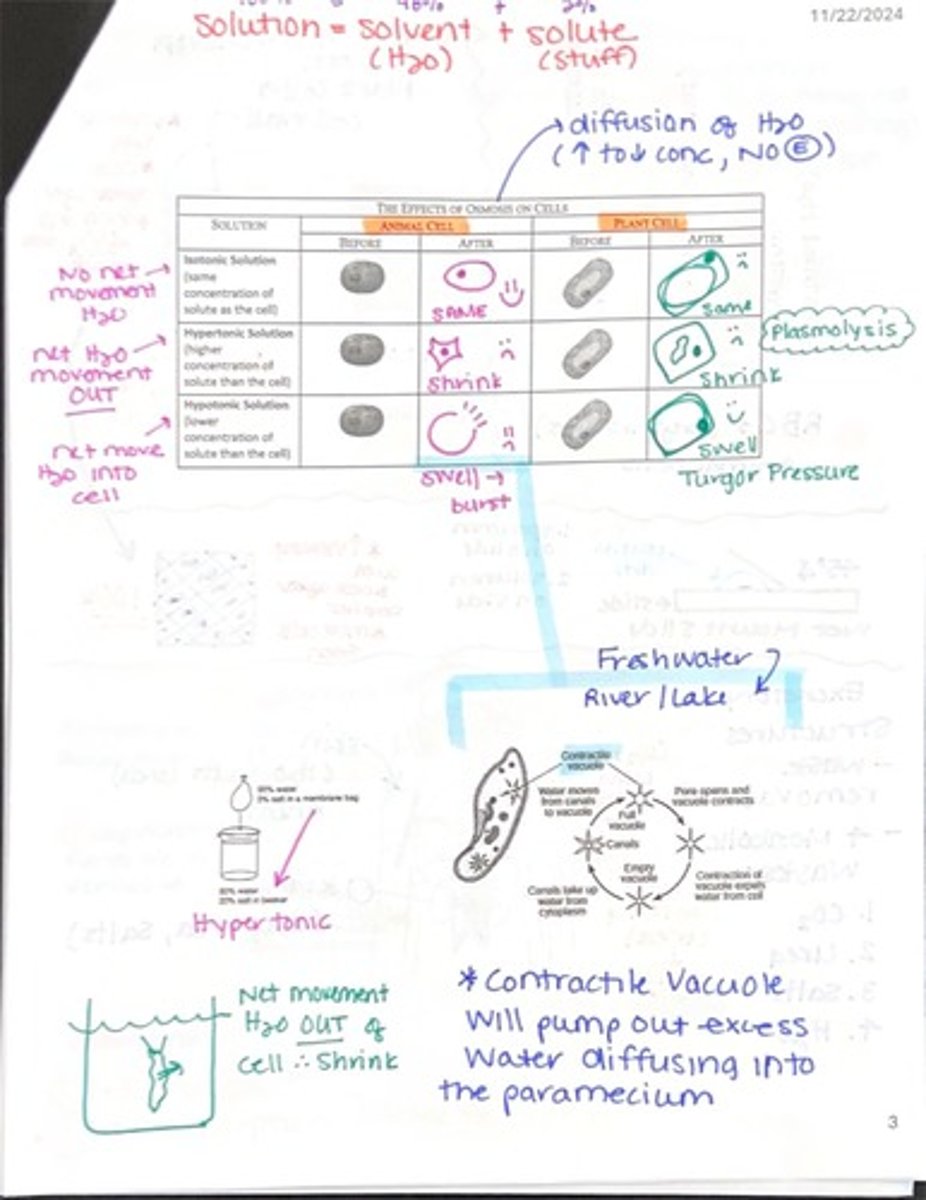
What happens to cells in a hypotonic solution?
Cells swell and may burst due to water moving in.
What is turgor pressure?
The pressure exerted by fluid in a plant cell's vacuole against the cell wall.
What is the function of a contractile vacuole?
To expel excess water from certain cells, maintaining osmotic balance.
What is the effect of osmosis on animal cells in isotonic solutions?
There is no net movement of water; cells maintain their size.
What is the role of the kidneys in homeostasis?
To filter blood and regulate water, salts, and waste removal.
What is the primary function of the endocrine system in homeostasis?
To release hormones that regulate various bodily functions, including metabolism and growth.
What is thermoregulation?
The process by which the body maintains its internal temperature within a normal range.
What is the significance of vasoconstriction during cold temperatures?
It conserves heat by reducing blood flow to the skin.
What is the role of the nervous system in maintaining homeostasis?
To send signals that trigger responses to changes in the internal environment.