MKT 305 Midterm 2 (Module 6 Market Segmentation/Target Markets)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Heterogeneous Demand (Markets and Target Marketing)
Different Groups of Customers have Differing Needs from Products
Market Segmentation (Markets and Target Marketing)
The Separation of Markets into Distinctive Groups Based on Homogeneous Characteristics
Target Market (Markets and Target Marketing)
The Specific Group of Customers Towards which a Firm Directs its Marketing Efforts
Niche and Mass Markets (Mass Markets Vs Individual Customers)
Mass Markets: The Market as a Whole (Entire Circle)
Niche Markets: A Mass Market Broken into Segments
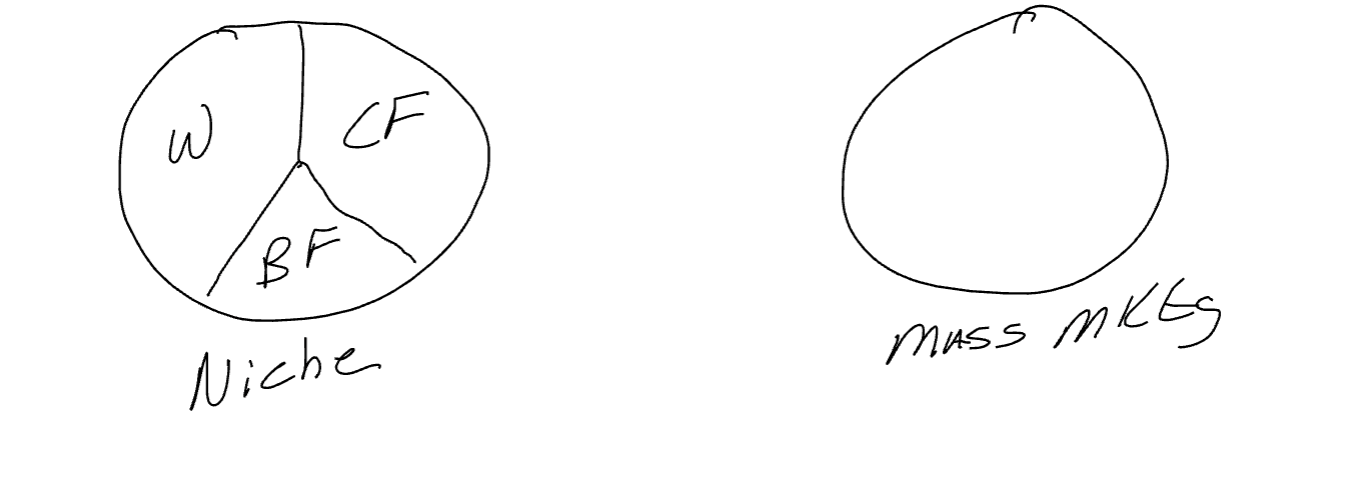
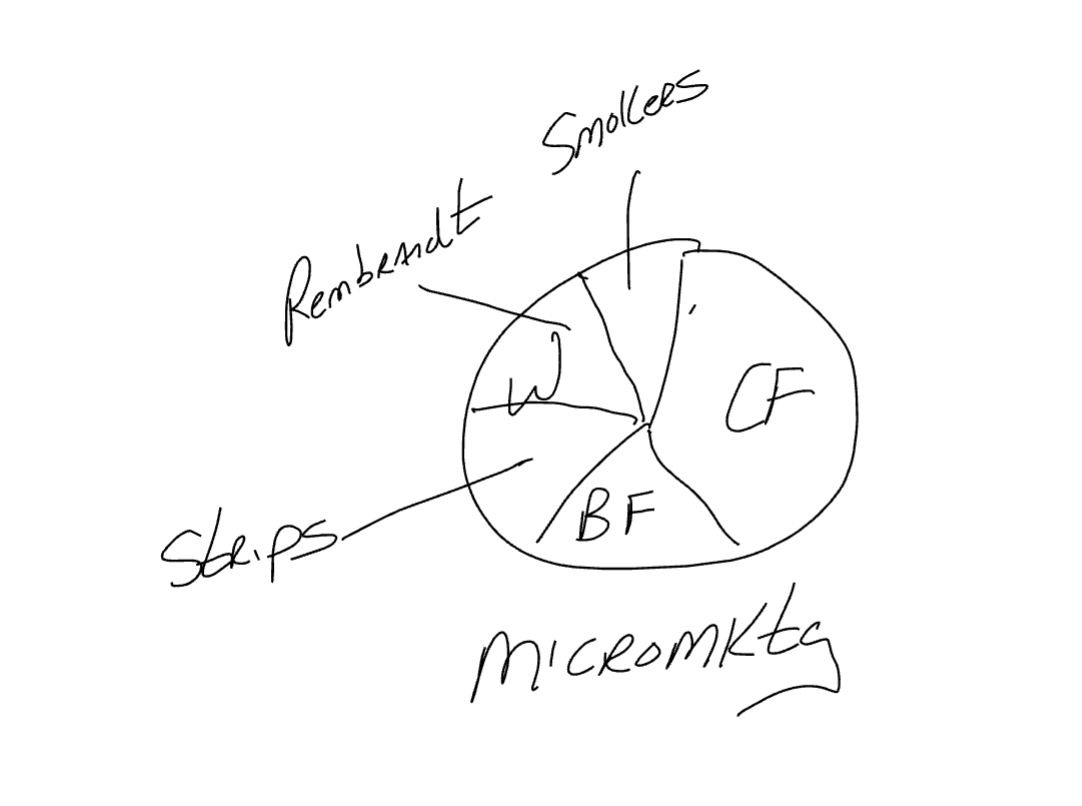
Micro-Market (Mass Markets Vs. Individual Customers)
Micro-Markets: A Niche Market Thats Further Segmented
Advantages of Segmentation (Mass Markets Vs. Individual Customers)
Better understand potential and actual consumers
Develop and Implement a Marketing Mix Tailored to a Specific Market
Assess Potential Demand
Identify Competing Products in Specific Markets
Allows Firms to Position Products
Allows Firms to Identify Opportunities
Downsides of Segmentation (Mass Markets Vs. Individual Customers)
More Expensive
Proliferation of Products that Becomes Overly Burdensome and Costly to Manage
Too small Niches may be Viewed Cynically
Requires a lot of Data
Reinforces Stereotypes
Segmentable Markets Are… (Criteria for Market Segmentation)
Heterogeneous (Demand)
Measurable (Identifiable)
Substantial (Size and Purchasing Power)
Actionable (Must be Able to Respond with an Appropriate Marketing Mix)
Accessible (Market Must be Efficiently Reachable)
Undifferentiated Targeting Strategy (Mass Markets Vs Individual Customers)
Mass Marketing Strategy
Concentrated Strategy (Mass Markets Vs Individual Customers)
Going after one Segment in a Segmented Market
Differentiated Strategy (Mass Markets Vs. Individual Customers)
Going after all Market Segments
Demographic (6 Key Ways to Segment)
Most Popular
Age, Education, Ethnicity, Income, and Family Life Cycle
Geographic (6 Key Ways to Segment)
Based on Region or Location
Psychographic (6 Key Ways to Segment)
Grouping based on Social Class, Lifestyle, and Psychological Characteristics
Benefit-Sought (6 Key Ways to Segment)
Benefits Consumer Desires from using a Specific Product
Situational (6 Key Ways to Segment)
Purchase Situation or Occasion
Physical Surroundings (Beach)
Social Surroundings (Date Vs Friends)
Temporal Perspective (How Much Time to make a Purchase? [Fast Food])
Task Definition (Wedding Gift Vs Yourself)
Pre-Purchase Attitude
Behavior/Usage (6 Key Ways to Segment)
80/20 Principle: 80% of Revenue is Generated from 20% of Customers
Effective Positioning (Positioning and Key Positioning Strategy)
What Customers Currently Think about the Product, Especially in Relation to Competing Products
What a Marketer wants Consumers to think About the Product
Differentiation Strategy (Positioning and Key Positioning Strategy)
Price/Quality
Product Attributes that Lead to Benefits
Product Users
Product Class (Usage)
Competition
Repositioning: The Process of Creating a New Image about an Existing Products in Consumers Minds