SSEH1103 Module 2
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Acute Cardiovascular Response to Exercise, The Energy Systems, Chronic Adaptations to Endurance Training, Types of Endurance Training
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Exercise is Stress
fight or flight response to prepare the body for physical work
Cardiorespiratory System Functions
Provide O2 to the working muscles
Distribute key nutrients to muscles (CHO, fats)
Removing waste products (CO2, lactic acid)
Respiratory Response to Exercise
the onset of exercise is accompanied by an immediate increase in pulmonary ventilation
this is a result of an increase in respiratory rate and tidal volume
Tidal Volume
the depth of each breath
Cardiovascular Response to Exercise
increase in cardiac output, stroke volume, heart rate and blood pressure
Cardiac Output
the volume of blood pumped from the left ventricle per minute
Cardiac Output =
Stroke Volume x Heart Rate
Stroke Volume
the amount of blood ejected from the ventricle with each stroke
Heart Rate
the frequency of contraction
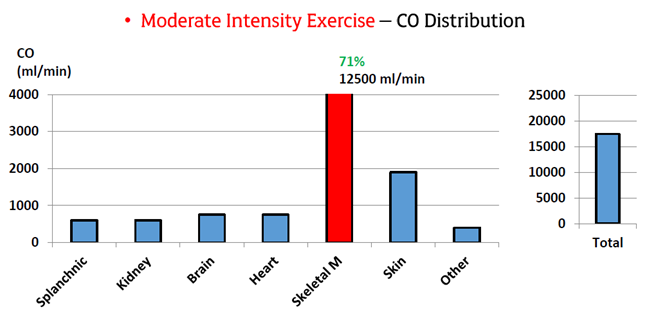
Peripheral Responses to Exercise: Rest
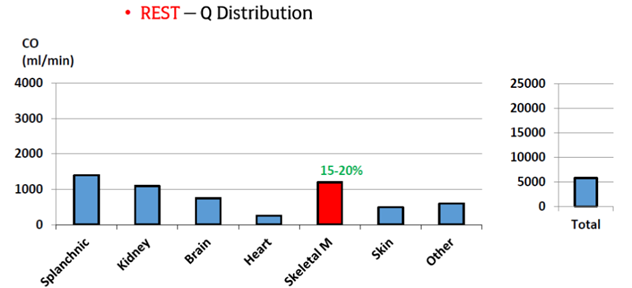
Peripheral Responses to Exercise: Easy Intensity Exercise
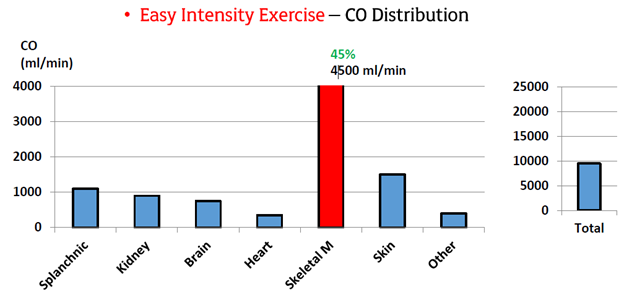
Peripheral Responses to Exercise: Moderate Intensity Exercise
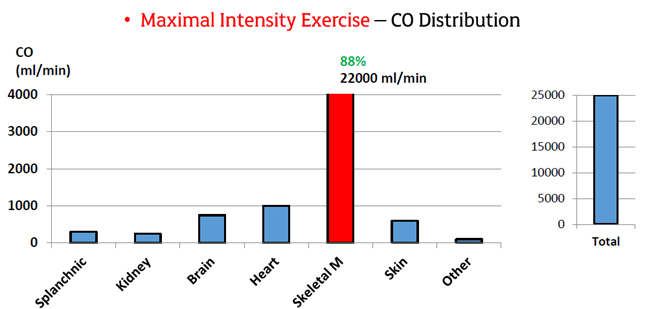
Peripheral Responses to Exercise: Maximal Intensity Exercise
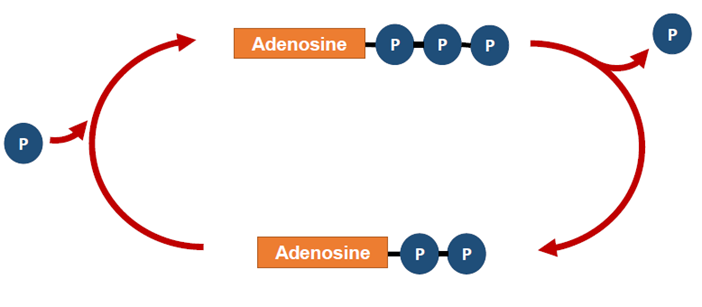
ATP
Adenosine Triphosphate
ATP-ADP Cycle
ATP Synthesis
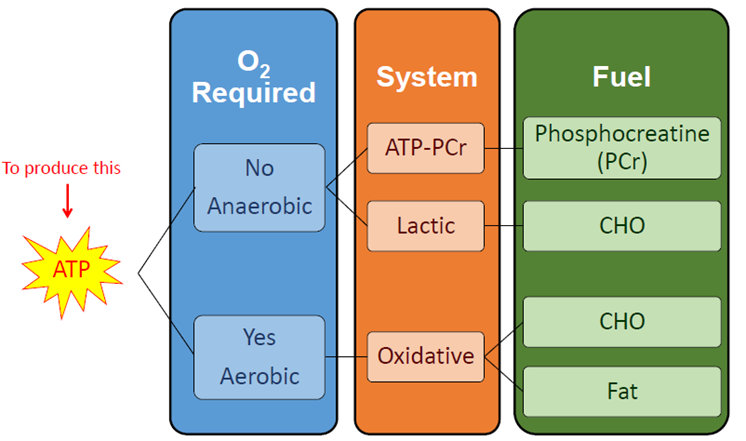
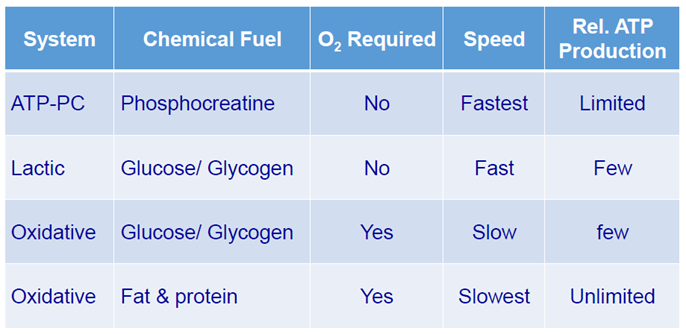
ATP-PC System
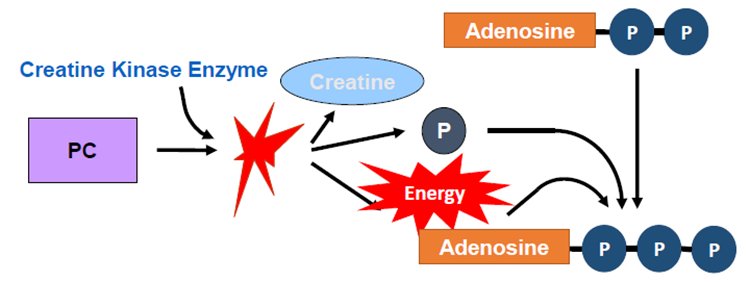
a rapid energy system used during high-intensity, short-duration activities like sprinting
relies on the stored ATP and phosphocreatine to regenerate ATP quickly
Glycolysis and Aerobic Glycolysis
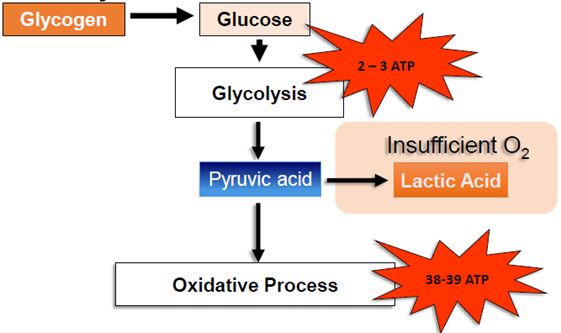
the metabolic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate, producing ATP and NADH in the process
in aerobic conditions, pyruvate is further oxidised in the mitochondria
The Bodys Energy Systems
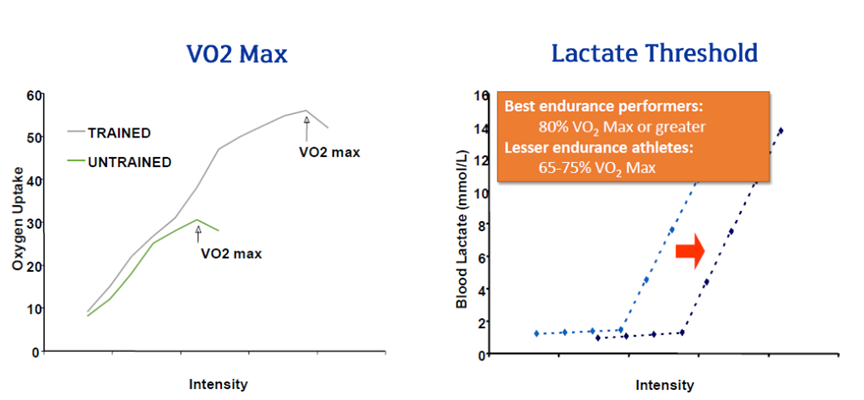
VO2 Max
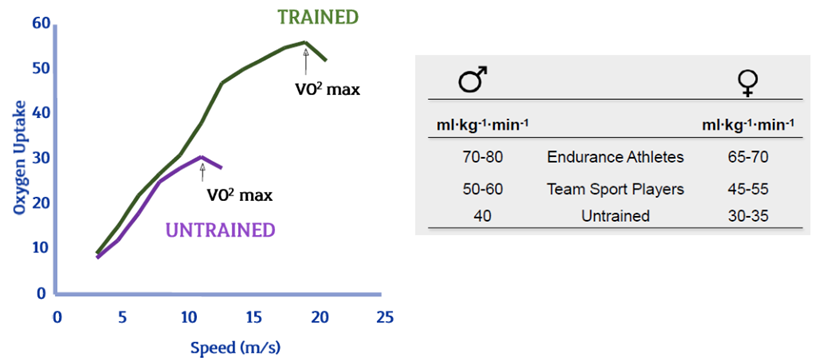
used to measure the aerobic capacity of an individual.
the maximum rate at which the heart, lungs, and muscles can effectively use oxygen during exercise
Effects of Endurance Training
improvement in the ability to sustain a particular level of physical effort largely through more efficient aerobic energy systems
Central System
the ability to deliver oxygen and nutrients to, and remove waste from, the working muscles
Peripheral System
the ability of the working muscles to utilise oxygen and nutrients to produce ATP
Central Adaptation
what drives the ability to deliver oxygen and nutrients to, and remove waste from, the working muscles
Respiration
Cardiac Output
Blood Flow
Peripheral Adaptation
so now there's more blood getting to the muscles, how to muscle improve its ability to utilise the extra oxygen and nutrients to produce ATP
Myoglobin content
Mitochondria and Oxidative Enzymes
Central Adaptation: Respiration: Pulmonary Ventilation
Increased fitness of respiratory muscles
Reduced ventilation rate at sub-maximal intensity
Increased max ventilation capacity
Central Adaptation: Respiration: Pulmonary Diffusion
Enhanced capacity due to increased pulmonary blood flow
Increased density of capillary network in the lungs
Central Adaptation: Cardiac Output
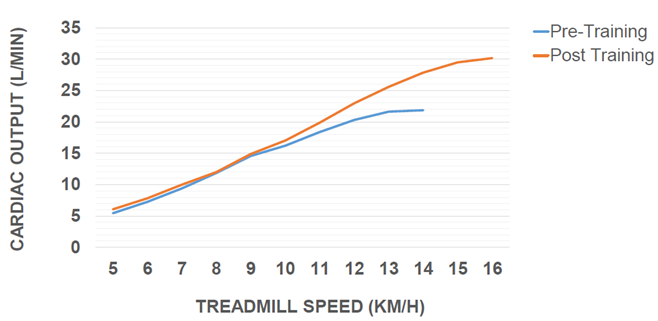
Increase size of left ventricular activity
Increase size of left ventricular wall
Central Adaptation: Blood Flow
Increased blood volume
Increased capillarisation
More effective blood redistribution
VO2 Max and Lactate Threshold