Paper 2 biology flashcards
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/107
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:02 PM on 6/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
1
New cards
describe the structure of a nucleotide
phosphate
(phosphate attached to a) sugar
(which has 1 of 4) base(s)
(bases) are A, C, G and T
(phosphate attached to a) sugar
(which has 1 of 4) base(s)
(bases) are A, C, G and T
2
New cards
Describe how non-coding parts of DNA can affect the expression of genes.
(non-coding parts) can switch genes on / off
3
New cards
control variables other than time, temp, conc & volume
time of day
quantity
quantity
4
New cards
monocultures
the cultivation or growth of a single crop or organism especially on agricultural or forest land
5
New cards
Suggest one reason why some people are concerned about the use of golden rice.
may harm (human) health allow may cause side effects
6
New cards
what do giberellins do
to increase fruit size
to promote flower production
to promote flower production
7
New cards
What is the advantage of golden rice compared with non-GM rice?
golden rice has improved nutritional value
8
New cards
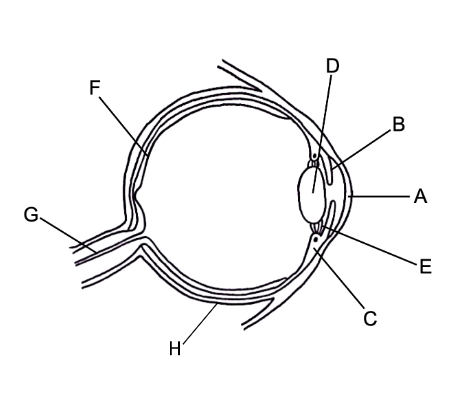
label it
A- cornea
B- iris
C- cilary muscles
D - lense
E - suspensory ligaments
F - retina
G - optic nerve
H - sclera
B- iris
C- cilary muscles
D - lense
E - suspensory ligaments
F - retina
G - optic nerve
H - sclera
9
New cards
cornea
(transparent layer at the front that allows light to be focused onto the retina
10
New cards
iris
(muscle which controls the size of the pupil to adapt to bright or dim lighting)
11
New cards
cillary muscles and suspensory ligaments
(hold lense in place ans control it’s shape)
12
New cards
retina
(light sensitive layer at the back of the eye which, stimulates retinal cells, sending impulses to the brain)
13
New cards
optic nerve
(connects eye and brain so impulses r carried to the brain for an image to b visualised)
14
New cards
sclera
(tough outer layer of the eye which protects it’s internal structures
15
New cards
how does the iris alter to bright lighting
CIRCULAR MUSCLES CONTRCAT
RADIAL MUSCLES RELAX
makes pupil smaller, avoids retinal damage
RADIAL MUSCLES RELAX
makes pupil smaller, avoids retinal damage
16
New cards
how does the iris alter to dim lighting
CIRCULAR MUSCLES relax
RADIAL MUSCLES contract
makes pupil larger so more light enters
RADIAL MUSCLES contract
makes pupil larger so more light enters
17
New cards
how does the eye focus on a nearby object
1. ciliary muscles contract
2. (so ciliary muscles have a) smaller diameter
3. (so) suspensory ligaments loosen / slacken
4. (so) lens thickens or lens becomes more curved / rounded
5. (thicker) lens is more convergent
6. light rays / image focused on retina

18
New cards
how does the eye focus on a fraway object
cillary muscles relx
suspendory ligaments tightern
lense becomes thingner and light rays are refracted weakly
suspendory ligaments tightern
lense becomes thingner and light rays are refracted weakly
19
New cards
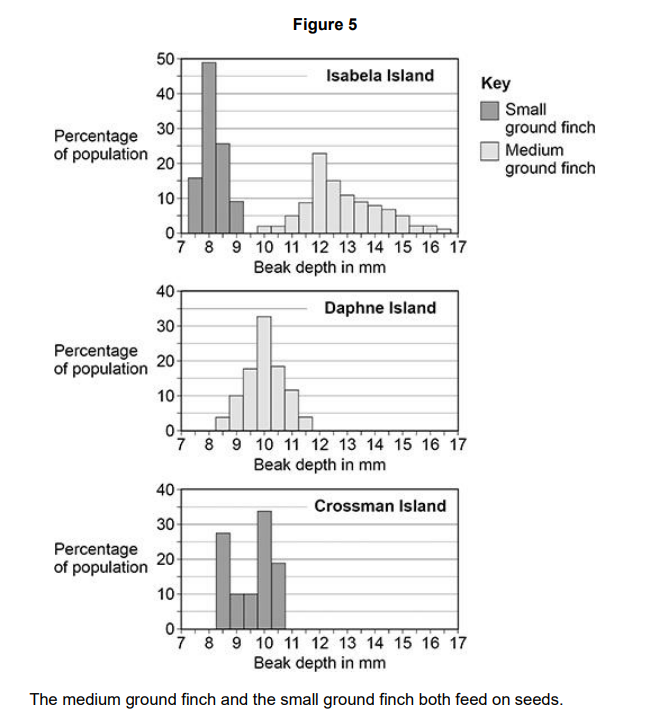
The medium ground finch and the small ground finch both feed on seeds
The size of seeds eaten by each bird depends on the depth of the bird’s beak
The range of beak depth of medium ground finches on Isabela Island is different from the range on Daphne Island. Explain what might have caused this difference.
The size of seeds eaten by each bird depends on the depth of the bird’s beak
The range of beak depth of medium ground finches on Isabela Island is different from the range on Daphne Island. Explain what might have caused this difference.
1. colonisers of Isabela have a range of beak depths
2. due to mutation
3. large range of size seeds on Isabella
4. more competition for seeds on Isabela
5. birds with larger beaks get enough food to survive and reproduce
6. survivors pass on beneficial alleles to offspring
20
New cards
how to correct long sighted ness
convex / converging lens
light rays bent / refracted (inwards) more
light rays focused on retina
light rays bent / refracted (inwards) more
light rays focused on retina
21
New cards
marathon runners often drink sports drink during a race explain why
to replace water ions an salt, that is lost in sweat
22
New cards
why might estimates of graph values with the x axis being time be inaccurate
the readings are too far apart
23
New cards
The results show that when the ice-cold water was drunk, the temperature near the brain decreased.
Explain why the temperature near the brain decreased.
Explain why the temperature near the brain decreased.
blood is cooled at the mouth, this cooled blood then flows to the brain
24
New cards
How does the thermoregulatory centre send information to sweat glands in the skin?
via neurones
25
New cards
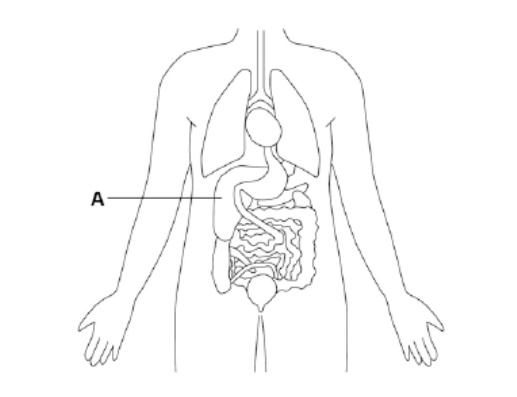
name organ a
liver
26
New cards
If the eye then focuses on the words in a book, changes would occur in the eye.
The light rays would be refracted more by the lens.
How does the lens refract the light more?
The light rays would be refracted more by the lens.
How does the lens refract the light more?
by becoming thicker
27
New cards
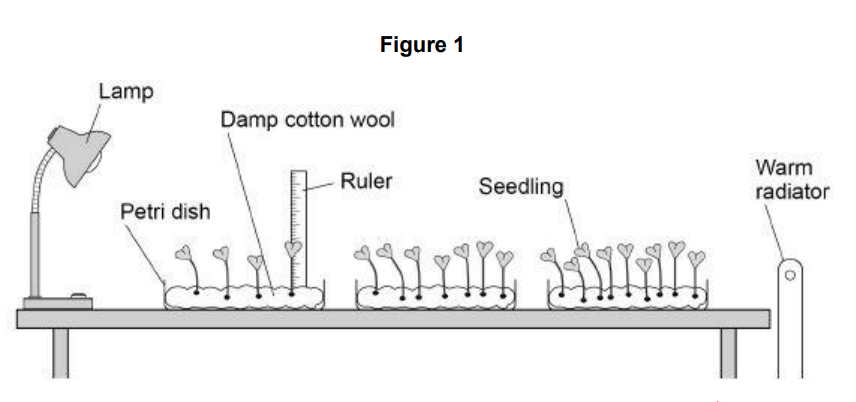
describe two improvements the students should make to their investigation
• keep temperature the same (for all dishes)
• use equal numbers of seedlings (in each dish)
• measure light intensity
• use equal numbers of seedlings (in each dish)
• measure light intensity
28
New cards
A gene is a length of DNA. What type of substance does a gene code for?
protein
29
New cards
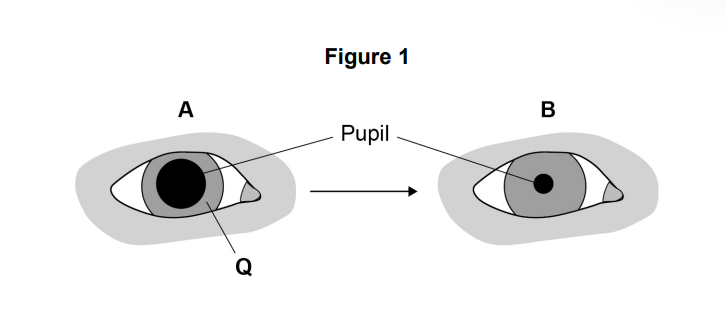
Describe how structure Q causes the change in the size of the pupil from A to B.
**muscle** contraction
30
New cards
Give two possible effects of an increase in global air temperature on living organisms.
• (some) plants grow faster / higher yield
• loss of habitat
• migration or change in distribution
• extinction
• loss of habitat
• migration or change in distribution
• extinction
31
New cards
Explain why more water was lost through the skin during the race. (she was running)
more energy needed
(so) more (aerobic) respiration
(so) increased breathing (rate / depth)
(so) more (aerobic) respiration
(so) increased breathing (rate / depth)
32
New cards
Light is an environmental factor that affects the growth of dandelion plants.
Give two other environmental factors that affect the growth of dandelion plants
Give two other environmental factors that affect the growth of dandelion plants
• temperature
• water
• (soil) pH
• minerals / ions
• wind
• herbivores
• water
• (soil) pH
• minerals / ions
• wind
• herbivores
33
New cards
One advantage of asexual reproduction for bluebells is that only one parent is needed.
Suggest two other advantages of asexual reproduction for bluebells.
Suggest two other advantages of asexual reproduction for bluebells.
• many offspring produced
• takes less time
• (more) energy efficient
• genetically identical offspring
• successful traits maintained due to offspring being genetically identical
• no transfer of gametes or seed dispersal
• takes less time
• (more) energy efficient
• genetically identical offspring
• successful traits maintained due to offspring being genetically identical
• no transfer of gametes or seed dispersal
34
New cards
Explain why sexual reproduction is an advantage for bluebells.
1. genetic variation (in offspring)
2. (so) better adapted survive
3. (and) colonise new areas by seed dispersal
4. many offspring so higher probability some will survive
35
New cards
A large amount of untreated sewage entered the river. Many fish died.
Untreated sewage contains organic matter and bacteria.
Explain why many fish died.
Untreated sewage contains organic matter and bacteria.
Explain why many fish died.
bacteria decay organic matter / sewage / algae / dead plants
(by) digestion
(and) bacteria respire aerobically
(which) lowers oxygen concentration
(so) reduced energy supply causes death of fish
(by) digestion
(and) bacteria respire aerobically
(which) lowers oxygen concentration
(so) reduced energy supply causes death of fish
36
New cards
Suggest why IVF and embryo transfer were used rather than allowing animals 7 and 8 to mate naturally.
takes less time (to obtain results)
or more offspring at the same time
or more offspring at the same time
37
New cards
The scientists will selectively breed some of the animals shown in Figure 11.
Describe how the scientists would do this
Describe how the scientists would do this
1. find females with low fat in milk and high milk yield
2. find males whose female offspring have high milk yield and low fat in milk
3. cross the best (for both features) female with the best male
4. select the best offspring (for both features) from each generation and repeat for several generations
38
New cards
what is the order of the classification system Linnaeus
kingdom
phylum
class
order
family
genus
species
phylum
class
order
family
genus
species
39
New cards
Due to evidence available from chemical analysis, there is now a ‘three domain system’ developed by Carl Woese. In this system, organisms are divided into:
• archaea (primitive bacteria usually living in extreme environments)
• bacteria (true bacteria)
• eukaryota (which includes protists, fungi, plants and animals).
• bacteria (true bacteria)
• eukaryota (which includes protists, fungi, plants and animals).
40
New cards
Describe how the ancestors of modern species A may have evolved into the species B
isolation of different populations
habitat variation
genetic variation or mutation
better adapted survive
(eventually) cannot produce fertile offspring with other populations
habitat variation
genetic variation or mutation
better adapted survive
(eventually) cannot produce fertile offspring with other populations
41
New cards
drawbacks of selective breeding
reduces the __**gene pool**__ of the population
inbreeding; makes them prone to disease or inherited defects as the gene pool is so small
inbreeding; makes them prone to disease or inherited defects as the gene pool is so small
42
New cards
what is a gene pool
collection of different alleles in a population
43
New cards
what is selective breeding
selecting for certain alleles that code for the traits that we want
44
New cards
uses of selective breeding
• Disease resistance in food crops.
• Animals which produce more meat or milk.
• Domestic dogs with a gentle nature.
• Large or unusual flowers.
• Animals which produce more meat or milk.
• Domestic dogs with a gentle nature.
• Large or unusual flowers.
45
New cards
steps of genetic engineering (transfering the gene from one organism to another)
dna is cut at specific base with restrictive enzyme to create a sticky end
vector dna is cut using the same restrictive enzymes to create complementary sticky ends
ligas enzymes, join the sticky ends together to form a recombinant dna
recombinant dna is mixed up with and taken up by target cells
vector dna is cut using the same restrictive enzymes to create complementary sticky ends
ligas enzymes, join the sticky ends together to form a recombinant dna
recombinant dna is mixed up with and taken up by target cells
46
New cards
how do you isolate a section of dna
using enzymes
47
New cards
what did darwin do?
studied geology & fossils
developed the theory of evolution by natural selection
developed the theory of evolution by natural selection
48
New cards
darwin’s natural selection
• Individual organisms within a particular species show a wide range of variation for a characteristic. '
• Individuals with characteristics most suited to the environment are more likely to survive to breed successfully.
• The characteristics that have enabled these individuals to survive are then passed on to the next generation.
• Individuals with characteristics most suited to the environment are more likely to survive to breed successfully.
• The characteristics that have enabled these individuals to survive are then passed on to the next generation.
49
New cards
The theory of evolution by natural selection was only gradually accepted because
• the theory challenged the idea that God made all the animals and plants that live on Earth
• there was insufficient evidence at the time the theory was published to convince many scientists • the mechanism of inheritance and variation was not known until 50 years after the theory was published.
• there was insufficient evidence at the time the theory was published to convince many scientists • the mechanism of inheritance and variation was not known until 50 years after the theory was published.
50
New cards
Jean-Baptiste Lamarck’s idea
Changes that occur in an organism during its lifetime can be inherited.
We now know that in the vast majority of cases this type of inheritance cannot occur
We now know that in the vast majority of cases this type of inheritance cannot occur
51
New cards
speciation
closely related species were often separated by geographical barriers such as a wide river
52
New cards
how does speciation happen
over time, natural selection will favour different alleles on the two sides on each side of the geographical barrier
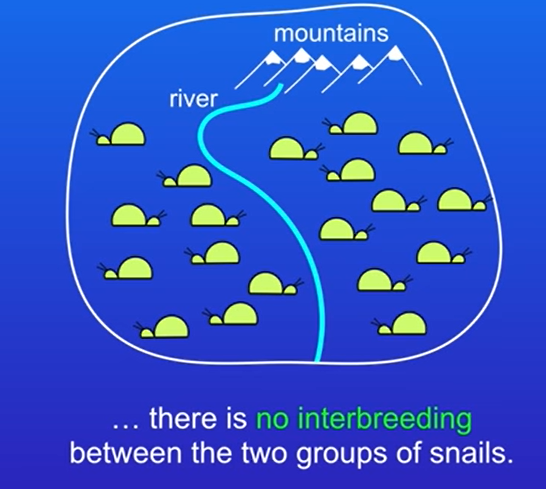
53
New cards
In the **mid-19th century,** Gregor Mendel carried out breeding experiments on plants. One of his observations was …
In the **late 19th century** he observed….
In the **late 19th century** he observed….
1. that the inheritance of each characteristic is determined by ‘units’ that are passed on to descendants unchanged.
2. the behaviour of chromosomes during cell division
54
New cards
In the early 20th century it was observed that chromosomes and Mendel’s ‘units’ behaved in __________ ways. This led to the idea that …..
1. similar
2. the ‘units’, now called genes, were located on chromosomes.
55
New cards
In the mid-20th century the structure of ______ was determined and the mechanism of gene function worked out.
1. DNA
56
New cards
what happens in meiosis
1. copies of the genetic information are made
2. the cell divides twice to form four gametes, each with a single set of chromosomes
3. all gametes are genetically different from each other
57
New cards
what are substances labelled ACGT
bases
58
New cards
describe how non coding parts of DNA can affect the expression of genes
the non coding parts can turn on /off
59
New cards
describe how scientists would selectively breed a type of cattle that makes **large volumes** of **low-fat milk**
1. find female with low(est) fat in milk **and** high(est) milk yield
2. find male whose female offspring have high(est) milk yield **and** low(est) fat in milk
3. cross the best (for both features) female with the best male
4. select the best offspring (for both features) from each generation and repeat for several generations
60
New cards
who developed the three domain system of classification
carl woese
61
New cards
suggest how scientists can estimate when X animal was alive by looking at the fossile
compare to other fossils of known age
62
New cards
two factors that may have caused the extinction of species X
* (new) predators
* new disease
* competition for food
* comp for mates
* habitat change
* new disease
* competition for food
* comp for mates
* habitat change
63
New cards
when using tissue culture to produced many plants from one plant why are **several groups scraped off the leaf**
so many / several plants can be produced
64
New cards
when using tissue culture to produced many plants from one plant why are **nutrients added to the agar jelly**
for making protein / amino acids
for making chlorophyll
for providing energy
for respiration
for making chlorophyll
for providing energy
for respiration
65
New cards
when using tissue culture to produced many plants from one plant why are **hormones added to the agar jelly**
so differentiation occurs
so roots / shoots develop
so roots / shoots develop
66
New cards
when using tissue culture to produced many plants from one plant why are **plant cells kept at 20*C**
so optimum / good growth
67
New cards
which two scientists proposed the theory of evolution by natural selection
Alfred Russel Wallace
Charles Darwin
Charles Darwin
68
New cards
what is a fossil
remains of an organism
from a long time ago
from a long time ago
69
New cards
why is fossils for older things, harder to find
• fossils buried deep(er) so hard(er) to find
• more likely to be destroyed by geological activity / earthquakes
• oldest organisms were soft-bodied so most of the tissue decayed
• more likely to be destroyed by geological activity / earthquakes
• oldest organisms were soft-bodied so most of the tissue decayed
70
New cards
pros of mass extinction
allows evolution of new species / varieties
71
New cards
con of mass extinction
• loss of potential, future biodiversity
72
New cards
what is deamination
Deamination is the removal of an amine group from a molecule.
amino acid → ammonia → urea
excess amino acids are broken down in the liver through deamination
amino acid → ammonia → urea
excess amino acids are broken down in the liver through deamination
73
New cards
what is the role of the kidney
filtration of blood to make urine
maintaining water ballance
maintaining water ballance
74
New cards
why is it important to maintain water ballance
prevent bursting or shrivelling of red blood cells
75
New cards
what is filtered in the blood into the kidney
amino acids, glucose, water, salt, urea
76
New cards
what is reabsorbed back into the blood
amino acids and glucose via active transport
(some salt and water is also absorbed)
(some salt and water is also absorbed)
77
New cards
describe how a healthy kidney produces urine
kidney filters the blood
reabsorbs all the glucose
reabsorbs some ions and water
releases the rest in urea
reabsorbs all the glucose
reabsorbs some ions and water
releases the rest in urea
78
New cards
How should the student decide where to place the quadrat?
coordinates
to achieve randomness
to achieve randomness
79
New cards
Using the mean from this investigation to calculate the number of daisy plants on the lawn may not be accurate.
too few quadrats,
sample may not be representative of the lawn
sample may not be representative of the lawn
80
New cards
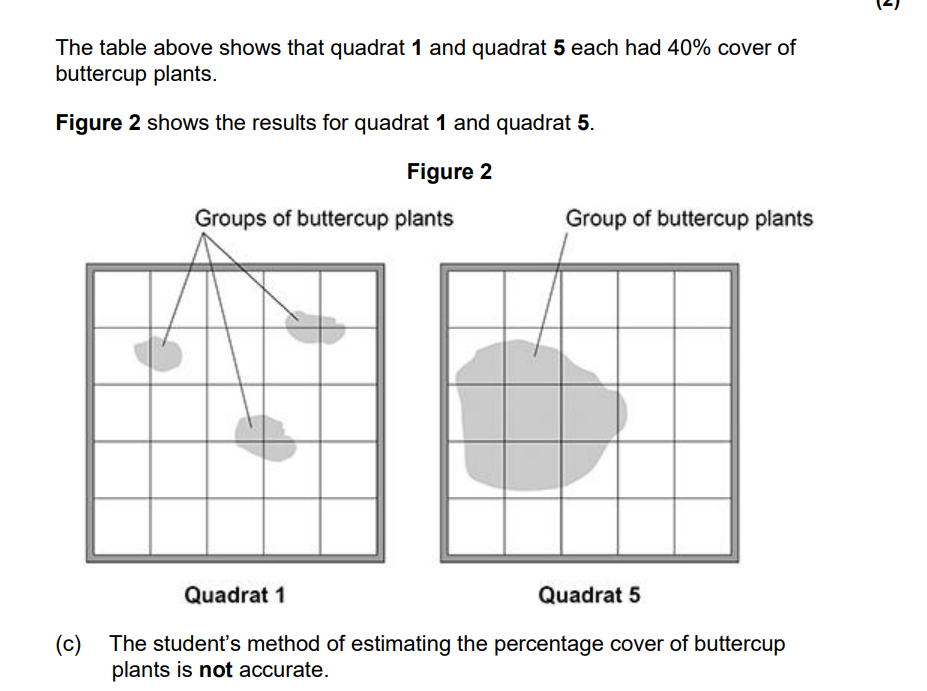
Suggest two improvements to the method to make the results more valid.
place (many) more quadrats
divide quadrats into more / smaller squares
estimate actual percentage cover in quadrat (instead of counting squares)
divide quadrats into more / smaller squares
estimate actual percentage cover in quadrat (instead of counting squares)
81
New cards
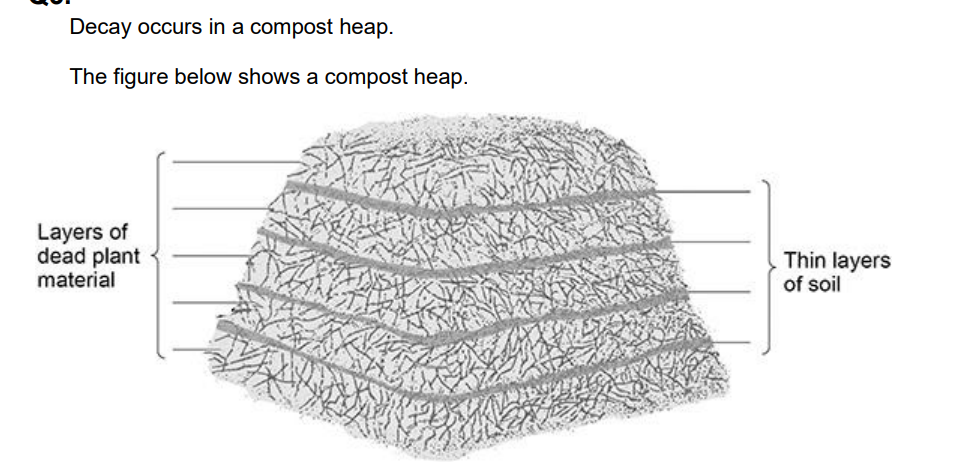
Describe:
• how microorganisms in the layers of soil help to recycle chemicals in the dead plants
• how the chemicals are used again by living plants
• how microorganisms in the layers of soil help to recycle chemicals in the dead plants
• how the chemicals are used again by living plants
*in microorganisms*
• enzymes
• respiration
• production of carbon dioxide
*in plants*
• carbon dioxide (from air) taken in by leaves
• by diffusion
• via stomata
• carbon dioxide used in photosynthesis
• enzymes
• respiration
• production of carbon dioxide
*in plants*
• carbon dioxide (from air) taken in by leaves
• by diffusion
• via stomata
• carbon dioxide used in photosynthesis
82
New cards
difference between the process of meiosis and mitosis (3 marks)
1. one cell division in mitosis but two cell divisions in meiosis
2. mitosis produces genetically identical cells, but meiosis produced genetically different cells
3. mitosis produces diploid cells but meiosis produces haploid cells
83
New cards
similarity between mitosis and mieosis
**DNA** doubles / copies / replicates
84
New cards
85
New cards
A functional MRI (fMRI) scanner allows a person to move while the scanner makes images of the person’s brain activity.
Suggest how the fMRI scanner could help to find out more about the brain damage a person has.
Suggest how the fMRI scanner could help to find out more about the brain damage a person has.
• can ask people to do different tasks (while taking scan)
• to see which part of brain is active / inactive
• to compare with a person without brain damage
• to see (exactly) where the damage is
• to see which part of brain is active / inactive
• to compare with a person without brain damage
• to see (exactly) where the damage is
86
New cards
Describe how the brain receives information about light entering the eye.
1. (cells in) retina sensitive to light
2. impulse passes along (sensory) neurone
3. (along) optic nerves
87
New cards
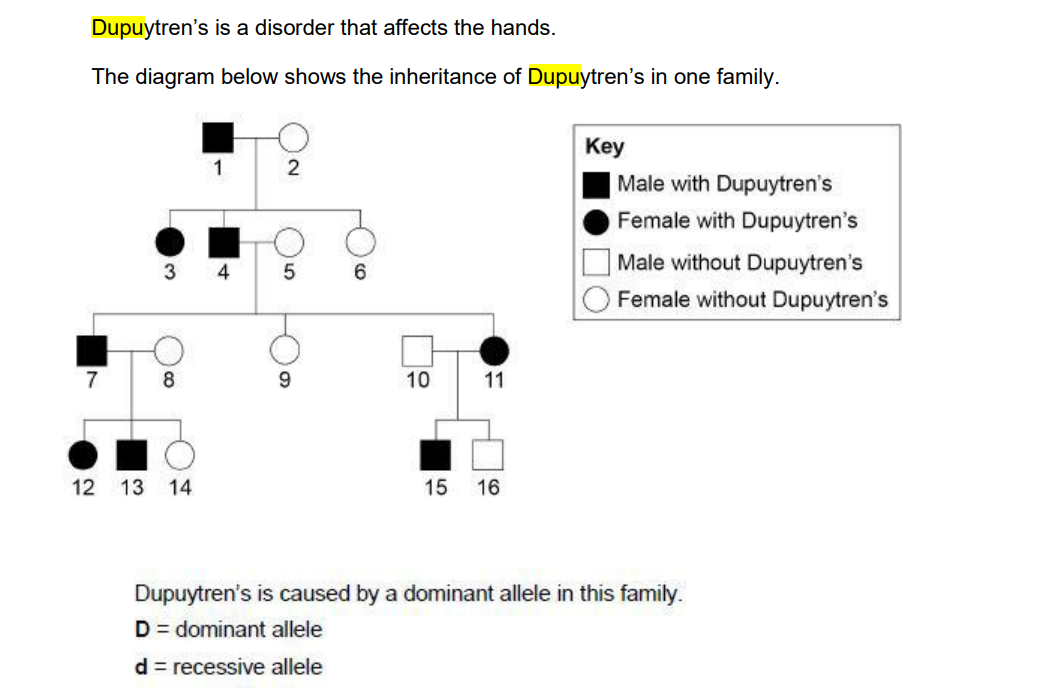
why is the genotype Dd
has D because has Dupuytren’s and cannot be homozygous / DD or all the children would have Dupuytren’s
88
New cards
classes of organisation as determined by CARL LINEAUS
kingdom
phylum
class
order
family
genus
speicies
phylum
class
order
family
genus
speicies
89
New cards
binomial system
genus then species
90
New cards
why wer new classification models proposed
developments in microscopy allowed for better examination of internal structures
improvement in understanding of biochemical processesw
improvement in understanding of biochemical processesw
91
New cards
what are the 3 domains
archaea → bacteria usiually living in extreme environments go here
eukarya
bacteria
eukarya
bacteria
92
New cards
which kingdoms belong in the domain eukarya
plants animals fungi protists
93
New cards
how are evolutionary trees created
by examining the dna of diff species and analysing how similar the sequences are
94
New cards
what does progesterone inhibit
FSH and LH
95
New cards
explain hohw photo tropism in a plant shoot helps the plant to survive
more light absorbed
increased photosynthesis
more glucose
increased photosynthesis
more glucose
96
New cards
give 1 reason why the total biomass of the daphnia in the pond is different from the total biomass of algae
* • non-digestible parts (of algae) or lost in faeces
* • not all absorbed
* • lost in urine / urea
* • not all absorbed
* • lost in urine / urea
97
New cards
explain how food from insects can improve human food security
less land required
(so) more space for crops (for humans)
less methane (from animals)
therefore less global warming
(therefore) less harmful effects of global warming on (human) food production
(so) more space for crops (for humans)
less methane (from animals)
therefore less global warming
(therefore) less harmful effects of global warming on (human) food production
98
New cards
why is it more difficult to find older fossils
* fossils buried deep(er) so hard(er) to find
* older eras less researched by scientists because less to find
* allow oldest organisms were soft-bodied so there were very few fossils
* older eras less researched by scientists because less to find
* allow oldest organisms were soft-bodied so there were very few fossils
99
New cards
advantages of mass extinction
allows evolution of new species / varieties
100
New cards
benefits of studying the whole human genome
• diagnosis of inherited / genetic disorder
• gene therapy or treatment of inherited disorders
• understanding (human) evolution
• diagnosis of inherited / genetic disorder
• gene therapy or treatment of inherited disorders
• understanding (human) evolutions
• gene therapy or treatment of inherited disorders
• understanding (human) evolution
• diagnosis of inherited / genetic disorder
• gene therapy or treatment of inherited disorders
• understanding (human) evolutions