Ventricles, CSF Flow, Blood Brain Barrier
1/191
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
192 Terms
The two major functions of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) are __________ and __________ buffering.
mechanical
chemical
What are the three main processes involved in the regulation of CSF?
Production
Circulation
Absorption
What condition can result from changes in CSF production, circulation, or absorption?
Hydrocephalus
The __________ is a selective barrier that separates the blood from the cerebrospinal fluid.
blood-bran barrier
What is one primary mechanical function of CSF?
CSF supports the brain by allowing it to float, reducing its effective weight
Without CSF, the brain would rest directly on __________, which could lead to damage.
bone
What property of CSF prevents the brain from tearing due to contact with the rough surface of the skull?
Its cushioning effect as a mechanical buffer
What is the approximate effective weight of the brain when supported by CSF?
48 grams (3% of its actual weight)
What is the formula to calculate the brain's effective weight in situ when supported by CSF?
Weight in situ = Weight in air × (1 - Sg CSF / Sg nervous tissue)
The specific gravity (Sg) of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is approximately __________.
1.007
The specific gravity (Sg) of nervous tissue is approximately __________.
1.040
If the actual brain weight is 1500 grams, what is the purpose of using the specific gravity values in the formula?
It calculates how much the brain is buoyed by the CSF, reducing its effective weight
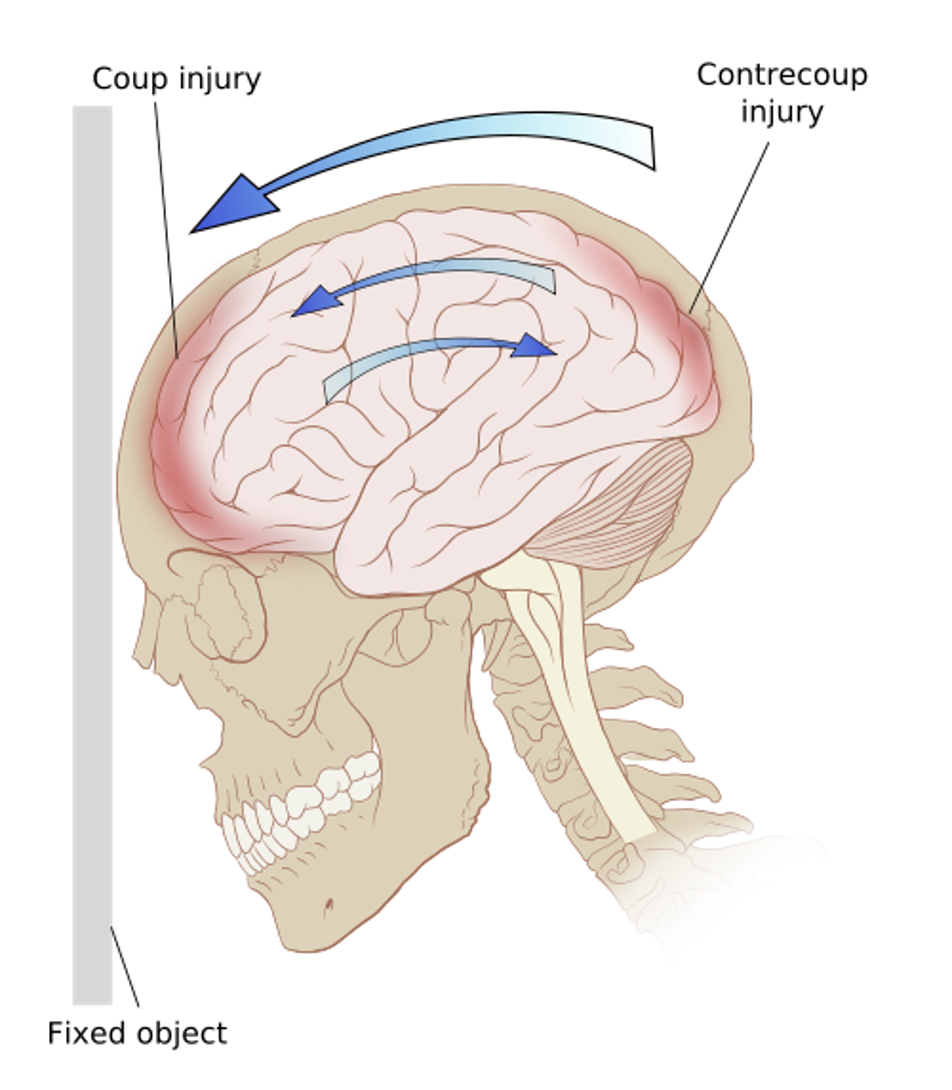
What is a coup injury?
When the brain strikes the skull at the point of impact
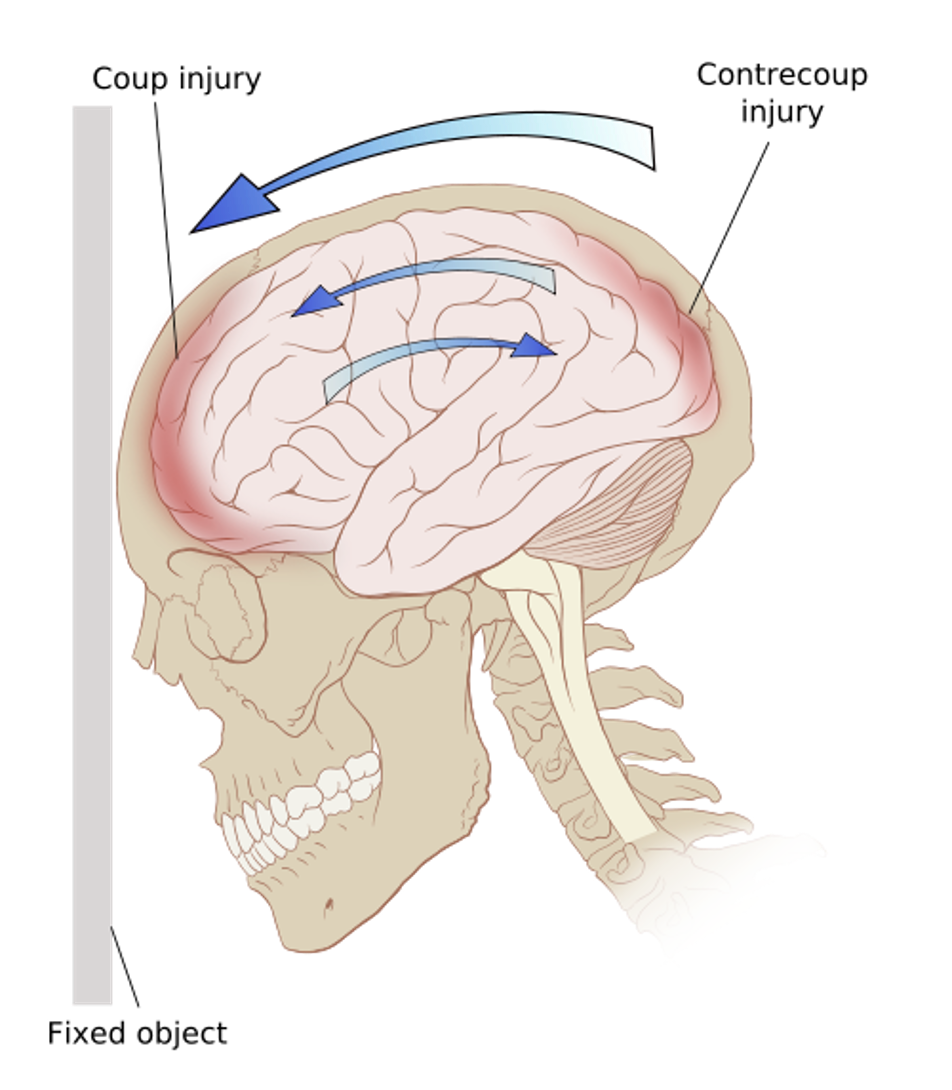
What is a contrecoup injury?
When the brain rebounds and strikes the opposite side of the skull, often causing more severe damage
Contrecoup injuries are typically __________ than coup injuries due to the brain’s inertia.
more severe
How does cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) help protect the brain during trauma?
CSF disperses the energy of the impact over a larger area, reducing the severity of injury
When the skull comes to a sudden stop, the brain continues to move due to __________, leading to a contrecoup injury.
inertia
Why is the protective capacity of CSF limited during severe trauma?
It can only absorb and distribute a limited amount of force; excessive force can lead to brain damage
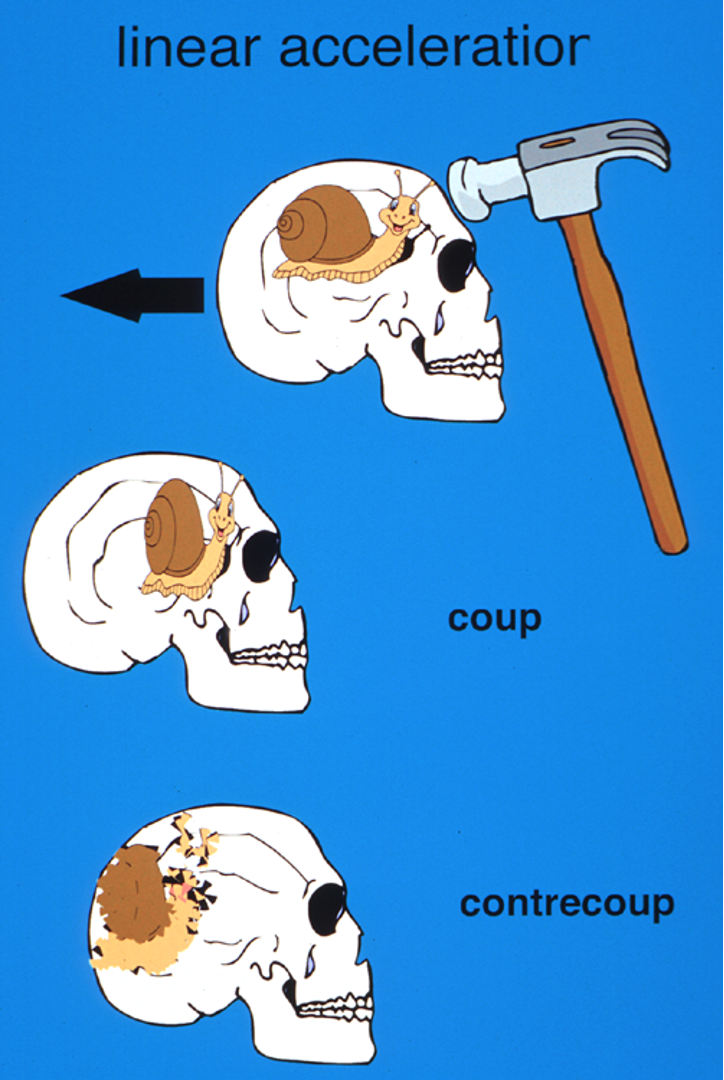
What type of injury occurs at the site of impact during a head trauma caused by linear acceleration?
Coup injury
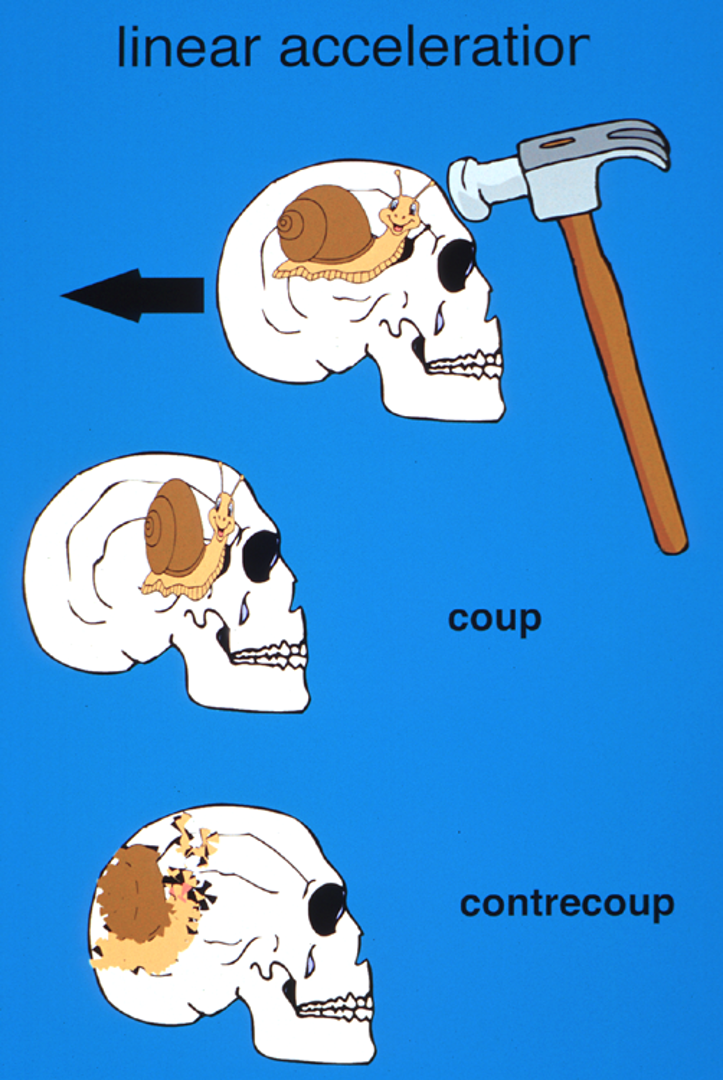
What type of injury occurs on the side opposite to the site of impact due to brain movement?
Contrecoup injury
CSF protects the brain from __________ damage by cushioning it during sudden movements.
minor
What happens when the force of linear acceleration exceeds the protective capacity of CSF?
Brain lesions or severe injuries may occur, resulting in coup and contrecoup injuries
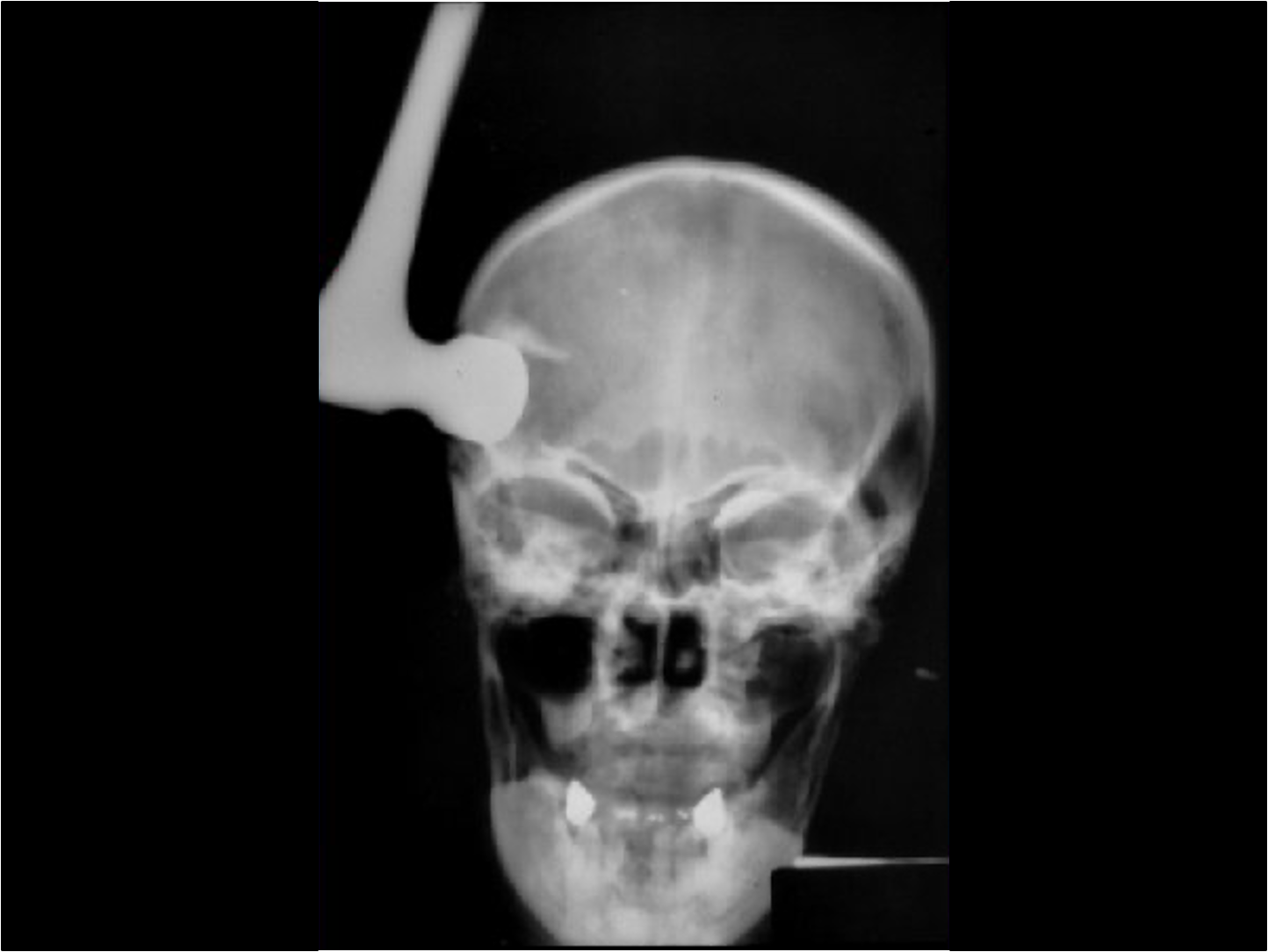
In severe cases of TBI, objects such as a __________ can penetrate the skull, causing extensive damage.
Hammer (or any other blunt or sharp object)
Why might cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) offer little protection in cases of penetrating head trauma?
It primarily cushions against blunt force trauma, not sharp or penetrating injuries
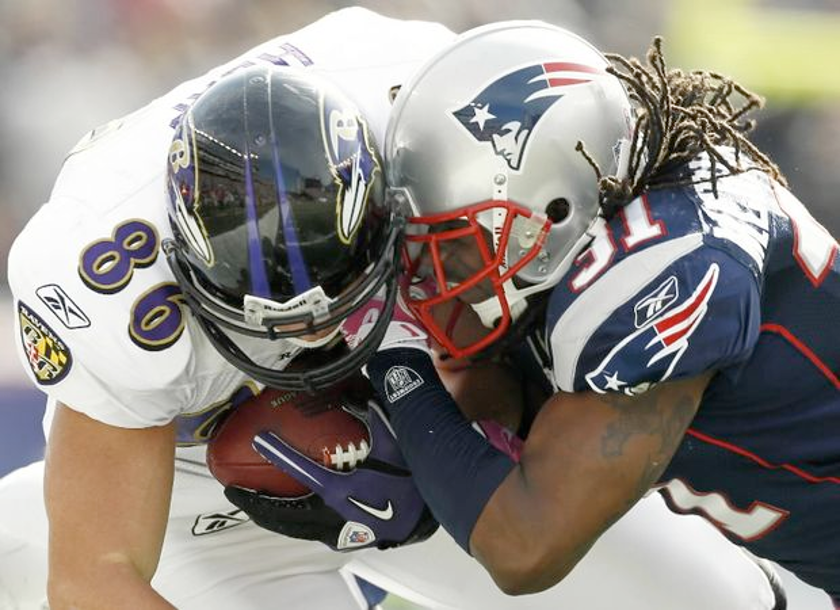

Why might helmets provide a false sense of security in contact sports?
Helmets protect against skull fractures but do not prevent the brain from moving inside the skull, which can still lead to concussions or traumatic brain injuries

In sports like soccer, players are advised to __________ their head through the ball to minimize impact.
move
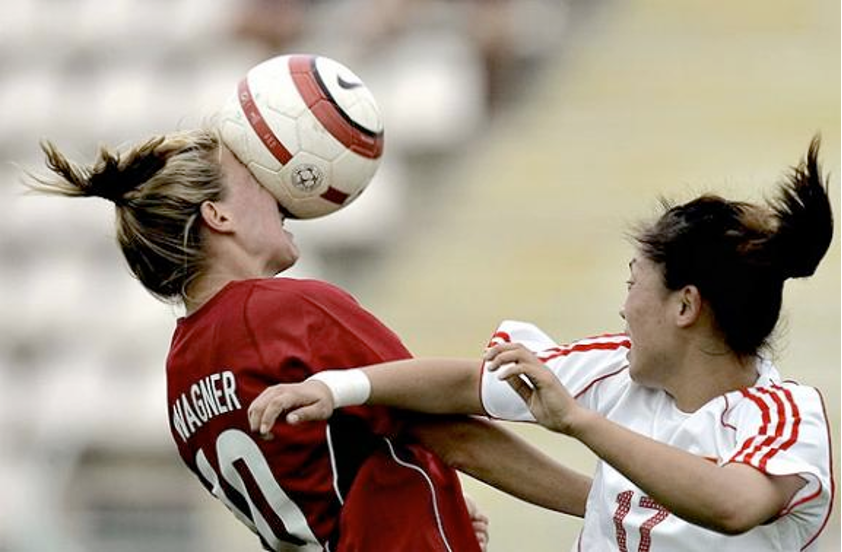

What happens when a soccer player heads the ball without following proper technique?
The ball can cause the skull to move rapidly, increasing the risk of brain injury or concussion
Repeated head trauma, especially in sports, can lead to __________ brain injury if undetected and untreated.
chronic
Why might athletes not receive a CT scan after a head injury?
Often reserved for severe symptoms, while mild concussions may go undiagnosed without visible damage
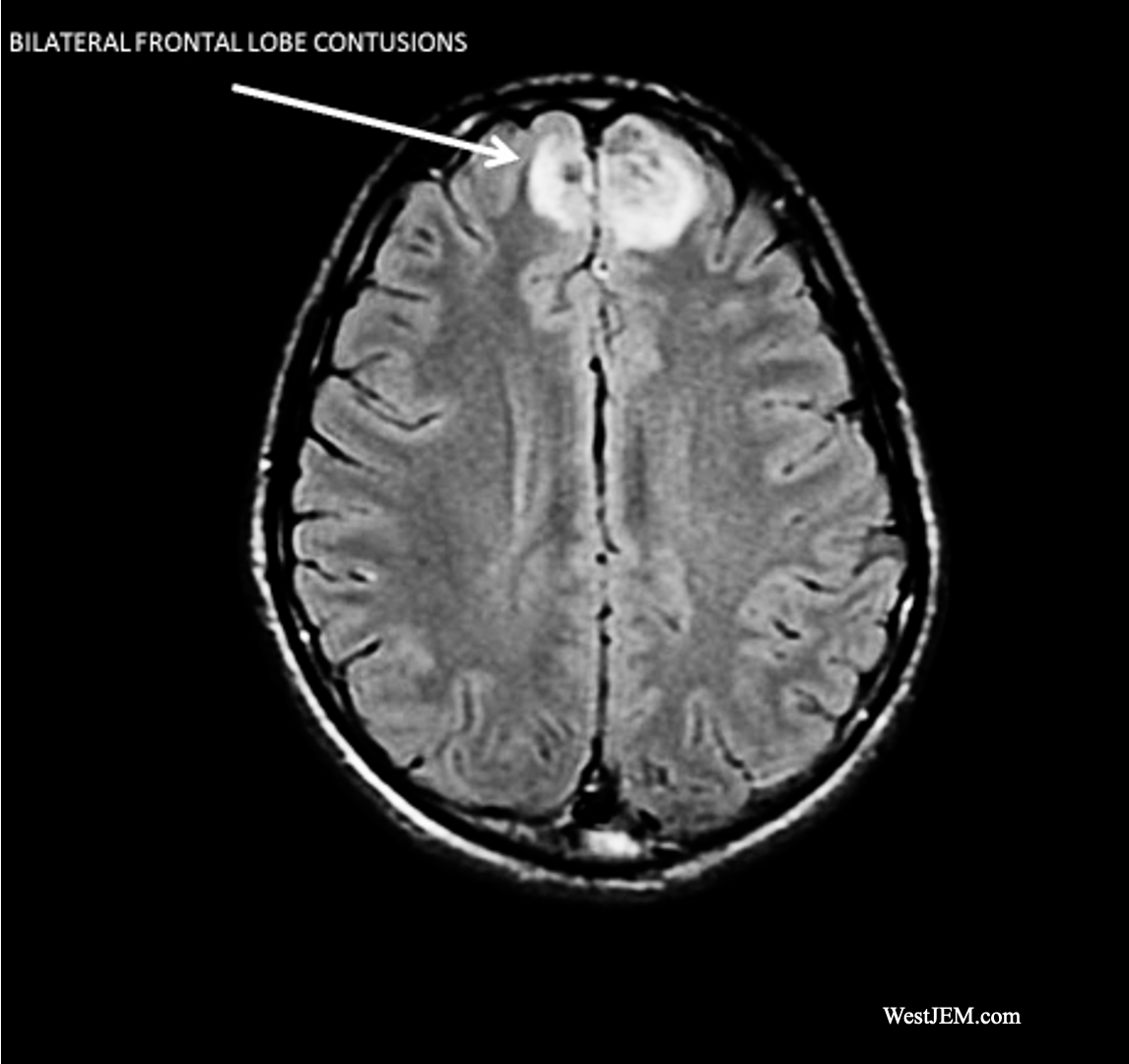
__________ contusions are bruises on both sides of the brain, commonly resulting from coup-contrecoup injuries.
Bilateral
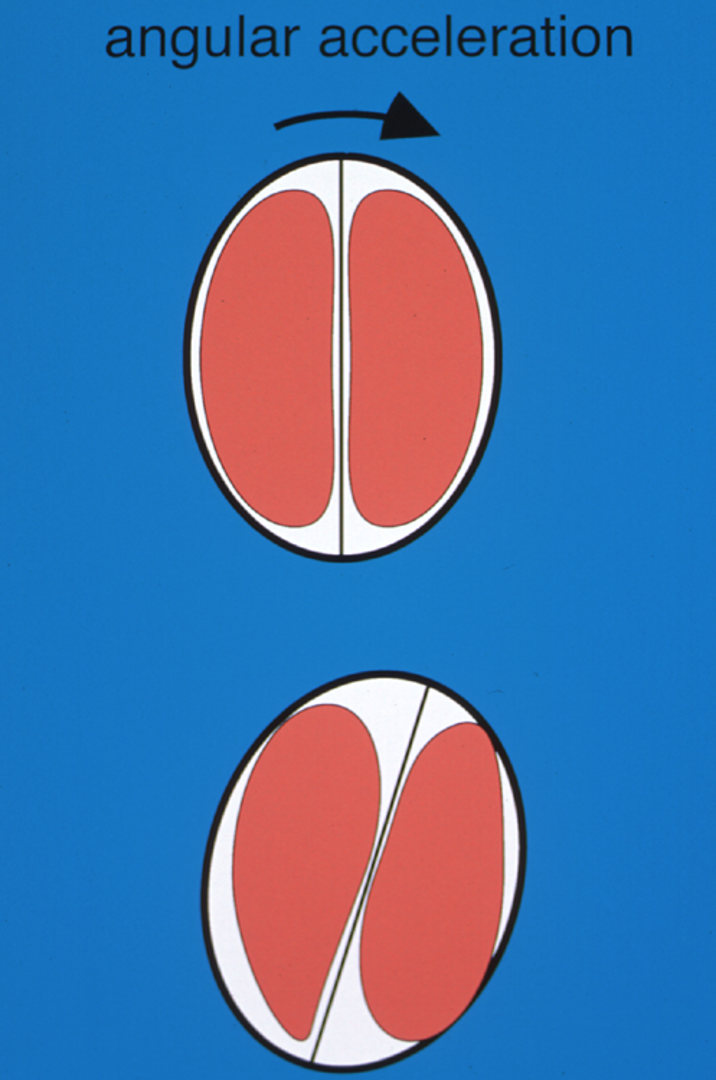
What is angular acceleration in the context of brain injury?
The rotational movement of the head, often causing the brain to twist within the skull
Unlike linear acceleration, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) does not protect the brain from __________ acceleration.
angular
Why is CSF ineffective in preventing injury from angular acceleration?
CSF reduces friction between the brain and skull, but it cannot prevent rotational forces that cause the brain to move separately from the skull
The __________ and __________ are structures within the brain that can cut into brain tissue during rotational acceleration.
Falx cerebri
Tentorium cerebelli
In boxing, an effective __________ can generate significant angular acceleration, leading to brain damage.
uppercut
What is the primary difference between the brain's response to linear acceleration versus angular acceleration?
Linear acceleration causes the brain to move back and forth, while angular acceleration causes twisting and shearing forces that damage brain tissue
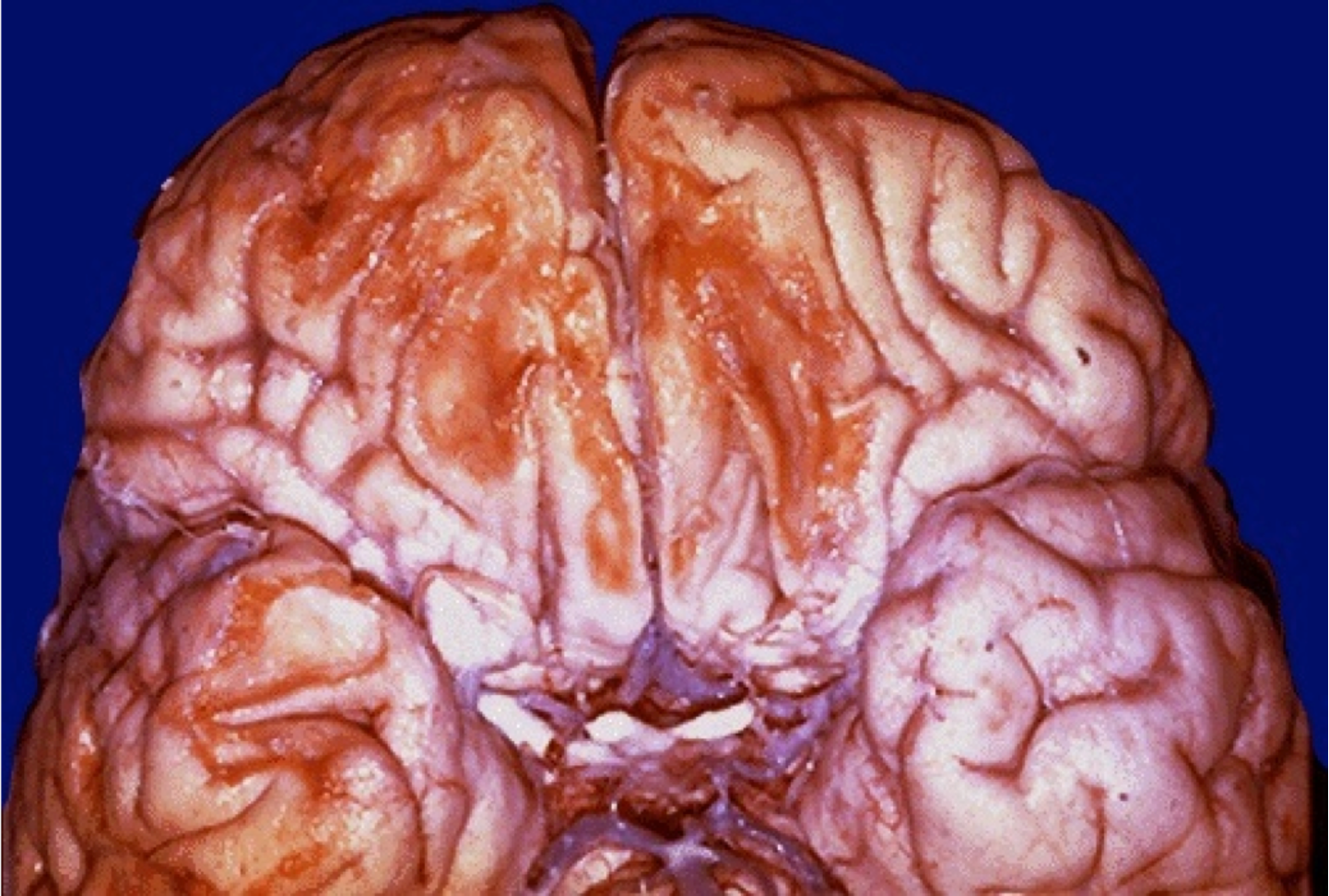
What does the term "sore brain" refer to in the context of traumatic brain injury?
The appearance of bruising, swelling, or contusions on the brain surface due to trauma
Where is cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) primarily produced?
By the choroid plexus in the lateral, third, and fourth ventricles
The __________ plexus is responsible for the production of CSF.
choroid
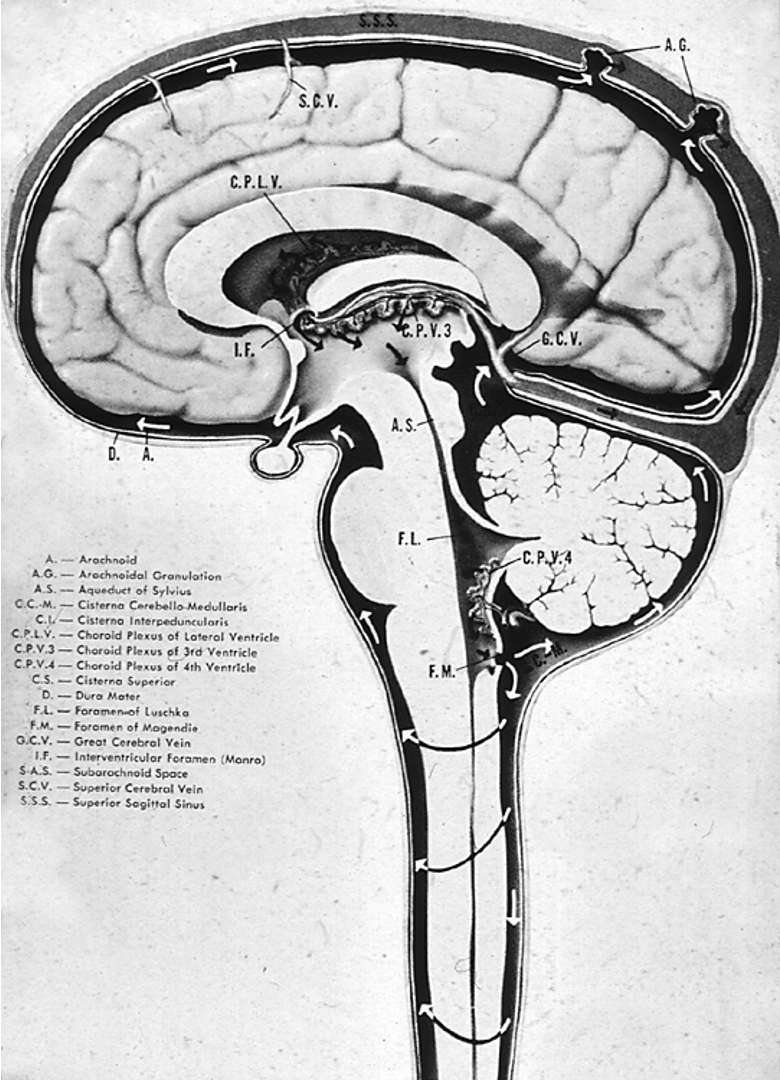
What is the correct order of CSF flow through the ventricular system?
Lateral ventricles → Interventricular foramen (Foramen of Monro) → Third ventricle → Cerebral aqueduct (Aqueduct of Sylvius) → Fourth ventricle → Foramen of Luschka and Foramen of Magendie → Subarachnoid space
After circulating through the subarachnoid space, CSF is absorbed into the bloodstream via the __________.
Arachnoid granulations
What role does CSF play in maintaining brain health?
CSF cushions the brain, removes waste, provides nutrients, and maintains a stable environment
What are the three primary driving forces for CSF flow?
Pressure wave generation at the production site, respiration, and ciliary beat of ependymal cells
During __________, CSF moves towards the cranium, and during __________, CSF moves towards the spinal column.
inspiration
expiration
How does respiration influence CSF flow?
Inspiration increases venous return, reducing brain volume and promoting CSF movement towards the cranium. Expiration has the opposite effect.
The most important factor driving CSF flow is the __________ of cells in the ependymal lining.
ciliary beat
What can result from impaired ciliary function in the ependymal lining?
Hydrocephalus
*Due to disrupted CSF circulation
Loss of ciliary function can be caused by genetic mutations, such as a mutation in __________.
CFAp4
Why is the ciliary beat particularly important in the absence of strong pressure waves or respiratory effects?
It provides a consistent and regulated mechanism for CSF movement through the ventricular system
What does the unidirectional movement of microspheres in the CSF suggest?
It indicates the effective role of ciliary beating in maintaining CSF flow
The study of CSF flow using fluorescent microspheres is helpful in understanding disorders related to impaired __________.
CSF circulation
CSF production can occur against a __________ pressure gradient.
hydrostatic
What drug can inhibit CSF production by blocking the Na⁺/K⁺ pump?
Ouabain
__________ is an inhibitor of carbonic anhydrase that can reduce CSF production.
Diamox (Acetazolamide)
How does carbonic anhydrase contribute to CSF production?
Carbonic anhydrase facilitates the formation of bicarbonate ions, which drive the secretion of CSF
CSF is a primary secretion product that has a different __________ composition than blood plasma.
ionic
Why can CSF still be produced even if the pressure in the ventricles is higher than the pressure in the blood?
The Na⁺/K⁺ pump in the choroid plexus actively transports ions to drive CSF secretion against the pressure gradient
Elevated CSF production or impaired absorption can lead to a condition known as __________.
Hydrocephalus
What is the difference between nascent CSF and bulk CSF?
Nascent CSF is freshly produced at the site of production in the ventricles, while bulk CSF is collected from the subarachnoid space, often through a lumbar puncture.
The primary site for collecting bulk CSF for diagnostic purposes is the __________ through a lumbar puncture.
Lumbar cistern
The __________ transporter moves Na⁺, K⁺, and Cl⁻ together into the CSF, contributing to fluid volume.
NKCC1 (Na⁺/K⁺/2Cl⁻ co-transporter)
Which enzyme plays a major role in CSF production by generating bicarbonate (HCO₃⁻) and hydrogen ions (H⁺)?
Carbonic anhydrase (CA)
Sodium (Na⁺) is exchanged with __________ during CSF production, maintaining ionic balance.
Potassium (K⁺)
How does water move during CSF production to contribute to the fluid volume?
Follows the osmotic gradient created by the movement of ions, primarily through aquaporin channels and NKCC1 co-transport
How does CO₂ contribute to CSF production?
CO₂ easily diffuses across membranes and is converted by carbonic anhydrase into HCO₃⁻ and H⁺, facilitating ion transport
The movement of ions through the NKCC1 transporter also facilitates the movement of __________ into the CSF by osmosis.
Water (H₂O)
CSF absorption follows the __________ pressure gradient.
hydrostatic
Can CSF absorption be blocked by transport inhibitors like ouabain?
No
Where does CSF absorption primarily occur?
By the arachnoid villi into the superior sagittal sinus
How does CSF absorption occur through the arachnoid villi?
Through free bulk flow, allowing components of different sizes to pass at similar rates
CSF absorption is strictly __________, preventing the backflow of blood into the CSF.
directional
What can happen if there is a disruption in the absorption of CSF?
It can lead to hydrocephalus, increased intracranial pressure, and severe brain damage
Backflow of blood into the CSF can result in severe __________ of the brain
inflammation
What is the normal CSF pressure in a horizontal (lying down) position?
~100 mm H₂O
In an upright position, CSF pressure in the head can be __________, while in the lumbar spinal column it can reach __________ mm H₂O.
negative
500
How many mm Hg are equivalent to 100 mm H₂O of CSF pressure?
7.6 mm Hg
__________ is equivalent to 760 mm Hg, which represents one atmosphere of pressure.
10 m H₂O
What is the most common method used to measure CSF pressure?
Lumbar puncture (spinal tap)
A lumbar puncture is typically performed between the __________ and __________ vertebrae to avoid the spinal cord.
L3
L4
Why is it safer to perform a lumbar puncture at the L3-L4 level?
The spinal cord ends around L1-L2, and the cauda equina (nerve roots) are present, reducing the risk of damaging the spinal cord.
What is pneumocephalus?
The presence of air within the cranial cavity, typically caused by trauma or surgery
Pneumoencephalus is the consequence of air entering the brain through a ____________. Driving force is the pressure difference between air at atmospheric pressure and the negative pressure in the calvarium when the person is in _____________.
skull lesion
upright position
A classic sign of a skull fracture leading to CSF leakage is __________, which is the leakage of CSF from the nose.
Cerebrospinal rhinorrhea
How can you differentiate between nasal mucus and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
Perform a glucose test — CSF contains glucose, while mucus does not
CSF has a slightly __________ taste
sweet
What simple technique can reduce CSF leakage from the nose?
Adjust the patient’s head tilt to around 25-30 degrees to reduce pressure and stop the leakage
Extreme tilting should be avoided as it may worsen the pressure difference and increase the risk of __________.
Air entry into the brain (pneumocephalus)
In the case of persistent CSF leakage, what further treatment may be necessary?
Surgical repair of the skull fracture
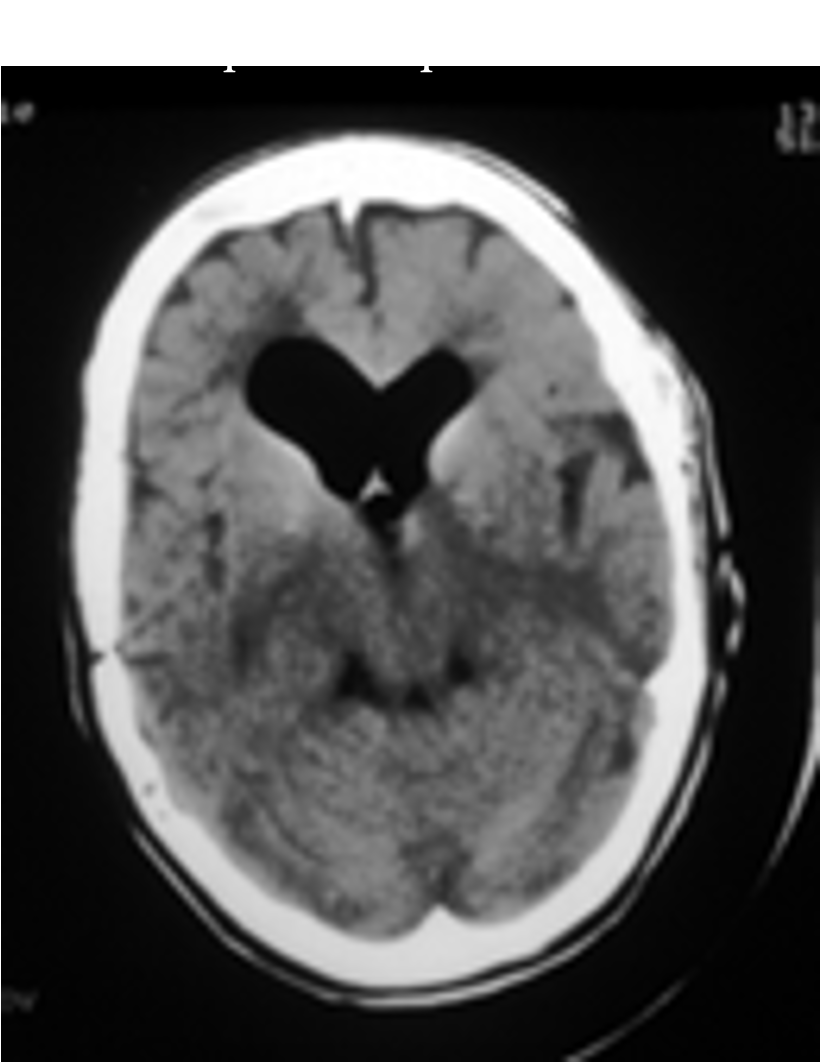
On a CT scan, air in the brain appears as __________ areas.
Black (hypodense)
A severe form of pneumocephalus with increased intracranial pressure is called __________.
Tension pneumocephalus
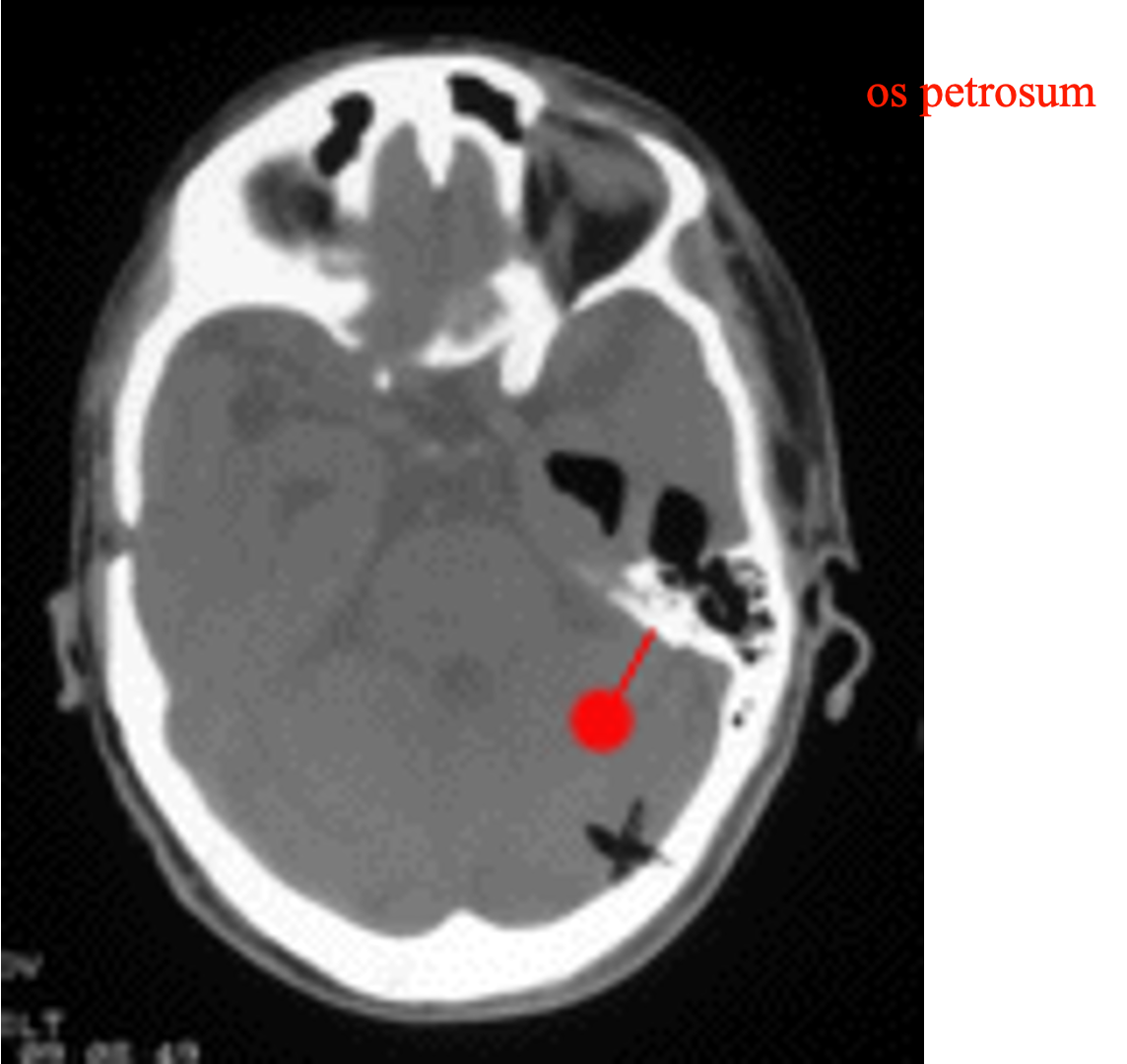
What is a potential cause of spontaneous pneumocephalus in the absence of trauma?
A defect in the petrous bone, often linked to an ear infection or mastoid air cell involvement
The petrous part of the temporal bone contains the __________, which can be a site of air leakage into the brain.
Mastoid air cells
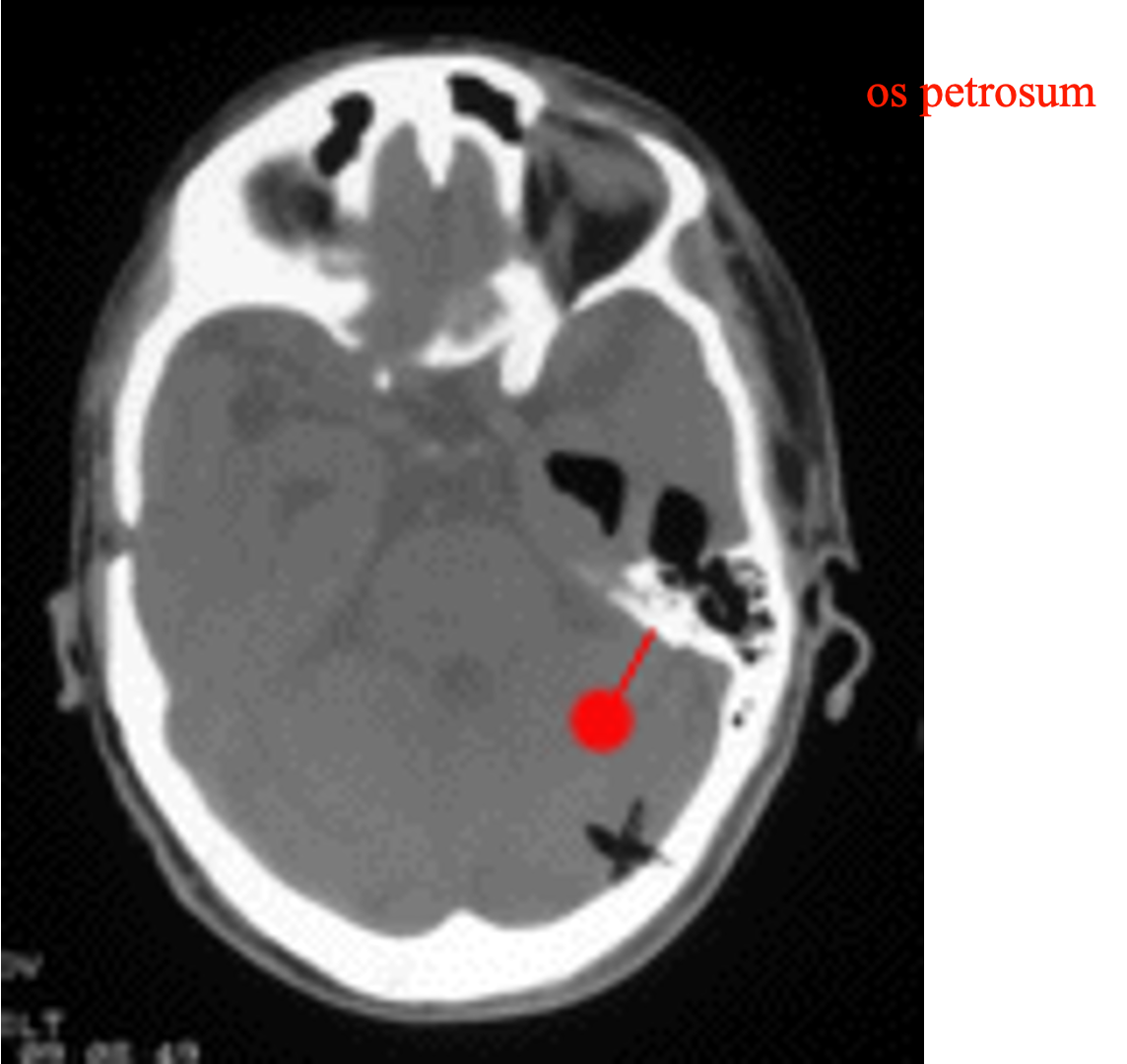
72 year old woman, defect in petrous bone
A temporary measure to relieve symptoms in this case was the placement of a __________.
Surgical procedure performed: A subtemporal craniotomy with extradural exploration and repair using cadaveric dura and fibrin glue.
Successful repair of the petrous bone defect resulted in the __________ of the pneumocephalus.
Ventriculostomy
Resolution
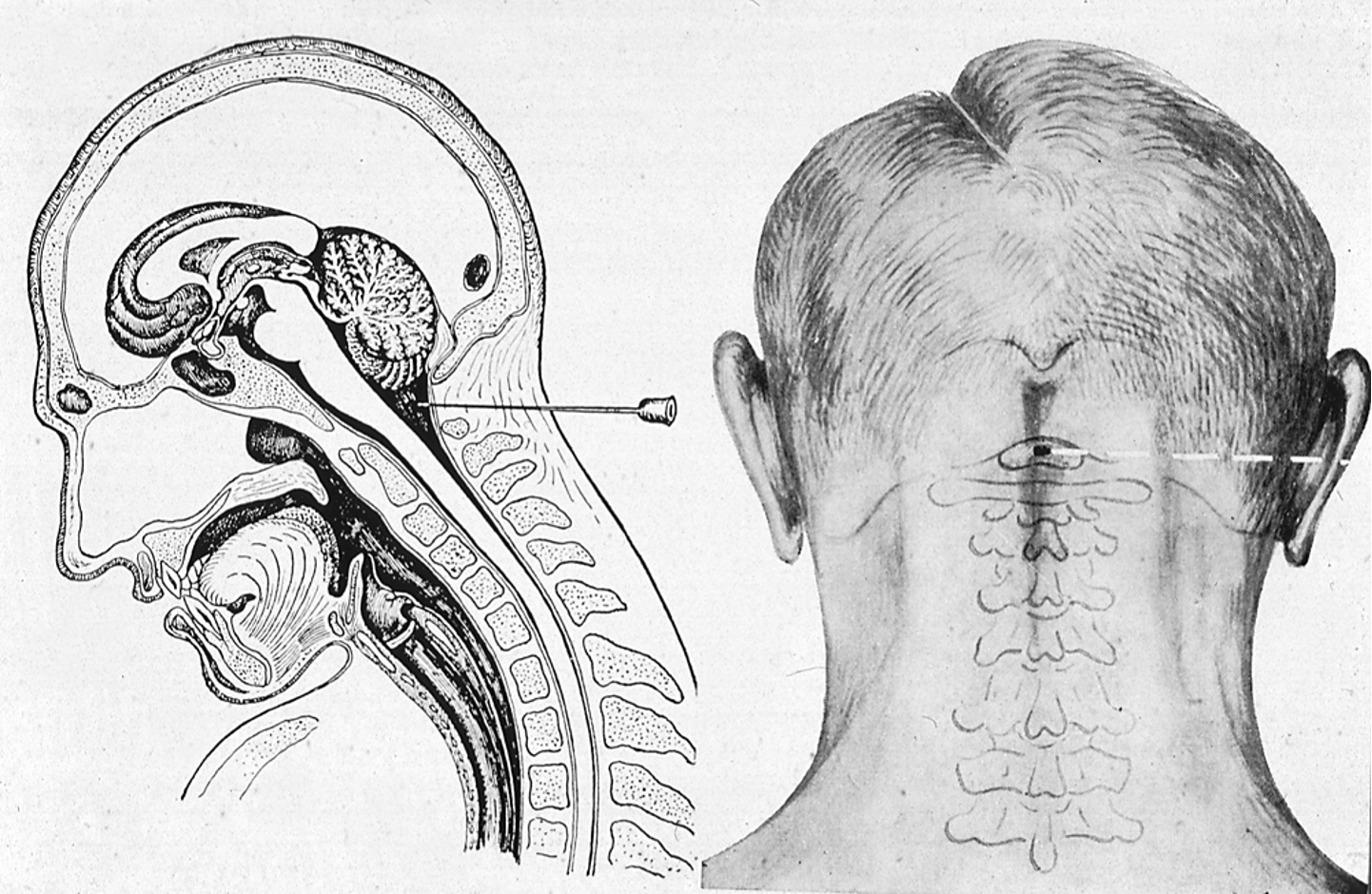
What is a cisterna magna puncture?
A procedure where cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is collected from the cisterna magna, located at the base of the skull
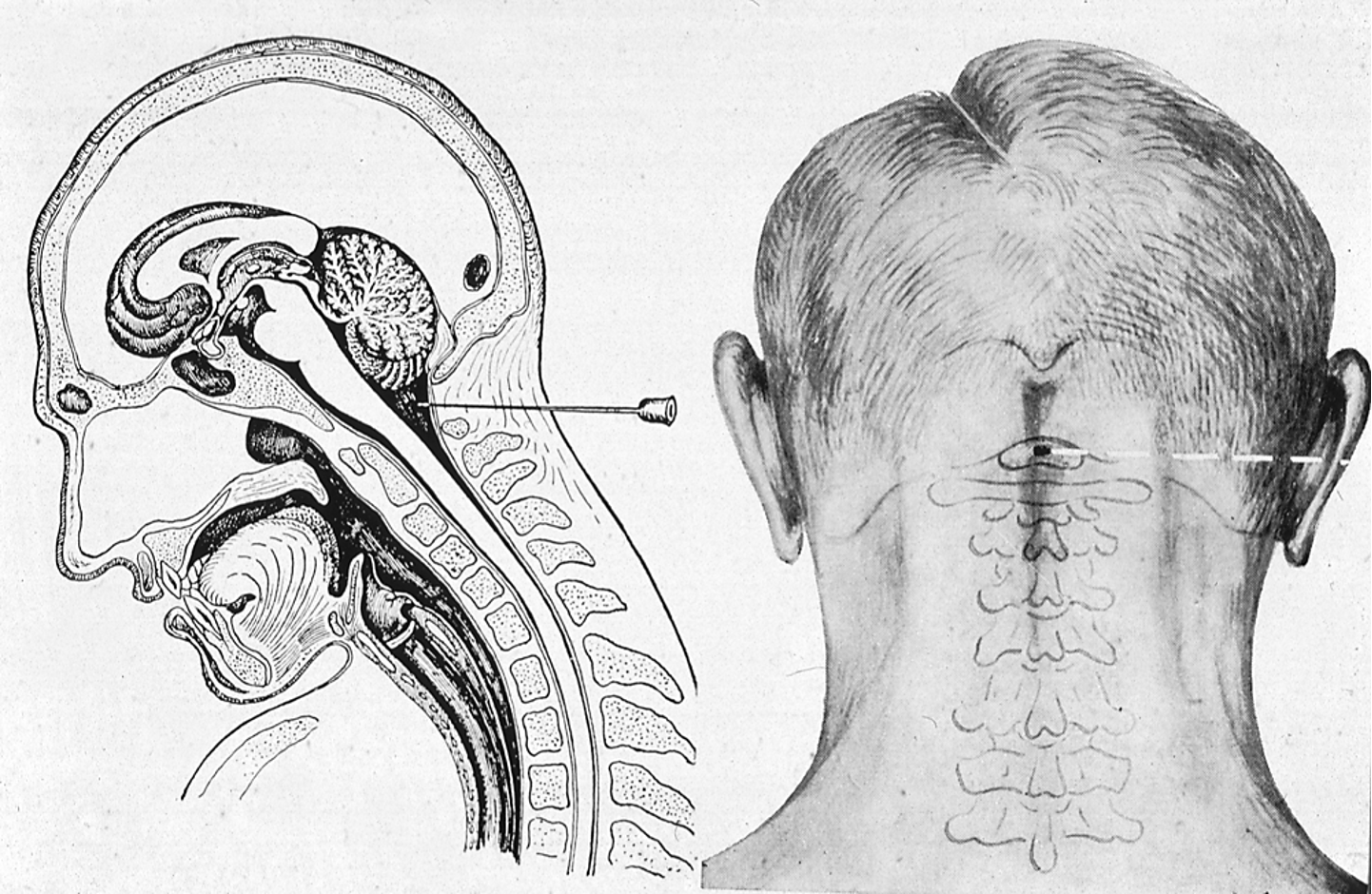
The cisterna magna is a large subarachnoid space situated between the __________ and the __________.
Cerebellum
Medulla Oblongata
When is a cisterna magna puncture typically performed instead of a lumbar puncture?
When a lumbar puncture is contraindicated or inaccessible, such as in cases of spinal deformity or severe spinal trauma
Why is a cisterna magna puncture considered more dangerous than a lumbar puncture?
The proximity to vital structures like the brainstem increases the risk of neurological injury
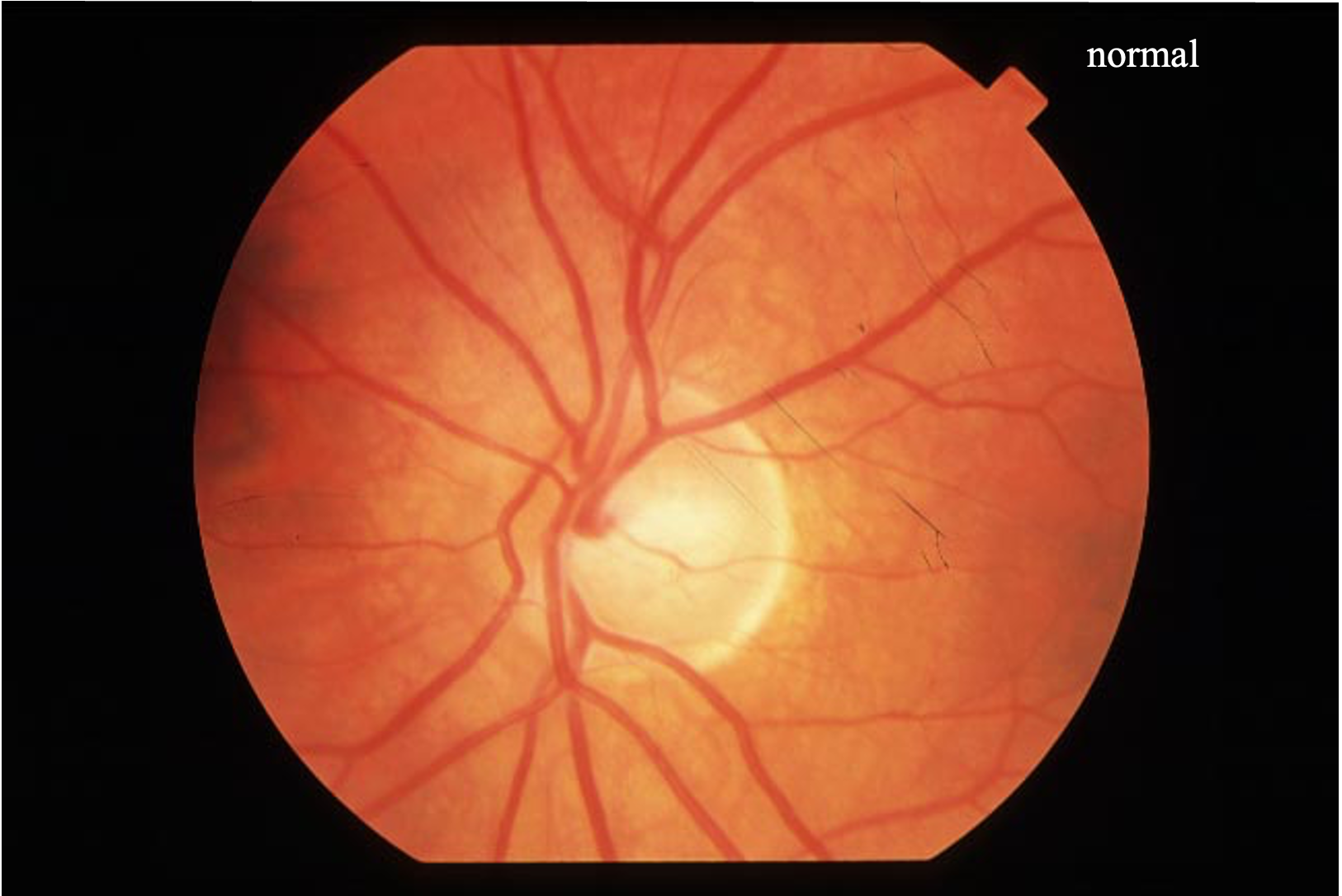
What is the papilla, also known as the optic disc?
The point where the optic nerve enters the retina, visible as a circular, slightly elevated area during fundoscopic examination
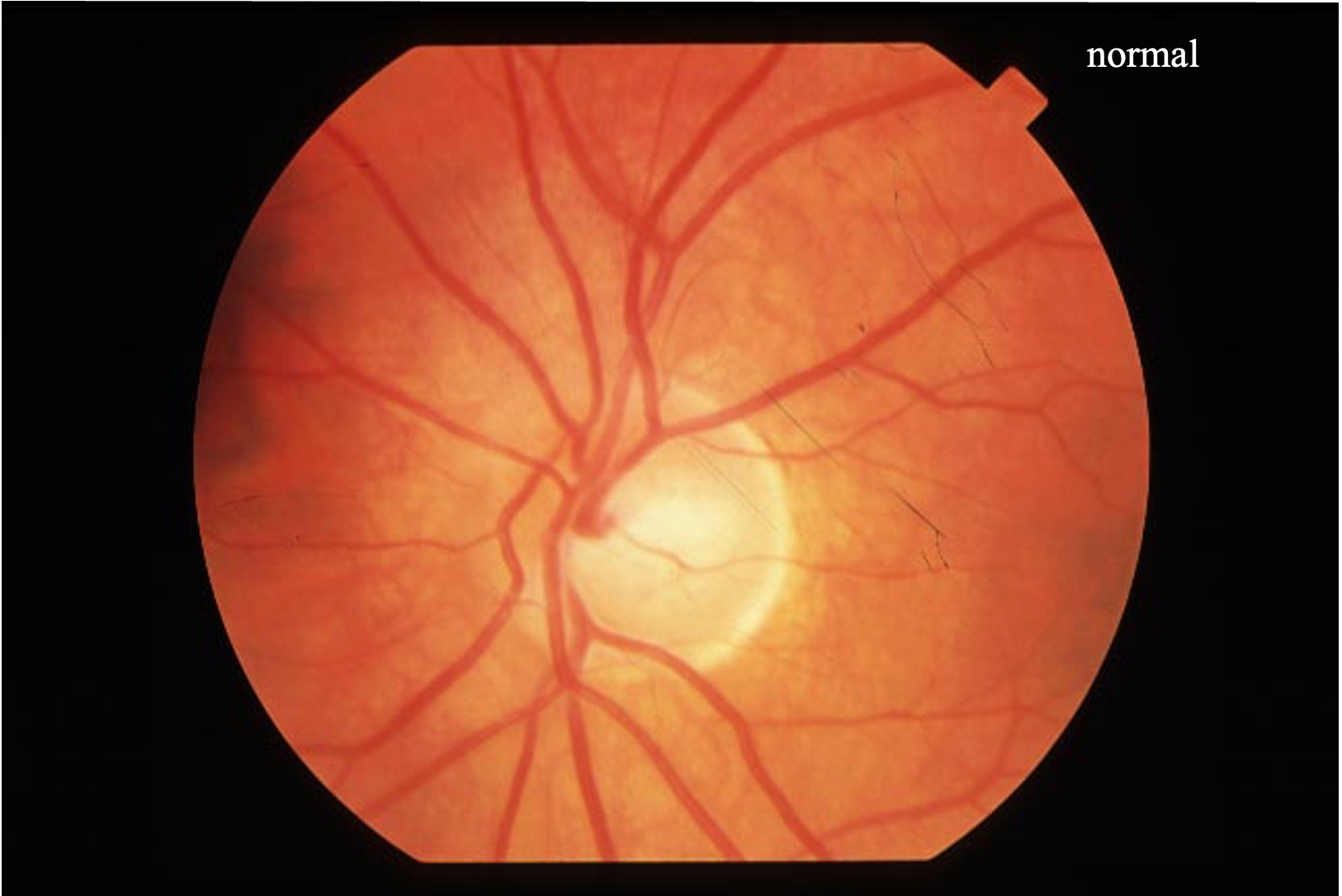
What is the appearance of a normal optic disc on fundoscopic examination?
A round, well-defined structure with a central pale area called the cup, surrounded by a pinkish rim
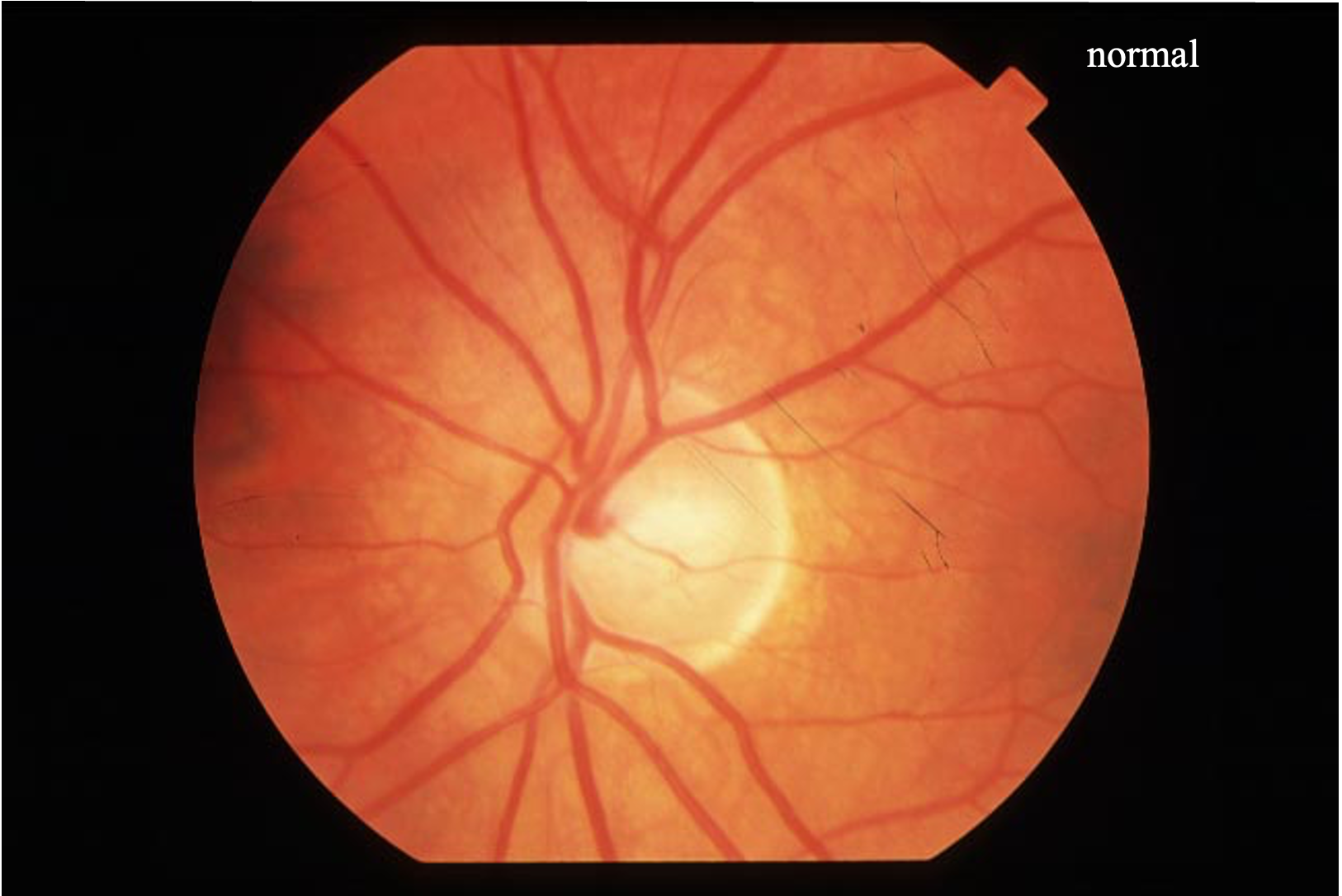
The absence of __________ is a characteristic of a normal optic disc.
Papilledema