Kidney Mega
1/216
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
217 Terms
What is the difference between polycystic kidney disease and polycystic kidneys?
Polycystic kidney disease is congenital and polycystic kidneys are acquired
What are the functions of the urinary system?
Urine formation and voiding
Acid base balance
Water and electrolyte regulation
What are the endocrine roles of the kidney?
EPO
RAAS
Vitamin D
What are the two types of nephrons?
Cortical nephrons and juxtamedullary nephrons
Describe cortical nephrons?
Make up 85% of nephrons and are deep in the renal cortex
Describe juxtamedullary nephrons
Make up 15% of nephrons, are in the renal cortex but close to the renal medulla
What is an end artery?
An artery that is the only supply of oxygenated blood to a portion of tissue
What is the significance of end arteries?
There is no collateral circulation because they do not anastomose to their neighbors
What nephron type is longer?
Juxtamedullary
How does the kidney manage acid base balance?
Bicarbonate reclamation
How doe sthe kidney manage extracellular potassium concentration?
Aldosterone and PCTs
Where is the RAAS located?
Juxtaglomerular apparatus
What does the RAAS system do?
Maintain renal blood pressure
Stimulate aldosterone from adrenals to change sodium reabsorption
What does the kidney do in regards to Vitamin D?
Conversion to active form, calcitriol
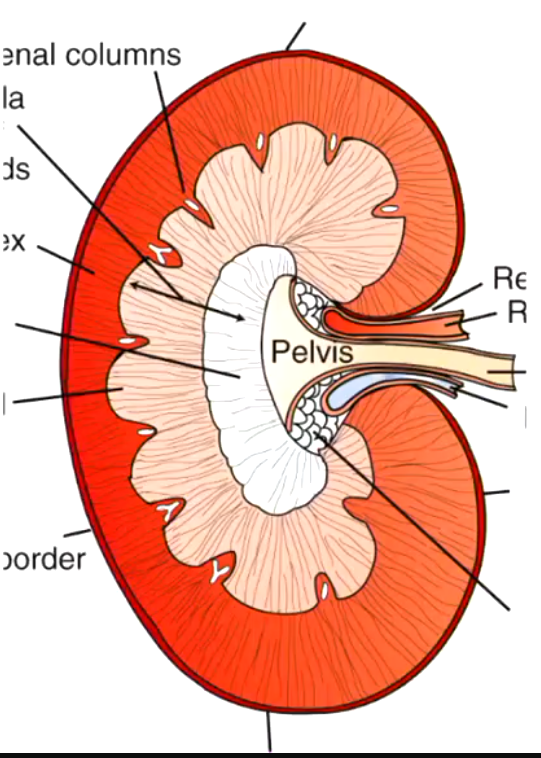
Unilobar kidney
Unilobar kidney grossly
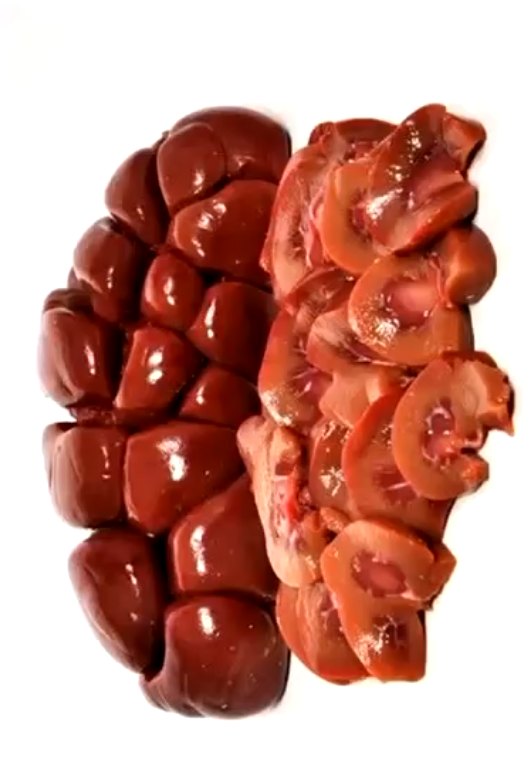
Multilobar
What species has a multilobar kidney?
Cattle
What species has a grossly unilobar kidney?
Pigs
What species has a unilobar kidney?
Dogs, cats
What disease can reach the kidney from lymphatics?
FIP
Why does adrenal cancer travel to the kidney so easily?
The adrenal vein is right next to kidney vessels
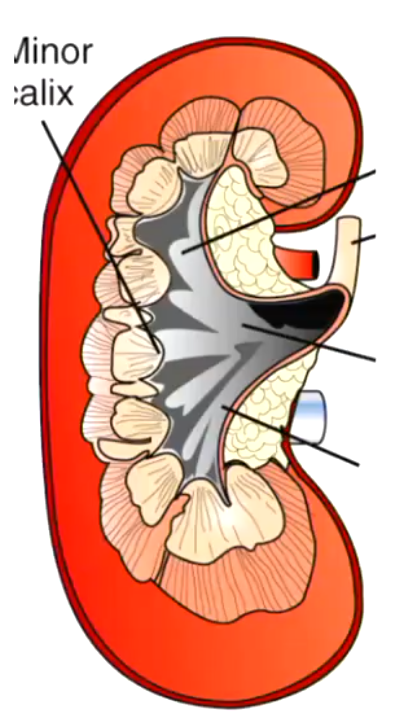
What are branches of the renal artery called?
Interlobar vessels
When do interlobar vessels become intralobular vessels
Corticomedullary junction
What is the juxtaglomerular apparatus?
Feel the pressure of the bowman’s capsule to increase pressure if needed
How does the juxtaglomerular apparatus change blood pressure?
If it is low, they stimulate the RAAS system and causes constriction of afferent vessels
What suffers the most from ischemia?
Tubules because they get the oxygenated blood last
What are stable cells?
Cells that have a limited ability to regenerate
What type of cells are nephrons?
Stable cells
What happens if a nephron takes irreversible damge?
They are unable to regenerate for ever
What is the intact nephron theory?>
Damage to one segment of the nephron affects functions in other segments of the nephron
How many nephrons do humans and horses have per kidney?
1 million
How many nephrons do dogs have per kidney?
400,000
How many nephrons do cats have per kidney?
200,000
How many nephrons do mice have per kidney?
14,000
How many nephrons do rats have per kidney?
30,000-35,000
How many nephrons do cattle have per kidney?
several million
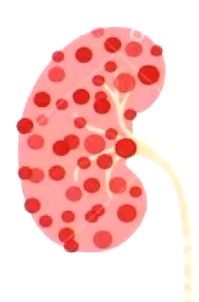
Polycystic kidney disease
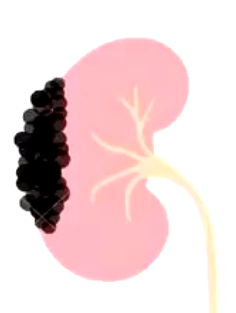
Kidney cancer
When is it classified as renal failure?
When you lose 75% functional capacity
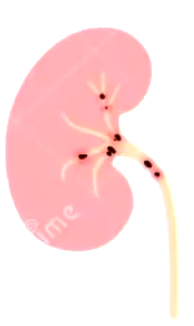
Kidney stones
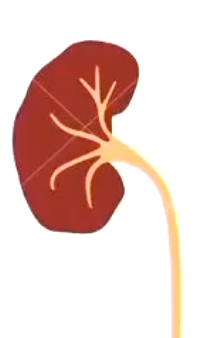
Kidney failure
What species has the maximum number of nephrons?
Cattle
What are the congenital diseases of the kidney?
Aplasia
Hypoplasia
Dysplasia
Polycystic Kidney Disease
What are the acquired diseases of the kidney?
Nephritides can lead to polycystic kidney
Hemorrhage/infarction
Nephropathy (degeneration)
What are the routes that a pathogen can get to the kidney?
Blood or urine or lymphatics
What is an example of renal dysplasia?
Juvenile progressive nephropathy
What are the causes of having one large and one small kidney?
Hypoplasia if it is young
Atrophy if it is old
What animal gets polycystic kidney disease the most?
Cheetahs due to inbreeding
What mutation causes polycystic kidney disease?
Polycystin 1,2 or fibrocystin
What part of the kidney does a polycystin 1 or 2 mutation effect?
Tubule
What part of the kidney does a fibrocystin mutation effect?
Interstitium
What 3 things cause the cysts during polycystic kidney disease?
Abnormal extracellular matrix
Cell proliferation
Fluid secretion
What type of inheritance if polycystic kidney disease?
Autosomal dominant (more in males)
What species can get polycystic kidney disease?
Pigs, and lambs
Dogs
Persian cats
What breeds of dogs are more likely to get polycystic kidney disease?
Cairn, West Highland terriers, Collie
What organs can get get cysts with polycystic kidney disease?
Kidneys
Liver
Pancreas
What is the origin of embolic bacteria causing a spotted kidney?
Aorta/bacteremia
What is the morphology of the kidney with an ascending bacterial infection?
What are the ascending infection agents seen in the kidney?
E. coli
Proteus
Enterobacter
What is a predisposing factor to ascending bacterial infecitons in the kidney?
Diabetes Mellitus due to increased sugar
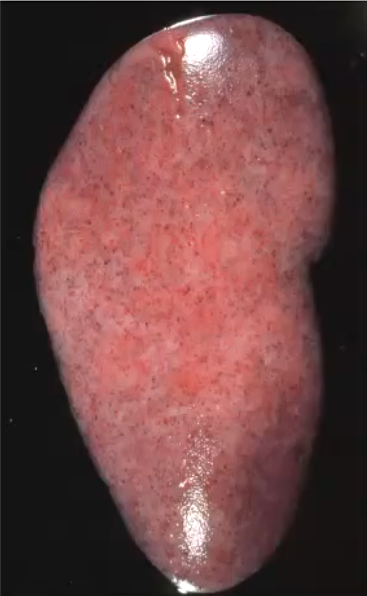
Septic (embolic) nephritis
What is the main cause of hemolytic uremic syndroume?
E. coli O157:H7 causing DIC with tubular necrosis usually from eating rare meat
What is a viral cause of acute renal hemorrhage?
Herpes
What is a bacterial cause of acute renal hemorrhage?
Embolic nephritis
What does trauma look like with acute renal hemorrhage?
Suffusive hemorrhage
What are the general causes of acute renal hemorrhage?
Viral
Bacterial
Trauma
Thrombosis
Anticoagulants
What causes a wedge shape necrosis in a kidney?
An acute renal infarct of an end artery
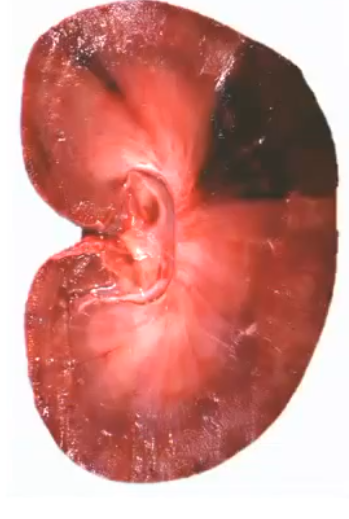
Cause
An acute renal infarct of an end artery
How can you feel an acute renal infarct with your hands?
It will be significantly raised
What is a line of demarcation in the kidney?
It is caused by a subacute renal infarct. They kidney dilates vessels to try and save it after multiple infarcts
How can you feel a subacute renal infarct with your hands?
It will be slightly raised
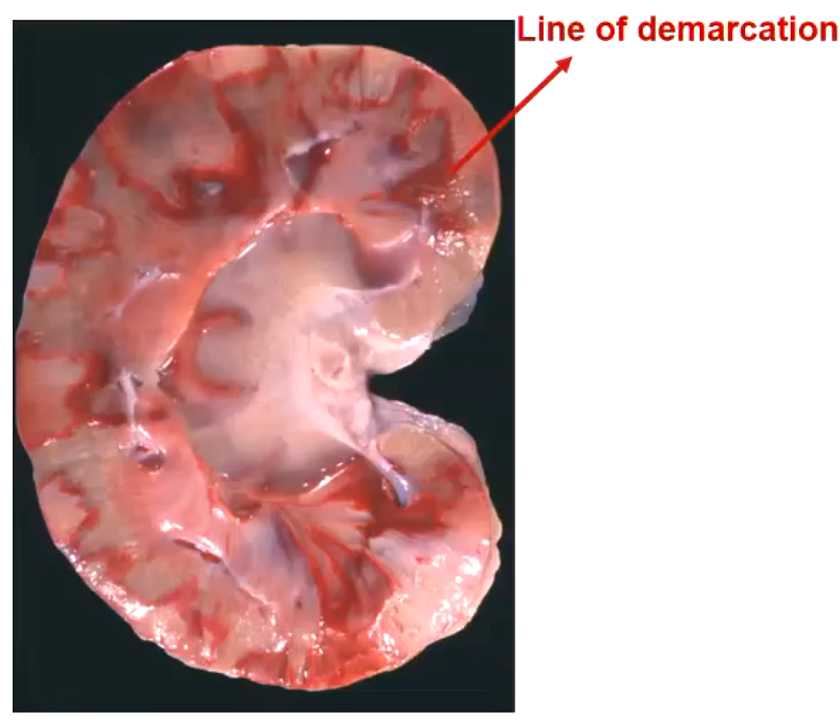
Subacute renal infarct
How do feel a chronic renal infarct with your hands?
It will be depressed
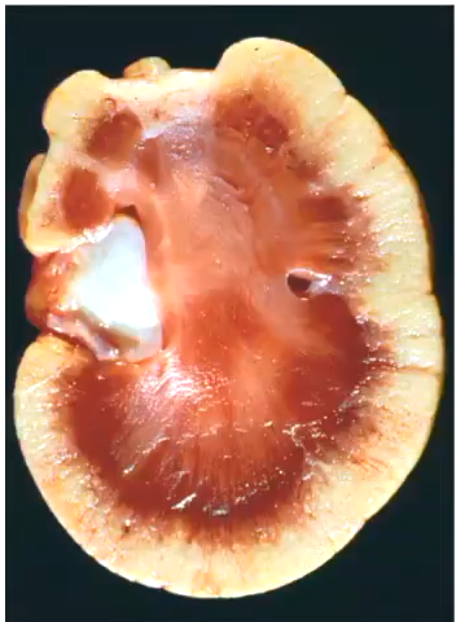
Chronic renal infarct
How do you measure the chronicity of a renal infarct?
If it is raised or depressed
What are the components of the renal tubules?
Epithelium and basement membranes
How do you differentiate a toxic or an infarct in a kidney?
If nothing is viable then it is an infarct
If the basement membrane is intact it is a toxicity
What are the main etiologies of direct tubular damage?
Ischemia and toxin
What are 2 toxins that affect the renal tubules?
Mercury and lead
How can tubules respond to injury?
With casts
T/F toxins target different parts of the tubules than each other?
True
What do cellular casts indicate?
Tubular damage
How does hyperglycemia cause a thickened GBM?
Collagen type IV, fibronectin are increased, and decreased heparan sulfate proteoglycan are
What are the damages caused from hyperglycemia during diabetic nephropathy?
Thickened GBM due to metabolic defect
Nonenzymatic glycosylation of proteins
Hemodynamic changes
What are the glomerular hemodynamic changes of hyperglycemia?
Increased GFR
Glomerular hypertrophy
Describe SGLT-2s role in diabetic treatment?
You can give them jardiance to keep SGLT-2 open and reduce the hyperglycemia
What is type 1 diabetes?
The pancreas cannot make enough insulin
What is type 2 diabetes?
There is insulin resistance
What is Fanconi syndrome?
There is proximal renal tubular acidosis causing a lack of reabsorption of some solutes form urine
What are the most commonly affected solutes with Fanconi Syndrome?
Glucose and Bicarbonate
What breed is predisposed to Fanconi Syndrome?
Basenji
What is an example of paradoxical glucose uria?
Fanconi syndrome
What are the gross lesions of fanconi syndrome?
None, only hitologic
What are two causes of renal tubular necrosis due to pigments?
Hemoglobin and myoglobin
How can hemoglobin get to the kidney?
Hemolysis
Copper toxicity
What is the color of hemoglobin pigment in the kidney?
Gunmetal color (dark)
Why can you not give your goat sheep feed?
There is more copper causing toxicity
How does myoglobin cause renal tubular necrosis due to pigment?
Myonecrosis due to exertional myopathy or consumening monensin
How can you differentiate from hematuria and hemoglobinuria?
RBCs will pellet when centrifugated