Unit 2 AP Psych ppt review
1/203
Earn XP
Description and Tags
taken directly from the ppt and work we have done
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
204 Terms
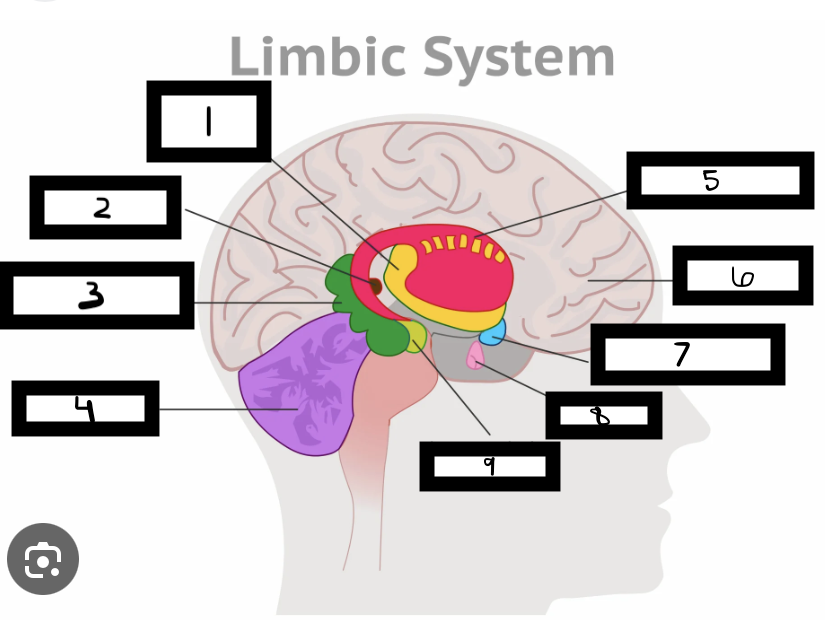
what is 1
thalamus
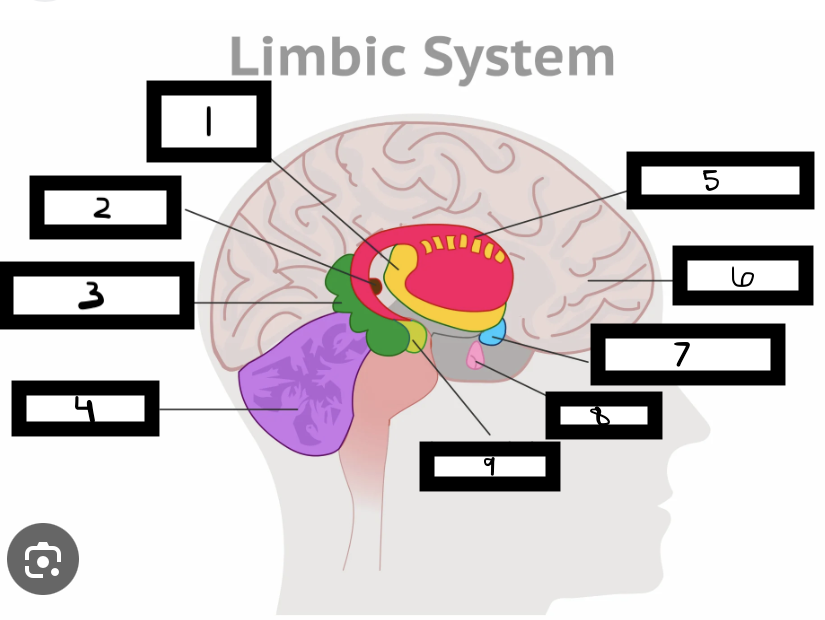
what is 2
pineal gland
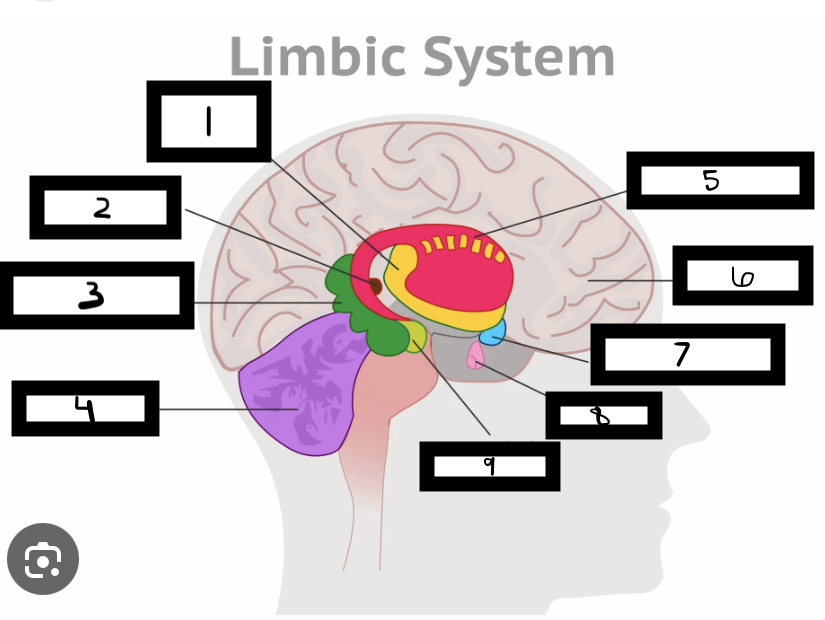
what is 3
hippocampus
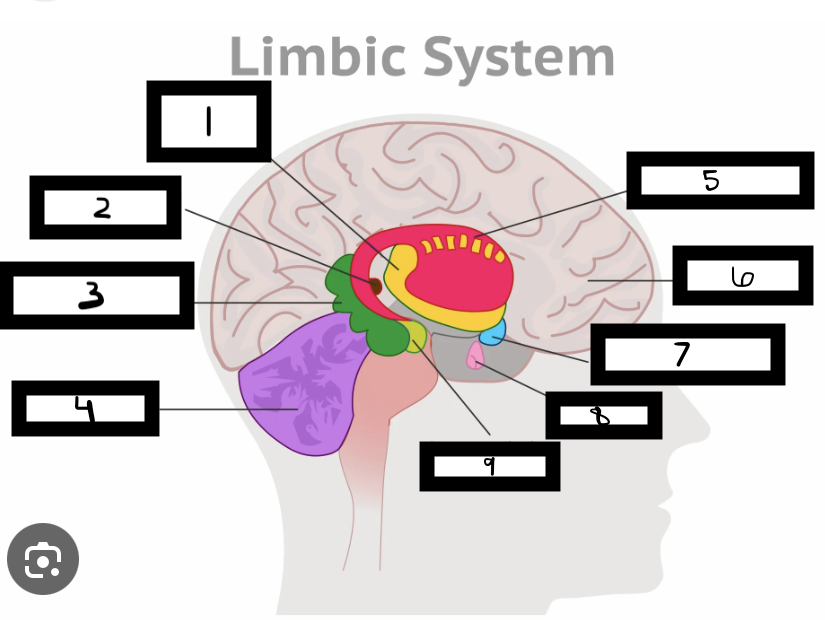
what is 4
cerebellum
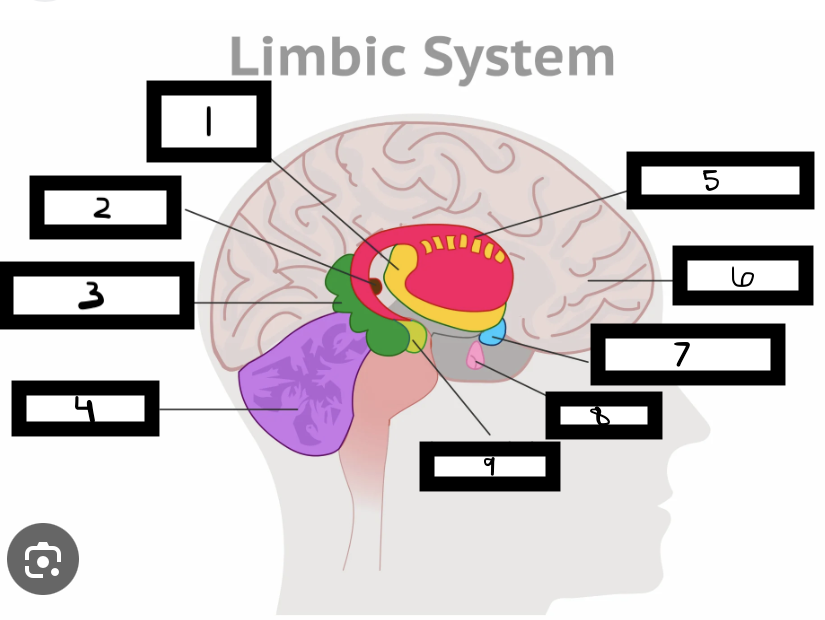
what is 5
basal ganglia
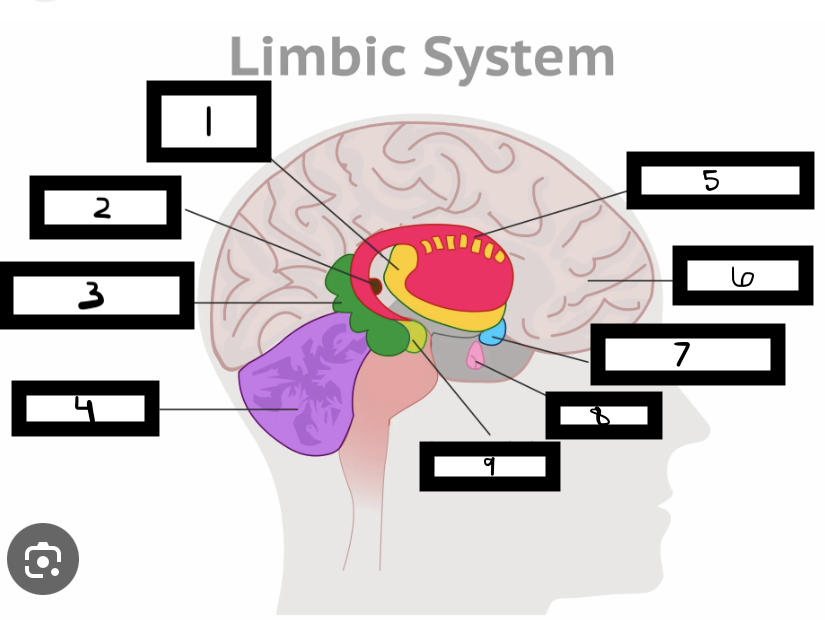
what is 6
cerebrum
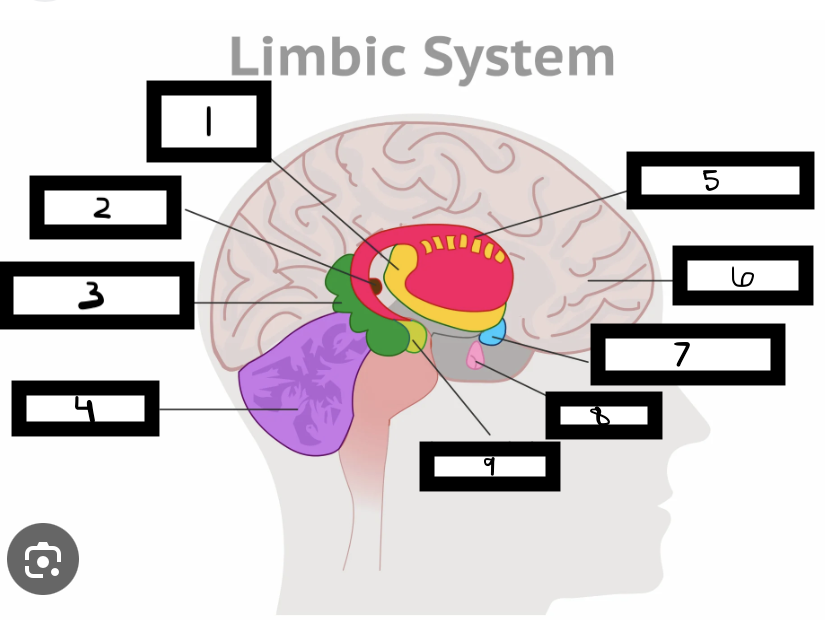
what is 7
hypothalamus
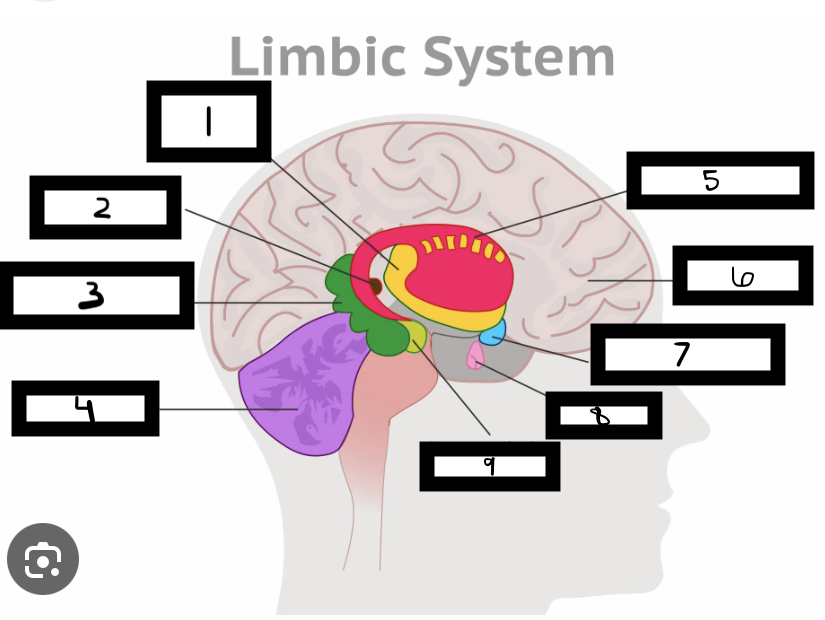
what is 8
pituitary gland
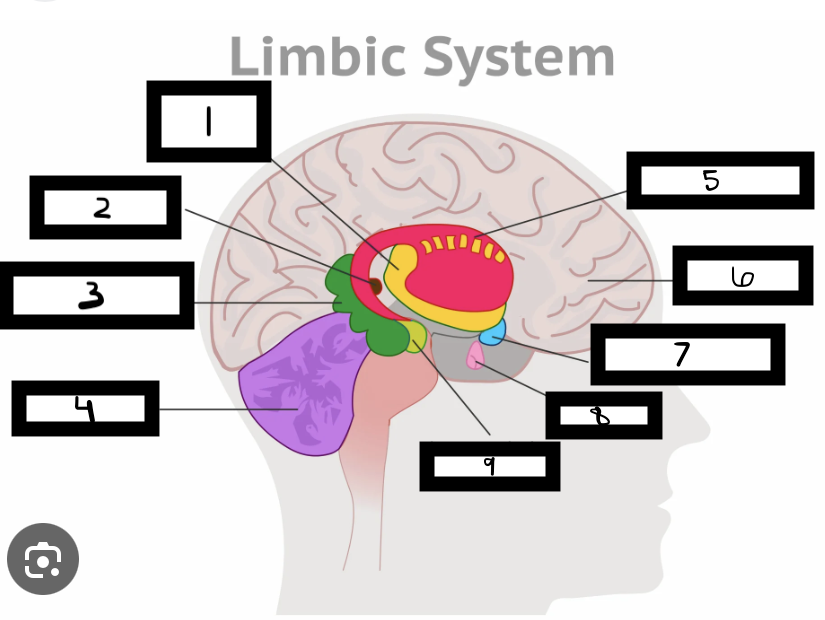
what is 9
amygdala
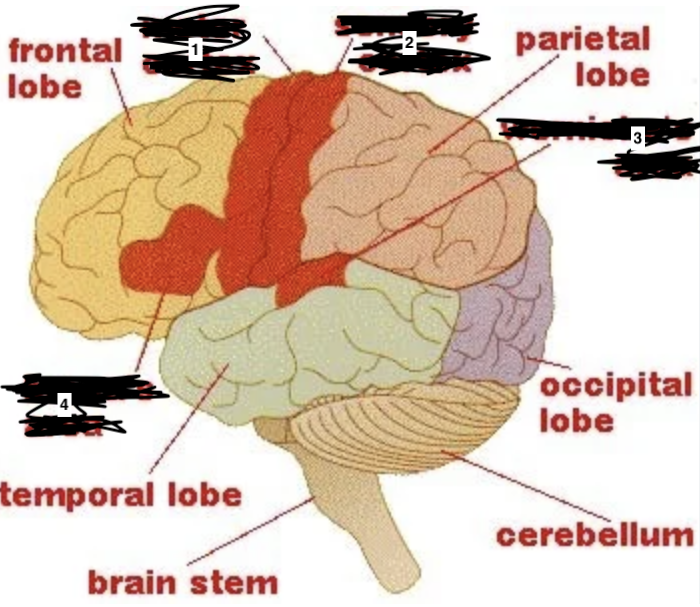
what is 1
motor cortex
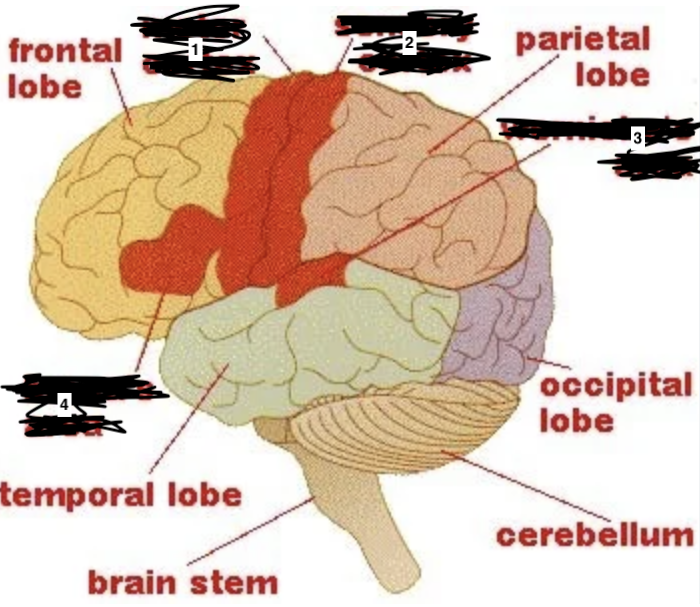
what is 2
sensory cortex
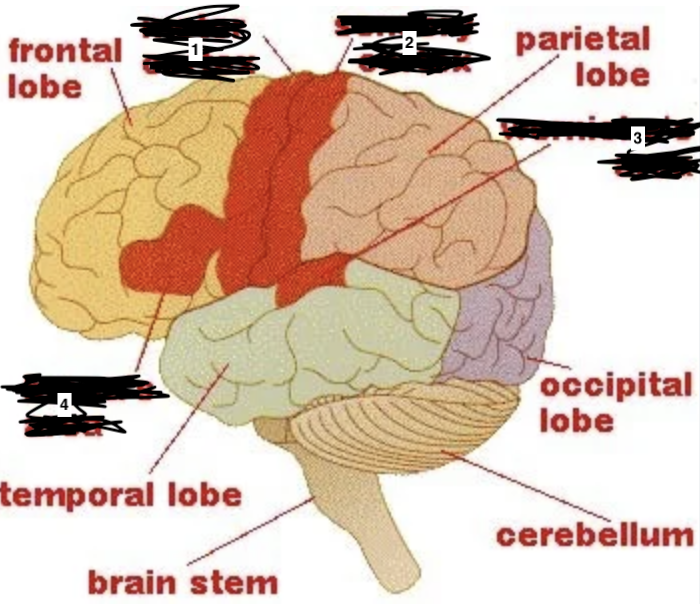
what is 3
wernickes area
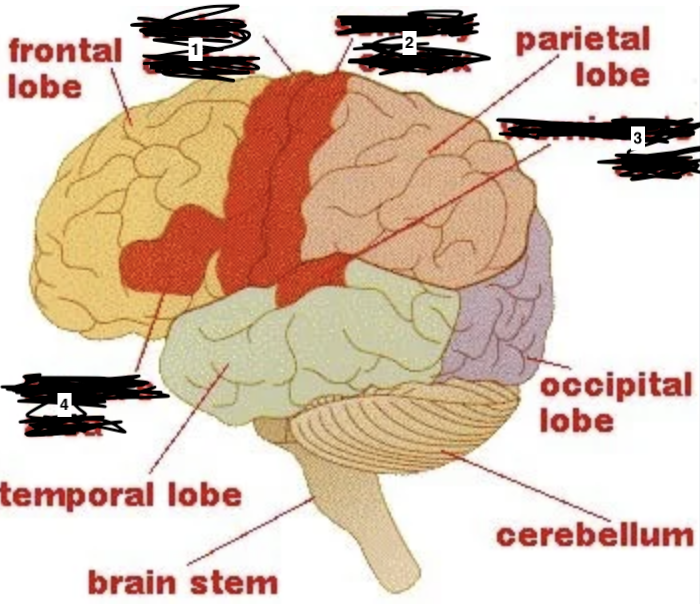
what is 4
brocas area
what did Broca do
discovered brocas area
what did Wernicke do
discovered Wernickes area
what is an excitatory neurotransmitter
signals neuron activation
what is an inhibitory neurotransmitter
inhibits neuron activation
is serotonin a inhibitory or excitatory
inhibitory
is norepinephrine a inhibitory or excitatory
excitatory
is epinephrine a inhibitory or excitatory
excitatory
is dopamine a inhibitory or excitatory
both
is gaba a inhibitory or excitatory
inhibitory
is glutamate a inhibitory or excitatory
excitatory
are endorphins a inhibitory or excitatory
inhibitory
is acetylcholine a inhibitory or excitatory
inhibitory
what is phrenology
a complex process that involved feeling the bumps in the skull to determine an individuals psychological attributes. These bumps contributed to his brain map.
who invented phrenology
Frantz Joseph Gall
what were the basic assumptions of Gall?
by examining the shape and unevenness of the skull, one could discover the development of certain cerebral organs which are responsible for different intellectual aptitudes and character traits
Phrenological parlors
abused the science for commercial purposes and created a bad reputation of the science
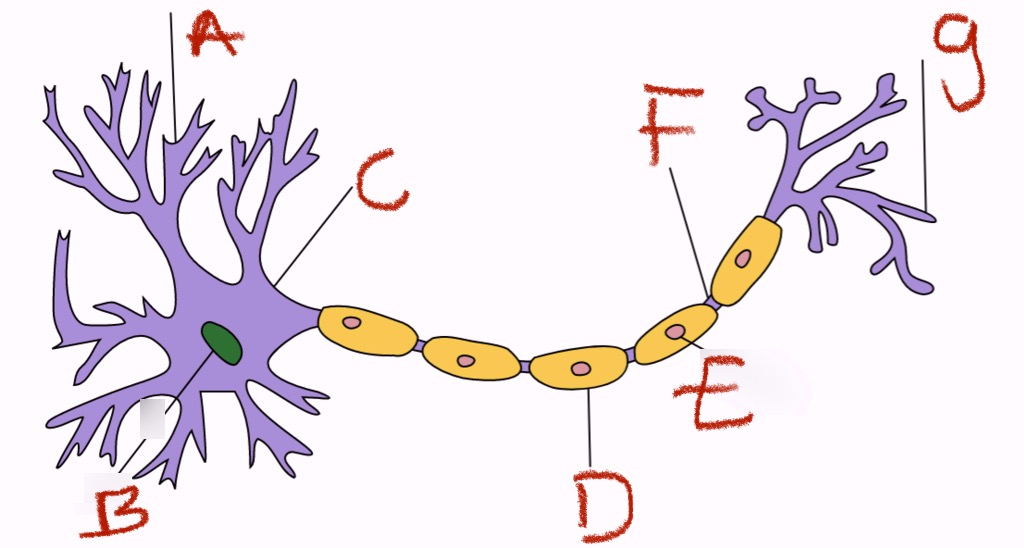
what is a and what does it do
dendrites, receivers
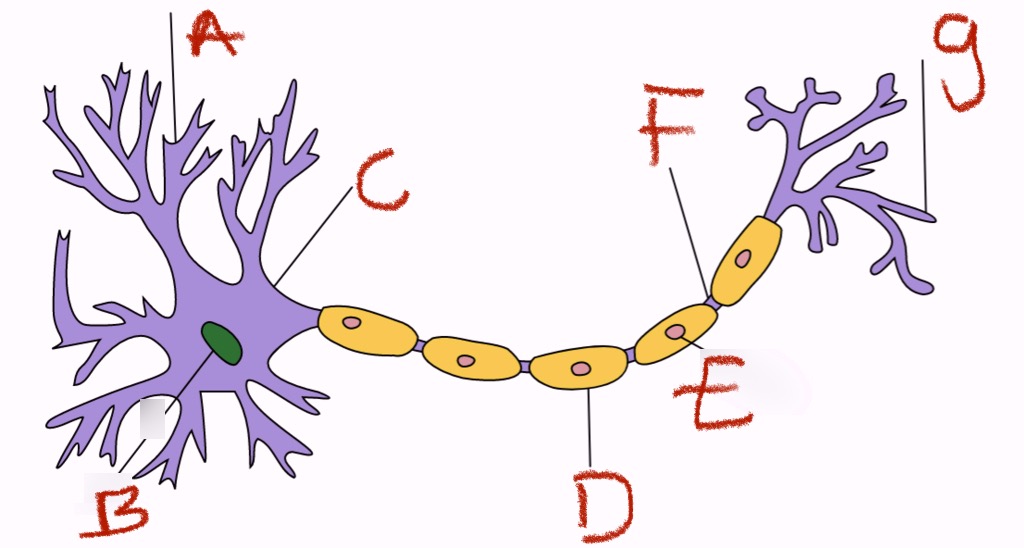
what is b and what does it do
nucleus, control cell
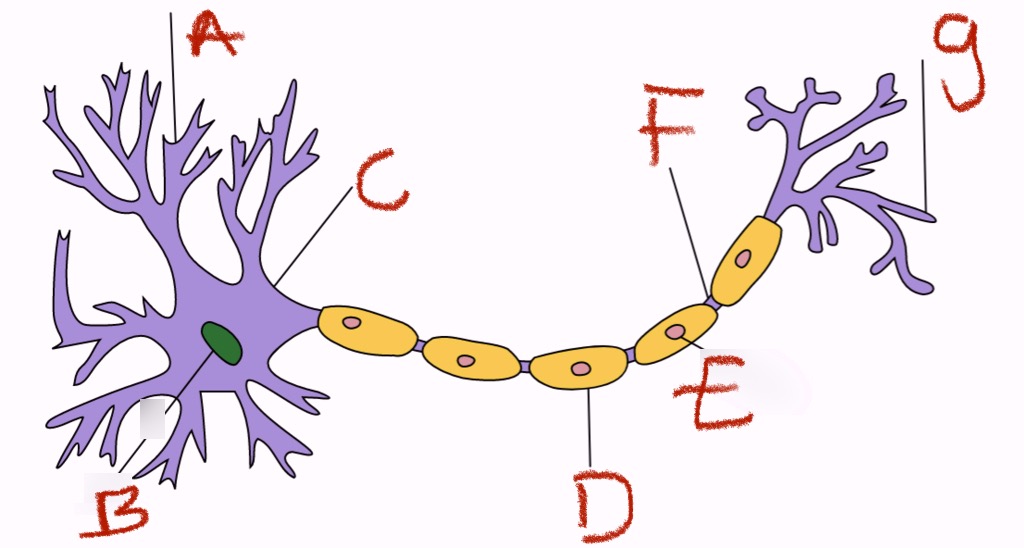
what is c
cell body
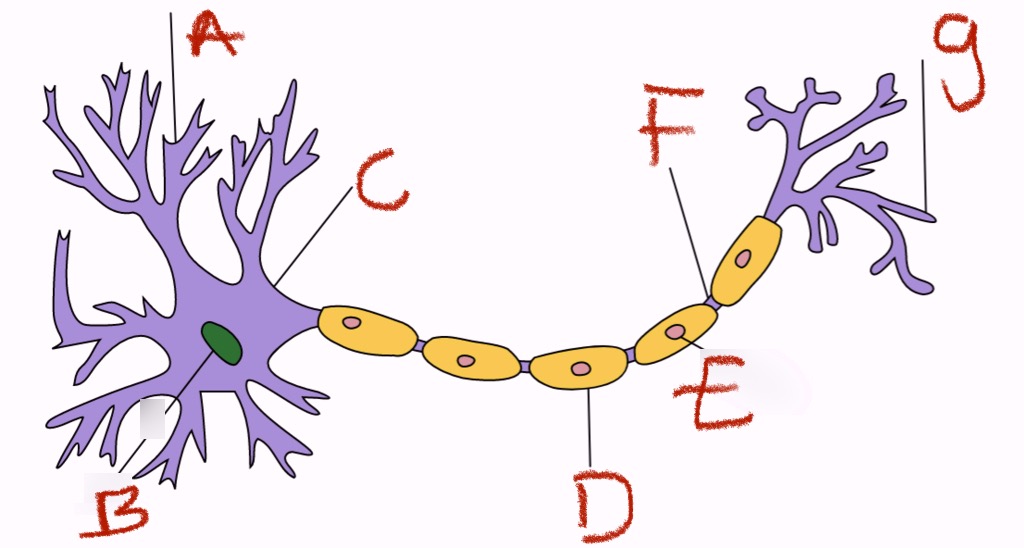
what is d and what does it do
myelin sheath, insulating fatty layer that speeds transmission
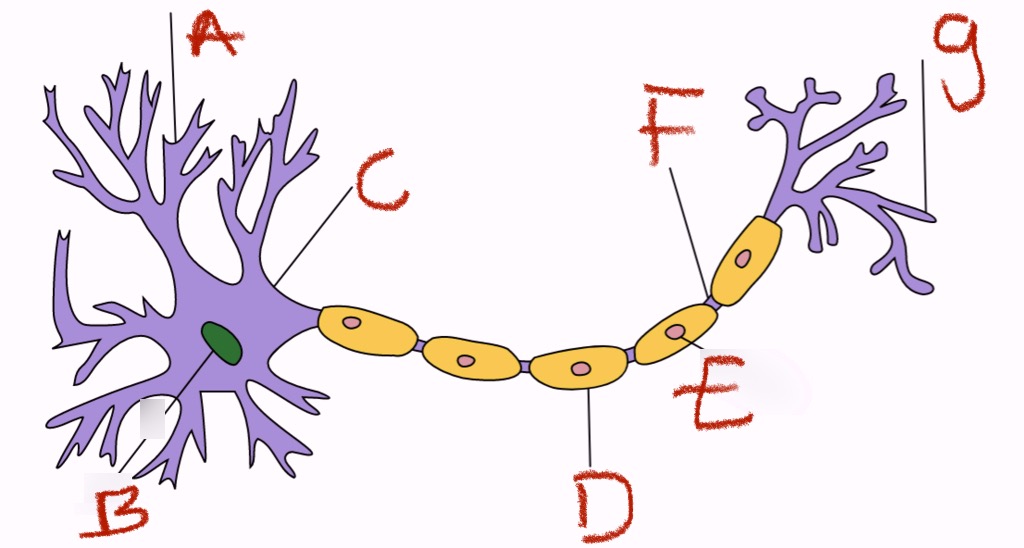
what is e and what does it do
schwann’s cells, they make the myelin
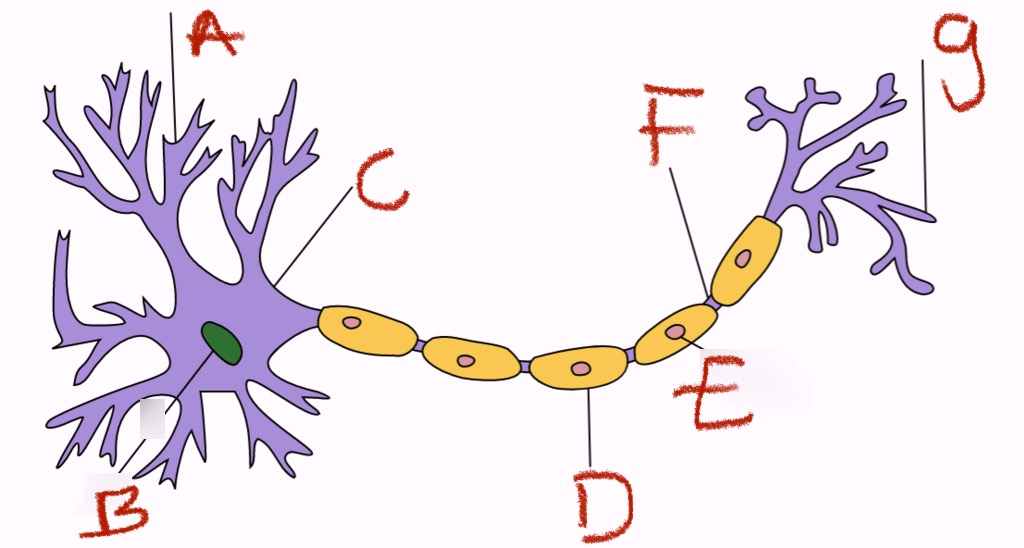
what is f and what does it do
axon (the conducting fiber) and/or the node of ranvier (axonal membrane that is not insulated by the myelin sheath)
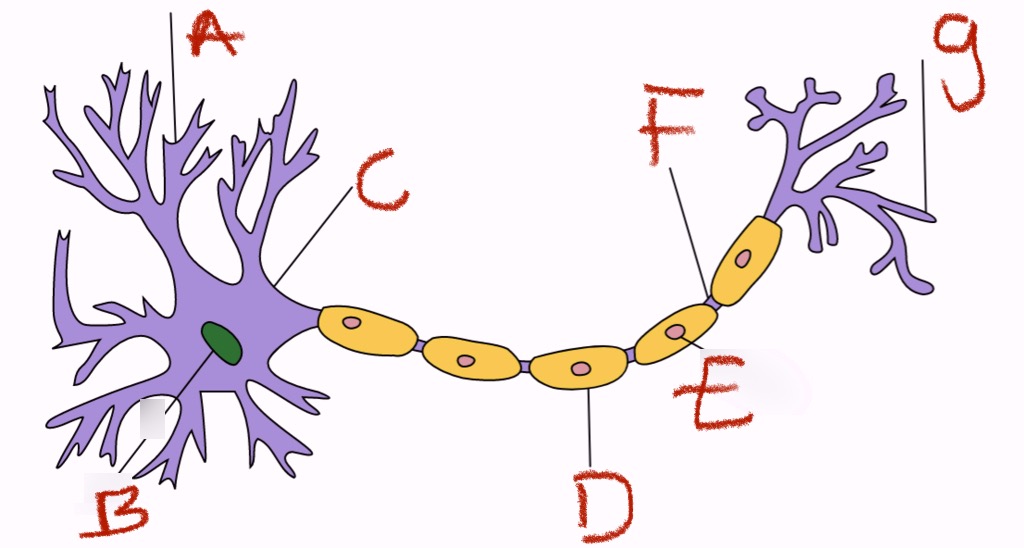
what is g and what does it do
axon terminals, transmitters
what do sensory (afferent) neurons do
they bring info from sensory receptors to the cns
what do interneurons do
neurons in the brain and spinal cord that serve as intermediary between sensory and motor neurons
what do motor (efferent) neurons do
carry info from the cns to the appropriate muscles to carry out behaviors and body movements
what is a neural impulse
the electrical and chemical transmission of info from one neuron to another
communication within a neuron is
electrical
communication between neurons is
chemical
how does a neuron pass its messages to another neuron
by releasing chemical neurotransmitters into the synapse
change of the neuron during a neural impulse
inside a neuron ions are negative, outside they are positive
what is an ion
a particle that is electrically charged, an atom or molecule or group that has lost or gained one or more electrons
what are the two kinds of ions during a neural impulse
sodium (Na+, outside), potassium (K+, inside)
what is a selectively permeable membrane
the outer membrane of the neuron which selectively allows some ions to pass back and forth, only small ions can fit
what is the order of the firing of a neuron
resting, stimulus, threshold, absolute refractory period, repolarization
what is resting potential
the neuron is polarized, stable, inactive, and ready to fire (receive and send info)
what is stimulus
stimulation that triggers the firing of a neuron and the info is brought to the body by a sensory receptor and then brought to the dendrites of a neuron
what is threshold
if it is reached then action potential will occur. It determines if the stimulus is strong enough to create action
what is all or nothing law
a neural impulse will either occur or not if threshold is reached
what is action potential
when the stimulus reaches a certain threshold and the neural membrane opens at one area to allow the positively charged ions to come in and the negative to go out
what is the absolute refractory period
brief period which the neuron is unable to have another action potential
what is repolarization
the neuron tries to restore its charge by dumping out the positive ions and bringing back the negative ones
what is the cns
the brain and spinal cord
neurons in the cns
interneurons
what is encases the nerves in the cns
bone
what does the cns communicate with
sensory receptors, muscles, glands via the peripheral nervous system
what is the peripheral nervous system
divided into the autonomic and somatic systems, all the nerves not encased in bone
Peripheral nervous system function
carry messages to and from the cns
what kind of neurons are in the peripheral nervous system
all but mainly motor and sensory
what is the somatic nervous system
controls voluntary muscle movement, carries messages from the cns to coordinate muscles
what is the autonomic nervous system
controls glands and muscles related to our organs, mostly involuntary but possible to override
parts of the autonomic nervous system
sympathetic, parasympathetic, and enteric nervous system
What does the autonomic nervous system do
bodys involuntary (automatic) actions
what is the sympathetic nervous system
arousal responses, how we respond to stress or environmental cues
what is the parasympathetic nervous system
parasympathetic nervous system functions
quiet and calm the body to restore its energy, return to homeostasis, sends signals to slow your heart rate, breathing, and speed up digestive tract
“fight or flight“
sympathetic nervous system
“rest and digest“
parasympathetic nervous system
what is the enteric nervous system
directly controls gastrointestinal tract, pancreas, and gall bladder. Operates independently from the cns
enteric nervous system function
in charge of the digestive process
what kind of neurons does the enteric nervous system have
efferent, afferent, and interneurons
what is the brain stem
where the spinal cord and brain meet
brain stem functions
automatic survival functions
what is the pons
acts as a pathway for motor and sensory info between the body and brain
pons function
recognition of facial expressions, implicated in sleep paralysis, and generates dreams
medulla oblongata functions
autonomic functions: breathing, blood pressure, heart rate
cerebellum functions
muscle movements, motor control, balance, coordination, precision, accurate judgement of time
what is the midbrain
coordinates movements with sensory info, contains reticular formation
midbrain functions
arousal, focus ability, wake/sleep cycle, filter incoming stimuli (discriminate irrelevant background stimuli)
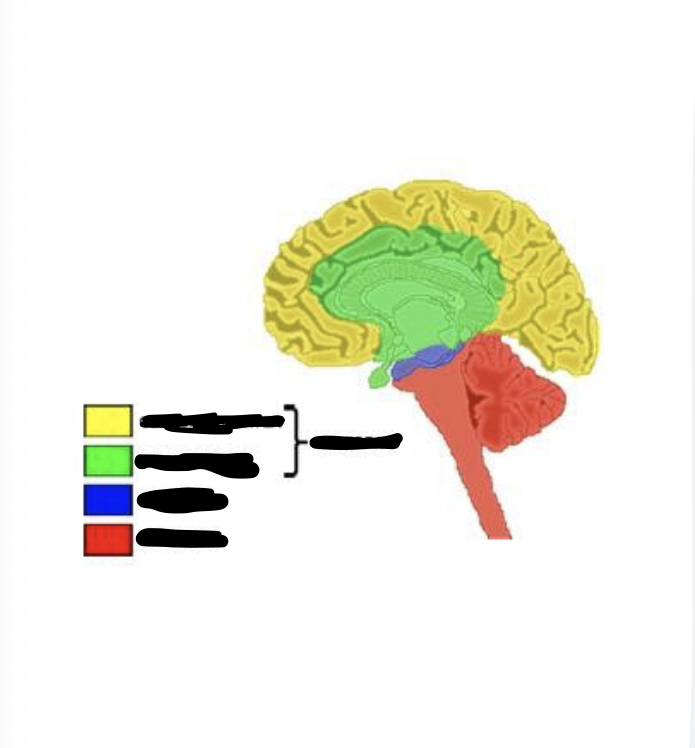
what is yellow
cerebral cortex
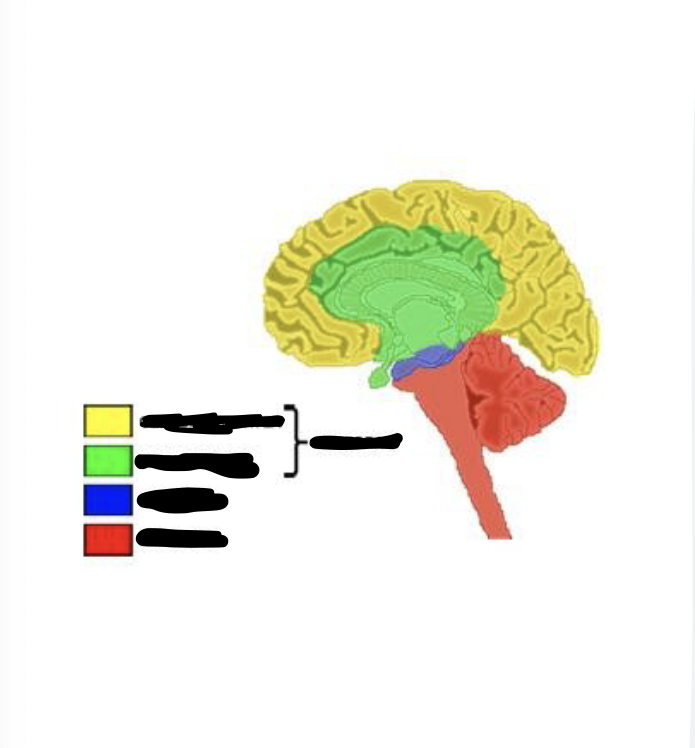
what is green
limbic system
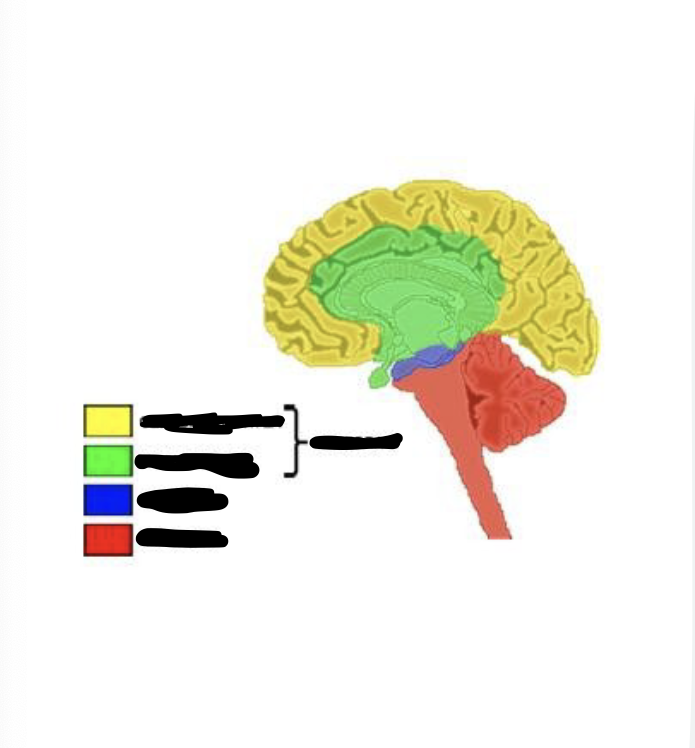
what is blue
midbrain
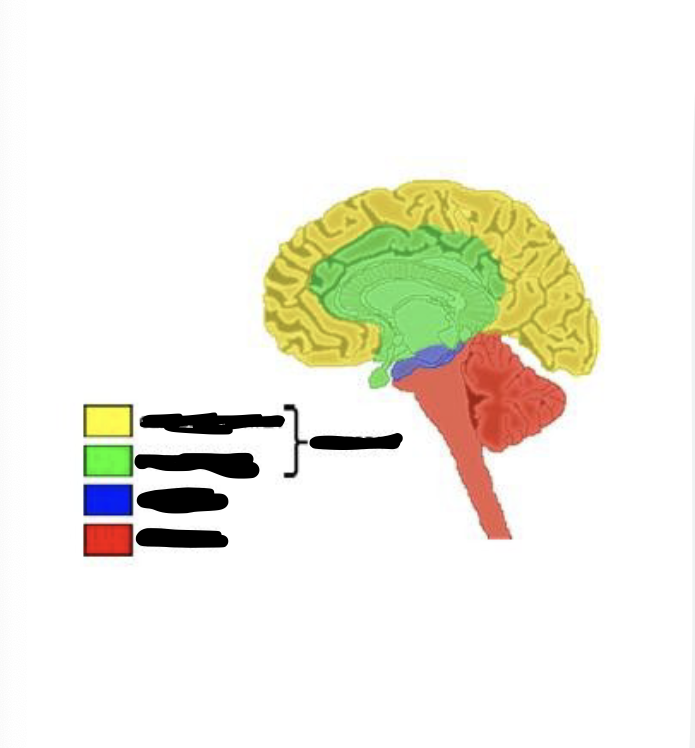
what is red
hindbrain
reticular formation functions
arousal, ability to focus, wake/sleep cycle, filter incoming stimuli
what is the reticular activation system (RAS)
regulates sleep and wake cycle by turning sensory processing on and off
what is the limbic system
includes the thalamus, hypothalamus, hippocampus, amygdala
limbic system functions
emotional life, formation of memories
what is the thalamus
in the forebrain, like a hub through which all sensory traffic passes
what is the thalamus function
receives sensory info (except smell), and sends it to the appropriate area
what is the reward center
hypothalamus
hypothalamus functions
reward system, body temp, hunger and thirst, sexual. arousal, influence pituitary gland and endocrine system, maintain homeostasis
hippocampus functions
involved in memory formation, organization, and storing
why is the limbic system important
forms new memories, connects emotions and senses (smell and sound) to memories
where is the hippocampus located
one in each brain hemisphere
amygdala functions
involved in emotions and motivations
how is the brain controlled
contralateral (left controls right side, vice versa)
what is brain lateralization
functions of each brain hemisphere are managed differently